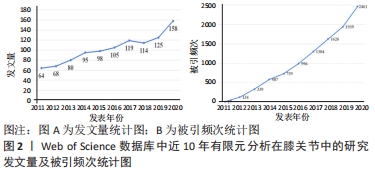
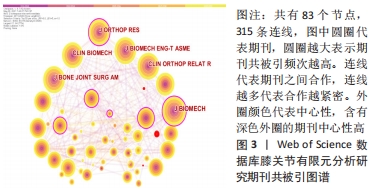
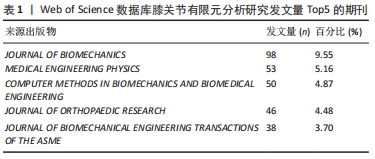
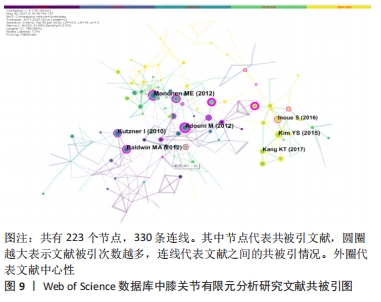
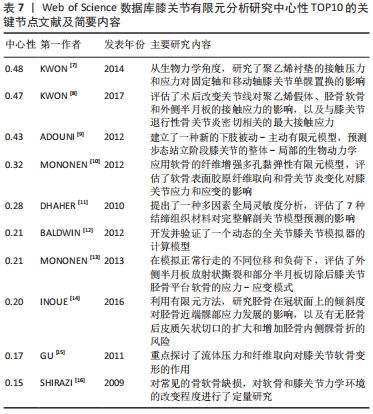
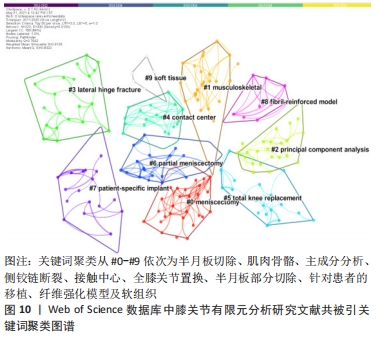
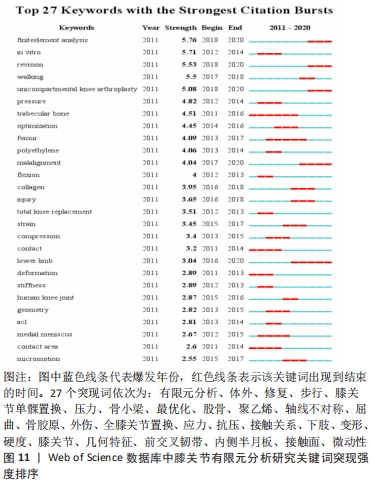
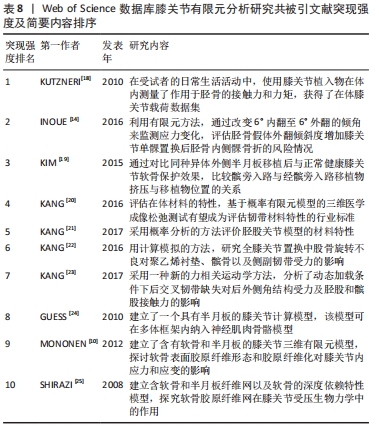
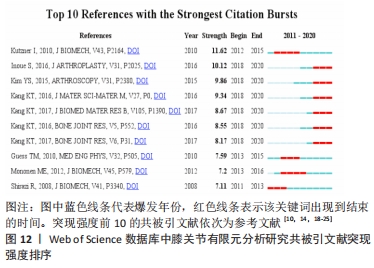
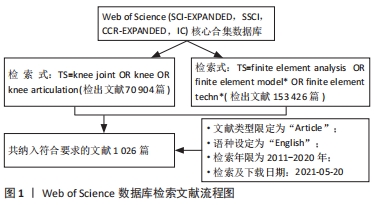
[1] 张立超,张立敏,吕永明,等.膝关节屈伸运动形态的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(3):396-400.
