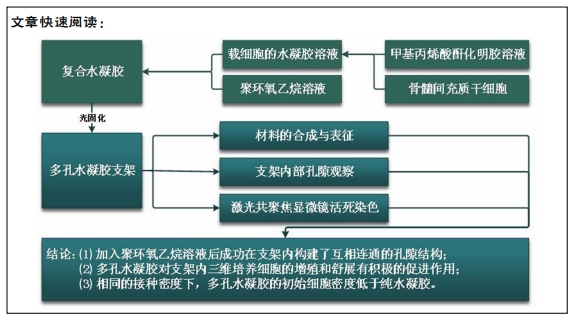
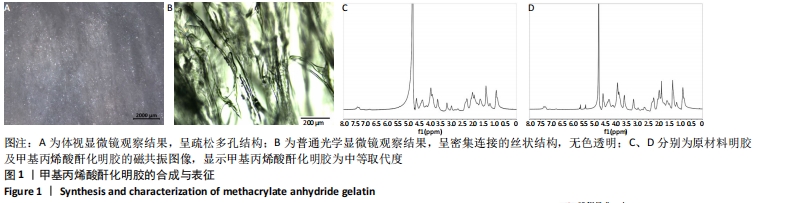
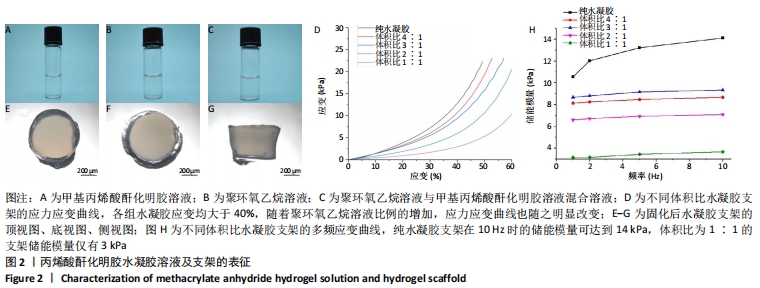
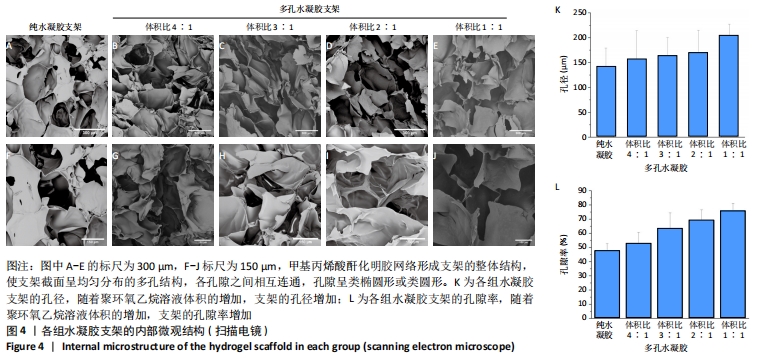
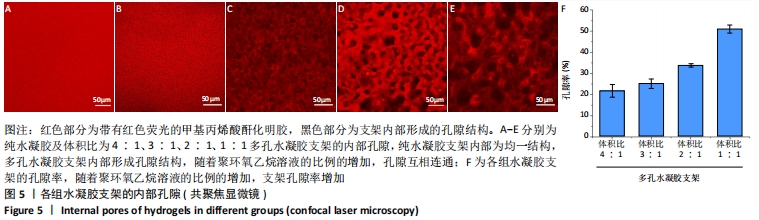
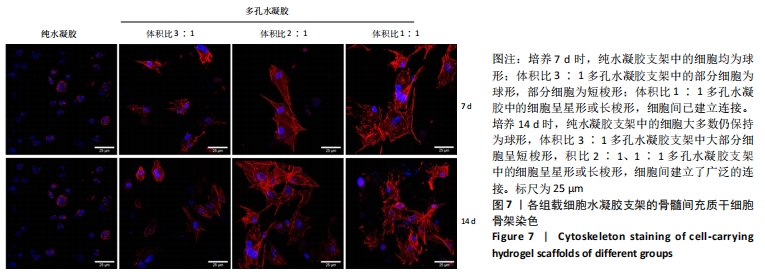
[1] LI JJ, EBIED M, XU J, et al. Current Approaches to Bone Tissue Engineering: The Interface between Biology and Engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(6):e1701061.
[2] 杨思敏,王新卫.自体骨移植修复骨缺损的临床研究进展[J].中国疗养医学,2019,28(9):945-948.
[3] 马武秀,程迅生.自体骨移植修复骨缺损的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(6):574-576.
[4] AZI ML, APRATO A, SANTI I, et al. Autologous bone graft in the treatment of post-traumatic bone defects: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):465.
[5] BRACEY DN, JINNAH AH, WILLEY JS, et al. Investigating the Osteoinductive Potential of a Decellularized Xenograft Bone Substitute. Cells Tissues Organs. 2019;207(2):97-113.
