Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 799-804.doi: 10.12307/2023.115
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of short-foot training on foot and ankle function in patients with flat feet: Meta-analysis and systematic review
Feng Liang1, Gong Shuhui2, Huo Hongfeng1, 3
- 1School of Physical Education, Hebei Normal University, Shijiazhuang 050024, Hebei Province, China; 2People’s Hospital of Hebei Province, Shijiazhuang 050024, Hebei Province, China; 3Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Human Movement Bioinformatics Measurement, Shijiazhuang 050024, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-11Accepted:2022-05-06Online:2023-02-18Published:2022-07-25 -
Contact:Huo Hongfeng, Master, Senior experimentalist, School of Physical Education, Hebei Normal University, Shijiazhuang 050024, Hebei Province, China; Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Human Movement Bioinformatics Measurement, Shijiazhuang 050024, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Feng Liang, Master candidate, School of Physical Education, Hebei Normal University, Shijiazhuang 050024, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:The Government-Funded Clinical Medicine Outstanding Talent Training Project, No. 201913 (to GSH); Hebei Provincial Science and Technology Support Project, No. 16275709 (to HHF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Feng Liang, Gong Shuhui, Huo Hongfeng. Effect of short-foot training on foot and ankle function in patients with flat feet: Meta-analysis and systematic review[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 799-804.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
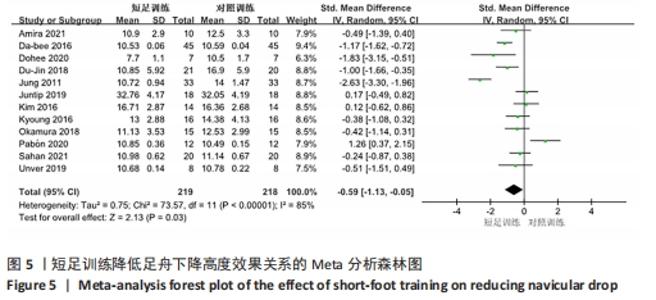
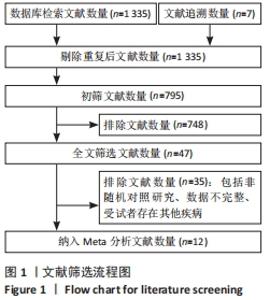
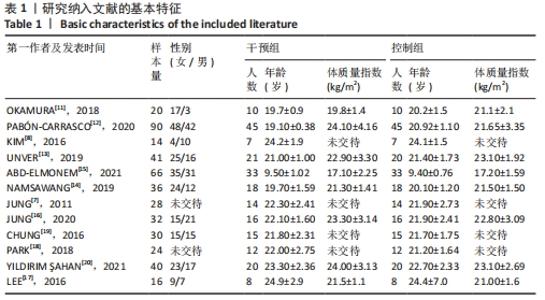
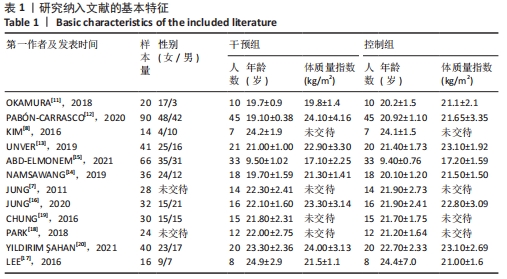
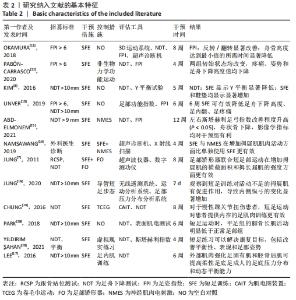
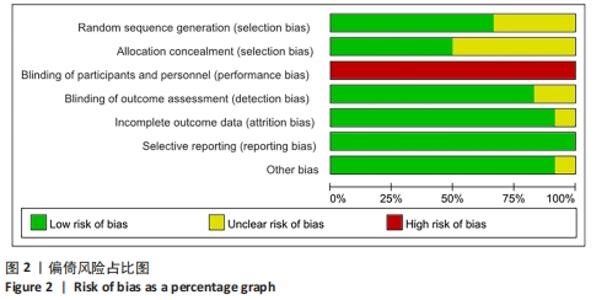
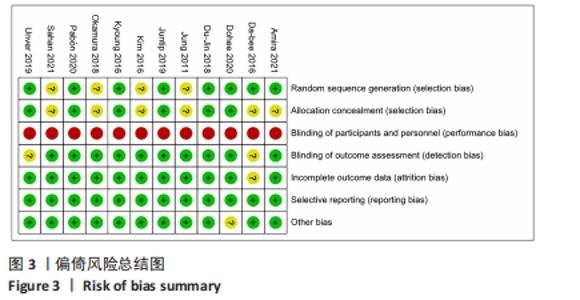
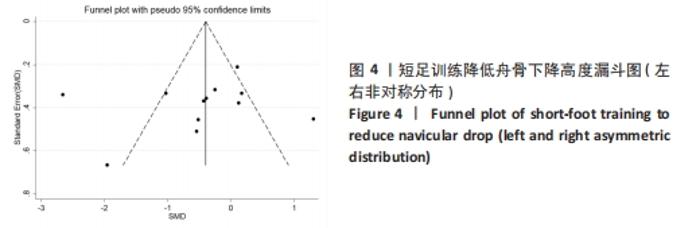
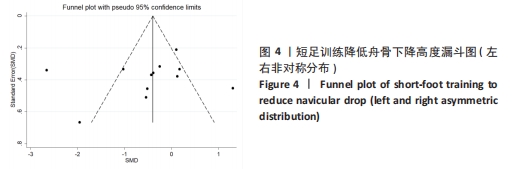
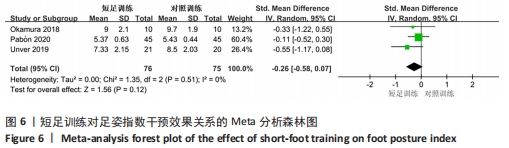
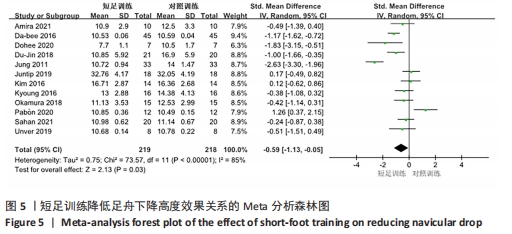
2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 短足训练对足舟下降高度的影响 首先,对纳入文献进行整体效应检验发现,短足训练具有降低足舟下降高度的效果(SMD=-0.59,P=0.03),见图5。纳入文献的整体同质性检验结果为(I2=85%,P < 0.05),存在异质性,故采用随机效应模型。根据Cohen(1988)的解释,可以根据合并后的SMD值确定效应等级,SMD < 0.2为小效应,0.2 < SMD < 0.8为中效应,而SMD > 0.8为大效应量。短足训练减小足舟下降高度的合并效应量为SMD=-0.59,达到了明显降低足舟下降高度的效果。双尾检验的结果(P < 0.05)表示多组数据合并统计量具有统计学意义,95%的置信区间为(-1.13,-0.05),以上数据说明了短足训练对于降低足舟下降高度取得了较好的效果。但由于异质性很高,需要讨论异质性的来源。"
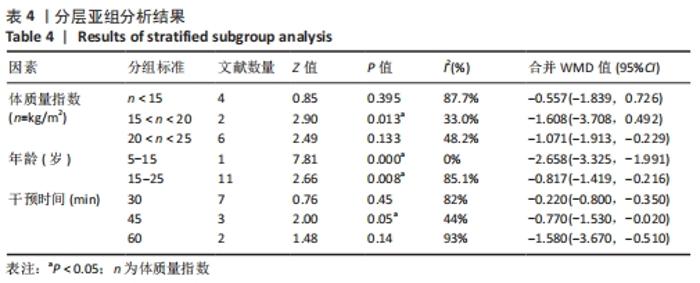
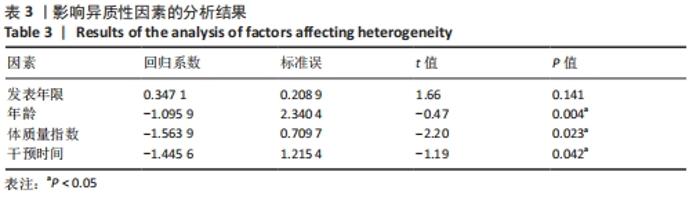
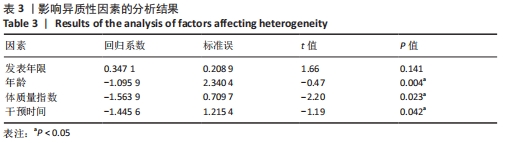
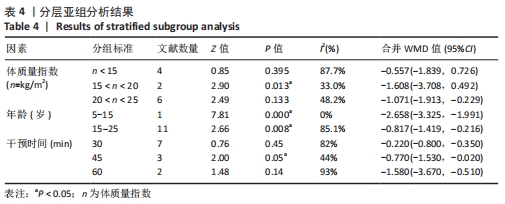