[2] INZANA JA, VARGA P, WINDOLF M. Implicit modeling of screw threads for efficient finite element analysis of complex bone-implant systems. J Biomech. 2016;49(9):1836-1844.
[3] 陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等.CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J].科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253.
[4] CHEN CM. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inform Sci Tech. 2006; 57(3):359-377.
[5] 范婷,杨树,赵志刚.基于CiteSpace的国内外抗菌药物透过血脑屏障的研究进展及可视化分析[J].中国抗生素杂志,2019,44(7):868-875.
[6] 侯剑华,刘则渊.纳米技术研究前沿及其演化的可视化分析[J].科学学与科学技术管理,2009,30(5):23-30.
[7] KWON OR, KANG KT, SON J, et al. Biomechanical comparison of fixed- and mobile-bearing for unicomparmental knee arthroplasty using finite element analysis. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(2):338-345.
[8] KWON OR, KANG KT, SON J, et al. Importance of joint line preservation in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: finite element analysis. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(2):347-352.
[9] ADOUNI M, SHIRAZI-ADL A, SHIRAZI R. Computational biodynamics of human knee joint in gait: from muscle forces to cartilage stresses. J Biomech. 2012;45(12):2149-2156.
[10] MONONEN ME, MIKKOLA MT, JULKUNEN P, et al. Effect of superficial collagen patterns and fibrillation of femoral articular cartilage on knee joint mechanics-a 3D finite element analysis. J Biomech. 2012;45(3):579-587.
[11] DHAHER YY, KWON TH, BARRY M. The effect of connective tissue material uncertainties on knee joint mechanics under isolated loading conditions. J Biomech. 2010;43(16):3118-3125.
[12] BALDWIN MA, CLARY CW, FITZPATRICK CK, et al. Dynamic finite element knee simulation for evaluation of knee replacement mechanics. J Biomech. 2012;45(3):474-483.
[13] MONONEN ME, JURVELIN JS, KORHONEN RK. Effects of radial tears and partial meniscectomy of lateral meniscus on the knee joint mechanics during the stance phase of the gait cycle--A 3D finite element study. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(8):1208-1217.
[14] INOUE S, AKAGI M, ASADA S, et al. The valgus inclination of the tibial component increases the risk of medial tibial condylar fractures in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(9):2025-2030.
[15] GU KB, LI LP. A human knee joint model considering fluid pressure and fiber orientation in cartilages and menisci. Med Eng Phys. 2011;33(4):497-503.
[16] SHIRAZI R, SHIRAZI-ADL A. Computational biomechanics of articular cartilage of human knee joint: effect of osteochondral defects. J Biomech. 2009;42(15):2458-2465.
[17] CHEN CM, IBEKWE-SANJUAN F, HOU JH. The structure and dynamics of cocitation clusters: a multiple-perspective cocitation analysis. J Am Soc Inform Sci Tech. 2010;61(7):1386-1409.
[18] KUTZNER I, HEINLEIN B, GRAICHEN F, et al. Loading of the knee joint during activities of daily living measured in vivo in five subjects. J Biomech. 2010;43(11):2164-2173.
[19] KIM YS, KANG KT, SON J, et al. Graft extrusion related to the position of allograft in lateral meniscal allograft transplantation: biomechanical comparison between parapatellar and transpatellar approaches using finite element analysis. Arthroscopy. 2015,31(12):2380-2391.
[20] KANG KT, KIM SH, SON J, et al. Computational model-based probabilistic analysis of in vivo material properties for ligament stiffness using the laxity test and computed tomography. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27(12):183.
[21] KANG KT, KIM SH, SON J, et al. Probabilistic evaluation of the material properties of the in vivo subject-specific articular surface using a computational model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(6): 1390-1400.
[22] KANG KT, KOH YG, SON J, et al. Measuring the effect of femoral malrotation on knee joint biomechanics for total knee arthroplasty using computational simulation. Bone Joint Res. 2016;5(11):552-559.
