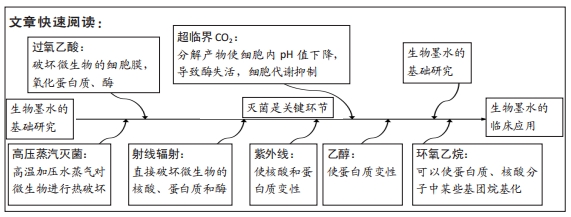
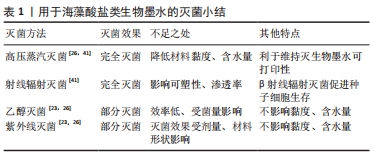
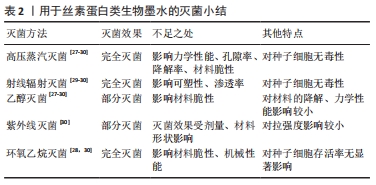
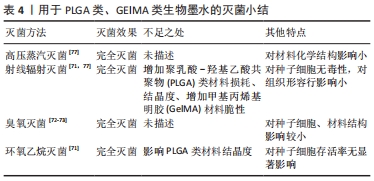
[1] DERAKHSHANFAR S, MBELECK R, XU K, et al. 3D bioprinting for biomedical devices and tissue engineering: a review of recent trends and advances. Bioact Mater. 2018;3(2):144-156.
[2] NGUYEN D, HÄGG DA, FORSMAN A, et al. Cartilage tissue engineering by the 3d bioprinting of ips cells in a nanocellulose/alginate bioink. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):658-658.
[3] SINGH YP, BANDYOPADHYAY A, MANDAL BB. 3D Bioprinting using cross-linker-free silk–gelatin bioink for cartilage tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(37):33684-33696.
[4] KIM BS, DAS S, JANG J, et al. Decellularized extracellular matrix-based bioinks for engineering tissue- and organ-specific microenvironments. Chem Rev. 2020;120(19):10608-10661.
[5] XIE Z, GAO M, LOBO AO, et al. 3D bioprinting in tissue engineering for medical applications:the classic and the hybrid. Polymers (Basel). 2020; 12(8):1717.
[6] VARKEY M, VISSCHER DO, VAN ZUIJLEN PPM, et al. Skin bioprinting:the future of burn wound reconstruction? Burns Trauma. 2019;7:4.
[7] HE P, ZHAO J, ZHANG J, et al. Bioprinting of skin constructs for wound healing. Burns Trauma. 2018;6:5.
[8] FUEST M, YAM GHF, MEHTA JS, et al. Prospects and challenges of translational corneal bioprinting. Bioengineering (Basel). 2020;7(3):71.
[9] FAROOQI KM, COOPER C, CHELLIAH A, et al. 3D printing and heart failure: the present and the future. JACC: Heart Failure. 2019;7(2):132-142.
[10] POTYONDY T, UQUILLAS JA, TEBON PJ, et al. Recent advances in 3D bioprinting of musculoskeletal tissues. Biofabrication. 2021;13(2): 022001.
[11] HODDER E, DUIN S, KILIAN D, et al. Investigating the effect of sterilisation methods on the physical properties and cytocompatibility of methyl cellulose used in combination with alginate for 3D-bioplotting of chondrocytes. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(1):10.
[12] GALANTE R, PINTO TJA, COLAÇO R, et al. Sterilization of hydrogels for biomedical applications: a review. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(6):2472-2492.
[13] DI FOGGIA M, CORDA U, PLESCIA E, et al. Effects of sterilisation by high-energy radiation on biomedical poly-(ε-caprolactone)/hydroxyapatite composites. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(6):1789-1797.
[14] SONG JJ, OTT HC. Organ engineering based on decellularized matrix scaffolds. Trends Mol Med. 2011;17(8):424-432.
[15] SCHENKE-LAYLAND K, VASILEVSKI O, OPITZ F, et al. Impact of decellularization of xenogeneic tissue on extracellular matrix integrity for tissue engineering of heart valves. J Struct Biol. 2003;143(3):201-208.
[16] GOUK SS, LIM TM, TEOH SH, et al. Alterations of human acellular tissue matrix by gamma irradiation: histology, biomechanical property, stability, in vitro cell repopulation, and remodeling. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;84B(1):205-217.
[17] ROSARIO DJ, REILLY GC, ALI SALAH E, et al. Decellularization and sterilization of porcine urinary bladder matrix for tissue engineering in the lower urinary tract. Regen Med. 2008;3(2):145-156.
[18] DAI Z, RONHOLM J, TIAN Y, et al. Sterilization techniques for biodegradable scaffolds in tissue engineering applications. J Tissue Eng. 2016. doi:10.1177/2041731416648810.
[19] AHMED EM. Hydrogel:Preparation, characterization, and applications: a review. J Adv Res. 2015;6(2):105-121.
[20] EL-ASHHAB F, SHEHA L, ABDALKHALEK M, et al. The influence of gamma irradiation on the intrinsic properties of cellulose acetate polymers. J Assoc Arab Univ Basic App Sci. 2013;14(1):46-50.
[21] PALMER I, CLARKE S, NELSON J, et al. Identification of a suitable sterilisation method for collagen derived from a marine Demosponge. Int J Nano Biomater. 2012;4:148-163.
[22] MEECHAN P, WILSON C. Use of ultraviolet lights in biological safety cabinets:a contrarian view. Applied Biosafety. 2006;11(4):222-227.
[23] STOPPEL WL, WHITE JC, HORAVA SD, et al. Terminal sterilization of alginate hydrogels:efficacy and impact on mechanical properties. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014;102(4):877-884.
[24] PAN T, SONG W, CAO X, et al. 3D bioplotting of gelatin/alginate scaffolds for tissue engineering: influence of crosslinking degree and pore architecture on physicochemical properties. J Mater Sci Technol. 2016; 32(9):889-900.
[25] SIRITIENTONG T, SRICHANA T, ARAMWIT P. The effect of sterilization methods on the physical properties of silk sericin scaffolds. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2011;12(2):771-781.
[26] CHANSORIA P, NARAYANAN LK, WOOD M, et al. Effects of autoclaving, etoh, and uv sterilization on the chemical, mechanical, printability, and biocompatibility characteristics of alginate. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(9):5191-5201.
[27] GIL ES, PARK SH, HU X, et al. Impact of sterilization on the enzymatic degradation and mechanical properties of silk biomaterials. Macromol Biosci. 2014;14(2):257-269.
[28] HOFMANN S, STOK KS, KOHLER T, et al. Effect of sterilization on structural and material properties of 3-D silk fibroin scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(1):308-317.
[29] GEORGE KA, SHADFORTH AMA, CHIRILA TV, et al. Effect of the sterilization method on the properties of Bombyx mori silk fibroin films. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(2):668-674.
[30] DE MORAES MA, WESKA RF, BEPPU MM. Effects of sterilization methods on the physical, chemical, and biological properties of silk fibroin membranes. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014;102(4): 869-876.
[31] BEDNARSKI DM, LANTZ EE, BOBST CE, et al. Sterilization of epidermal growth factor with supercritical carbon dioxide and peracetic acid; analysis of changes at the amino acid and protein level. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020;1868(2):140334.
[32] KARAJANAGI SS, YOGANATHAN R, MAMMUCARI R, et al. Application of a dense gas technique for sterilizing soft biomaterials. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2011;108(7):1716-1725.
[33] BERNHARDT A, WEHRL M, PAUL B, et al. Improved sterilization of sensitive biomaterials with supercritical carbon dioxide at low temperature. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0129205-e0129205.
[34] RIBEIRO N, SOARES GC, SANTOS-ROSALES V, et al. A new era for sterilization based on supercritical CO2 technology. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(2):399-428.
[35] LEE KY, MOONEY DJ. Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Prog Polym Sci. 2012;37(1):106-126.
