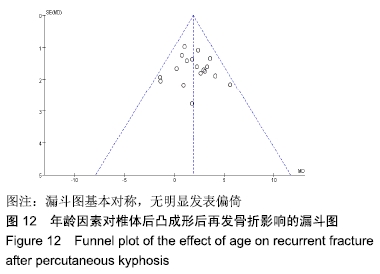
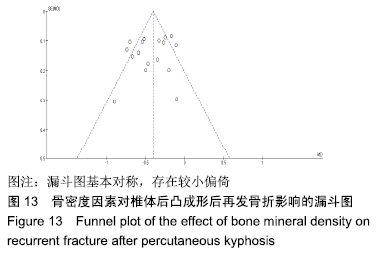
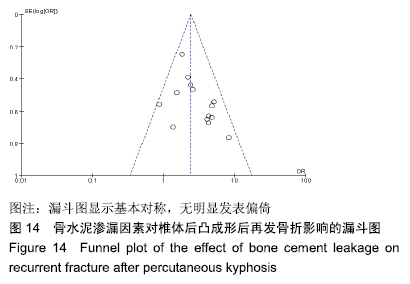
[1] LEE SK, LEE SH, YOON SP, et al. Quality of life comparison between vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Asian Spine J. 2014;8(6):799-803.
[2] DRAMPALOS E, NIKOLOPOULOS K, BALTAS C, et al. Vertebral fracture assessment:Current research status and application in patients with kyphoplasty. World J Orthop. 2015;6:680-687.
[3] JOHNELL O, KANIS JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2006; 17:1726-1733.
[4] KRAPPINGER D, KASTENBERGER TJ, SCHMID R. Augmented posterior instrumentation for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body fractures. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2012;24:4-12.
[5] ZOU D, ZHANG K, REN Y. Therapeutic effects of PKP on chronic painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with or without intravertebral cleft. Int J Clin Exp Med.2014;8:15780-15786.
[6] YANG LY, WANG XL, ZHOU L, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of unilateral versus bilateral kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Pain Physician. 2013;16(4): 277-290.
[7] STANG A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):603-605.
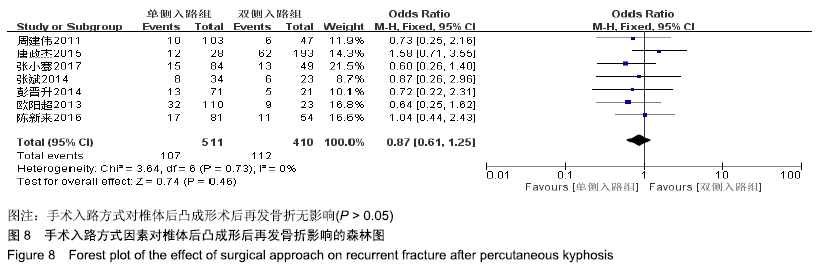
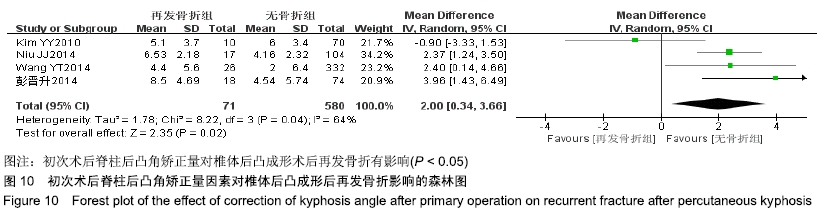
[8] 吕世桥,王磊升,沈炳华,等.经皮穿刺椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折术后发生继发性椎体骨折的危险因素分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(11):1045-1048.
[9] 周建伟,马华松,邹德威,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折经皮穿刺球囊扩张后凸成形术后再骨折的相关因素研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011, 25(10):1180-1183.
[10] 欧阳超,陈志明,马华松,等.椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折术后非手术椎体新发骨折的相关因素分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013, 23(3):222-227.
