中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (3): 354-358.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2408
• 脊柱植入物 spinal implant • 上一篇 下一篇
经口寰枢椎复位钉棒系统内固定与口咽部气道狭窄的关系
易红蕾1,陈兴捷1,2,陈旭琼1,吴增晖1,马向阳1,艾福志1,王建华1,章 凯1,夏 虹1
- 1解放军南部战区总医院,广东省广州市 510000;2南方医科大学研究生院,广东省广州市 510000
Relationship between transoral atlantoaxial reduction screw-rod system fixation and oropharyngeal airway stenosis
Yi Honglei1, Chen Xingjie1, 2, Chen
Xuqiong1, Wu Zenghui1, Ma Xiangyang1, Ai Fuzhi1,
Wang Jianhua1,
- 1General Hospital of Southern Theater Command, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Graduate School of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
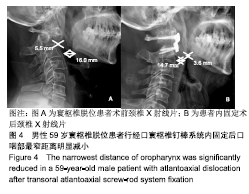
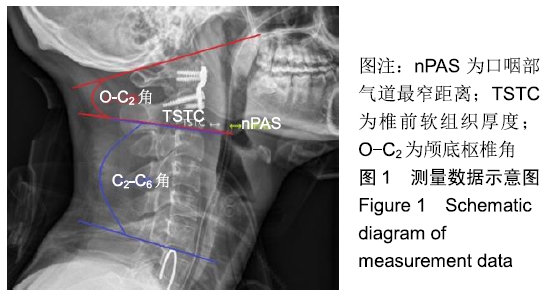
口咽部气道最窄距离:于颈椎侧位X射线片上分别找出悬雍垂及会厌的软组织影,并在悬雍垂下缘及会厌上缘各作一平行线,在两平行线之间直接找出气管影的最窄距离并进行测量。
椎前软组织厚度:为排除脱位的寰椎对C2椎前软组织的影响,测量起始点选于C2椎体下缘,测量此起始点至气管阴影后方的水平距离。
背景:经口寰枢椎复位内固定治疗的患者,寰枢椎前方放置钢板、软组织肿胀等因素都可能影响口咽部空间。目前尚未见到寰枢椎脱位前路术后出现吞咽困难或呼吸困难解剖学因素的相关报道。
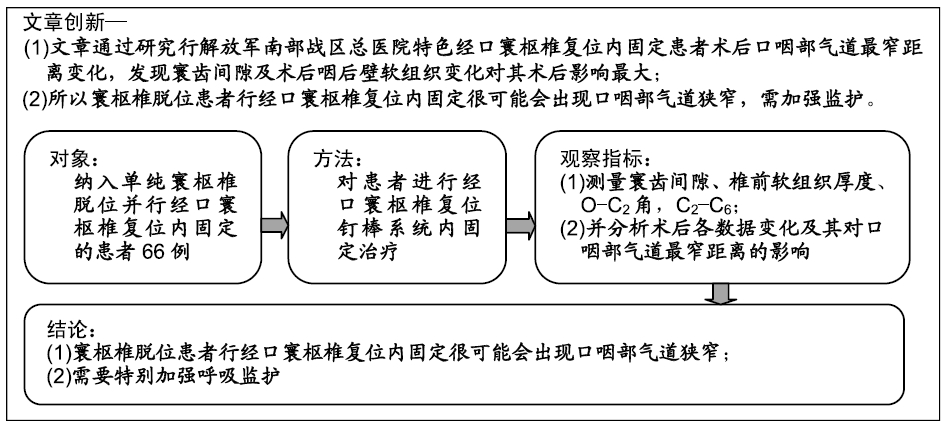
目的:观察寰枢椎脱位并行经口寰枢椎复位钉棒系统内固定后患者口咽部气道空间变化及相关影响因素分析
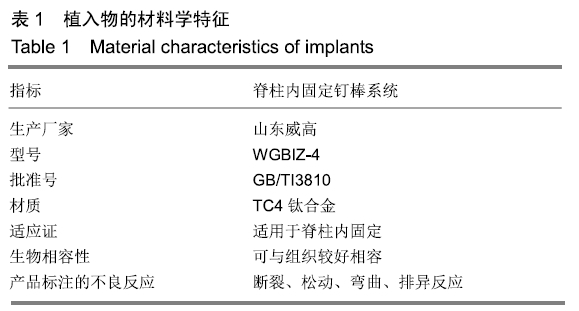
方法:纳入2012年1月至2016年12月在解放军南部战区总医院因单纯寰枢椎脱位行前路经口寰枢椎复位钉棒系统内固定的患者66例,男38例,女28例,年龄11-71岁。所有入选患者对治疗及测量方案均知情同意,且得到医院伦理委员会批准。分别测量术前及术后站立中立位颈椎侧位X射线片的口咽部气道最窄距离、C2椎前软组织厚度、寰齿间隙、颅底枢椎角(O-C2角)、C2-C6角,并分析术后各数据的变化及其对口咽部气道最窄距离的影响。
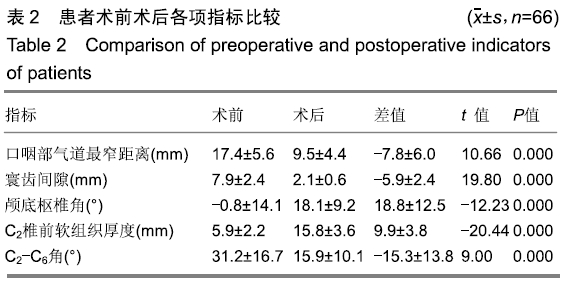
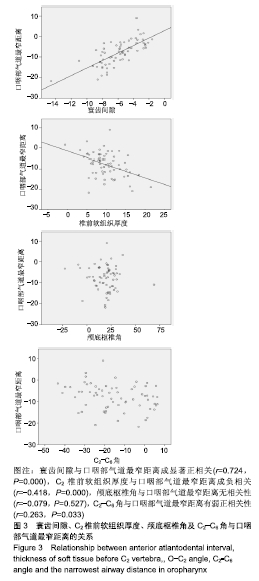
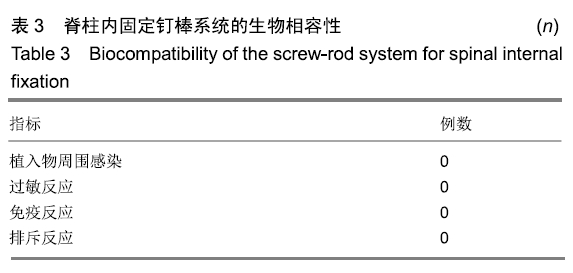
结果与结论:①患者术后口咽部气道最窄距离、寰齿间隙、C2-C6角度均较术前明显减少(P < 0.001);而C2椎前软组织厚度、颅底枢椎角均较术前明显增加(P < 0.001);②在进行多元回归分析中,口咽部气道最窄距离变化的最大影响因素是寰齿间隙(β=7.070)及C2椎前软组织厚度(β=0.387),而与颅底枢椎角无明显相关性;③提示对于单纯寰枢椎脱位患者行经口寰枢椎复位钉棒系统内固定后会造成口咽部气道狭窄,原因在于寰齿间隙的减少以及椎前筋膜增厚。说明经口寰枢椎复位钉棒系统内固定治疗寰枢椎脱位即使维持了较好的颅底枢椎角,但仍可能造成患者吞咽障碍或呼吸困难。
ORCID: 0000-0001-9387-2374(易红蕾)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: