中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (3): 348-353.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2407
• 脊柱植入物 spinal implant • 上一篇 下一篇
颈脊髓中央管综合征钛板内固定和药物治疗的预后因素分析
张 辉,徐南伟,农鲁明,汤雪明,周鑫叠,蒋 巍
- 南京医科大学附属常州第二人民医院脊柱外科,江苏省常州市 213003
Factors influencing the prognosis of central cord syndrome treated with drug therapy and titanium plate fixation
Zhang Hui, Xu Nanwei, Nong Luming, Tang Xueming, Zhou Xindie, Jiang Wei
- Department of Spinal Surgery, Changzhou Second People’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Changzhou 213003, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
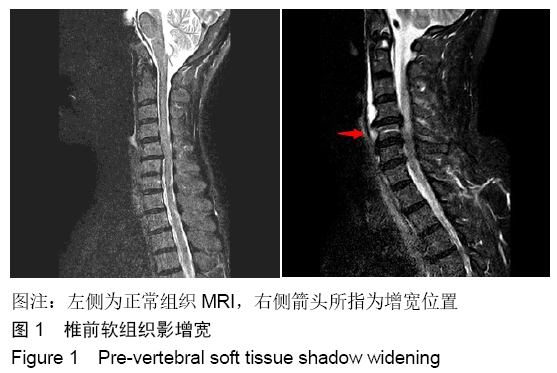
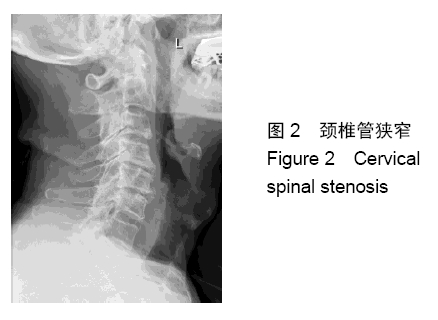
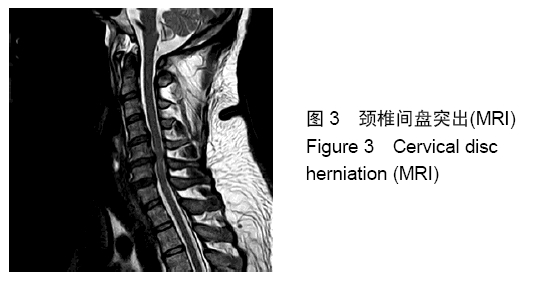
