Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 805-812.doi: 10.12307/2023.097
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of blood flow restriction training on muscle strength, muscle mass and physical performance in older adults: a Meta-analysis
Pan Weimin1, Wang Bing2, Han Yabing3, Li Ting3, Song Jiaqi3, Qin Huasheng4, Liu Yang3
- 1Sports and Health Science School, 3Graduate School, Xi’an Physical Education University, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Basic Science School, Xi’an Technological University, Xi’an 710021, Shaanxi Province, China; 4Physical Education Department, Shaanxi Xueqian Normal University, Xi’an 710100, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-12-09Accepted:2022-04-26Online:2023-02-18Published:2022-07-25 -
Contact:Pan Weimin, Sports and Health Science School, Xi’an Physical Education University, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Pan Weimin, PhD, Professor, Sports and Health Science School, Xi’an Physical Education University, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Social Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province, No. 2019R020 (to PWM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Pan Weimin, Wang Bing, Han Yabing, Li Ting, Song Jiaqi, Qin Huasheng, Liu Yang. Effects of blood flow restriction training on muscle strength, muscle mass and physical performance in older adults: a Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 805-812.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
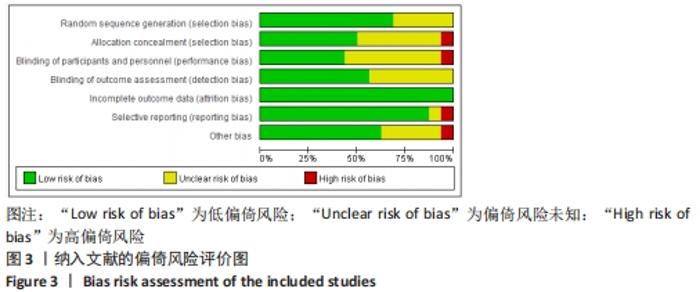
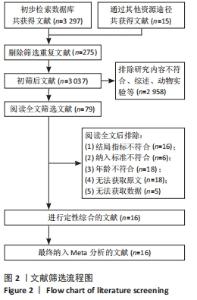
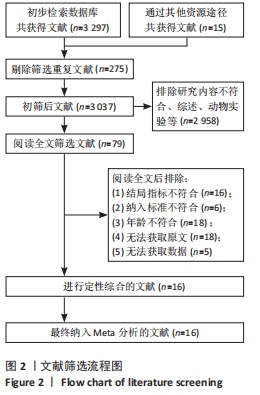
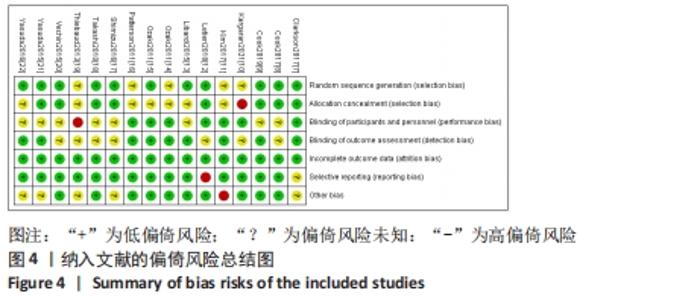
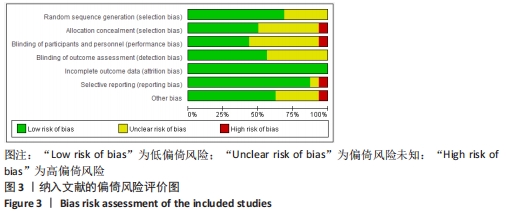
2.3 纳入文献质量评估结果 采用Cochrane协作网的偏倚风险评价工具对纳入的文献进行评分。共有11篇研究说明采用随机方法进行分组[7-9,12-13,15,17-18,20-22],3篇研究介绍了随机分组的具体方法[8,12,17],5篇未提及随机方法[10-11,14,16,19],8篇进行了分配隐藏[7-9,12,17-18,20-21],9篇研究均未对研究者和受试者实施盲法,但都进行了基线比较,研究数据结果均为完整[8-9,13,17-22],9篇研究对结局评价者施盲[7,9,11,13-16,21-22],所有文献均没有不完整数据报告。文献质量分级:11篇研究为B级[7-9,12-16,18,20-21],其他均为C级,见图3,4。"
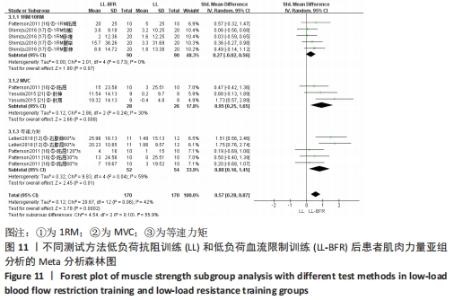
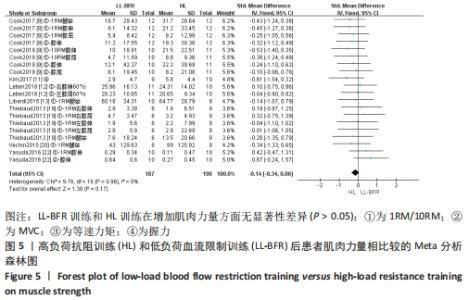
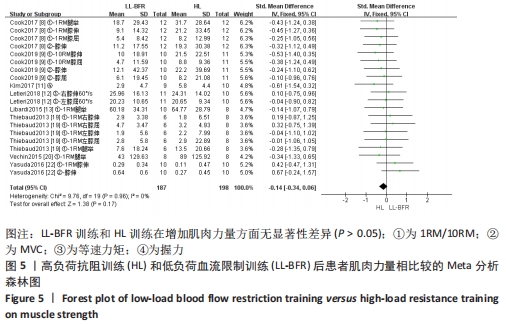
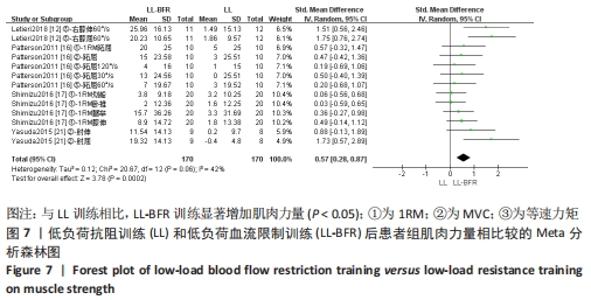
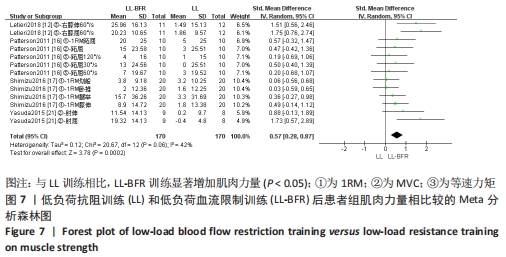
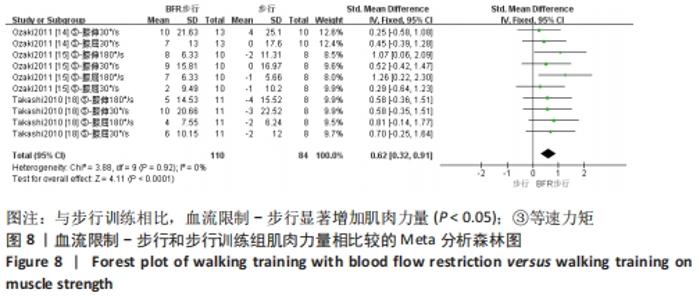
