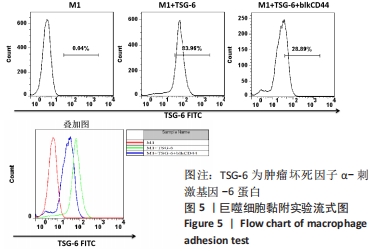
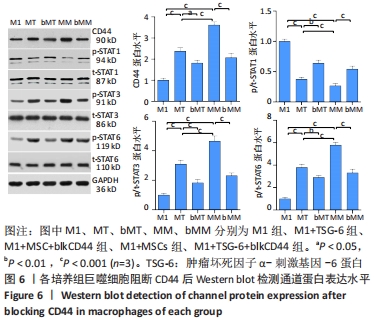
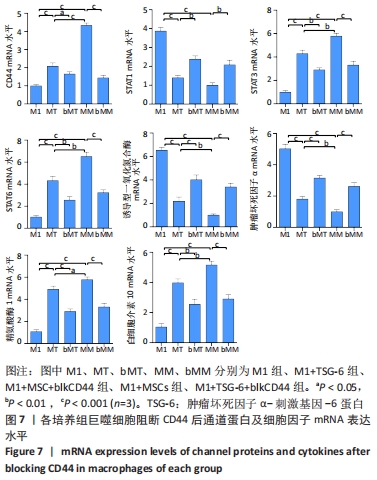
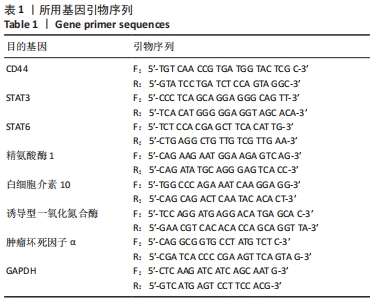
[1] VAN DER VORST EPC, WEBER C. Novel Features of Monocytes and Macrophages in Cardiovascular Biology and Disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(2):e30-e37.
[2] MCNELIS JC, OLEFSKY JM. Macrophages, immunity, and metabolic disease. Immunity. 2014;41(1):36-48.
[3] MUNSHI NV. Resident Macrophages: Near and Dear to Your Heart. Cell. 2017;169(3):376-377.
[4] FRODERMANN V, NAHRENDORF M. Macrophages and Cardiovascular Health. Physiol Rev. 2018;98(4):2523-2569.
[5] DAS A, SINHA M, DATTA S, et al. Monocyte and macrophage plasticity in tissue repair and regeneration. Am J Pathol. 2015;185(10):2596-2606.
[6] WYNN TA, VANNELLA KM. Macrophages in Tissue Repair, Regeneration, and Fibrosis. Immunity. 2016;44(3):450-462.
[7] BEN-MORDECHAI T, HOLBOVA R, LANDA-ROUBEN N, et al. Macrophage subpopulations are essential for infarct repair with and without stem cell therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(20):1890-1901.
[8] FRANTZ S, NAHRENDORF M. Cardiac macrophages and their role in ischaemic heart disease. Cardiovasc Res. 2014;102(2):240-248.
[9] SWIRSKI FK, ROBBINS CS, NAHRENDORF M. Development and Function of Arterial and Cardiac Macrophages. Trends Immunol. 2016;37(1):32-40.
[10] FRANGOGIANNIS NG. Inflammation in cardiac injury, repair and regeneration. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2015;30(3):240-245.
[11] WILLIAMS JW, GIANNARELLI C, RAHMAN A, et al. Macrophage Biology, Classification, and Phenotype in Cardiovascular Disease: JACC Macrophage in CVD Series (Part 1). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(18): 2166-2180.
[12] MOORE KJ, KOPLEV S, FISHER EA, et al. Macrophage Trafficking, Inflammatory Resolution, and Genomics in Atherosclerosis: JACC Macrophage in CVD Series (Part 2). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(18): 2181-2197.
[13] FAYAD ZA, SWIRSKI FK, CALCAGNO C, et al. Monocyte and Macrophage Dynamics in the Cardiovascular System: JACC Macrophage in CVD Series (Part 3). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(18):2198-2212.
[14] DEBERGE M, SHAH SJ, WILSBACHER L, et al. Macrophages in Heart Failure with Reduced versus Preserved Ejection Fraction. Trends Mol Med. 2019;25(4):328-340.
[15] DE COUTO G, LIU W, TSELIOU E, et al. Macrophages mediate cardioprotective cellular postconditioning in acute myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(8):3147-3162.
[16] PAPAGEORGIOU N, TOUSOULIS D. Healing of Myocardial Infarction//Myocardial Preservation. Cham: Springer, 2019:151-169.
[17] HULSMANS M, SAM F, NAHRENDORF M. Monocyte and macrophage contributions to cardiac remodeling. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016;93:149-155.
[18] GOMBOZHAPOVA A, ROGOVSKAYA Y, SHURUPOV V, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization in post-infarction cardiac remodeling. J Biomed Sci. 2017;24(1):13.
[19] SHI Y, SU J, ROBERTS AI, et al. How mesenchymal stem cells interact with tissue immune responses. Trends Immunol. 2012;33(3):136-143.
[20] LIU W, ZHANG S, GU S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells recruit macrophages to alleviate experimental colitis through TGFβ1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(3):858-865.
[21] WANG N, SHAO Y, MEI Y, et al. Novel mechanism for mesenchymal stem cells in attenuating peritoneal adhesion: accumulating in the lung and secreting tumor necrosis factor α-stimulating gene-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012;3(6):51.
[22] BERNARDO ME, FIBBE WE. Mesenchymal stromal cells: sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;13(4):392-402.
[23] PENG Y, CHEN B, ZHAO J, et al. Effect of intravenous transplantation of hUCB-MSCs on M1/M2 subtype conversion in monocyte/macrophages of AMI mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;111:624-630.
[24] UM S, KIM HY, LEE JH, et al. TSG-6 secreted by mesenchymal stem cells suppresses immune reactions influenced by BMP-2 through p38 and MEK mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;368(3):551-561.
[25] LEE RH, PULIN AA, SEO MJ, et al. Intravenous hMSCs improve myocardial infarction in mice because cells embolized in lung are activated to secrete the anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5(1):54-63.
[26] DAY AJ, MILNER CM. TSG-6: A multifunctional protein with anti-inflammatory and tissue-protective properties. Matrix Biol. 2019;78-79:60-83.
[27] CHOI H, LEE RH, BAZHANOV N, et al. Anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6 secreted by activated MSCs attenuates zymosan-induced mouse peritonitis by decreasing TLR2/NF-κB signaling in resident macrophages. Blood. 2011;118(2):330-338.
[28] SONG WJ, LI Q, RYU MO, et al. TSG-6 released from intraperitoneally injected canine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate inflammatory bowel disease by inducing M2 macrophage switch in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):91.
[29] LIU L, SONG H, DUAN H, et al. TSG-6 secreted by human umbilical cord-MSCs attenuates severe burn-induced excessive inflammation via inhibiting activations of P38 and JNK signaling. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30121.
[30] LI R, LIU W, YIN J, et al. TSG-6 attenuates inflammation-induced brain injury via modulation of microglial polarization in SAH rats through the SOCS3/STAT3 pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):231.
[31] LEE JL, WANG MJ, CHEN JY. Acetylation and activation of STAT3 mediated by nuclear translocation of CD44. J Cell Biol. 2009;185(6):949-957.
[32] YAN D, WANG HW, BOWMAN RL, et al. STAT3 and STAT6 Signaling Pathways Synergize to Promote Cathepsin Secretion from Macrophages via IRE1α Activation. Cell Rep. 2016;16(11):2914-2927.
[33] BOURGUIGNON LY, BIKLE D. Selective Hyaluronan-CD44 Signaling Promotes miRNA-21 Expression and Interacts with Vitamin D Function during Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinomas Progression Following UV Irradiation. Front Immunol. 2015;6:224.
[34] CHANG SH, YEH YH, LEE JL, et al. Transforming growth factor-β-mediated CD44/STAT3 signaling contributes to the development of atrial fibrosis and fibrillation. Basic Res Cardiol. 2017;112(5):58.
[35] PONTA H, SHERMAN L, HERRLICH PA. CD44: from adhesion molecules to signalling regulators. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4(1):33-45.
[36] FRANGOGIANNIS NG. Cardiac fibrosis: Cell biological mechanisms, molecular pathways and therapeutic opportunities. Mol Aspects Med. 2019;65:70-99.
[37] ANZAI A, ANZAI T, NAGAI S, et al. Regulatory role of dendritic cells in postinfarction healing and left ventricular remodeling. Circulation. 2012;125(10):1234-1245.
[38] SHORTMAN K, LIU YJ. Mouse and human dendritic cell subtypes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(3):151-161.
[39] HIRATA Y, TABATA M, KUROBE H, et al. Coronary atherosclerosis is associated with macrophage polarization in epicardial adipose tissue. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(3):248-255.
[40] WYNN TA, CHAWLA A, POLLARD JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. 2013;496(7446):445-455.
|