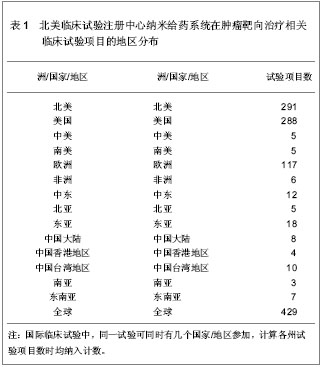
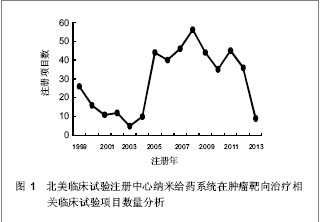
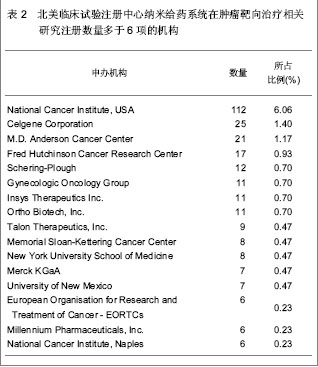
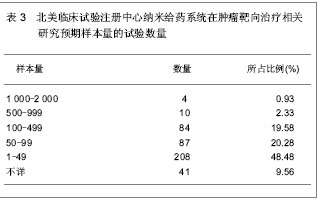
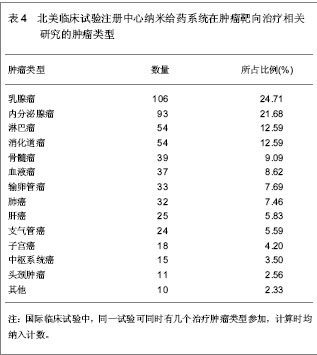
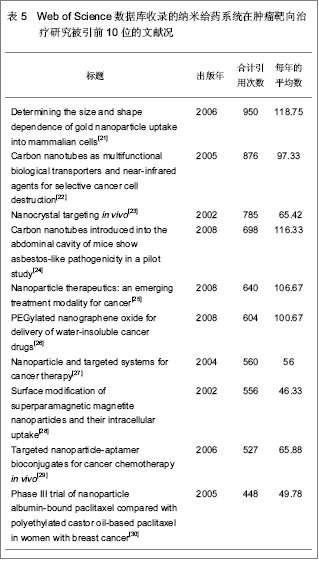
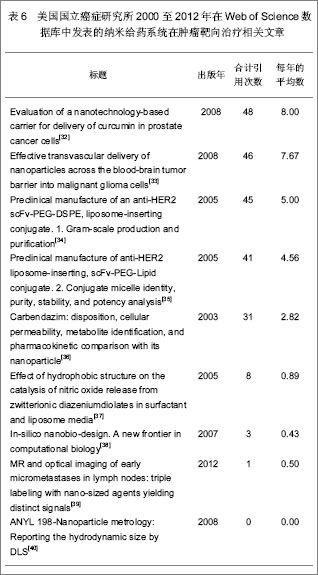
| [1] Kodaira H, Tsutsumi Y, Yoshioka Y, et al. The targeting of anionized polyvinylpyrrolidone to the renal system. Biomaterials. 2004;25(18):4309-4315.[2] Langer R. Drug delivery and targeting. Nature. 1998;392 (6679 Suppl):5-10.[3] Pierce WM, Leonard WC. Bone targeted inhibitors of carbonic anhydraseP. Eur Patent: 201057, 1986-11-12.[4] Hwang HY, Kim IS, Kwon IC, et al. Tumor targetability and antitumor effect of docetaxel-loaded hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2008;128(1): 23-31.[5] Omelyanenko V, Kopecková P, Gentry C, et al. Targetable HPMA copolymer-adriamycin conjugates. recognition, internalization, and subcellular fate. J Control Release. 1998;53(1-3):25-37.[6] Goldberg M, Langer R, Jia X. Nanostructured materials for applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2007;18(3):241-268.[7] Donbrow M, Friedman M .Timed release from polymeril films containing drugs and kinetics of drug release. J Pharm Sci. 1975;64(1):76-80.[8] Saltzman WM, Fung LK. Polymeric implants for cancer chemotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997;26(2-3):209-230.[9] Yoshioka Y, Tsutsumi Y, Mukai Y, et al.Effective accumulation of poly(vinylpyrrolidone-co-vinyl laurate) into the spleen.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004;70(2):219-223.[10] Nishiyama N, Kataoka K. Current state, achievements, and future prospects of polymeric micelles as nanocarriers for drug and gene delivery. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;112(3): 630-648.[11] Archakov AI, Ivanov YD. Analytical nanobiotechnology for medicine diagnostics. Mol Biosyst. 2007;3(5):336-342.[12] Han M, He CX, Fang QL, et al. A novel camptothecin derivative incorporated in nano-carrier induced distinguished improvement in solubility, stability and anti-tumor activity both in vitro and in vivo. Pharm Res. 2009;26(4):926-935.[13] 易承学,余江南,徐希明.纳米药物载体在中药制剂研发中的应用[J].中国中药杂志,2008;33(16):1936-1940.[14] Thompson WW, Anderson DB, Heiman ML. Biodegradable microspheres as a delivery system for rismorelin porcine, a porcine-growth-hormone-releasing-hormone. J Control Release. 1997;43(1):9-22.[15] Davis SS. Biomedical applications of nanotechnology implications for drug targeting and gene therapy. Trends Biotechnol. 1997;15(6):217-224.[16] Foster TP, Moseley WM, Caputo JF, et al. Sustained elevated serum somatotropin concentrations in Holstein steers following subcutaneous delivery of a growth hormone releasing factor analog dispersed in water, oil or microspheres. J Control Release.1997;47(1):91-99.[17] Janes KA, Calvo P, Alonso MJ. Polysaccharide colloidal particles as delivery systems for macromolecules. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;47(1):83-97.[18] 王斌.靶向抗肿瘤药物载体系统研究近况[J].广东药学学报, 1998,14(4):311-314.[19] Takeuchi H, Yamamoto H, Kawashima Y. Mucoadhesive nanoparticulate systems for peptide drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;47(1):39-54.[20] Jain KK. Nanomedicine: application of nanobiotechnology in medical practice. Med Prine Pract.2008;17(2):89-101.[21] Chithrani BD, Ghazani AA, Chan WC. Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett. 2006;6(4):662-668.[22] Kam NW, O'Connell M, Wisdom JA, et al. Carbon nanotubes as multifunctional biological transporters and near-infrared agents for selective cancer cell destruction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(33):11600-11605. [23] Akerman ME, Chan WC, Laakkonen P, et al. Nanocrystal targeting in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(20): 12617-12621.[24] Poland CA, Duffin R, Kinloch I, et al. Carbon nanotubes introduced into the abdominal cavity of mice show asbestos-like pathogenicity in a pilot study. Nat Nanotechnol. 2008;3(7):423-428. [25] Davis ME, Chen ZG, Shin DM. Nanoparticle therapeutics: an emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7(9):771-782. [26] Liu Z, Robinson JT, Sun X, et al. PEGylated nanographene oxide for delivery of water-insoluble cancer drugs. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130(33):10876-10877. [27] Brannon-Peppas L, Blanchette JO.Nanoparticle and targeted systems for cancer therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004;56(11): 1649-1659.[28] Zhang Y, Kohler N, Zhang M. Surface modification of superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles and their intracellular uptake. Biomaterials. 2002;23(7):1553-1561.[29] Farokhzad OC, Cheng J, Teply BA, et al. Targeted nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates for cancer chemotherapy in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(16):6315-6320. [30] Gradishar WJ, Tjulandin S, Davidson N, et al. Phase III trial of nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel compared with polyethylated castor oil-based paclitaxel in women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(31):7794-7803. [31] Cancer centers. http://cancercenters.cancer.gov/cancer_centers/map-cancer-centers.html. 2011-12-03.[32] Thangapazham RL, Puri A, Tele S, et al. Evaluation of a nanotechnology-based carrier for delivery of curcumin in prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2008;32(5):1119-1123.[33] Sarin H, Kanevsky AS, Wu H, et al. Effective transvascular delivery of nanoparticles across the blood-brain tumor barrier into malignant glioma cells. J Transl Med. 2008;6:80.[34] Nellis DF, Ekstrom DL, Kirpotin DB, et al. Preclinical manufacture of an anti-HER2 scFv-PEG-DSPE, liposome-inserting conjugate. 1. Gram-scale production and purification. Biotechnol Prog. 2005;21(1):205-220.[35] Nellis DF, Giardina SL, Janini GM, et al. Preclinical manufacture of anti-HER2 liposome-inserting, scFv-PEG-lipid conjugate. 2. Conjugate micelle identity, purity, tability, and potency analysis. Biotechnol Prog. 2005;21(1):221-232.[36] Jia L, Wong H, Wang Y, et al. Carbendazim: disposition, cellular permeability, metabolite identification, and pharmacokinetic comparison with its nanoparticle. J Pharm Sci. 2003;92(1):161-172.[37] Dinh B, Dove K, Jappar D, et al. Effect of hydrophobic structure on the catalysis of nitric oxide release from zwitterionic diazeniumdiolates in surfactant and liposome media. Nitric Oxide. 2005;13(3):204-209.[38] Cachau RE, Gonzalez-Nilo FD, Ventura ON, et al. In-silico nanobio-design. A new frontier in computational biology. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(15):1537-1540.[39] Kosaka N, Bernardo M, Mitsunaga M, et al. MR and optical imaging of early micrometastases in lymph nodes: triple labeling with nano-sized agents yielding distinct signals. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2012;7(2):247-253. [40] Clogston JD, Zheng JW, Ramalinga U, et al. ANYL 198-Nanoparticle metrology: Reporting the hydrodynamic size by DLS. Front Nanoscale Mater Anal. The 236th ACS National Meeting, Philadelphia, PA, August 17-21, 2008. |