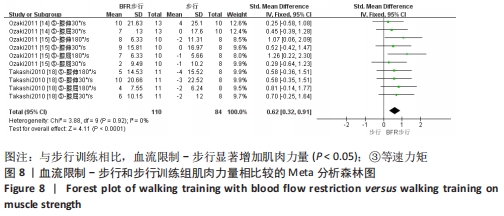
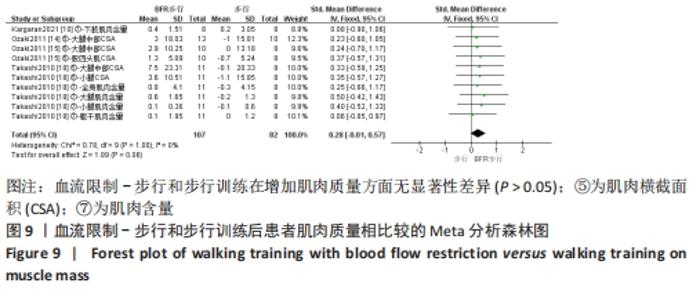
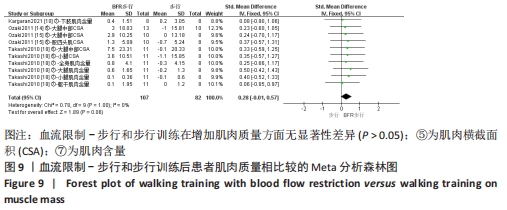
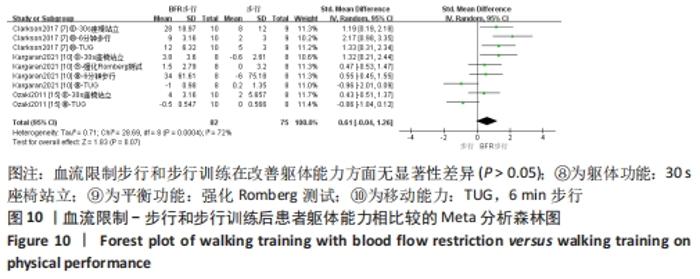
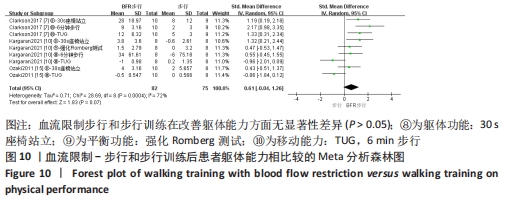
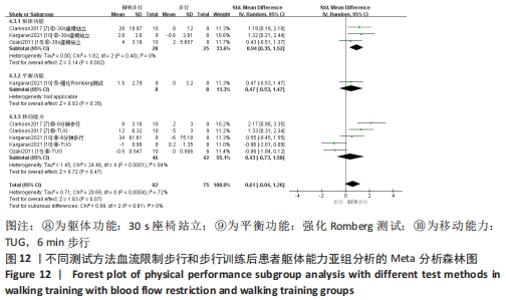
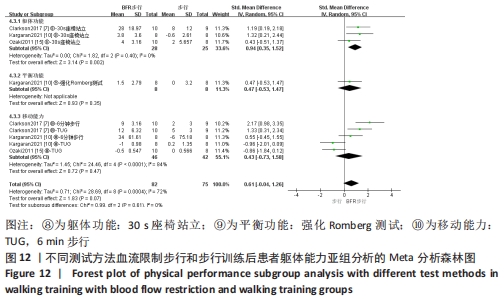
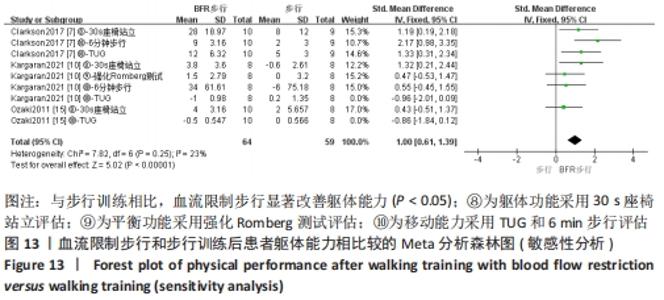
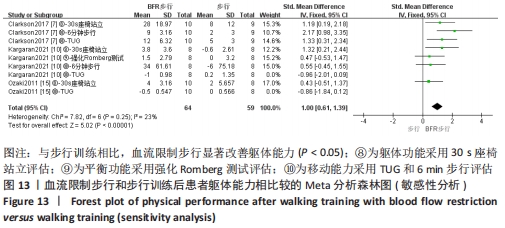
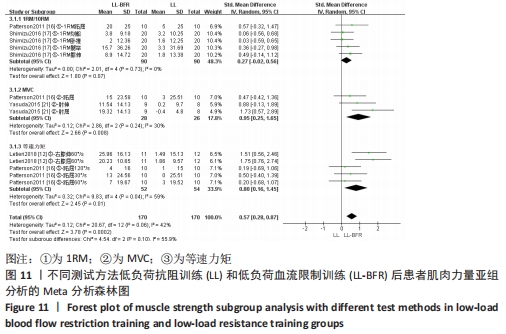
2.5 亚组分析结果 根据Meta分析结果显示,LL-BFR和LL训练对肌肉力量影响存在异质性(P=0.06,I2=42%),血流限制步行和步行训练对躯体能力影响存在异质性(P=0.000 4,I2=72%),考虑全部研究结局指标的测试方法不同可能是产生异质性的主要原因,因此对该方面的异质性进行进一步分析。 2.5.1 LL-BFR和LL训练对肌肉力量影响的亚组分析结果 对肌肉力量的测试方法进行亚组分析:2篇文献采用1RM测试肌肉力量评估[16-17],2篇文献采用MVC测试肌肉力量评估[16,21],2篇文献采用等速力矩测试肌肉力量评估[12,16]。结果显示:①1RM的分析结果无异质性(I2=0%);②MVC的分析结果存在低异质性(I2=30%);③等速力矩的分析结果存在高异质性(I2=59%),提示在目前纳入研究中,测试方法的不同是异质性来源的可能性较高。合并效应结果显示:采用MVC测试时,LL-BFR较LL训练增加肌肉力量,且呈显著性差异(P=0.008);采用等速力矩测试时,LL-BFR较LL训练增加肌肉力量,且呈显著性差异(P=0.01),提示不同测试方法对结局指标可能存在影响,见图11。"
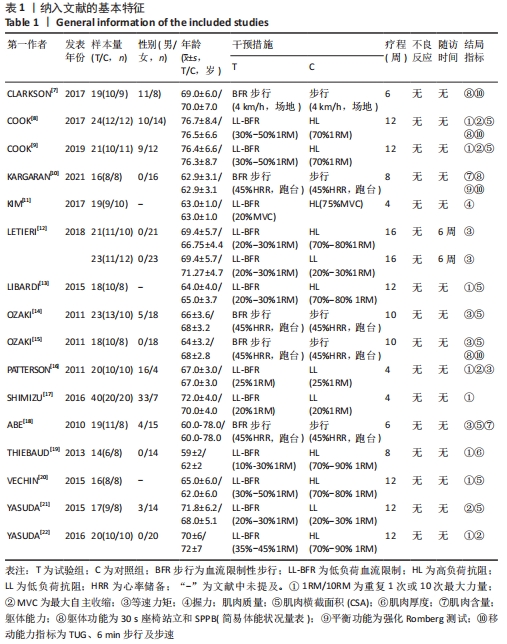
| [1] 姜珊,康琳,刘晓红. 2019亚洲肌少症诊断及治疗共识解读[J].中华老年医学杂志,2020, 39(4):373-376. [2] FRAGALA MS, CADORE EL, DORGO S, et al. Resistance training for older adults: position statement from the national strength and conditioning association. J Strength Cond Res. 2019;33(8):2019-2052. [3] LORENZ DS, BAILEY L, WILK KE, et al. Blood Flow Restriction Training. J Athl Train. 2021;56(9):937-944. [4] WANG DXM, YAO J, ZIREK Y, et al. Muscle mass, strength, and physical performance predicting activities of daily living: a meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020;11(1):3-25. [5] 汪洋.Cochrane偏倚风险评估工具简介[J].中国全科医学,2019,22(11):1322. [6] 刘鸣,吴红梅,卫茂玲.系统评价、Meta-分析设计与实施方法[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2011:68-71. [7] CLARKSON MJ, CONWAY L, WARMINGTON SA. Blood flow restriction walking and physical function in older adults: a randomized control trial. J Sci Med Sport. 2017;20(12):1041-1046. [8] COOK SB, LAROCHE DP, VILLA MR, et al. Blood flow restricted resistance training in older adults at risk of mobility limitation. Exp Gerontol. 2017; 99(1):138-145. [9] COOK SB, CLEARY CJ. Progression of blood flow restricted resistance training in older adults at risk of mobility limitations. J Frontiers in Physiology, 2019;12(6)10:738. [10] KARGARAN A, ABEDINPOUR A, SAADATMEHR Z, et al. Effects of dual-task training with blood flow restriction on cognitive functions, muscle quality, and circulatory biomarkers in elderly women.J Physiol Behav. 