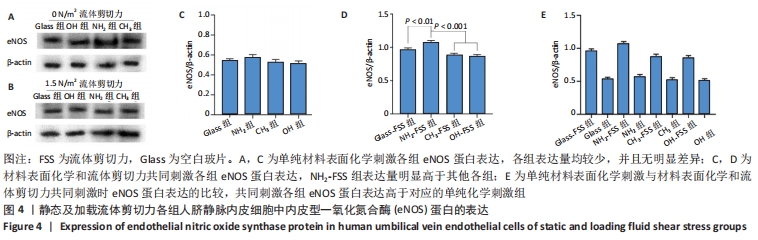
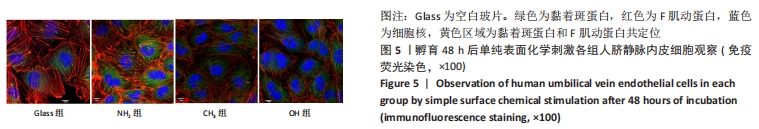
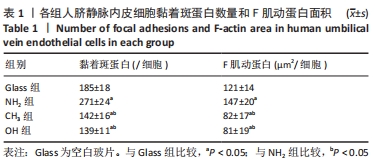
[1] YIN S, ZHANG W, ZHANG Z, et al. Recent Advances in Scaffold Design and Material for Vascularized Tissue-Engineered Bone Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(10):e1801433.
[2] ROSETI L, PARISI V, PETRETTA M, et al. Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: State of the art and new perspectives. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;78:1246-1262.
[3] INOMATA K, HONDA M. Co-Culture of Osteoblasts and Endothelial Cells on a Microfiber Scaffold to Construct Bone-Like Tissue with Vascular Networks. Mater. 2019;12(18):2869.
[4] LIU J, CHUAH YJ, FU J, et al. Co-culture of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human bone marrow stromal cells into a micro-cavitary gelatin-methacrylate hydrogel system to enhance angiogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;102(9):6-16.
[5] YANG D, XIAO J, WANG B, et al. The immune reaction and degradation fate of scaffold in cartilage/bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;(104)109927.
[6] ARIMA Y, IWATA H. Effect of wettability and surface functional groups on protein adsorption and cell adhesion using well-defined mixed self-assembled monolayers. Biomaterials. 2007;28(20):3074-3082.
[7] WANG W, LIU D, LI D, et al. Nanofibrous vascular scaffold prepared from miscible polymer blend with heparin/stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha for enhancing anticoagulation and endothelialization. Colloids Surf B. 2019;(181):963-972.
[8] KOHN JC, ZHOU DW, BORDELEAU F, et al. Cooperative effects of matrix stiffness and fluid shear stress on endothelial cell behavior. Biophys J. 2015;108(3):471-478.
[9] MALEK AM, IZUMO S. Mechanism of endothelial cell shape change and cytoskeletal remodeling in response to fluid shear stress. J Cell Sci. 1996;109(Pt4):713-726.
[10] CHISTIAKOV DA, OREKHOV AN, BOBRYSHEV Y V. Effects of shear stress on endothelial cells: go with the flow. Acta Physiol. 2017;219(2):382-408.
[11] CHEN ZZ, YUAN WM, XIANG C, et al. A microfluidic device with spatiotemporal wall shear stress and ATP signals to investigate the intracellular calcium dynamics in vascular endothelial cells. Biomech Model Mechan. 2019;18(1):189-202.
[12] MARKOS F, RUANE O’HORA T, NOBLE MI. What is the mechanism of flow-mediated arterial dilatation. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2013; 40(8):489-494.
[13] 张燕,王玉彩,刘振东,等.流体剪切力对内皮细胞miR-21和miR-199a表达的影响[J].生物信息学,2016,14(1):19-25.
[14] 王艺璇,蔡军.剪切力和拉伸应力对血管内皮细胞的影响[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2012,4(8):38-41.
[15] 陈满军,洪文娟,洪志鹏.血液剪切力诱导的血管内皮细胞形态学变化和信号通路[J].山东医药,2014(40):99-102.
[16] LI Y, ZHENG J, BIRD IM, et al. Effects of pulsatile shear stress on signaling mechanisms controlling nitric oxide production, endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation, and expression in ovine fetoplacental artery endothelial cells. Endothelium J Endoth. 2005;12(1-2):21-39.
[17] HONG HG, JIANG M, SLIGAR SG, et al. Cysteine-specific surface tethering of genetically engineered cytochromes for fabrication of metalloprotein nanostructures. Langmuir. 1994;10(1):153-158.
[18] FAUCHEUX N, SCHWEISS R, LüTZOW K, et al. Self-assembled monolayers with different terminating groups as model substrates for cell adhesion studies. Biomaterials. 2004;25(14):2721-2730.
[19] REN Y J, ZHANG H, HUANG H, et al. In vitro behavior of neural stem cells in response to different chemical functional groups. Biomaterials. 2009;30(6):1036-1044.
[20] TAO J, YANG Z, WANG JM, et al. Effects of fluid shear stress on eNOS mRNA expression and NO production in human endothelial progenitor cells. Cardiology. 2006;106(2):82-88.
[21] GHIMIRE K, ZARIC J, ALDAY-PAREJO B, et al. MAGI1 Mediates eNOS Activation and NO Production in Endothelial Cells in Response to Fluid Shear Stress. Cells. 2019;8(5):388
[22] MOTT RE, HELMKE BP. Mapping the dynamics of shear stress-induced structural changes in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007; 293(5):C1616-1626.
[23] RUSSELL-PULERI S, DELA PAZ NG, ADAMS D, et al. Fluid shear stress induces upregulation of COX-2 and PGI(2) release in endothelial cells via a pathway involving PECAM-1, PI3K, FAK, and p38. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017;312(3):H485-H500.
[24] XANTHIS I, SOUILHOL C, SERBANOVIC-CANIC J, et al. β1 integrin is a sensor of blood flow direction. J Cell Sci. 2019;132(11):229542.
[25] GONG X, ZHAO X, LI B, et al. Quantitative Studies of Endothelial Cell Fibronectin and Filamentous Actin (F-Actin) Coalignment in Response to Shear Stress. Microsc Microanal. 2017;23(5):1013-1023.
[26] NGUYEN H, HUYNH K, STOLDT VR. Shear-dependent fibrillogenesis of fibronectin: Impact of platelet integrins and actin cytoskeleton. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2018;497(2):797-803.
[27] BOESPFLUG GL, MAIRE M, DE CRESCENZO G, et al. Characterization and comparison of N‐, O‐, and N+O‐functionalized polymer surfaces for efficient (HUVEC) endothelial cell colonization. Plasma Process Polym. 2017;14(7): 1600139.
[28] NATALE CF, LAFAURIE-JANVORE J, VENTRE M, et al. Focal adhesion clustering drives endothelial cell morphology on patterned surfaces. J R Soc Interface. 2019;16(158):20190263.
[29] LI T, HAO L, LI J, et al. Insight into vitronectin structural evolution on material surface chemistries: The mediation for cell adhesion. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(4):1044-1052.
[30] BARRIAS CC, MARTINS MC, ALMEIDA-PORADA G, et al. The correlation between the adsorption of adhesive proteins and cell behaviour on hydroxyl-methyl mixed self-assembled monolayers. Biomaterials. 2009; 30(3):307-316.
|