颈脊髓中央管综合征:是最常见的创伤性颈髓损伤模式,占所有颈脊髓损伤的20%和不完全性颈髓损伤的约70%。虽然一些关于中心脊髓综合征的确切病理生理学的争议仍然存在,但最近与磁共振成像结果相关的组织病理学证据表明,外侧皮质脊髓束是患者发生最严重损伤的位置。
颈脊髓中央管综合征的治疗:在颈脊髓中央管综合征的治疗中,因为患者神经恢复速度以及程度的不同使临床难以预测神经恢复的程度。颈脊髓中央管综合征的治疗,特别是关于治疗方式,仍然存在争议。
背景:在颈脊髓中央管综合征的治疗中,因为患者神经恢复速度以及程度的不同使临床难以预测神经恢复的程度。颈脊髓中央管综合征的治疗,特别是关于治疗方式,仍然存在争议。
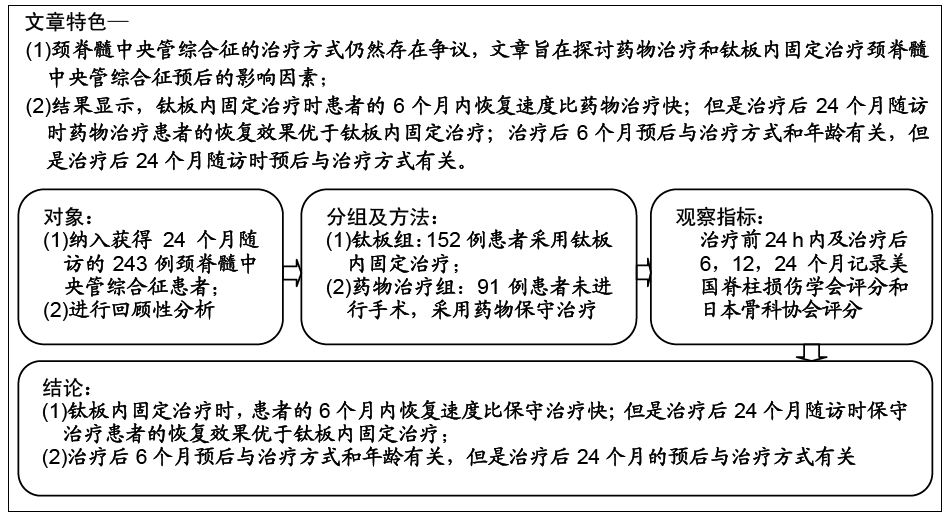
目的:探讨药物治疗和钛板内固定治疗颈脊髓中央管综合征预后的影响因素。
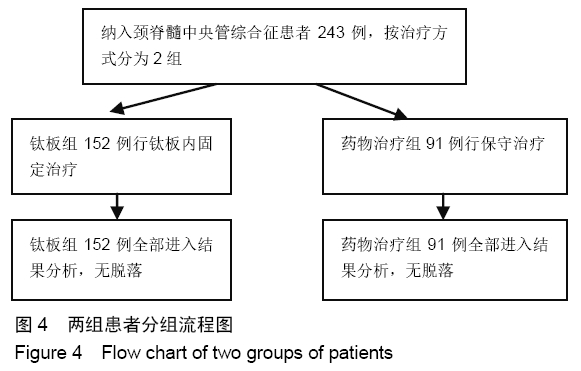
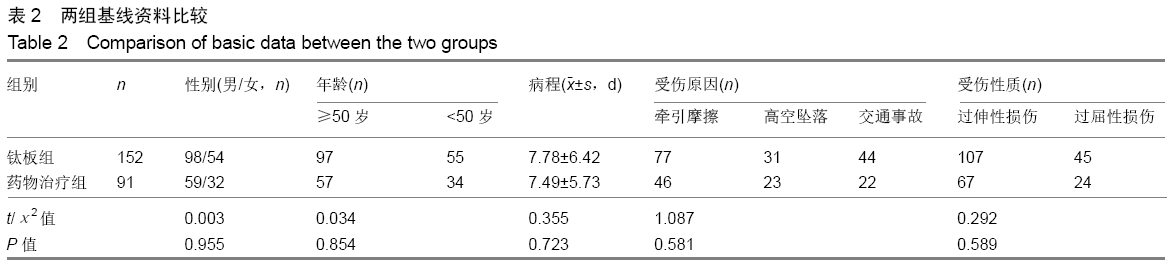
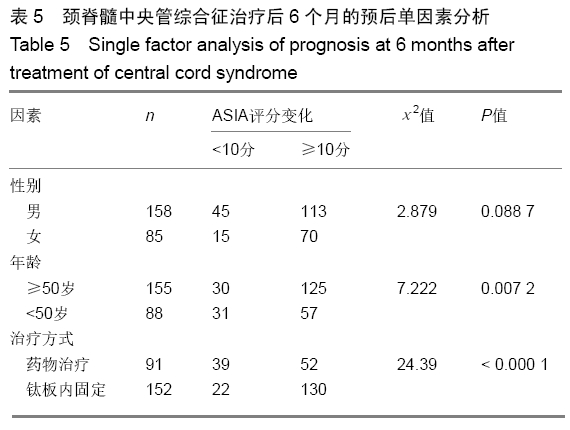
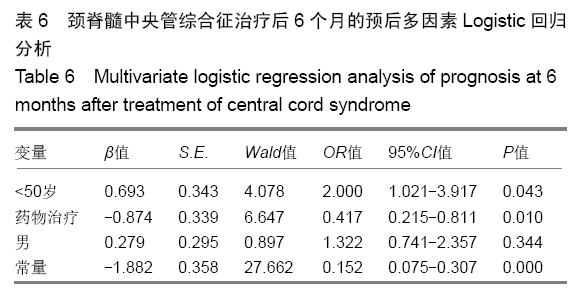
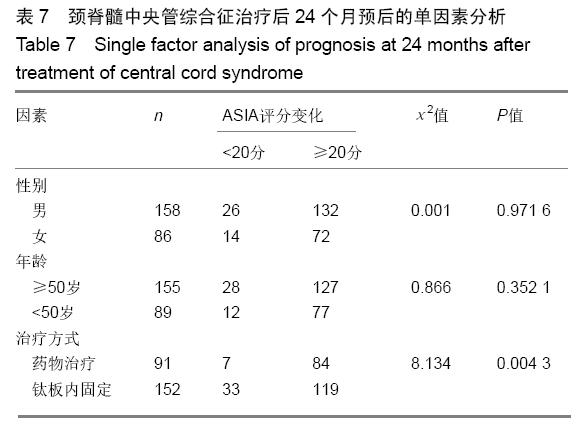
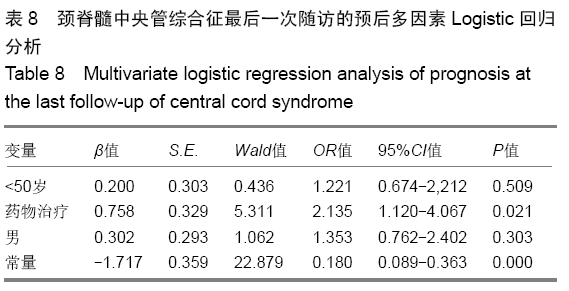
方法:对2012年6月至2017年6月南京医科大学附属常州第二人民医院收治并获得随访的243例颈脊髓中央管综合征患者进行回顾性分析,根据治疗方案分为2组,钛板组152例行钛板置入内固定,药物治疗组91例给予药物治疗。所有患者对治疗方案均知情同意,且得到医院伦理委员会批准。