[23] KANG KT, KOH YG, JUNG M, et al. The effects of posterior cruciate ligament deficiency on posterolateral corner structures under gait- and squat-loading conditions: a computational knee model. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6(1):31-42.
[24] GUESS TM, THIAGARAJAN G, KIA M, et al. A subject specific multibody model of the knee with menisci. Med Eng Phys. 2010;32(5):505-515.
[25] SHIRAZI R, SHIRAZI-ADL A, HURTIG M. Role of cartilage collagen fibrils networks in knee joint biomechanics under compression. J Biomech. 2008; 41(16):3340-3348.
[26] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5):301-317.
[27] MO FH, LI F, BEHR M, et al. A lower limb-pelvis finite element model with 3d active muscles. Ann Biomed Eng. 2018;46(1):86-96.
[28] MO FH, LI J, DAN MC, et al. Implementation of controlling strategy in a biomechanical lower limb model with active muscles for coupling multibody dynamics and finite element analysis. J Biomech. 2019,91:51-60.
[29] ZHANG J, CHEN ZX, WANG L, et al. A patient-specific wear prediction framework for an artificial knee joint with coupled musculoskeletal multibody-dynamics and finite element analysis. Tribol Int. 2017;109:382-389.
[30] SHAIFI M, SHIRAZI-ADL A, MAROUANE H. Sensitivity of the knee joint response, muscle forces and stability to variations in gait kinematics-kinetics. J Biomech. 2020;99:109472.
[31] KABIR W, DI BELLA C, CHOOGN PFM, et al. Assessment of native human articular cartilage: a biomechanical protocol. Cartilage. 2020. doi:10.1177/ 1947603520973240.
[32] IMENI M, SEYFI B, FATOURAEE N, et al. Constitutive modeling of menisci tissue:a critical review of analytical and numerical approaches. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2020;19(6):1979-1996.
[33] OROZCO GA, TANSKA P, MONONEN ME, et al. The effect of constitutive representations and structural constituents of ligaments on knee joint mechanics. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2323.
[34] KWON HM, KANG KT, KIM JH, et al. Medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty to patients with a ligamentous deficiency can cause biomechanically poor outcomes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(9):2846-2853.
[35] CHEN J, KIM J, SHAO W, et al. An anterior cruciate ligament failure mechanism. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(9):2067-2076.
[36] LUEKEMEYER CM, MARCHI BC, ASHTON-MILLER JA, et al. Femoral entheseal shape and attachment angle as potential risk factors for anterior cruciate ligament injury. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;88:313-321.
[37] WANG Y, QI E, ZHANG X, et al. A finite element analysis of relationship between fracture, implant and tibial tunnel. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1781.
[38] WANG H, ZHANG M, CHENG CK. Changing the diameter of the bone tunnel is more effective than changing the tunnel shape for restoring joint functionality after ACL reconstruction. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:173.
[39]. CHEN Y, HUANG YC, YAN CH, et al. Abnormal subchondral bone remodeling and its association with articular cartilage degradation in knees of type 2 diabetes patients. Bone Res. 2017;5(4):305-316.
[40] LI L, YANG LF, ZHAN KJ, et al. Three-dimensional finite-element analysis of aggravating medial meniscus tears on knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2020;20:47-55.
[41] KOH YG, LEE JA, LEE HY, et al. Anatomy-mimetic design preserves natural kinematics of knee joint in patient-specific mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(5):1465-1472.
[42] KANG KT, KWON OR, SON J, et al. Effect of joint line preservation on mobile-type bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: finite element analysis. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2018;41(1):201-208.
[43] KANG KT, SON J, KWON SK, et al. Preservation of femoral and tibial coronal alignment to improve biomechanical effects of medial unicompartment knee arthroplasty: computational study. Biomed Mater Eng. 2018,29(5):651-664.
[44] KANG KT, SON J, KOH YG, et al. Effect of femoral component position on biomechanical outcomes of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2018;25(3):491-498.
[45] PARK KK, KOH YG, PARK KM, et al. Biomechanical effect with respect to the sagittal positioning of the femoral component in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Biomed Mater Eng. 2019;30(2):171-182.
|