Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 486-492.doi: 10.12307/2023.029
Systematic evaluation of six dressings on wound safety following total hip and knee arthroplasty
You Aijia, Li Wenjie, Zhou Junli, Li Chun
- School of Nursing, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2021-12-29Accepted:2022-02-09Online:2023-01-28Published:2022-06-01 -
Contact:Li Chun, Associate professor, School of Nursing, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:You Aijia, Master candidate, School of Nursing, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Featured Innovation Project of General Universities in Guangdong Province in 2020, No. 2020KTSCX025 (to LC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
You Aijia, Li Wenjie, Zhou Junli, Li Chun. Systematic evaluation of six dressings on wound safety following total hip and knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 486-492.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
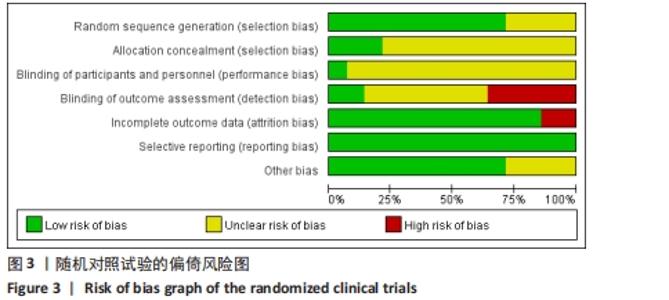
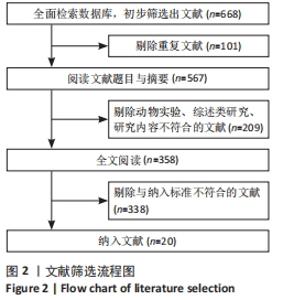
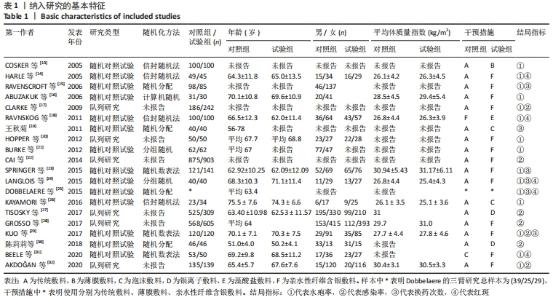
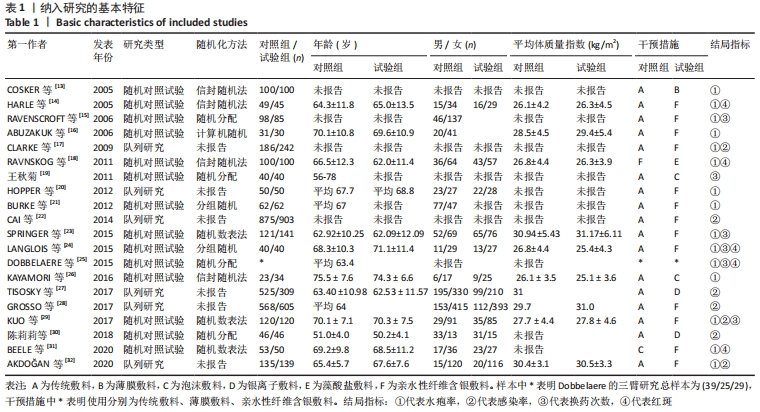
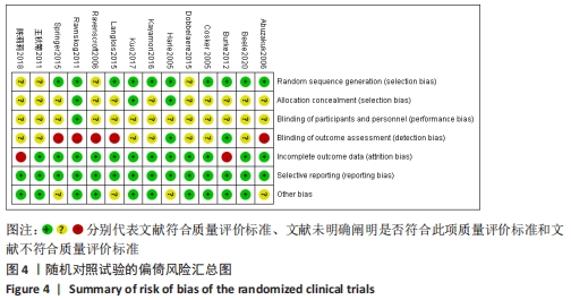
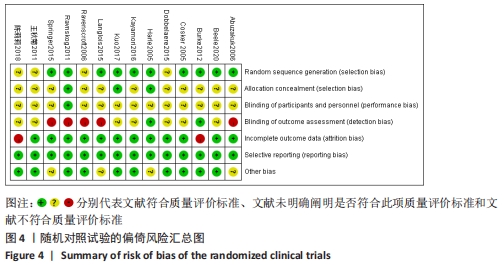
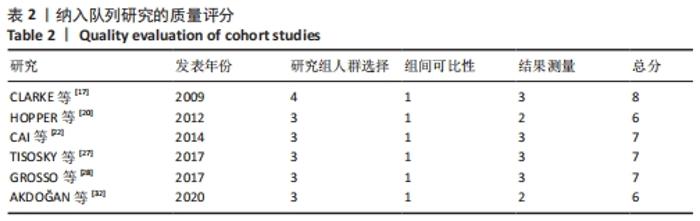
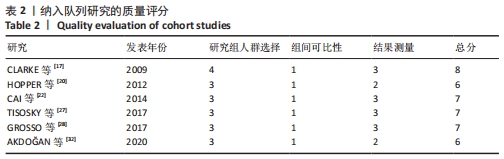
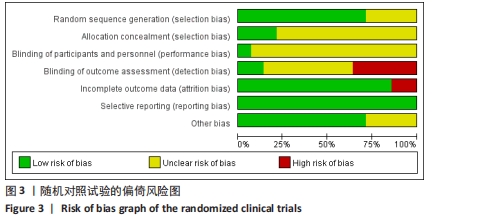
2.3 文献质量评价 纳入的14项随机对照试验均提及随机分配,其中10项随机对照试验报告了随机序列的具体生成方法[13-14,16,18,21,23-24,26,29,31],主要包含信封随机法[13-14,18,26]、计算机随机产生序列法[16]、分组随机法[21,24]、随机数表法[23,29,31];3项研究报告了分配隐藏方法[14,18,29];盲法实施方面,1项研究做到了对研究者和受试者施盲[18],2项研究做到对结果评价者施盲[14,21],2项研究可能存在结果数据不全[21,25],其余研究数据完整,有4项研究可能存在其他偏倚风险[14,16,23,24],见图3,4。通过NOS量表评价6项队列研究的质量[17,20,22,27-28,32],3项被评为7分[22,27-28],2项被评为6分[20,32],1项被评为8分[17],质量较高,见表2。"
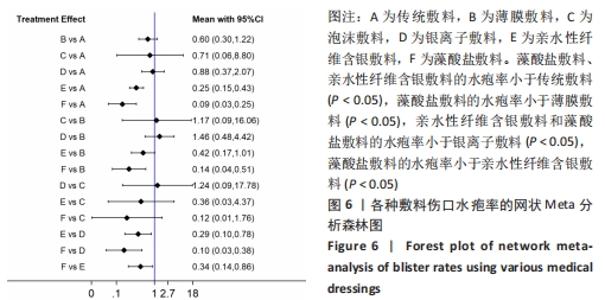
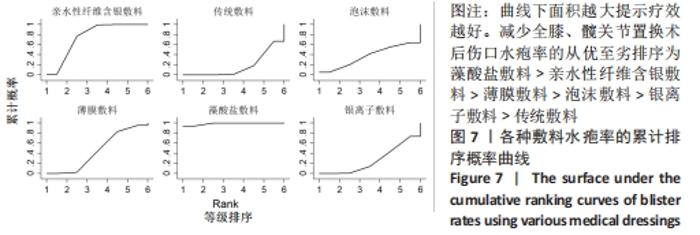
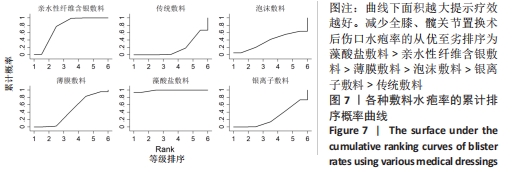
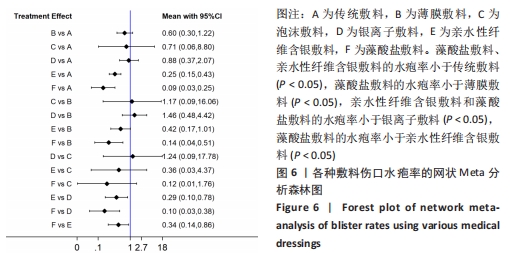