将与异质性有关的因素进行多层次多水平的亚组分析,见表4。在体质量指数方面,15 kg/m2< n < 20 kg/m2组的异质性比较小(I2=33%,P < 0.05),提示该组短足训练的干预效果显著高于对照组。n < 15 kg/m2亚组分析后异质性仍然较高,通过敏感性分析后,建议剔除PARK等[18]和JUNG等[7]文献后研究间的异质性明显降低(I2=0%,P < 0.05);20 kg/m2< n < 25 kg/m2亚组分析后异质性偏高,通过敏感性分析发现,无法通过剔除单项研究而降低异质性,因而采取随机效应模型(I2=48.2%,P > 0.05);在年龄方面,年龄在5-15岁和15-25岁两组P值均有统计学意义(I2=0%,P < 0.05)和(I2=85.1%,P < 0.05),提示该组短足训练的干预效果显著高于对照组;15-25岁组异质性比较高,通过敏感性分析发现,无法通过剔除单项研究而降低异质性,因而采取随机效应模型(I2=85.1%,P < 0.05);在训练时间方面,单次训练在45 min的干预计划中P值有统计学意义(I2=44%,P < 0.05),提示该组短足训练的干预效果显著高于对照组;30 min组异质性比较高,通过敏感性分析发现,无法通过剔除单项研究而降低异质性,因而采取随机效应模型(I2=82%,P > 0.05);60 min组由于纳入文献只有2篇,因而没有进行敏感性分析(I2=93%,P > 0.05)。 "
| [1] BORDIN D, DE GIORGI G, MAZZOCCO G, et al. Flat and cavus foot, indexes of obesity and overweight in a population of primary-school children. Minerva Pediatr. 2001;53(1):7-13. [2] SICHTING F, HOLOWKA NB, HANSEN OB, et al. Effect of the upward curvature of toe springs on walking biomechanics in humans. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):14643. [3] FILARDI V. Flatfoot and normal foot a comparative analysis of the stress shielding. J Orthop. 2018;15(3):820-825. [4] KODITHUWAKKU ARACHCHIGE SNK, CHANDER H, et al. Flatfeet: Biomechanical implications, assessment and management. Foot (Edinb). 2019;38:81-85. [5] PITA-FERNANDEZ S, GONZALEZ-MARTIN C, ALONSO-TAJES F, et al. Flat Foot in a Random Population and its Impact on Quality of Life and Functionality. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(4): LC22-LC27. [6] 崔科东. 12周足弓功能训练结合跑姿转换对足部形态及功能的影响[D].上海:上海体育学院,2019. [7] JUNG DY, KOH EK, KWON OY. Effect of foot orthoses and short-foot exercise on the cross-sectional area of the abductor hallucis muscle in subjects with pes planus: a randomized controlled trial. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2011;24(4):225-231. [8] KIM EK, KIM JS. The effects of short foot exercises and arch support insoles on improvement in the medial longitudinal arch and dynamic balance of flexible flatfoot patients. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28(11):3136-3139. [9] 周旭毓,方积乾. Meta分析的常见偏倚[J].循证医学,2002,2(4):216-220. [10] MOHER D, LIBERATI A, TETZLAFF J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264-269. [11] OKAMURA K, KANAI S, HASEGAWA M, et al. The effect of additional activation of the plantar intrinsic foot muscles on foot dynamics during gait. Foot (Edinb). 2018;34:1-5. [12] PABÓN-CARRASCO M, CASTRO-MÉNDEZ A, VILAR-PALOMO S, et al. Randomized Clinical Trial: The Effect of Exercise of the Intrinsic Muscle on Foot Pronation. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(13):4882. [13] UNVER B, ERDEM EU, AKBAS E. Effects of Short-Foot Exercises on Foot Posture, Pain, Disability, and Plantar Pressure in Pes Planus. J Sport Rehabil. 