[11] 贾璞,费琦,李锦军,等.椎体后凸成形术后椎体再骨折相关因素分析研究[J].中国骨与关节外科,2013,6(2):153-156.
[12] 张斌.PKP术后继发邻近椎体骨折的相关因素分析及骨量变化趋势的研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2014.
[13] 彭晋升,邹德威,周建伟,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术后相邻与远节段椎体再骨折危险因素分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2014,35(6):414-418.
[14] 唐政杰,侯宇,张亘瑷,等.椎体后凸成形术后再发骨折的相关危险因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(2):124-131.
[15] 曲道奎,焦守国,杨明,等.PKP术后新发有症状椎体压缩骨折的影响因素分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(7):701-703.
[16] 陈新来,于志勇,黄春选,等.球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术后继发相邻节段椎体骨折的危险因素分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(1):37-39.
[17] 张小骞,吴天顺,邱奕雁,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折后非手术椎体骨折的原因分析[J].骨科,2017,8(3):184-189.
[18] 雷飞,何雯,杨函,等.PKP术后新发椎体骨折危险因素分析[J].重庆医科大学学报,2017,42(2):145-149.
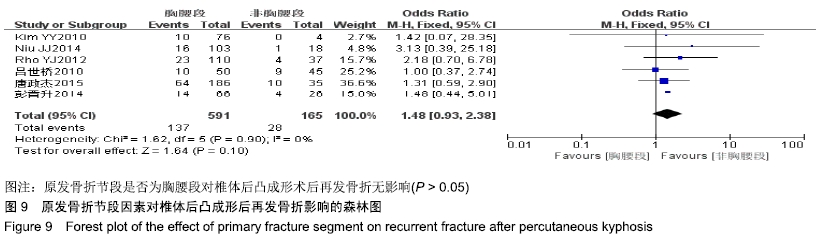
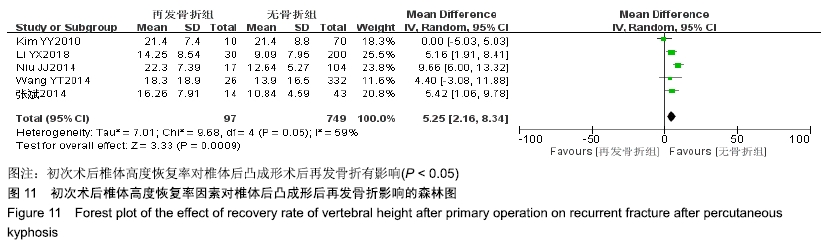
[19] RHYU KW, KIM YY. Recompression of vertebral body after balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(11):1907-1912.
[20] RHO YJ, CHOE WJ, CHUN YI. Risk factors predicting the new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(5):905-911.
[21] SPROSS C, AGHAYEV E, KOCHER R, et al. Incidence and risk factors for early adjacent vertebral fractures after balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic fractures: analysis of the SWISSspine registry. Eur Spine J. 2013;23(6):1332-1338.
[22] WANG YT, WU XT, CHEN H, et al. Adjacent-level symptomatic fracture after percutaneous vertebral augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a retrospective analysis. J Orthop Sci. 2014; 19(6):868-876.
[23] LIN D, HAO J, LI L, et al. Effect of bone cement volume fraction on adjacent vertebral fractures after unilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(3):E270-E275.
[24] NIU J , ZHOU H , MENG Q , et al. Factors affecting recompression of augmented vertebrae after successful percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty: a retrospective analysis. Acta Radiologica. 2014: 0284185114556016.
[25] NING L, WAN S, LIU C, et al. New levels of vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous kyphoplasty: retrospective analysis of styles and risk factors. Pain Physician. 2015;18(6):565.
[26] YANG S, LIU Y, YANG H, et al. Risk factors and correlation of secondary adjacent vertebral compression fracture in percutaneous kyphoplasty. Int J Surg. 2016:S1743919116309864.
