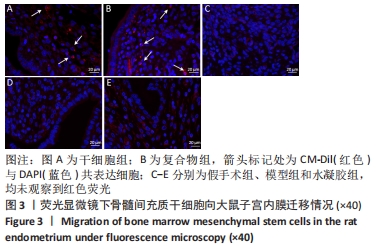
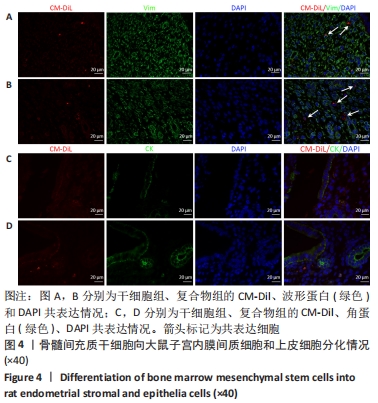
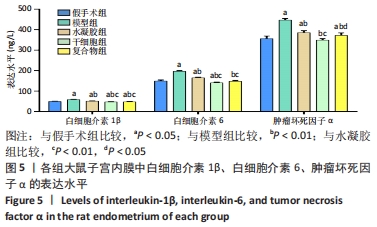
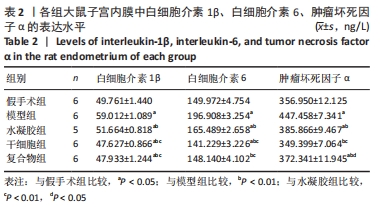
[1] SANTAMARIA X, ISAACSON K, SIMÓN C. Asherman’s Syndrome: it may not be all our fault. Hum Reprod. 2018;33(8):1374-1380.
[2] PAREKKADAN B, MILWID JM. Mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutics. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2010;12:87-117.
[3] SHI J, ZHANG X, ZENG X, et al. One-step articular cartilage repair: combination of in situ bone marrow stem cells with cell-free poly(L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold in a rabbit model. Orthopedics. 2012; 35(5):e665-e671.
[4] XIONG XY, TAM KC, GAN LH. Synthesis and thermal responsive properties of P(LA-b-EO-b-PO-b-EO-b-LA) block copolymers with short hydrophobic poly(lactic acid) (PLA) segments. Polymer. 2005;46(6): 1841-1850.
[5] ZHANG SS, XIA WT, XU J, et al. Three-dimensional structure micelles of heparin-poloxamer improve the therapeutic effect of 17β-estradiol on endometrial regeneration for intrauterine adhesions in a rat model. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:5643-5657.
[6] AMIN T, SARIDOGAN E, DOOLEY M, et al. Morphological appearance of uterine cavity on ultrasound prior to development of intrauterine adhesions. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2018;51(1):142-143.
[7] AZIZI R, AGHEBATI-MALEKI L, NOURI M, et al. Stem cell therapy in Asherman syndrome and thin endometrium: Stem cell- based therapy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;102:333-343.
[8] ROY KK, BARUAH J, SHARMA JB, et al. Reproductive outcome following hysteroscopic adhesiolysis in patients with infertility due to Asherman’s syndrome. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2010;281(2):355-361.
[9] XIA L, MENG Q, XI J, et al. The synergistic effect of electroacupuncture and bone mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on repairing thin endometrial injury in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):244.
[10] XU XX, CAO LB, WANG Z, et al. Creation of a rabbit model for intrauterine adhesions using electrothermal injury. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2018;19(5):383-389.
[11] ZHANG XH, LIU ZZ, TANG MX, et al. Morphological Changes and Expression of Cytokine After Local Endometrial Injury in a Mouse Model. Reprod Sci. 2015;22(11):1377-1386.
[12] HU J, ZENG B, JIANG X, et al. The expression of marker for endometrial stem cell and fibrosis was increased in intrauterine adhesious. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(2):1525-1534.
