| [1] Hayto?lu S, Arikan OK, Muluk NB, et al. Comparison of anterior palatoplasty and uvulopalatal flap placement for treating mild and moderate obstructive sleep apnea. Ear Nose Throat J. 2018;97(3): 69-78.[2] Fernández-Julián E, Pérez-Carbonell T, Marco R, et al. Impact of an oral appliance on obstructive sleep apnea severity, quality of life, and biomarkers. Laryngoscope. 2017 ;12 (20):1-7.[3] Marklund M, Verbraecken J, Randerath W.Non-CPAP therapies in obstructive sleep apnoea: mandibular advancement device therapy. Eur Respir. 2012;39(5):1241-1247.[4] Gupta A, Tripathi A, Sharma P.The long-term effects of mandibular advancement splint on cardiovascular fitness and psychomotor performance in patients with mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnea: a prospective study.Sleep Breath. 2017,21(3):781-789[5] Pavoni C, Cretella Lombardo E, Lione R, et al. Orthopaedic treatment effects of functional therapy on the sagittal pharyngeal dimensions in subjects with sleep-disordered breathing and Class II malocclusion. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2017;37(6):479-485.[6] 弓煦,高雪梅,赵颖,等.口腔矫治器治疗OSAHS患者长期主观疗效评价[J].中华口腔正畸学,2010,17(4):212-215. [7] Flores-Mir C, Korayem M, Heo G, et al. Craniofacial morphological characteristics in children with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am Dent Assoc.2013; 144(3):269-277.[8] Simmons HC, Oxford DE, Hill MD. The prevalence of skeletal Class II patients found in a consecutive population presenting for TMD treatment compared to the national average. Tenn Dent Assoc.2008;88(4):16-18.[9] Alm??an OC, B?ciu? M, Alm??an HA,et al. Skeletal pattern in subjects with temporomandibular joint disorders. Arch Med Sci. 2013;9(1): 118-126. [10] Ruf S, Pancherz H. Temporomandibular joint growth adaptation in Herbs treatment: a prospective magnetic resonance imaging and cephalometric roentgenographic study. Eur J Orthod.1998;20(4): 375-388.[11] 熊磊垃,查云飞,刘士斌,等.张口位MRI动态研究在诊断颞下颌关节盘前移位中的应用[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2013, 29 (8):457-459. [12] Ikeda K. A reference line on temporomandibular joint MRI. Prosthodont. 2013;22(8):603-607.[13] Zheng JS, Jiao ZX, Zhang SY, et al.Correlation between the disc status in MRI and the different types of traumatic temporomandibular joint ankylosis. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2015; 10:20140201.[14] Navallas M, Inarejos EJ, Iglesias E, et al. MR Imaging of the Temporomandibular Joint in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Technique and Findings. Radiographics. 2017;37(2):595-612.[15] Mavreas D, Athanasiou AE. Tomographic assessment of alterations of thetemporomandibular joint after orthognathic surgery. Eur J Orthod.1992;14(1):3-15.