不一致性和异质性检验:通过Stata 16.0软件的network程序包进行结局指标的分析,拟合不一致模型得P=0.979 9,表明整体的不一致性模型不显著,一致性模型拟合显示P > 0.05,表明一致性较好。节点劈裂法检验显示存在1个闭合环,不一致因子(IF)=0.07,Loop(传统敷料-泡沫敷料-亲水性纤维含银敷料)的95%CI(0.00,5.20),表明各研究的异质性较小,具有一致性。 网状Meta分析结果:不同医用敷料应用于全膝、髋关节置换后伤口的水疱率存在差异。藻酸盐敷料、亲水性纤维含银敷料的水疱率小于传统敷料(P < 0.05);藻酸盐敷料的水疱率小于薄膜敷料(P < 0.05);亲水性纤维含银敷料和藻酸盐敷料的水疱率小于银离子敷料(P < 0.05);藻酸盐敷料的水疱率小于亲水性纤维含银敷料(P < 0.05)。其余敷料之间的比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图6。 "
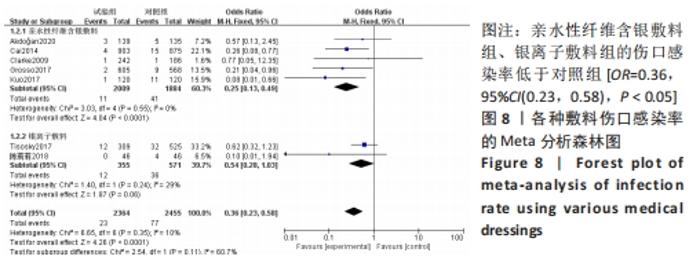
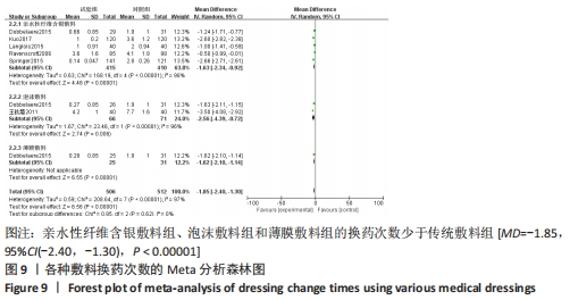
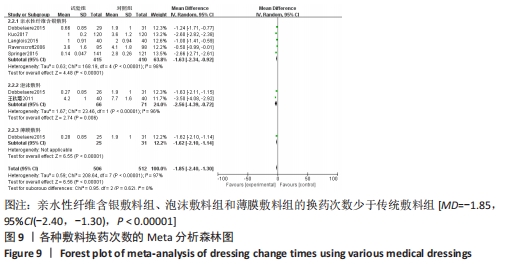
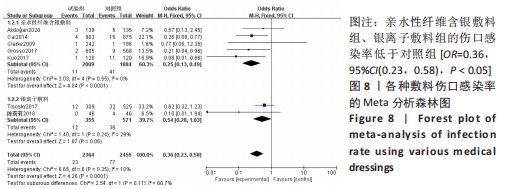
2.4.2 各种敷料伤口感染率的Meta分析结果 有7项研究报告了全膝/髋关节置换后的伤口感染率差异[17,22,27-30,32],其中5项研究为亲水性纤维含银敷料组,2项研究为银离子敷料组,对照组为传统敷料。Meta分析异质性检验显示I2=10%、P=0.35,异质性不明显,故采用固定效应模型合并分析。结果显示,亲水性纤维含银敷料组、银离子敷料组的伤口感染率低于对照组[OR=0.36,95%CI(0.23,0.58),P < 0.05]。亚组分析显示亲水性纤维含银敷料组的伤口感染率低于对照组(P < 0.000 1);银离子敷料组在伤口感染率方面与对照组比较差异无显著性意义(P=0.06),可能与纳入研究数量不足有关,见图8。"
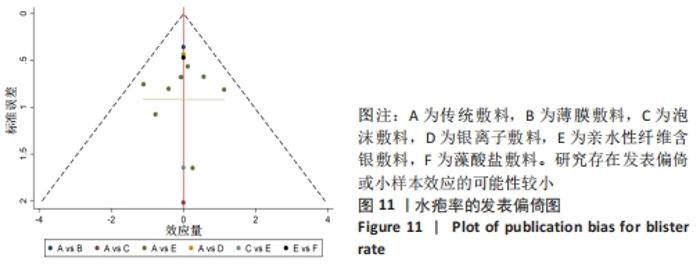
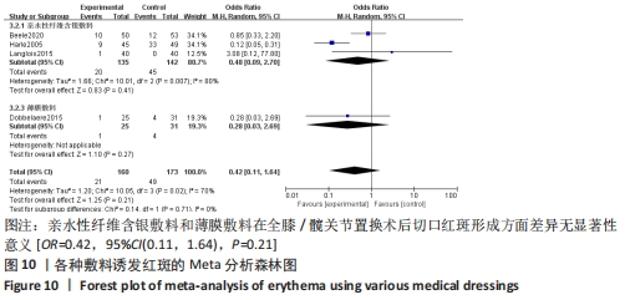
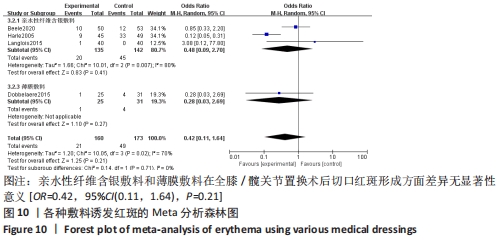
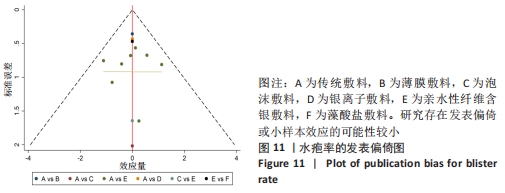
2.5 敏感性分析 针对换药次数的Meta分析,逐一剔除文章后,异质性仍然存在,敏感性较高。针对红斑的Meta分析,采用逐一剔除文章法,发现剔除HARLE等[14]的研究之后异质性消失(I2=0%,P=0.47),原因可能是该研究的干预时间较其他研究更长。剔除该研究之后重新合并效应量,结果显示差异无显著性意义[MD=0.80,95%CI(0.34,1.85),P=0.60],未发现某一研究对异质性贡献大,提示Meta分析结果可信。 2.6 发表偏倚分析 通过Stata 16.0软件绘制水疱率的漏斗图,颜色圆点代表不同干预措施的两两比较,同一颜色圆点表示两两比较的数量。目测类比评分纳入结局指标基本对称分布于X=0垂直线的两侧,表示研究存在发表偏倚或小样本效应的可能性较小,见图11。"
| [1] KURTZ S, ONG K, LAU E, et al. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):780-785. [2] CHUA H, BRADY B, FARRUGIA M, et al. Implementing early mobilisation after knee or hip arthroplasty to reduce length of stay: a quality improvement study with embedded qualitative component. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020; 21(1):765. [3] 戴尅戎,李慧武,严孟宁.