采用美国脊柱损伤学会和日本骨科协会标准对患者神经功能进行评定,记录所有患者治疗前24 h内及治疗后6,12,24个月随访的美国脊柱损伤学会和日本骨科协会评分。将年龄、治疗方式和性别因素纳入颈脊髓中央管综合征治疗后6,24个月随访时的预后单因素分析。之后将年龄、治疗方式和性别因素纳入颈脊髓中央管综合征治疗后6,24个月随访时的预后多因素Logistic回归分析。
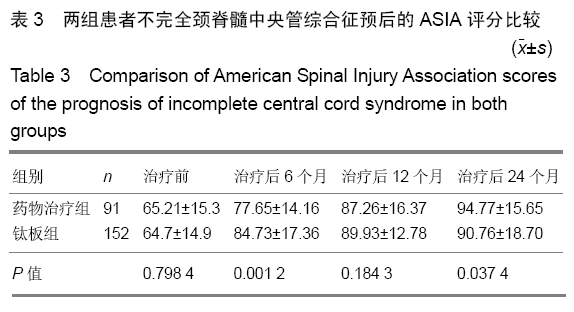
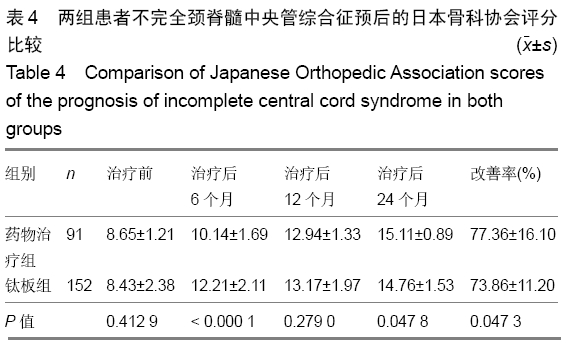
结果与结论:①243例患者均获24个月以上随访,治疗后恢复良好;②治疗后6个月药物治疗组美国脊柱损伤学会评分和日本骨科协会评分均低于钛板组(P=0.001 2,0.000 0);但治疗后24个月随访时药物治疗组的美国脊柱损伤学会和日本骨科协会评分均高于钛板组(P=0.037 4,0.047 8);③颈脊髓中央管综合征患者治疗后6个月的预后与患者年龄和治疗方式有相关性(P=0.007 2,P < 0.000 1),且药物治疗及年龄大于50岁与颈脊髓中央管综合征患者治疗后6个月不良预后相关(P=0.043,P=0.010);④颈脊髓中央管综合征治疗24个月随访时的预后与患者的治疗方式有相关性(P=0.004 3),且药物治疗与颈脊髓中央管综合征患者治疗后24个月随访时预后相关(P=0.021);⑤结果提示,钛板内固定治疗时患者的6个月内恢复速度比药物治疗快;但是治疗后24个月随访时药物治疗患者的恢复效果优于钛板内固定治疗;治疗后6个月预后与治疗方式和年龄有关,但是治疗后24个月随访时预后与治疗方式有关。ORCID: 0000-0002-0064-0003(张辉)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: