中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (3): 464-469.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0598
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
白藜芦醇修复内皮细胞氧化损伤抑制促血栓分子表达的作用和机制
何 卫,娄振凯,王 兵,李兴国,赵冲宇,赵学凌
- (昆明医科大学第一附属医院骨科,云南省昆明市 650032)
Resveratrol protects endothelial cells from oxidative damage and inhibits expression of pro-thrombosis molecules: the underlying mechanisms
He Wei, Lou Zhenkai, Wang Bing, Li Xingguo, Zhao Chongyu, Zhao Xueling
- (Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
氧化应激:机体在遭受各种有害刺激时,体内高活性分子如活性氧自由基(reactive oxygen species,ROS)和活性氮自由基(reactive nitrogen species,RNS)产生过多,氧化系统和抗氧化系统失衡,导致组织损伤。被认为是导致衰老和疾病的一个重要因素。
PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β信号通路:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(PI3-K/Akt)通路首先在肿瘤细胞中被发现,该通路通过调控下游的多种效应分子对葡萄糖转运、细胞增殖、分化和凋亡等过程起重要调节作用,其中糖原合成酶激酶3B(GSK3B)是主要效应分子,两者联合被称为PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β信号通路。
文题释义:
氧化应激:机体在遭受各种有害刺激时,体内高活性分子如活性氧自由基(reactive oxygen species,ROS)和活性氮自由基(reactive nitrogen species,RNS)产生过多,氧化系统和抗氧化系统失衡,导致组织损伤。被认为是导致衰老和疾病的一个重要因素。
PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β信号通路:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(PI3-K/Akt)通路首先在肿瘤细胞中被发现,该通路通过调控下游的多种效应分子对葡萄糖转运、细胞增殖、分化和凋亡等过程起重要调节作用,其中糖原合成酶激酶3B(GSK3B)是主要效应分子,两者联合被称为PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β信号通路。
.jpg) 文题释义:
氧化应激:机体在遭受各种有害刺激时,体内高活性分子如活性氧自由基(reactive oxygen species,ROS)和活性氮自由基(reactive nitrogen species,RNS)产生过多,氧化系统和抗氧化系统失衡,导致组织损伤。被认为是导致衰老和疾病的一个重要因素。
PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β信号通路:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(PI3-K/Akt)通路首先在肿瘤细胞中被发现,该通路通过调控下游的多种效应分子对葡萄糖转运、细胞增殖、分化和凋亡等过程起重要调节作用,其中糖原合成酶激酶3B(GSK3B)是主要效应分子,两者联合被称为PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β信号通路。
文题释义:
氧化应激:机体在遭受各种有害刺激时,体内高活性分子如活性氧自由基(reactive oxygen species,ROS)和活性氮自由基(reactive nitrogen species,RNS)产生过多,氧化系统和抗氧化系统失衡,导致组织损伤。被认为是导致衰老和疾病的一个重要因素。
PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β信号通路:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(PI3-K/Akt)通路首先在肿瘤细胞中被发现,该通路通过调控下游的多种效应分子对葡萄糖转运、细胞增殖、分化和凋亡等过程起重要调节作用,其中糖原合成酶激酶3B(GSK3B)是主要效应分子,两者联合被称为PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β信号通路。摘要
背景:相关研究表明,白藜芦醇具有抗氧化、抑制动脉血栓的作用。
目的:探讨白藜芦醇保护内皮细胞氧化损伤,抑制深静脉血栓形成的分子作用。
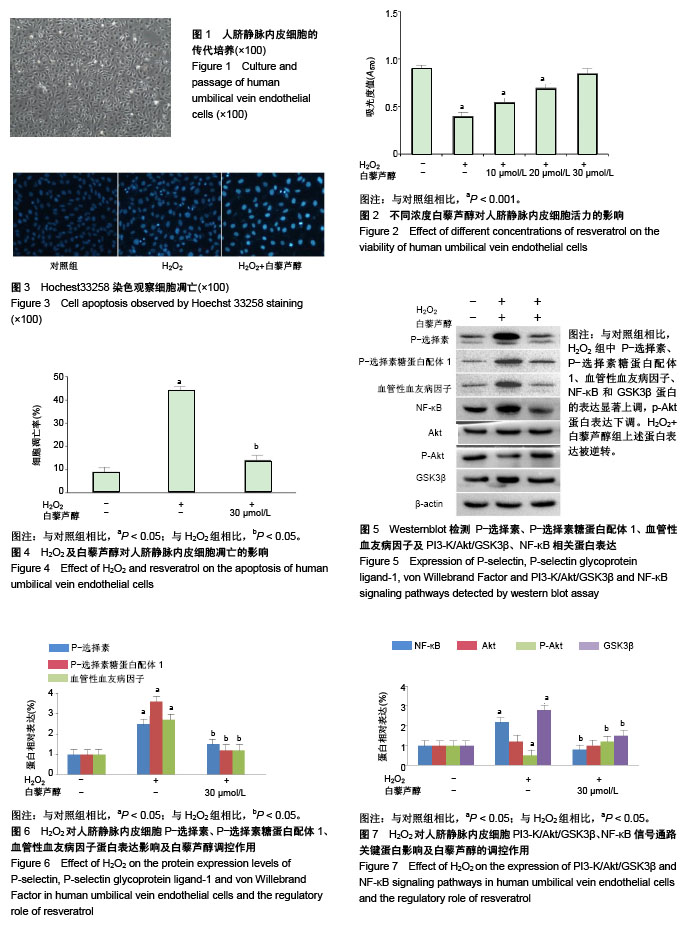
方法:使用人脐静脉内皮细胞进行传代培养;实验分3组:①对照组为正常培养液中培养24 h;②H2O2组在培养液中加入200 μmol/L H2O2培养24 h;③H2O2+白藜芦醇组:先分别予以10,20,30 μmol/L的白藜芦醇预处理2 h,再加入200 μmol/L H2O2培养24 h。采用MTT法检测细胞活力;Hoechst 33258染色法、荧光显微镜观察细胞凋亡;Western blot检测P-选择素、P-选择素糖蛋白配体1、血管性血友病因子及PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β、NF-κB信号通路关键蛋白表达。
结果与结论:①与对照组相比,H2O2能够诱导内皮细胞损伤,白藜芦醇对H2O2诱导的内皮细胞损伤具有修复作用(P < 0.05);②与对照组相比,H2O2组细胞凋亡率明显增加(P < 0.05);与H2O2组相比,H2O2+白藜芦醇组细胞凋亡率明显减少(P < 0.05);③与对照组相比,H2O2组P-选择素、P-选择素糖蛋白配体1、血管性血友病因子、NF-κB和GSK3β蛋白的表达显著上调(P < 0.05),Akt总蛋白无明显变化(P > 0.05),pAkt蛋白表达下调(P < 0.05);与H2O2组相比,H2O2+白藜芦醇组上述蛋白表达被逆转(P < 0.05);④结果表明,白藜芦醇能够修复静脉内皮细胞氧化损伤,对P-选择素、P-选择素糖蛋白配体1、血管性血友病因子蛋白表达具有抑制作用,其机制可能与PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β、NF-κB信号通路相关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-2603-4167(何卫)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
氧化应激:机体在遭受各种有害刺激时,体内高活性分子如活性氧自由基(reactive oxygen species,ROS)和活性氮自由基(reactive nitrogen species,RNS)产生过多,氧化系统和抗氧化系统失衡,导致组织损伤。被认为是导致衰老和疾病的一个重要因素。
PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β信号通路:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(PI3-K/Akt)通路首先在肿瘤细胞中被发现,该通路通过调控下游的多种效应分子对葡萄糖转运、细胞增殖、分化和凋亡等过程起重要调节作用,其中糖原合成酶激酶3B(GSK3B)是主要效应分子,两者联合被称为PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β信号通路。
文题释义:
氧化应激:机体在遭受各种有害刺激时,体内高活性分子如活性氧自由基(reactive oxygen species,ROS)和活性氮自由基(reactive nitrogen species,RNS)产生过多,氧化系统和抗氧化系统失衡,导致组织损伤。被认为是导致衰老和疾病的一个重要因素。
PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β信号通路:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(PI3-K/Akt)通路首先在肿瘤细胞中被发现,该通路通过调控下游的多种效应分子对葡萄糖转运、细胞增殖、分化和凋亡等过程起重要调节作用,其中糖原合成酶激酶3B(GSK3B)是主要效应分子,两者联合被称为PI3-K/Akt/GSK3β信号通路。