[36] ANDERSEN T, STRAND B, FORMO K, et al. Alginates as biomaterials in tissue engineering. Carbohydrate Chem. 2011;37(6):227-258.
[37] SILVA R, SINGH R, SARKER B, et al. Hydrogel matrices based on elastin and alginate for tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;114:614-625.
[38] SHACHAR M, TSUR-GANG O, DVIR T, et al. The effect of immobilized RGD peptide in alginate scaffolds on cardiac tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(1):152-162.
[39] CHANSORIA P, NARAYANAN LK, SCHUCHARD K, et al. Ultrasound-assisted biofabrication and bioprinting of preferentially aligned three-dimensional cellular constructs. Biofabrication. 2019;11(3):035015.
[40] JOVIC T, KUNGWENGWE G, MILLS A, et al. Plant-derived biomaterials:a review of 3d bioprinting and biomedical applications. Front Mechan Eng. 2019;5:19.
[41] CHANSORIA P, SHIRWAIKER R. 3D bioprinting of anisotropic engineered tissue constructs with ultrasonically induced cell patterning. Add Manufact. 2020;32:101042.
[42] LAFUENTE-MERCHAN M, RUIZ-ALONSO S, ESPONA-NOGUERA A, et al. Development, characterization and sterilisation of Nanocellulose-alginate-(hyaluronic acid)- bioinks and 3D bioprinted scaffolds for tissue engineering. Materi Sci Eng C. 2021;126:112160.
[43] FU S, THACKER A, SPERGER DM, et al. Relevance of rheological properties of sodium alginate in solution to calcium alginate gel properties. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2011;12(2):453-460.
[44] AYOUB NA, GARB JE, TINGHITELLA RM, et al. Blueprint for a high-performance biomaterial: full-length spider dragline silk genes. PLoS One. 2007;2(6):e514-e514.
[45] YANG M. Silk-based biomaterials. Microsc Res Tech. 2017;80(3):321-330.
[46] MACINTOSH AC, KEARNS VR, CRAWFORD A, et al. Skeletal tissue engineering using silk biomaterials. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2008;2(2-3):71-80.
[47] BONNANS C, CHOU J, WERB Z. Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(12):786-801.
[48] YAO Q, CHOI JH, DAI Z, et al. Improving tumor specificity and anticancer activity of dasatinib by dual-targeted polymeric micelles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(42):36642-36654.
[49] LINDE-MEDINA M, MARCUCIO R. Living tissues are more than cell clusters: the extracellular matrix as a driving force in morphogenesis. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2018;137:46-51.
[50] HOSHIBA T, CHEN G, ENDO C, et al. Decellularized extracellular matrix as an in vitro model to study the comprehensive roles of the ECM in stem cell differentiation. Stem Cells Int. 2016. doi:10.1155/2016/6397820.
[51] BINDER M J, MCCOOMBE S, WILLIAMS ED, et al. The extracellular matrix in cancer progression: role of hyalectan proteoglycans and ADAMTS enzymes. Cancer Lett. 2017;385:55-64.
[52] SUTHERLAND AJ, CONVERSE GL, HOPKINS RA, et al. The bioactivity of cartilage extracellular matrix in articular cartilage regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(1):29-39.
[53] YU T, WEN L, HE J, et al. Fabrication and evaluation of an optimized acellular nerve allograft with multiple axial channels. Acta Biomater. 2020;115:235-249.
[54] FIDALGO C, IOP L, SCIRO M, et al. A sterilization method for decellularized xenogeneic cardiovascular scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2018;67:282-294.
[55] CHOE J A, JANA S, TEFFT B J, et al. Biomaterial characterization of off-the-shelf decellularized porcine pericardial tissue for use in prosthetic valvular applications. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(7):1608-1620.
[56] FERCANA GR, YERNENI S, BILLAUD M, et al. Perivascular extracellular matrix hydrogels mimic native matrix microarchitecture and promote angiogenesis via basic fibroblast growth factor. Biomaterials. 2017;123: 142-154.
[57] GULER S, ASLAN B, HOSSEINIAN P, et al. Supercritical carbon dioxide-assisted decellularization of aorta and cornea. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2017;23(9):540-547.
[58] HELDER MRK, HENNESSY RS, SPOON DB, et al. Low-dose gamma irradiation of decellularized heart valves results in tissue injury in vitro and in vivo. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;101(2):667-674.
[59] HUSSEIN KH, PARK KM, TEOTIA PK, et al. Sterilization using electrolyzed water highly retains the biological properties in tissue-engineered porcine liver scaffold. Int J Artif Organs. 2013;36(11):781-792.
[60] GOSZTYLA C, LADD MR, WERTS A, et al. A Comparison of sterilization techniques for production of decellularized intestine in mice. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2020;26(2):67-79.
[61] FENG L, HU YL, MA P, et al. Decellularized gastric matrix as a mesh for gastric perforation repair. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021;109(3):451-462.
[62] BONENFANT NR, SOKOCEVIC D, WAGNER DE, et al. The effects of storage and sterilization on de-cellularized and re-cellularized whole lung. Biomaterials. 2013;34(13):3231-3245.
[63] BALESTRINI JL, LIU A, GARD AL, et al. Sterilization of lung matrices by supercritical carbon dioxide. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2016;22(3): 260-269.
[64] JOHNSON CM, GUO D, RYALS S, et al. The feasibility of gamma radiation sterilization for decellularized tracheal grafts. Laryngoscope. 2017; 127(8):E258-E264.
[65] MORADI L, MOHAMMADI JOBANIA B, JAFARNEZHAD-ANSARIHA F, et al. Evaluation of different sterilization methods for decellularized kidney tissue. Tissue Cell. 2020;66:101396.
[66] GAO R, WU W, XIANG J, et al. Hepatocyte culture in autologous decellularized spleen matrix. Organogenesis. 2015;11(1):16-29.
[67] EDWARDS J H, HERBERT A, JONES GL, et al. The effects of irradiation on the biological and biomechanical properties of an acellular porcine superflexor tendon graft for cruciate ligament repair. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(8):2477-2486.
[68] SUN Y, LOVRIC V, WANG T, et al. Effects of SCCO(2), Gamma irradiation, and sodium dodecyl sulfate treatments on the initial properties of tendon allografts. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(5):1565.
[69] YOU L, WEIKANG X, LIFENG Y, et al. In vivo immunogenicity of bovine bone removed by a novel decellularization protocol based on supercritical carbon dioxide. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018; 46(sup2):334-344.
[70] KAKABADZE A, MARDALEISHVILI K, LOLADZE G, et al. Reconstruction of mandibular defects with autogenous bone and decellularized bovine bone grafts with freeze-dried bone marrow stem cell paracrine factors. Oncol Lett. 2017;13(3):1811-1818.
[71] GRADWOHL M, CHAI F, PAYEN J, et al. Effects of two melt extrusion based additive manufacturing technologies and common sterilization methods on the properties of a medical grade PLGA copolymer. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(4):572.
[72] REDIGUIERI CF, PINTO T, BOU-CHACRA NA, et al. Ozone gas as a benign sterilization treatment for PLGA nanofiber scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2016;22(4):338-347.
[73] YUE K, TRUJILLO-DE SANTIAGO G, ALVAREZ MM, et al. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;73:254-271.
[74] ADIB AA, SHEIKHI A, SHAHHOSSEINI M, et al. Direct-write 3D printing and characterization of a GelMA-based biomaterial for intracorporeal tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2020;12(4):045006.
[75] XIE M, GAO Q, ZHAO H, et al. Electro-Assisted Bioprinting of Low-Concentration GelMA Microdroplets. Small. 2019;15(4):1804216.
[76] YING G, JIANG N, YU C, et al. Three-dimensional bioprinting of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA). Bio-Design and Manufacturing. 2018;1(4):215-224.
[77] RIZWAN M, PEH GSL, ANG HP, et al. Sequentially-crosslinked bioactive hydrogels as nano-patterned substrates with customizable stiffness and degradation for corneal tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials. 2017;120:139-154.
|