2021;239(1):113500. [11] KIM J, LANG JA, PILANIA N, et al. Effects of blood flow restricted exercise training on muscular strength and blood flow in older adults. Exp Gerontol. 2017;99(1):127-132. [12] LETIERI RV, TEIXEIRA AM, FURTADO GE, et al. Effect of 16 weeks of resistance exercise and detraining comparing two methods of blood flow restriction in muscle strength of healthy older women: a randomized controlled trial. Exp Gerontol. 2018;114(9):78-86. [13] LIBARDI CA, CHACON-MIKAHIL MP, CAVAGLIERI CR, et al. Effect of concurrent training with blood flow restriction in the elderly. Int J Sports Med. 2015;36(5):395-399. [14] OZAKI H, MIYACHI M, NAKAJIMA T, et al. Effects of 10 weeks walk training with leg blood flow reduction on carotid arterial compliance and muscle size in the elderly adults. J Angiology. 2011;62(1):81-86. [15] OZAKI H, SAKAMAKI M, YASUDA T, et al. Increases in thigh muscle volume and strength by walk training with leg blood flow reduction in older participants. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2011; 66(3):257-263. [16] PATTERSON SD, FERGUSON RA. Enhancing strength and postocclusive calf blood flow in older people with training with blood-flow restriction. J Aging Phys Act. 2011;19(3):201-213. [17] SHIMIZU R, HOTTA K, YAMAMOTO S, et al. Low-intensity resistance training with blood flow restriction improves vascular endothelial function and peripheral blood circulation in healthy elderly people. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2016;116(4):749-757. [18] ABE T, SAKAMAKI M, FUJITA S, et al. Effects of low-intensity walk training with restricted leg blood flow on muscle strength and aerobic capacity in older adults. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2010;33(1):34-40. [19] THIEBAUD RS, LOENNEKE JP, FAHS CA, et al. The effects of elastic band resistance training combined with blood flow restriction on strength, total bone-free lean body mass and muscle thickness in postmenopausal women. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2013;33(5):344-352. [20] VECHIN FC, LIBARDI CA, CONCEICAO MS, et al. Comparisons between low-intensity resistance training with blood flow restriction and high-intensity resistance training on quadriceps muscle mass and strength in elderly. J Strength Cond Res. 2015;29(4):1071-1076. [21] YASUDA T, FUKUMURA K, UCHIDA Y, et al. Effects of low-load, elastic band resistance training combined with blood flow restriction on muscle size and arterial stiffness in older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015;70(8):950-958. [22] YASUDA T, FUKUMURA K, TOMARU T, et al. Thigh muscle size and vascular function after blood flow-restricted elastic band training in older women. Oncotarget. 2016;7(23):33595-33607. [23] CENTNER C, WIEGEL P, GOLLHOFER A, et al. Effects of blood flow restriction training on muscular strength and hypertrophy in older Individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2019;49(1):95-108. [24] SARTO F, FRANCHI MV, RIGON PA, et al. Muscle activation during leg-press exercise with or without eccentric overload. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020;120(7):1651-1656. [25] VOPAT BG, VOPAT LM, BECHTOLD MM, et al. Blood flow restriction therapy: where we are and where we are going. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(12):e493-e500. [26] FATELA P, MENDONCA GV, VELOSO AP, et al. Blood flow restriction alters motor unit behavior during resistance exercise. Int J Sports Med. 2019; 40(9):555-562. [27] OKITA K, TAKADA S, MORITA N, et al. Resistance training with interval blood flow restriction effectively enhances intramuscular metabolic stress with less ischemic duration and discomfort. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2019;44(7):759-764. [28] GAVANDA S, ISENMANN E, SCHLÖDER Y, et al. Low-intensity blood flow restriction calf muscle training leads to similar functional and structural adaptations than conventional low-load strength training: a randomized controlled tria. J PLoS One. 2020;15(6):0235377. [29] PIGNANELLI C, PETRICK HL, KEYVANI F, et al. Low-load resistance training to task failure with and without blood flow restriction: muscular functional and structural adaptations. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020;318(2):R284-R295. [30] THIEBAUD RS, ABE T, LOENNEKE JP, et al. Acute muscular responses to practical low-load blood flow restriction exercise versus traditional low-load blood flow restriction and high-/low-load exercise. J Sport Rehabil. 