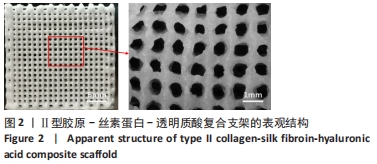
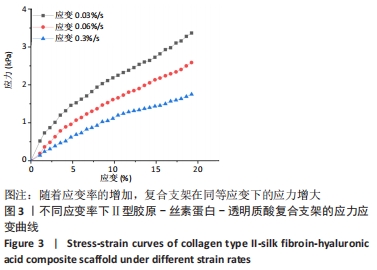
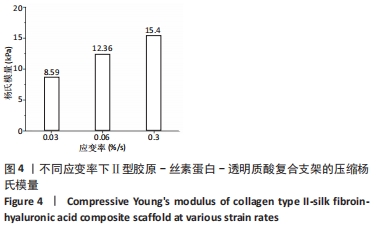
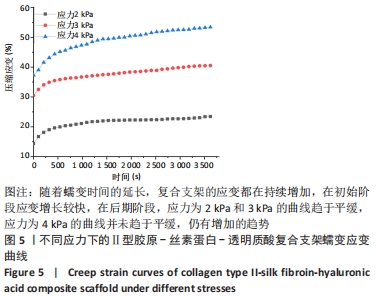
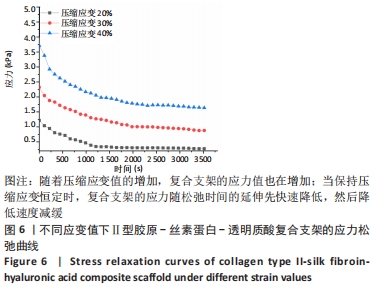
[1] 张荣,张向东,赵明宇.膝骨关节炎发病机制及治疗进展[J].风湿病与关节炎,2019,8(5):68-72.
[2] 胡坤,陈竹,罗栩伟,等.组织工程软骨的研究新进展[J].西部医学,2020,32(6):927-932.
[3] BORRELLI J, OLSON S A, GODBOUT C, et al. Understanding Articular Cartilage Injury and Potential Treatments. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33: S6-S11.
[4] ZHOU FF, ZHANG XZ, CAI DD, et al. Silk fibroin-chondroitin sulfate scaffold with immuno-inhibition property for articular cartilage repair. Acta Biomater. 2017;63:64-75.
[5] CHENG G, DAVOUDI Z, XING X, et al. Advanced Silk Fibroin Biomaterials for Cartilage Regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(8):2704-2715.
[6] ALMEIDA-GONZALEZ FR, GONZALEZ-VAZQUEZ A, MITHIEUX SM, et al. A step closer to elastogenesis on demand; Inducing mature elastic fibre deposition in a natural biomaterial scaffold. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2021;120:12.
[7] BHARADWAZ A, JAYASURIYA AC. Recent trends in the application of widely used natural and synthetic polymer nanocomposites in bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2020;110:30.
[8] ZHENG XF, YANG F, WANG SG, et al. Fabrication and cell affinity of biomimetic structured PLGA/articular cartilage ECM composite scaffold. J Mater Sci-Mater Med. 2011;22(3):693-704.
[9] ROGAN H, ILAGAN F, TONG XM, et al. Microribbon-hydrogel composite scaffold accelerates cartilage regeneration in vivo with enhanced mechanical properties using mixed stem cells and chondrocytes. Biomaterials. 2020;228:10.
[10] 林祥龙,高丽兰,李瑞欣,等.压缩载荷下软骨细胞/复合支架的三维培养[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(10):1483-1488.
[11] 满喜.生物软组织力学性质的理论研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古大学,2018.
[12] HUI E, GIRNENO KI, GUAN G, et al. Spatiotemporal Control of Viscoelasticity in Phototunable Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules. 2019;20(11):4126-4134.
[13] CHAUDHURI O, COOPER-WHITE J, JANMEY PA, et al. Effects of extracellular matrix viscoelasticity on cellular behaviour. Nature. 2020; 584(7822):535-546.
[14] 陈磊,葛为民,吕林蔚,等.人工软骨支架层间的力学性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(30):4763-4768.
[15] YODMUANG S, GUO HQ, BRIAL C, et al. Effect of interface mechanical discontinuities on scaffold-cartilage integration. J Orthop Res. 2019; 37(4):845-854.
[16] MCCULLEN SD, AUTEFAGE H, CALLANAN A, et al. Anisotropic Fibrous Scaffolds for Articular Cartilage Regeneration. Tissue Engineering Part A. 2012;18(19-20):2073-2083.
[17] ELHAMIAN S M M, ALIZADEH M, SHOKRIEH M M, et al. Transversely isotropic micromechanics model to determine effect of collagen fibre angle in mechanical properties of articular cartilage. Mater Technol. 2014;29(6):377-383.
[18] LIN XL, GAO LL, LI RX, et al. Mechanical property and biocompatibility of silk fibroin-collagen type II composite membrane . Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2019;105:110018.
[19] 刘志勤,刘浩,冯成宝,等.从牛软骨中提取Ⅱ型胶原蛋白及初步构建软骨支架[J].黑龙江大学自然科学学报,2016,33(3):386-391.
[20] YAMADA H, NAKAO H, TAKASU Y, et al. Preparation of undegraded native molecular fibroin solution from silkworm cocoons. Mater Sci Eng C-Biomimetic Supramol Syst. 2001;14(1-2):41-46.
[21] 杨泽龙,陈竹,冯刚.静电纺丝构建胶原-透明质酸钠-硫酸软骨素组织工程关节软骨支架的工艺探索[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2015,12(3):5-9.
[22] 孙凯,年争好,徐成,等.丝素蛋白复合胶原蛋白支架的制备及性能研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(7):903-908.
[23] FU N, DONG TZ, MENG A, et al. Research Progress of the Types and Preparation Techniques of Scaffold Materials in Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;13(7):583-590.
[24] TETSUKA H, SHIN SR. Materials and technical innovations in 3D printing in biomedical applications. J Mat Chem B. 2020;8(15):2930-2950.
[25] BONFANTI A, KAPLAN JL, CHARRAS G, et al. Fractional viscoelastic models for power-law materials. Soft Matter. 2020;16(26):6002-6020.
[26] HANYGA A, SEREDYNSKA M. Relations between relaxation modulus and creep compliance in anisotropic linear viscoelasticity. J Elast. 2007; 88(1):41-61.
[27] CHARPIN L, SANAHUJA J. Creep and relaxation Poisson’s ratio: Back to the foundations of linear viscoelasticity. Application to concrete. Int J Solids Struct. 2017;110:2-14.
[28] 魏朝磊,高丽兰,张春秋,等.单轴压缩下松质骨的应力率和蠕变性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(31):5014-5018.
[29] MANFERDINI C, GABUSI E, SARTORE L, et al. Chitosan-based scaffold counteracts hypertrophic and fibrotic markers in chondrogenic differentiated mesenchymal stromal cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(10):1896-1911.
[30] LATTANZIO C, TZAVARAS AE. Structural properties of stress relaxation and convergence from viscoelasticity to polyconvex elastodynamics. Arch Ration Mech Anal. 2006;180(3):449-492.
|