我国人工关节加速发展的二十年[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2015,9(6):691-694. [4] SLOAN M, PREMKUMAR A, SHETH NP. Projected Volume of Primary Total Joint Arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018; 100(17):1455-1460. [5] RAVI B, CROXFORD R, HOLLANDS S, et al. Increased risk of complications following total joint arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(2):254-263. [6] NAMBA RS, INACIO MC, PAXTON EW. Risk factors associated with deep surgical site infections after primary total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of 56,216 knees. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013; 95(9):775-782. [7] LOMBARDI AV JR, BEREND KR, ADAMS JB. Why knee replacements fail in 2013: patient, surgeon, or implant? Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(11 Supple A): 101-104. [8] CLARKE JV, DEAKIN AH, DILLON JM, et al. A prospective clinical audit of a new dressing design for lower limb arthroplasty wounds. J Wound Care. 2009;18(1):5-11. [9] 王巍巍,杨智荣,孙凤,等.网状Meta分析GRADE证据总结表的制订、解读与应用[J].中国循证医学杂志,2020,20(12):1471-1476. [10] WANG KH, WU JR, ZHANG D, et al. Comparative efficacy of Chinese herbal injections for treating chronic heart failure: a network meta-analysis. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018;18(1):41. [11] HIGGINS JP, ALTMAN DG, GØTZSCHE PC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928. [12] HUTTON B, SALANTI G, CALDWELL DM, et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162(11):777-784. [13] COSKER T, ELSAYED S, GUPTA S, et al. Choice of dressing has a major impact on blistering and healing outcomes in orthopaedic patients. J Wound Care. 2005;14(1):27-29. [14] HARLE S, KORHONEN A, KETTUNEN JA, et al. A randomised clinical trial of two different wound dressing materials for hip replacement patients. Orthop Nurs. 2005;9(4):205-210. [15] RAVENSCROFT MJ, HARKER J, BUCH KA. A prospective, randomised, controlled trial comparing wound dressings used in hip and knee surgery: Aquacel and Tegaderm versus Cutiplast. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2006;88(1):18-22. [16] ABUZAKUK TM, COWARD P, SHENAVA Y, et al. The management of wounds following primary lower limb arthroplasty: a prospective, randomised study comparing hydrofibre and central pad dressings. Int Wound J. 2006;3(2):133-137. [17] CLARKE JV, DEAKIN AH, DILLON JM, et al. A prospective clinical audit of a new dressing design for lower limb arthroplasty wounds. J Wound Care. 2009;18(1):5-8,10-11. [18] RAVNSKOG FA, ESPEHAUG B, INDREKVAM K. Randomised clinical trial comparing Hydrofiber and alginate dressings post-hip replacement. J Wound Care. 2011;20(3):136-142. [19] 王秋菊.吸水敷料在髋关节置换术后伤口护理中的应用[J].中国误诊学杂志,2011,11(11): 2574-2575. [20] HOPPER GP, DEAKIN AH, CRANE EO, et al. Enhancing patient recovery following lower limb arthroplasty with a modern wound dressing: a prospective, comparative audit. J Wound Care. 2012;21(4):200-203. [21] BURKE NG, GREEN C, MCHUGH G, et al. A prospective randomised study comparing the jubilee dressing method to a standard adhesive dressing for total hip and knee replacements. J Tissue Viability. 2012;21(3):84-87. [22] CAI J, KARAM J A, PARVIZI J, et al. Aquacel surgical dressing reduces the rate of acute PJI following total joint arthroplasty: a case-control study. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(6):1098-1100. [23] SPRINGER BD, BEAVER WB, GRIFFIN WL, et al. Role of Surgical Dressings in Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015;44(9):415-420. [24] LANGLOIS J, ZAOUI A, OZIL C, et al. Randomized controlled trial of conventional versus modern surgical dressings following primary total hip and knee replacement. Int Orthop. 2015;39(7):1315-1319. [25] DOBBELAERE A, SCHUERMANS N, SMET S, et al. Comparative study of innovative postoperative wound dressings after total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Belg. 2015;81(3):454-461. [26] KAYAMORI S, TSUKADA S, SATO M, et al. Impact of postoperative compression dressing using polyethylene foam pad on the multimodal protocol for swelling control following total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Arthroplast Today. 2016;2(4):199-204. [27] TISOSKY AJ, IYOHA-BELLO O, DEMOSTHENES N, et al. Use of a Silver Nylon Dressing Following Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Decreases the Postoperative Infection Rate. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2017;1(7):e034. [28] GROSSO MJ, BERG A, LARUSSA S, et al. Silver-Impregnated Occlusive Dressing Reduces Rates of Acute Periprosthetic Joint Infection After Total Joint Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(3):929-932. [29] KUO FC, CHEN B, LEE MS, et al. AQUACEL® Ag Surgical Dressing Reduces Surgical Site Infection and Improves Patient Satisfaction in Minimally Invasive Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Study. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:1262108. [30] 陈莉莉,陈澜,雷晓冬.银离子敷料对髋关节置换术后伤口愈合的护理研究[J].中国保健营养,2018,28(6):194-195. [31] BEELE H, VAN OVERSCHELDE P, OLIVECRONA C, et al. A prospective randomized controlled clinical investigation comparing two post-operative wound dressings used after elective hip and knee replacement; Mepilex® Border Post-Op versus Aquacel® surgical. Int J Orthop Trauma Nurs. 2020; 38:100772. [32] AKDOĞAN M, ATILLA H. Comparison of the Aquacel Ag Surgical Dressing vs Standard Dressing in the Treatment of the Wound Site Infection and Patient Comfort in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Erciyes Med J 2020;42(1):93-97. [33] LIANG CK, CHU S, HSU YH, et al. Effects of modified version of the Hospital Elder Life Program on post-discharge cognitive function and activities of daily living among older adults undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2021;93:104284. [34] CARR AJ, ROBERTSSON O, GRAVES S, et al. Knee replacement. Lancet. 