2019;29(7):984-992. [31] FRY CS, GLYNN EL, DRUMMOND MJ, et al. Blood flow restriction exercise stimulates mTORC1 signaling and muscle protein synthesis in older men. J Appl Physiol. 2010;108(5):1199-1209. [32] CENTNER C, LAUBER B. A systematic review and meta-analysis on neural adaptations following blood flow restriction training: what we know and what we don’t know. Front Physiol. 2020;11:887. [33] GRGIC J, LAZINICA B, SCHOENFELD BJ, et al. Test-retest reliability of the one-repetition maximum (1RM) strength assessment: a systematic review.Sports Med Open. 2020;6(1):31. [34] LEA JWD, O’DRISCOLL JM, COLEMAN DA, et al. Validity and reliability of the ‘Isometric Exercise Scale’ (IES) for measuring ratings of perceived exertion during continuous isometric exercise. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):5334. [35] OZAKI H, NAKAGATA T, YOSHIHARA T, et al. Effects of progressive walking and stair-climbing training program on muscle size and strength of the lower body in untrained older adults.J Sports Sci Med. 2019;18(4):722-728. [36] 毛宁,刘书芳,卫星.血流限制训练在老年人中的应用研究进展[J].中国老年保健医学,2020, 18(6):117-121. [37] SLYSZ J, STULTZ J, BURR JF. The efficacy of blood flow restricted exercise: a systematic review meta-analysis. J Sci Med Sport. 2016;19(8):669-675. [38] MASCIOCCHI E, MALTAIS M, ROLLAND Y, et al. Time effects on physical performance in older adults in nursing home: a narrative review.J Nutr Health Aging. 2019;23(6):586-594. [39] 孙志成,王彤,王青,等.虚拟现实训练对养老院老年人跌倒相关危险因素的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2018,33(6):687-692. [40] BALACHANDRAN AT, VIGOTSKY AD, QUILES N, et al. Validity, reliability, and measurement error of a sit-to-stand power test in older adults: a pre-registered study. Exp Gerontol. 2021;145:111202. |
| [1] | Liu Xinyue, Xing Xinyang, Huo Hongfeng. Differences in human dynamic stability during walking under different cognitive loads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Wang Yanjin, Zhou Yingjie, Chai Xubin, Zhuo Hanjie. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of 3D printed porous titanium alloy fusion cage in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1434-1440. |