2019;29(4):436-440. [14] NAMSAWANG J, EUNGPINICHPONG W, VICHIANSIRI R, et al. Effects of the Short Foot Exercise With Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Navicular Height in Flexible Flatfoot in Thailand: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Prev Med Public Health. 2019;52(4): 250-257. [15] ABD-ELMONEM AM, EL-NEGAMY EH, MAHRAN MA, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of corrective exercises and neuromuscular electrical stimulation in children with flexible flatfeet: A randomized controlled trial. Gait Posture. 2021;88:297-303. [16] JUNG D, YI C, CHOI WJ, et al. Effect of dynamic guidance-tubing short foot gait exercise on muscle activity and navicular movement in people with flexible flatfeet. NeuroRehabilitation. 2020;47(2):217-226. [17] LEE DB, CHOI JD. The Effects of Foot Intrinsic Muscle and Tibialis Posterior Strengthening Exercise on Plantar Pressure and Dynamic Balance in Adults Flexible Pes Planus. Physical Therapy Korea. 2016;23(4):27-37. [18] PARK DJ, PARK SY. Comparison of Subjects with and without Pes Planus during Short Foot Exercises by Measuring Muscular Activities of Ankle and Navicular Drop Height. J Korean Soc Phys Med. 2018;13(3):133-139. [19] CHUNG KA, LEE E, LEE S. The effect of intrinsic foot muscle training on medial longitudinal arch and ankle stability in patients with chronic ankle sprain accompanied by foot pronation. Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science. 2016; 5(2):78-83. [20] YILDIRIM ŞAHAN T, AYDOĞAN ARSLAN S, DEMIRCI C, et al. Comparison Of Short-Term Effects Of Virtual Reality and Short Foot Exercises In Pes Planus. Foot (Edinb). 2021; 47:101778. [21] OKAMURA K, FUKUDA K, OKI S, et al. Effects of plantar intrinsic foot muscle strengthening exercise on static and dynamic foot kinematics: A pilot randomized controlled single-blind trial in individuals with pes planus. Gait Posture. 2020;75:40-45. [22] MCKEON PO, FOURCHET F. Freeing the foot: integrating the foot core system into rehabilitation for lower extremity injuries. Clin Sports Med. 2015;34(2):347-361. [23] MCKEON PO, HERTEL J, BRAMBLE D, et al. The foot core system: a new paradigm for understanding intrinsic foot muscle function. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(5):290. [24] CHANG JH, WANG SH, KUO CL, et al. Prevalence of flexible flatfoot in Taiwanese school-aged children in relation to obesity, gender, and age. Eur J Pediatr. 2010;169(4):447-452. [25] HALLEMANS A, DE CLERCQ D, VAN DONGEN S, et al. Changes in foot-function parameters during the first 5 months after the onset of independent walking: a longitudinal follow-up study. Gait Posture. 2006;23(2):142-148. [26] SNYDER KR, EARL JE, O’CONNOR KM, et al. Resistance training is accompanied by increases in hip strength and changes in lower extremity biomechanics during running. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2009;24(1):26-34. [27] MICKLE KJ, STEELE JR, MUNRO BJ. The feet of overweight and obese young children: are they flat or fat. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2006; 14(11):1949-1953. [28] ANDREASEN J, MØLGAARD CM, CHRISTENSEN M, et al. Exercise therapy and custom-made insoles are effective in patients with excessive pronation and chronic foot pain--a randomized controlled trial. Foot (Edinb). 2013;23(1):22-28. [29] MURLEY GS, MENZ HB, LANDORF KB. Foot posture influences the electromyographic activity of selected lower limb muscles during gait. J Foot Ankle Res. 2009;2:35. [30] CHOUGALA A, PHANSE V, KHANNA E, et al. Screening of body mass index and functional flatfoot in adult: an observational study. Int J Physiother Res. 2015;3(3):1037-1041. [31] WILLIAMS DS 3RD, TIERNEY RN, BUTLER RJ. Increased medial longitudinal arch mobility, lower extremity kinematics, and ground reaction forces in high-arched runners. J Athl Train. 2014;49(3):290-296. [32] IRVING DB, COOK JL, YOUNG MA, et al. Obesity and pronated foot type may increase the risk of chronic plantar heel pain: a matched case-control study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2007;8:41. [33] NIELSEN MD, DODSON EE, SHADRICK DL, et al. Nonoperative care for the treatment of adult-acquired flatfoot deformity. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;50(3):311-314. [34] EVANS AM, COPPER AW, SCHARFBILLIG RW, et al. Reliability of the foot posture index and traditional measures of foot position. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2003;93(3):203-213. [35] PAYNE C, OATES M, NOAKES H. Static stance response to different types of foot orthoses. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2003;93(6):492-498. [36] MCLEAN SG, FELLIN RE, SUEDEKUM N, et al. Impact of fatigue on gender-based high-risk landing strategies. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(3):502-514. [37] MULLIGAN EP, COOK PG. Effect of plantar intrinsic muscle training on medial longitudinal arch morphology and dynamic function. Man Ther. 2013;18(5):425-430. [38] JUNG DY, KIM MH, KOH EK, et al. A comparison in the muscle activity of the abductor hallucis and the medial longitudinal arch angle during toe curl and short foot exercises. Phys Ther Sport. 2011;12(1):30-35. [39] 张新语,霍洪峰.足姿指数(FPI):足部姿势及足踝功能的定量表达[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(13):1194-1199. [40] REDMOND AC, CROSBIE J, OUVRIER RA. Development and validation of a novel rating system for scoring standing foot posture: the Foot Posture Index. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2006;21(1):89-98. |
| [1] | Wang Yanjin, Zhou Yingjie, Chai Xubin, Zhuo Hanjie. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of 3D printed porous titanium alloy fusion cage in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1434-1440. |