[16] Ruf Sabine, Pancherz H. Does bite-jumping damage the TMJ? A prospective longitudinal clinical and MRI study of herbst patients. Angle orthod.2000;70(3):183-199. [17] 邹冰爽.面部不对称畸形颞下颌关节的核磁共振研究[J].口腔正畸学, 2007,14(4):177-181.[18] Louro RS, Calasans-Maia JA, Mattos CT et al. Three-dimensional changes to the upper airway after maxillomandibular advancement with counterclockwise rotation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;12(25):1-8 .[19] Knappe SW, Bakke M, Svanholt P, et al. Long-term side effects on the temporomandibular joints and oro-facial function in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea treated with a mandibular advancement device.Oral Rehabil.2017;44(5):354-362.[20] 马燕燕,张晶晶,高雪梅.不同下颌前伸度口腔矫治器治疗阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征的系统评价[J].北京大学学报(医学版), 2017,49(4):691-698.[21] Rashmikant US, Chand P, Singh SV,et al. Cephalometric evaluation of mandibular advancement at different horizontal jaw positions in obstructive sleep apnoea patients: a pilot study. Aust Dent. 2013;58(3):293-300.[22] Anitua E, Durán-Cantolla J, Almeida GZ,et al. Minimizing the mandibular advancement in an oral appliance for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med. 2016;12(27) :1-22.[23] Doff MH, Veldhuis SK, Hoekema A, et al. Long-term oral appliance therapy in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: a controlled study on temporomandibular side effects. Clin Oral Investig.2012;16(3):689-697. [24] 韩建辉,雷杰,刘木清,等.颞下颌关节盘不可复性前移位患者骨关节病表现的锥形束CT观察[J].中国口腔医学杂志, 2017,52(1):22-26. [25] Gökalp H. Disc position in clinically asymptomatic, pretreatment adolescents with Class I, II, or III malocclusion : A retrospective magnetic resonance imagingstudy.J Orofac Orthop.2016;77(3): 194-202 .[26] 谷志远,冯剑颖,吴慧玲,等.颞下颌关节盘前移后双板区改建的实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2002,20(6):408-410. [27] 卓子昂,蔡协艺.颞下颌关节盘前移位的自然转归 [J].口腔医学研究, 2014,30(7):682-684. [28] Näpänkangas R, Raunio A, Sipilä K, et al. Effect of mandibular advancement device therapy on the signs and symptoms of temporomandibular disorders. Oral Maxillofac Res.2013;3(4):e5. [29] Jiang X, Fan S, Cai B, et al. Mandibular manipulation technique followed by exercise therapy and occlusal splint for treatment of acute anterior TMJ disk displacement without reduction. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue.2016 ;25(5):570-573.[30] Kuzmanovic Pficer J, Dodic S, Lazic V, et al. Occlusal stabilization splint for patients with temporomandibular disorders: Meta-analysis of short and long term effects. PLoS One. 2017; 12(2):e0171296.