| [3] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [4] | Li Wenjie, You Aijia, Zhou Junli, Fang Sujuan, Li Chun. Effects of different dressings in the treatment of burn wounds: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1141-1148. |
| [5] | Feng Liang, Gong Shuhui, Huo Hongfeng. Effect of short-foot training on foot and ankle function in patients with flat feet: Meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 799-804. |
| [6] | Liang Xiao, Zhao Panchao, Li Jiahui, Ji Zhongqiu, Jiang Guiping. Gait and biomechanical characteristics of lower limbs in multi-task walking of 4-6-year-old children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 505-512. |
| [7] | Yu Jiaan, Liu Xinwei, Lian Hongyu, Liu Kexin, Li Zitao. Medial open-wedge tibial osteotomy versus lateral closed-wedge tibial osteotomy for unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 632-639. |
| [8] | Xu Yangyang, He Peiliang, Meng Qingqi, Li Siming. A meta-analysis of the effects of continuous adductor canal block and continuous femoral nerve block on early activity after knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 640-645. |
| [9] | Chai Hao, Yang Deyong, Zhang Lei, Shu Li. 3D printing personalized osteotomy guide technology versus conventional total knee arthroplasty on the accuracy of lower limb force alignment: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 646-654. |
| [10] | You Aijia, Li Wenjie, Zhou Junli, Li Chun. Systematic evaluation of six dressings on wound safety following total hip and knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 486-492. |
| [11] | Hu Fei, Wang Jie. Safety and efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 76-82. |
| [12] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [13] | Liu Gang, Ma Chao, Wang Le, Zeng Jie, Jiao Yong, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Hu Chuanyu, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Ankle-foot orthoses improve motor function of children with cerebral palsy: a Meta-analysis based on 12 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1299-1304. |
| [14] | Wei Xing, Liu Shufang, Mao Ning. Roles and values of blood flow restriction training in the rehabilitation of knee joint diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 774-779. |
| [15] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||