[6] SHIBUYA N, JUPITER DC. Bone graft substitute: allograft and xenograft. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2015;32(1):21-34.
[7] PORZIONATO A, STOCCO E, BARBON S, et al. Tissue-Engineered Grafts from Human Decellularized Extracellular Matrices: A Systematic Review and Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(12):4117.
[8] SHANBHAG S, PANDIS N, MUSTAFA K, et al. Bone tissue engineering in oral peri-implant defects in preclinical in vivo research: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(1): e336-e349.
[9] 刘利永,周雷.组织工程用水凝胶研发现状和发展趋势:基于专利信息的分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(22):3527-3533.
[10] WOLF MT, DALY KA, BRENNAN-PIERCE EP, et al. A hydrogel derived from decellularized dermal extracellular matrix . Biomaterials. 2012; 33(29):7028-7038.
[11] RASTOGI P, KANDASUBRAMANIAN B. Review of alginate-based hydrogel bioprinting for application in tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2019; 11(4):042001.
[12] AHSAN SM, THOMAS M, REDDY KK, et al. Chitosan as biomaterial in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;110: 97-109.
[13] BURDICK JA, PRESTWICH GD. Hyaluronic acid hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv Mater. 2011;23(12):H41-56.
[14] KONG XB, TANG QY, CHEN XY, et al. Polyethylene glycol as a promising synthetic material for repair of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(6):1003-1008.
[15] 顾亚伟,李牧,范子文,等.3D挤压成型生物打印含细胞水凝胶的理化性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(22):3583-3588.
[16] ABDOLLAHIYAN P, OROOJALIAN F, MOKHTARZADEH A, et al. Hydrogel-Based 3D Bioprinting for Bone and Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Biotechnol J. 2020;15(12):e2000095.
[17] BROWN TE, ANSETH KS. Spatiotemporal hydrogel biomaterials for regenerative medicine. Chem Soc Rev. 2017;46(21):6532-6552.
[18] CHEN J, ZHANG D, ZHANG T, et al. Effect of the vascularized bone components on the survival of vascularized composite allografts. J Surg Res. 2018;224:132-138.
[19] TENG W, LONG TJ, ZHANG Q, et al. A tough, precision-porous hydrogel scaffold: ophthalmologic applications . Biomaterials. 2014;35(32): 8916-8926.
[20] YING GL, JIANG N, MAHARJAN S, et al. Aqueous Two-Phase Emulsion Bioink-Enabled 3D Bioprinting of Porous Hydrogels. Adv Mater(Deerfield Beach, Fla). 2018;30(50):e1805460.
[21] 屈华伟,韩振宇,卓越,等.骨组织工程多孔生物支架设计研究进展[J].机械工程学报,2019,55(15):71-80.
[22] CHENG A, SCHWARTZ Z, KAHN A, et al. Advances in Porous Scaffold Design for Bone and Cartilage Tissue Engineering and Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019;25(1):14-29.
[23] PANSERI S, RUSSO A, CUNHA C, et al. Osteochondral tissue engineering approaches for articular cartilage and subchondral bone regeneration . Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(6):1182-1191.
[24] ROSETI L, PARISI V, PETRETTA M, et al. Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: State of the art and new perspectives. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;78:1246-1262.
[25] NAAHIDI S, JAFARI M, LOGAN M, et al. Biocompatibility of hydrogel-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol Adv. 2017;35(5):530-544.
[26] YAMAMOTO S, OKADA K, SASAKI N, et al. Photoactivatable Hydrogel Interfaces for Resolving the Interplay of Chemical, Mechanical, and Geometrical Regulation of Collective Cell Migration. Langmuir. 2019;35(23):7459-7468.
[27] GIBBS DM, BLACK CR, DAWSON JI, et al. A review of hydrogel use in fracture healing and bone regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(3):187-198.
[28] AGARWAL R, GARCíA AJ. Biomaterial strategies for engineering implants for enhanced osseointegration and bone repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;94:53-62.
[29] HOSSEINI SA, MOHAMMADI R, NORUZI S, et al. Evolution of hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering of the knee: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88(1):105096.
[30] YUE K, TRUJILLO-DE SANTIAGO G, ALVAREZ MM, et al. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;73:254-271.
[31] KLOTZ BJ, GAWLITTA D, ROSENBERG A, et al. Gelatin-Methacryloyl Hydrogels: Towards Biofabrication-Based Tissue Repair. Trends Biotechnol. 2016;34(5):394-407.
[32] JENSEN C, TENG Y. Is It Time to Start Transitioning From 2D to 3D Cell Culture? Front Mol Biosci. 2020;7:33.
[33] BILLIET T, VANDENHAUTE M, SCHELFHOUT J, et al. A review of trends and limitations in hydrogel-rapid prototyping for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2012;33(26):6020-6041.
|