Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (14): 2283-2290.doi: 10.12307/2023.427
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of kinesio taping on chronic ankle instability: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
Wang Ling1, Chen Peng1, Wang Guanglan1, Zheng Cheng2
- 1College of Health Science, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Sports Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2022-06-18Accepted:2022-07-12Online:2023-05-18Published:2022-09-30 -
Contact:Zheng Cheng, MD, Attending physician, Department of Sports Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Wang Ling, Master candidate, College of Health Science, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China Chen Peng, Master candidate, College of Health Science, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China Wang Ling and Chen Peng contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 2019CFB397 (to ZC); Donghu Scholar Program of Wuhan Sports University and Research Fund for Young Teachers of Wuhan Sports University, No. 20Z01 (to ZC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Ling, Chen Peng, Wang Guanglan, Zheng Cheng. Effects of kinesio taping on chronic ankle instability: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(14): 2283-2290.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
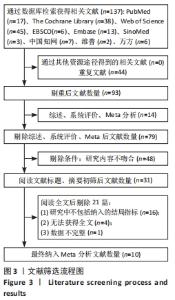
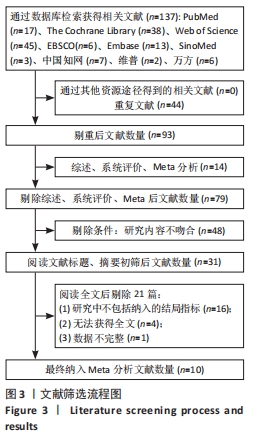
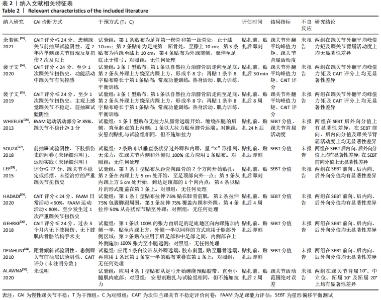
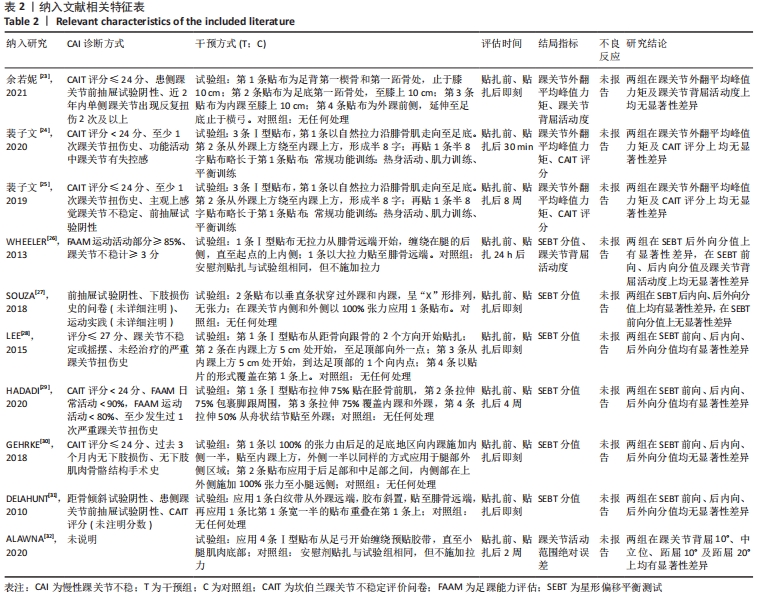
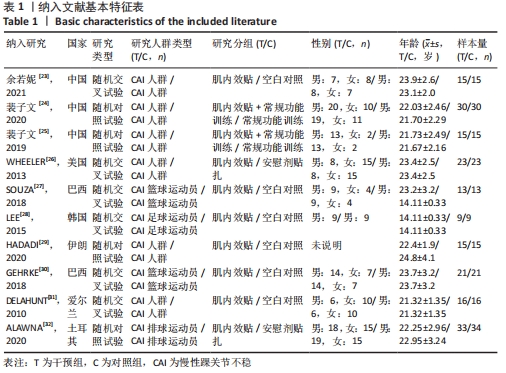
2.2 纳入研究的基本特征 最终纳入了在2010-2021年发表的10篇文献[23-32],总计381例患者,其中试验组190例,对照组191例。表1为纳入文献的基本特征表,6项为随机交叉试验[23,26-28,30-31],4项为随机对照试验[24-25,29,32]。表2为纳入文献的相关特征表,纳入的6项研究评估了SEBT分值,3项研究了踝关节外翻平均峰值力矩,1项研究了踝关节活动范围绝对误差,2项研究了踝关节背屈活动度和CAIT评分。所有研究进行了贴扎前的测试,但后测时间并不一致,其中有5项研究为贴扎后即刻测试,其他5项研究为肌内效贴干预30 min、24 h、2周、4周、8周后测试。"
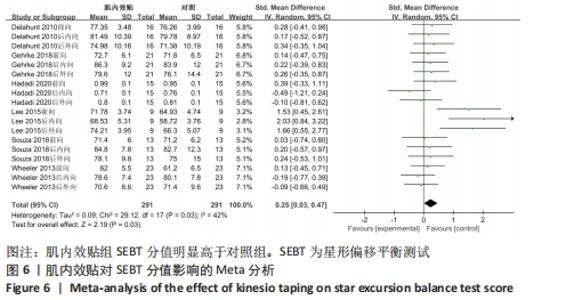
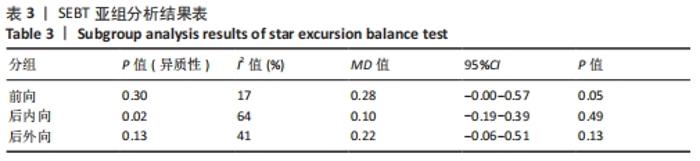
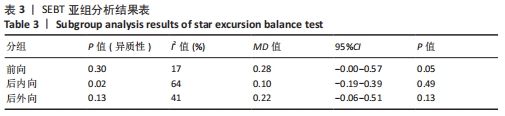
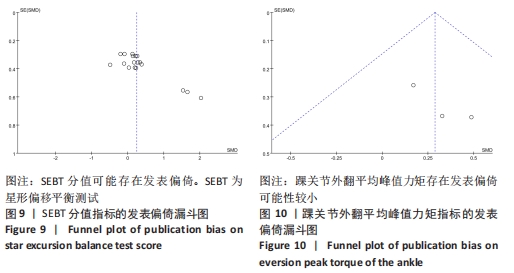
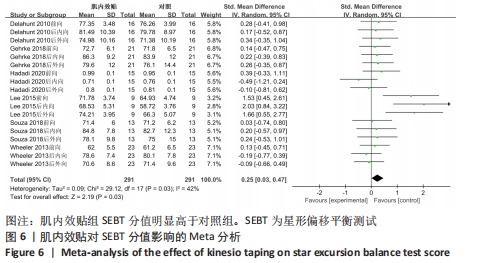
2.4 Meta分析结果 2.4.1 各组SEBT分值差异 有6篇文献报告了SEBT分值的结果[26-31],各文献之间异质性较大(I2=42%,P=0.03),采用随机效应模型进行分析;因均采用前向、后内向、后外向3个方向分析慢性踝关节不稳患者平衡功能,且异质性较大,因此根据不同方向进行亚组分析。由于测量方式不同,因此采用SMD进行合并。Meta分析结果显示,在改善SEBT分值上,肌内效贴组显著优于对照组(SMD=0.25,95%CI:0.03-0.47,P=0.03)。亚组分析结果显示,与对照组相比,肌内效贴组可以显著改善SEBT前向分值,但对SEBT后内向、后外向分值并无显著改善作用。具体情况见图6及表3。"
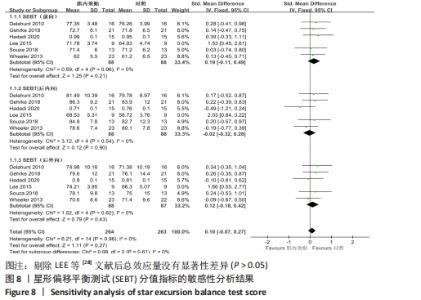
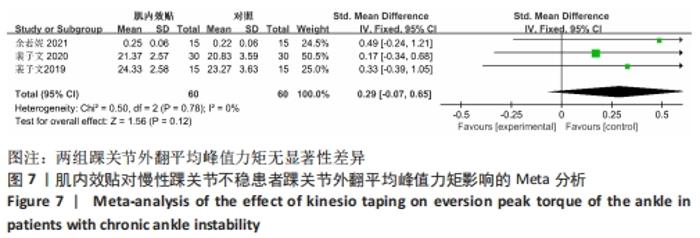
2.5 描述性分析结果 2.5.1 踝关节活动范围绝对误差 仅1篇文献报告了踝关节活动范围绝对误差的结果[32],未达到Meta分析的标准,故采用描述性分析。ALAWNA等[32]研究表明,应用肌内效贴后即刻,慢性踝关节不稳排球运动员踝关节活动范围绝对误差并无改善;但在应用肌内效贴治疗2周及2个月后,肌内效贴组在踝10°背屈位、踝中立位、踝10°跖屈位及踝20°跖屈位下的踝关节活动范围误差均显著低于安慰剂贴扎组。 2.5.2 踝关节背屈活动度 仅2篇文献报道了踝关节背屈活动度的结果[23,26],未达到Meta分析的标准,故采用描述性分析。余若妮[23]探究了应用不同长度的肌内效贴后即刻,慢性踝关节不稳患者踝关节背屈活动度的变化,结果显示,3种不同长度的肌内效贴均未能显著改善慢性踝关节不稳患者背屈活动度。WHEELER等[26]在2次测试中,分别使用肌内效贴和安慰剂贴扎对23例慢性踝关节不稳患者贴扎24 h,结果显示,应用肌内效贴和安慰剂贴扎均可小幅度增加踝关节背屈活动度,但组间差异并无统计学意义。 2.5.3 CAIT评分 仅2篇文献报告了CAIT评分的结果[24-25],无法达到Meta分析的标准,故采用描述性分析。裴子文等[24]将60例慢性踝关节不稳患者随机分为对照组和肌内效贴组,对照组采用常规功能训练,肌内效贴组在对照组的基础上辅以肌内效贴治疗,结果显示,治疗30 min后,肌内效贴组与对照组CAIT评分并无显著差异,但在贴扎4周后,肌内效贴组CAIT评分显著高于对照组。而他的另一项研究显示,对慢性踝关节不稳患者采用常规功能训练或在此基础上应用肌内效贴治疗8周后,患者CAIT评分均显著提高,然而组间差异并无统计学意义[25]。 2.6 敏感性分析结果 为进一步探究文献异质性的来源,对SEBT分值和踝关节外翻平均峰值力矩两项结局指标进行敏感性分析;对于SEBT,剔除LEE等[28]后效应量产生显著性改变(P > 0.05),其他任一文献未对总效应量大小造成显著性影响,提示LEE等[28]该篇文献可能是异质性来源,具体情况见图8;对于踝关节外翻平均峰值力矩,逐一去除单篇文献,总效应量并无显著改变,提示Meta分析结果较稳定。"

| [1] DOHERTY C, DELAHUNT E, CAULFIELD B, et al. The incidence and prevalence of ankle sprain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective epidemiological studies. Sports Med. 2014;44(1):123-140. [2] HERTEL J, CORBETT RO. An updated model of chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train. 2019; 54(6):572-588. [3] GRIBBLE PA, DELAHUNT E, BLEAKLEY C, et al. Selection criteria for patients with chronic ankle instability in controlled research: a position statement of the International Ankle Consortium. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2013; 43(8):585-591. [4] DOHERTY C, BLEAKLEY C, DELAHUNT E, et al. Treatment and prevention of acute and recurrent ankle sprain: an overview of systematic reviews with meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(2):113-125. [5] DELAHUNT E, BLEAKLEY CM, BOSSARD DS, et al. Clinical assessment of acute lateral ankle sprain injuries (ROAST): 2019 consensus statement and recommendations of the International Ankle Consortium. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(20):1304-1310. [6] GRIBBLE PA, BLEAKLEY CM, CAULFIELD BM, et al. 2016 consensus statement of the International Ankle Consortium: prevalence, impact and long-term consequences of lateral ankle sprains. Br J Sports Med. 2016; 50(24):1493-1495. [7] 覃华生,潘玮敏,李然,等.慢性踝关节不稳的运动康复:研究现状与特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(36):5865-5871. [8] KERKHOFFS GM, VAN DEN BEKEROM M, ELDERS LA, et al. Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of ankle sprains: an evidence-based clinical guideline. Br J Sports Med. 2012; 46(12):854-860. [9] RIVERA MJ, WINKELMANN ZK, POWDEN CJ, et al. Proprioceptive training for the prevention of ankle sprains: an evidence-based review. J Athl Train. 2017;52(11):1065-1067. [10] RENDOS NK, JUN HP, PICKETT NM, et al. Acute effects of whole body vibration on balance in persons with and without chronic ankle instability. Res Sports Med. 2017;25(4):391-407. [11] DONOVAN L, FEGER MA, HART JM, et al. Effects of an auditory biofeedback device on plantar pressure in patients with chronic ankle instability. Gait Posture. 2016;44:29-36. [12] BICICI S, KARATAS N, BALTACI G. Effect of athletic taping and kinesiotaping® on measurements of functional performance in basketball players with chronic inversion ankle sprains. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2012;7(2):154-166. [13] 余波,陈文华,王人卫.肌内效贴改善运动功能的临床研究现状与思考[J].中国运动医学杂志,2014,33(3):275-280. [14] 裴子文,孟宪梅,杨建强,等.慢性踝关节不稳患者下肢肌肉激活特征研究现状[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018,24(6):678-681. [15] LIN CF, CHEN CY, LIN CW. Dynamic ankle control in athletes with ankle instability during sports maneuvers. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(9):2007-2015. [16] JACKSON K, SIMON JE, DOCHERTY CL. Extended use of kinesiology tape and balance in participants with chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train. 2016;51(1):16-21. [17] SIMON J, GARCIA W, DOCHERTY CL. The effect of kinesio tape on force sense in people with functional ankle instability. Clin J Sport Med. 2014;24(4):289-294. [18] RAYMOND J, NICHOLSON LL, HILLER CE, et al. The effect of ankle taping or bracing on proprioception in functional ankle instability: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sci Med Sport. 2012;15(5):386-392. [19] CHO JH, LIM ST, KO J. Effectiveness of kinesio taping for dynamic postural stability in adolescent athletes with chronic ankle instability: a pilot study. J Kinesiol. 2021; 23(2):28-33. [20] WANG Y, GU Y, CHEN J, et al. Kinesio taping is superior to other taping methods in ankle functional performance improvement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2018;32(11):1472-1481. [21] NUNES GS, FELDKIRCHER JM, TESSARIN BM, et al. Kinesio taping does not improve ankle functional or performance in people with or without ankle injuries: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2021;35(2):182-199. [22] 谷鸿秋,王杨,李卫.Cochrane偏倚风险评估工具在随机对照研究Meta分析中的应用[J].中国循环杂志,2014,29(2):147-148. [23] 余若妮.不同长度的肌内效贴对慢性踝关节不稳患者踝关节功能影响的效应研究 [D].上海:上海体育学院,2021. [24] 裴子文,汪冕,言功立,等.肌内效贴治疗慢性踝关节不稳的即刻及短期疗效观察[J].中国康复,2020,35(9):463-466. [25] 裴子文.肌内效贴联合神经肌肉电刺激对功能性踝关节不稳的康复疗效研究[D].武汉:武汉体育学院,2019. [26] WHEELER TJ, BASNETT CR, HANISH MJ, et al. Fibular taping does not influence ankle dorsiflexion range of motion or balance measures in individuals with chronic ankle instability. J Sci Med Sport. 2013;16(6):488-492. [27] SOUZA HH, PACHECO I, GEHRKE LC, et al. Evaluation of the effect of elastic bandage on the ankle basketball players with and without chronic instability. Rev Bras Med. 2018;24(6): 460-464. [28] LEE BG, LEE JH. Immediate effects of ankle balance taping with kinesiology tape on the dynamic balance of young players with functional ankle instability. Technol Health Care. 2015;23(3):333-341. [29] HADADI M, HAGHIGHAT F, MOHAMMADPOUR N, et al. Effects of kinesiotape vs soft and semirigid ankle orthoses on balance in patients with chronic ankle instability: a randomized controlled trial. Foot Ankle Int. 2020;41(7):793-802. [30] GEHRKE LC, LONDERO LX, LOUREIRO-CHAVES RF, et al. Effects of athletic taping on performance of basketball athletes with chronic ankle instability. Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte. 2018;24(6):477-482. [31] DELAHUNT E, MCGRATH A, DORAN N, et al. Effect of taping on actual and perceived dynamic postural stability in persons with chronic ankle instability. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010;91(9):1383-1389. [32] ALAWNA M, MOHAMED AA. Short-term and long-term effects of ankle joint taping and bandaging on balance, proprioception and vertical jump among volleyball players with chronic ankle instability. Phys Ther Sport. 2020;46:145-154. [33] 张梅莹,赵蕾,李慧,等.髋周肌群力量训练对功能性踝关节不稳的疗效及表面肌电评价[J].中国康复理论与实践,2021,27(8): 936-942. [34] ROBBINS S, WAKED E, RAPPEL R. Ankle taping improves proprioception before and after exercise in young men. Br J Sports Med. 1995; 29(4):242-247. [35] LEE SM, LEE JH. The immediate effects of ankle balance taping with kinesiology tape on ankle active range of motion and performance in the Balance Error Scoring System. Phys Ther Sport. 2017;25:99-105. [36] CHINN L, DICHARRY J, HART JM, et al. Gait kinematics after taping in participants with chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train. 2014; 49(3):322-330. [37] VERHAGEN EA, VAN MECHELEN W, DE VENTE W. The effect of preventive measures on the incidence of ankle sprains. Clin J Sport Med. 2000;10(4):291-296. [38] STOFFEL KK, NICHOLLS RL, WINATA AR, et al. Effect of ankle taping on knee and ankle joint biomechanics in sporting tasks. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(11):2089-2097. [39] KOSIK KB, TERADA M, DRINKARD CP, et al. Potential corticomotor plasticity in those with and without chronic ankle instability. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017;49(1):141-149. [40] MCLEOD MM, GRIBBLE PA, PIETROSIMONE BG. Chronic ankle instability and neural excitability of the lower extremity. J Athl Train. 2015;50(8):847-853. [41] TERADA M, BOWKER S, THOMAS AC, et al. Corticospinal Excitability and Inhibition of the Soleus in Individuals With Chronic Ankle Instability. Pm r. 2016;8(11):1090-1096. [42] 尹彦,罗冬梅,刘卉,等.功能性踝关节不稳者姿势稳定性的研究进展[J].体育科学, 2016,36(4):61-67. [43] JELINEK HF, KHALAF K, POILVET J, et al. The effect of ankle support on lower limb kinematics during the y-balance test using non-linear dynamic measures. Front Physiol. 2019;10:935. [44] LEE JH, YOON TL. Effective Treatment for chronic ankle instability during lateral step-down-kinesiology tape, resistance exercise, or both accompanied with heel raise-lower exercise? J Sport Rehabil. 2019;28(8):809-816. [45] VERCELLI S, FERRIERO G, BRAVINI E, et al. How much is Kinesio taping a psychological crutch? Man Ther. 2013;18(3):e11. [46] DONNELLY L, DONOVAN L, HART JM, et al. Eversion strength and surface electromyography measures with and without chronic ankle instability measured in 2 positions. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;38(7):769-778. [47] KODESH E, DAR G. The effect of kinesiotape on dynamic balance following muscle fatigue in individuals with chronic ankle instability. Res Sports Med. 2015;23(4):367-378. [48] CSAPO R, ALEGRE LM. Effects of Kinesio(®) taping on skeletal muscle strength-A meta-analysis of current evidence. J Sci Med Sport. 2015;18(4):450-456. [49] CHERAGHI M, BOOZARI S, SVOBODA Z, et al. Effects of ankle Kinesio™ taping on jump biomechanics in collegiate athletes with chronic ankle instability. Sport Sci Health. 2021. doi:10.1007/s11332-021-00863-3. [50] WILLIAMS S, WHATMAN C, HUME P A, et al. Kinesio taping in treatment and prevention of sports injuries: a meta-analysis of the evidence for its effectiveness. Sports Med. 2012;42(2):153-164. [51] XUE X, MA T, LI Q, et al. Chronic ankle instability is associated with proprioception deficits: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sport Health Sci. 2021;10(2):182-191. [52] 袁海新,柴松,阚世锋,等.肌内效贴不同贴扎方法对于功能性踝关节不稳患者本体感觉的影响[J].中国保健医学,2016,26(29): 133-134. [53] HOSP S, BOTTONI G, HEINRICH D, et al. A pilot study of the effect of Kinesiology tape on knee proprioception after physical activity in healthy women. J Sci Med Sport. 2015;18(6):709-713. [54] GRIGG P. Peripheral neural mechanisms in proprioception. J Sport Rehabil. 1994;3(1):2-17. [55] EDIN BB. Quantitative analyses of dynamic strain sensitivity in human skin mechanoreceptors. J Neurophysiol. 2004;92(6):3233-3243. [56] 尹璐璐,王琳.肌内效贴对慢性踝关节不稳运动神经肌肉控制的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(11):1783-1789. [57] KILIC BB, YILDIZ S, SAHINKAYA T, et al. The effects of kinesio tape application on functional performance measurements in young female basketball players with chronic ankle instability. J Sports Sci. 2017;5(4):198-206. [58] YIN L, LIU K, LIU C, et al. Effect of Kinesiology tape on muscle activation of lower extremity and ankle kinesthesia in individuals with unilateral chronic ankle instability. Front Physiol. 2021;12:786584. [59] MIKLOVIC TM, DONOVAN L, PROTZUK OA, et al. Acute lateral ankle sprain to chronic ankle instability: a pathway of dysfunction. Phys Sportsmed. 2018;46(1):116-122. [60] LIN CC, LEE WC, CHEN JC, et al. The influence of kinesio tape and an ankle brace on the lower extremity joint motion in fatigued, unstable ankles during a lateral drop landing. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(11):6081. [61] SMITH MD, VITHARANA TN, WALLIS GM, et al. Response profile of fibular repositioning tape on ankle osteokinematics, arthrokinematics, perceived stability and confidence in chronic ankle instability. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2020;50:102272. [62] SARVESTAN J, ATAABADI PA, SVOBODA Z, et al. The effect of ankle Kinesio™ taping on ankle joint biomechanics during unilateral balance status among collegiate athletes with chronic ankle sprain. Phys Ther Sport. 2020;45:161-167. [63] YOSHIDA A, KAHANOV L. The effect of kinesio taping on lower trunk range of motions. Res Sports Med. 2007;15(2):103-112. [64] LEMOS TV, JúNIOR JRS, SANTOS M, et al. Kinesio Taping effects with different directions and tensions on strength and range of movement of the knee: a randomized controlled trial. Braz J Phys Ther. 2018;22(4):283-290. [65] WANG W, LIAO D, KANG X, et al. Development of a valid Chinese version of the Cumberland Ankle Instability Tool in Chinese-speaking patients with chronic ankle instability disorders. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):9747. |
| [1] | Wang Yanjin, Zhou Yingjie, Chai Xubin, Zhuo Hanjie. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of 3D printed porous titanium alloy fusion cage in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1434-1440. |
| [2] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [3] | Li Wenjie, You Aijia, Zhou Junli, Fang Sujuan, Li Chun. Effects of different dressings in the treatment of burn wounds: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1141-1148. |
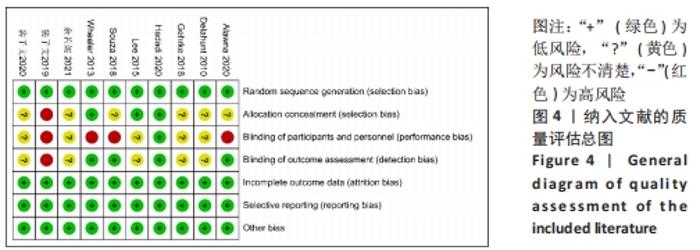
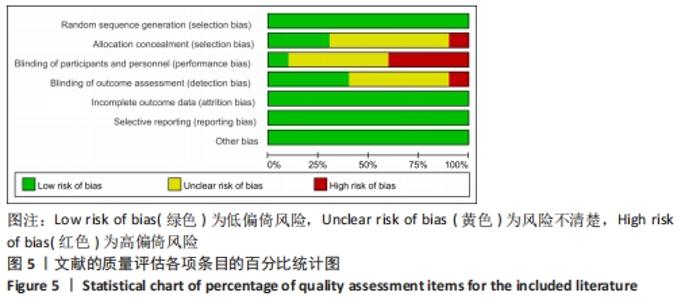
| [4] | Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Li Qingru. Meta-analysis of the value of exosomal miRNA for the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 970-976. |
| [5] | Yan Le, Zhang Huiping, Dai Lintong. Mesenchymal stem cells for allergic rhinitis: a meta-analysis based on animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 977-984. |
| [6] | Feng Liang, Gong Shuhui, Huo Hongfeng. Effect of short-foot training on foot and ankle function in patients with flat feet: Meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 799-804. |
| [7] | Pan Weimin, Wang Bing, Han Yabing, Li Ting, Song Jiaqi, Qin Huasheng, Liu Yang. Effects of blood flow restriction training on muscle strength, muscle mass and physical performance in older adults: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 805-812. |
| [8] | Yu Jiaan, Liu Xinwei, Lian Hongyu, Liu Kexin, Li Zitao. Medial open-wedge tibial osteotomy versus lateral closed-wedge tibial osteotomy for unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 632-639. |
| [9] | Xu Yangyang, He Peiliang, Meng Qingqi, Li Siming. A meta-analysis of the effects of continuous adductor canal block and continuous femoral nerve block on early activity after knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 640-645. |
| [10] | Chai Hao, Yang Deyong, Zhang Lei, Shu Li. 3D printing personalized osteotomy guide technology versus conventional total knee arthroplasty on the accuracy of lower limb force alignment: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 646-654. |
| [11] | You Aijia, Li Wenjie, Zhou Junli, Li Chun. Systematic evaluation of six dressings on wound safety following total hip and knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 486-492. |
| [12] | Wu Yihan, Wei Qiaoye, Pang Yu, Liu Zhongqiang. Proprioception characteristics of functional ankle instability: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2943-2952. |
| [13] | Peng Tuanhui, Yang Ling, Ding Xiaoge, Meng Pengjun. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of long-term exercise on blood lipids in healthy elderly people [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(14): 2276-2282. |
| [14] | Shang Wei, Fu Panfeng, Kang Zhe, Zhu Shaobo. Advantage of supramalleolar osteotomy for asymmetric ankle arthritis: a system evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 2124-2132. |
| [15] | Li Ruixin, Su Gang, Liu Jifei, Xu Dan, Gao Xin, Ma Tianfei, Zhang Zhenchang. Neuroprotective effect of stem cell transplantation on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1634-1640. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||