| [2] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [3] | Li Wenjie, You Aijia, Zhou Junli, Fang Sujuan, Li Chun. Effects of different dressings in the treatment of burn wounds: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1141-1148. |
| [4] | Pan Weimin, Wang Bing, Han Yabing, Li Ting, Song Jiaqi, Qin Huasheng, Liu Yang. Effects of blood flow restriction training on muscle strength, muscle mass and physical performance in older adults: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 805-812. |
| [5] | Bao Wenxia, Zhan Dongge, Wang Nian, Yang Xianjun, Ding Chengbiao. Foot-type recognition algorithm based on plantar pressure images [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 527-533. |
| [6] | Yu Jiaan, Liu Xinwei, Lian Hongyu, Liu Kexin, Li Zitao. Medial open-wedge tibial osteotomy versus lateral closed-wedge tibial osteotomy for unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 632-639. |
| [7] | Xu Yangyang, He Peiliang, Meng Qingqi, Li Siming. A meta-analysis of the effects of continuous adductor canal block and continuous femoral nerve block on early activity after knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 640-645. |
| [8] | Chai Hao, Yang Deyong, Zhang Lei, Shu Li. 3D printing personalized osteotomy guide technology versus conventional total knee arthroplasty on the accuracy of lower limb force alignment: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 646-654. |
| [9] | You Aijia, Li Wenjie, Zhou Junli, Li Chun. Systematic evaluation of six dressings on wound safety following total hip and knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 486-492. |
| [10] | Hu Fei, Wang Jie. Safety and efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 76-82. |
| [11] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [12] | Liu Gang, Ma Chao, Wang Le, Zeng Jie, Jiao Yong, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Ankle-foot orthoses improve motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a Meta-analysis based on 12 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1299-1304. |
| [13] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [14] | Wang Nan, Qian Yuzhang, Xie Lin. Network Meta-analysis of different acupuncture methods for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 813-820. |
| [15] | Wei Zhoudan, Li Wenjin, Zhu Li, Wang Yu, Zhao Jiaoyang, Chen Yanan, Guo Dong, Hao Min. Platelet-rich fibrin as a material for alveolar ridge preservation significantly reduces the resorption of alveolar bone height and width after tooth extraction: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 643-648. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||