[13] WANG X, MA N, SUN Q, et al. Elevated NF-κB signaling in Asherman syndrome patients and animal models. Oncotarget. 2017;8(9):15399-15406.
[14] 郭意欣,关婷.机械损伤联合不同感染方法建立大鼠宫腔粘连模型的对比研究[J].现代妇产科进展,2018,27(9):693-695.
[15] LIU Y, LI P, QIAO C, et al. Chitosan Hydrogel Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Myocardial Infarction by Alleviating Vascular Endothelial Cell Pyroptosis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020;75(1):75-83.
[16] GUO J, WANG R, LIU D. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Promoting Mitophagy of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells via the SIRT1/Parkin Axis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:639165.
[17] ZHANG R, ZHANG Q, ZOU Z, et al. Curcumin Supplementation Enhances Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Promote the Anabolism of Articular Chondrocytes and Cartilage Repair. Cell Transplant. 2021; 30:963689721993776.
[18] TAYLOR HS. Endometrial cells derived from donor stem cells in bone marrow transplant recipients. JAMA. 2004;292(1):81-85.
[19] PAAVOLA A, BERNARDS CM, ROSENBERG PH. Controlled release ibuprofen-poloxamer gel for epidural use - A pharmacokinetic study using microdialysis in pigs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016;108:180-186.
[20] MANIYAR AJ, PATEL GM, SHELAT PK, et al. Development and characterization of thermosensitive intranasal gel containing paliperidone loaded microspheres. J Young Pharm. 2016; 8(4):368-377.
[21] 吴洪福,邓宇斌,严云发,等.Pluronic F-127水凝胶复合骨髓间充质干细胞构建组织工程化脂肪的体外研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2011,28(6):1148-1153.
[22] 王一飞,宋阳,关永格,等.基于HOXA10调控网络探讨骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠薄型子宫内膜[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(9):1397-1402.
[23] 谭先杰,刘东远,郎景和,等.子宫内膜腺上皮及基质细胞分离、培养作为子宫内膜异位症体外细胞模型的探索[J].现代妇产科进展,2002,11(1):30-32.
[24] 林重辉,杨应明.白介素1β在二次脑损伤中的作用及机制[J].广东医学,2007,28(10):1704-1705.
[25] PRICOLA KL, KUHN NZ, HALEEM-SMITH H, et al. Interleukin-6 maintains bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell stemness by an ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108(3):577-588.
[26] 任俊.脑内炎症微环境在骨髓间充质干细胞定向迁移过程中的作用研究[D]. 济南:山东大学,2019.
[27] ORTIZ LA, DUTREIL M, FATTMAN C, et al. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist mediates the antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effect of mesenchymal stem cells during lung injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(26):11002-11007.
[28] 刘洁玲,梁媛.剖宫产术后应用透明质酸对产妇炎性因子及宫腔粘连发生的影响[J].中国医药导报,2018,15(24):95-98.
[29] 周芳,张耀超,郭娜,等.BMSCs膜片对静止期牙周病动物模型牙周组织IL-6表达水平的影响[J].山西医科大学学报,2020,51(5): 427-431.
[30] ZHANG LL, XIA GM, LIU YJ, et al. Effect of a poloxamer 407-based thermosensitive gel on minimization of thermal injury to diaphragm during microwave ablation of the liver. World J Gastroenterol. 2017; 23(12):2141-2148.
[31] YANG H, WU S, FENG R, et al. Vitamin C plus hydrogel facilitates bone marrow stromal cell-mediated endometrium regeneration in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):267.
[32] CAPP E, MILNER CM, WILLIAMS J, et al. Modulation of tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6 (TSG-6) expression in human endometrium. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014;289(4):893-901.
[33] BASTON-BÜST DM, GÖTTE M, JANNI W, et al. Syndecan-1 knock-down in decidualized human endometrial stromal cells leads to significant changes in cytokine and angiogenic factor expression patterns. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2010;8:133.
|