[31] Ivorra-Carbonell L, Montiel-Company JM, Almerich-Silla JM, et al. Impact of functional mandibular advancement appliances on the temporomandibular joint-a systematic review.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2016;21(5):e565-72.[32] 龙星.颞下颌关节盘穿孔的外科治疗[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2005, 40(5):423-424.[33] Pérez del Palomar A, Doblaré M. An accurate simulation model of anteriorly displaced TMJ discs with and without reduction. Med Eng Phys.2007;29( 2) :216 -226. [34] Heidsieck DSP, Koolstra JH, de Ruiter MHT, et al. Biomechanical effects of a mandibular advancement device on the temporomandibular joint. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017;12(13): 1-22.[35] Aidar LA, Dominguez GC, Yamashita HK, et al. Changes in temporomandibular joint disc position and form following Herbst and fixed orthodontic treatment. Angle Orthod. 2010;80(5): 843-852. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
下颌前伸与颞下颌关节盘:口腔矫治器治疗阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征的主要原理是在夜间睡眠时使患者的下颌处于前伸位,有效扩大上气道,从而改善患者的憋气症状,提高睡眠质量。戴用口腔矫治器治疗时,由于下颌骨的前伸,必将对颞下颌关节产生一个非正常生理性的牵张应力,从而导致关节盘组织结构的适应性反应。关节盘是颞下颌关节的重要组织结构,若其发生病理性改变,对颞下颌关节的正常生理和功能将造成严重影响。
颞下颌关节的MRI检查:MRI三维影像技术能清晰显示关节各软硬组织的形态和结构,尤其是关节盘可以清晰成像,这是其他X射线三维影像诊断技术无法达到的,被称为是诊断颞下颌关节疾病的“金标准”。同时,MRI技术还可以进行关节运动的动态观察及关节韧带、肌肉等的研究,是临床中探讨颞下颌关节组织结构的生理及病理变化的重要手段。
文题释义:
下颌前伸与颞下颌关节盘:口腔矫治器治疗阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征的主要原理是在夜间睡眠时使患者的下颌处于前伸位,有效扩大上气道,从而改善患者的憋气症状,提高睡眠质量。戴用口腔矫治器治疗时,由于下颌骨的前伸,必将对颞下颌关节产生一个非正常生理性的牵张应力,从而导致关节盘组织结构的适应性反应。关节盘是颞下颌关节的重要组织结构,若其发生病理性改变,对颞下颌关节的正常生理和功能将造成严重影响。
颞下颌关节的MRI检查:MRI三维影像技术能清晰显示关节各软硬组织的形态和结构,尤其是关节盘可以清晰成像,这是其他X射线三维影像诊断技术无法达到的,被称为是诊断颞下颌关节疾病的“金标准”。同时,MRI技术还可以进行关节运动的动态观察及关节韧带、肌肉等的研究,是临床中探讨颞下颌关节组织结构的生理及病理变化的重要手段。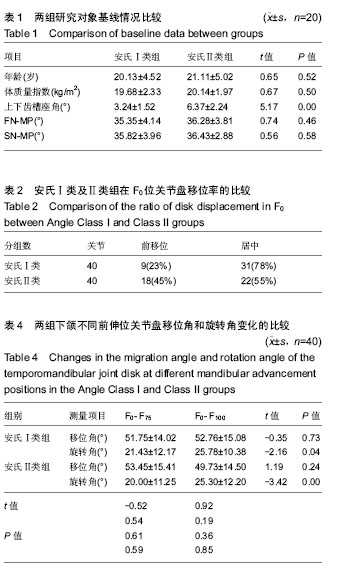
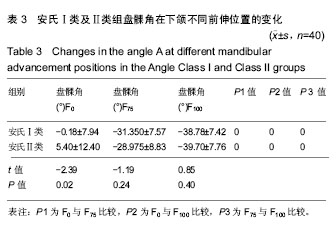
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
下颌前伸与颞下颌关节盘:口腔矫治器治疗阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征的主要原理是在夜间睡眠时使患者的下颌处于前伸位,有效扩大上气道,从而改善患者的憋气症状,提高睡眠质量。戴用口腔矫治器治疗时,由于下颌骨的前伸,必将对颞下颌关节产生一个非正常生理性的牵张应力,从而导致关节盘组织结构的适应性反应。关节盘是颞下颌关节的重要组织结构,若其发生病理性改变,对颞下颌关节的正常生理和功能将造成严重影响。
颞下颌关节的MRI检查:MRI三维影像技术能清晰显示关节各软硬组织的形态和结构,尤其是关节盘可以清晰成像,这是其他X射线三维影像诊断技术无法达到的,被称为是诊断颞下颌关节疾病的“金标准”。同时,MRI技术还可以进行关节运动的动态观察及关节韧带、肌肉等的研究,是临床中探讨颞下颌关节组织结构的生理及病理变化的重要手段。
文题释义:
下颌前伸与颞下颌关节盘:口腔矫治器治疗阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征的主要原理是在夜间睡眠时使患者的下颌处于前伸位,有效扩大上气道,从而改善患者的憋气症状,提高睡眠质量。戴用口腔矫治器治疗时,由于下颌骨的前伸,必将对颞下颌关节产生一个非正常生理性的牵张应力,从而导致关节盘组织结构的适应性反应。关节盘是颞下颌关节的重要组织结构,若其发生病理性改变,对颞下颌关节的正常生理和功能将造成严重影响。
颞下颌关节的MRI检查:MRI三维影像技术能清晰显示关节各软硬组织的形态和结构,尤其是关节盘可以清晰成像,这是其他X射线三维影像诊断技术无法达到的,被称为是诊断颞下颌关节疾病的“金标准”。同时,MRI技术还可以进行关节运动的动态观察及关节韧带、肌肉等的研究,是临床中探讨颞下颌关节组织结构的生理及病理变化的重要手段。