[27] KO BS, CHO KJ, PARK JW. Early adjacent vertebral fractures after balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Asian Spine J. 2019;13(2):210-215.
[28] LI YX, GUO DQ, ZHANG SC, et al. Risk factor analysis for re-collapse of cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty (PVP) or percutaneous kyphoplasty (PKP). Int Orthop. 2018;42(9):2131-2139.
[29] FRANKEL BM, MONROE T, WANG C. Percutaneous vertebral augmentation:an elevation in adjacent-level fracture risk in kyphoplasty as compared with vertebroplasty. Spine J.2007;7(5): 575-582.
[30] GRADOS F, DEPRIESTER C, CAYROLLE G, et al. Longterm observations of vertebral osteoporotic fractures treated by percutaneous vertebroplasty. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000; 39: 1410-1414.
[31] BERLEMANN U, FERGUSON SJ, NOLTE LP, et al. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty: A biomechanical investigation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84:748-752.
[32] UPPIN AA, HIRSCH JA, CENTENERA LV, et al. Occurrence of new vertebral body fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporosis.Radiology.2003;226:119-124.
[33] VOORMOLEN MH, LOHLE PN, JUTTMANN JR, et al. The risk of new osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the year after percutaneous vertebroplasty. J VascInterv Radiol. 2006; 17:71-76.
[34] KOMEMUSHI A, TANIGAWA N, KARIYA S, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fracture: Multivariate study of predictors of new vertebral body fracture. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol.2006;29:580-585.
[35] THOMAS T, BAROU O, VICO L, et al. Recurrence of vertebral fracture with cyclical etidronate therapy in osteoporosis: Histomorphometry and x-ray microanalysis evaluation. J Bone Miner Res.1999;14:198-205.
[36] OOMS ME, LIPS P, VAN LINGEN A, et al. Determinants of bone mineral density and risk factors for osteoporosis in healthy elderly women. J Bone Miner Res.1993;8:669-675.
[37] KAUFMAN JM, PALACIOS S, SILVERMAN S, et al.An evaluation of the fracture risk assessment tool (FRAX® ) as an indicator of treatment efficacy: The effects of bazedoxifene and raloxifene on vertebral,nonvertebral,and all clinical fractures as a function of baseline fracture risk assessed by FRAX®.Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(10):2561-2569.
[38] KLAZEN CA, VENMANS A, DE VRIES J, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty is not a risk factor for newosteoporotic compression fractures: results from VERTOS II.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(8): 1447-1450.
[39] ZHANG L, YANG G, WU L, et al.The biomechanical effects of osteo-porosis vertebral augmentation with cancellous bone granules orbone cement on treated and adjacent non-treated vertebral bodies:A finite element evaluation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2010;25(2): 166-172.
[40] BAROUD G, HEINI P, NEMES J, et al. Biomechanical explanation of adjacent fractures following vertebroplasty.Radiology.2003;229: 606-607.
[41] 蔡凯文,蒋国强,卢斌,等.椎间隙骨水泥渗漏的不同分型对邻椎相邻终板应力分布的影响:三维有限元研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(6):364-373.
[42] LIEBSCHNER MA, ROSENBERG WS, KEARENY TM, et al. Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty.Spine.2001;26(14):1547-1554.
[43] STEINMANN J,TINGEY CT,CRUZ G, et al. Biomechanical comparison of unipedicular versus bipedicular kyphoplasty.Spine. 2005;30(2):201-205.
[44] MOVRIN I, VENGUST R, KOMADINA R. Adjacent vertebral fracturesafter percutaneous vertebral augmentation of osteoporotic vertebralcompression fracture: A comparison of balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2010;130(9):1157-1166.
[45] KIM SH, KANG HS, CHOI JA, et al. Risk factors of new compression fractures in adjacent vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Acta Radiol. 2004;45:440-445.
[46] LIN WC, LEE YC, LEE CH, et al. Refractures in cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty: a retrospective analysis. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(4): 592-599.
|