2012;379(9823):1331-1340. [35] OKTAS B, VERGILI O. The effect of intensive exercise program and kinesiotaping following total knee arthroplasty on functional recovery of patients. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):233. [36] PATEL KM, MEARS SC, BARNES CL, et al. Sepsis and Total Joint Arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2022;53(1):13-24. [37] CLINGER BN, LINK HD, RICHTER DL, et al. Silver Coatings in Reconstructive Orthopaedics: Basic Science and Clinical Rationale. Surg Technol Int. 2021;39:413-417. [38] SALEH K, OLSON M, RESIG S, et al. Predictors of wound infection in hip and knee joint replacement: results from a 20 year surveillance program. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(3):506-515. [39] KARLAKKI SL, HAMAD AK, WHITTALL C, et al. Incisional negative pressure wound therapy dressings (iNPWTd) in routine primary hip and knee arthroplasties: A randomised controlled trial. Bone Joint Res. 2016;5(8):328-337. [40] 侯森荣,林炯同,刘军,等.全髋及全膝关节置换后假体周围感染抗生素应用方案研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(35):5687-5693. [41] ZHAO WY, FANG QQ, WANG XF, et al. Chitosan-calcium alginate dressing promotes wound healing: A preliminary study. Wound Repair Regen. 2020;28(3):326-337. [42] YANG D, JONES KS. Effect of alginate on innate immune activation of macrophages. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;90(2):411-418. [43] WANG T, GU Q, ZHAO J, et al. Calcium alginate enhances wound healing by up-regulating the ratio of collagen types I/III in diabetic rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(6):6636-6645. [44] 张振坤,李喆,李亚,等.海藻酸盐基水凝胶/敷料在创面愈合中的应用: 持续、动态与顺序释放[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(4):638-643. [45] ROTHFUSZ CA, EMARA AK, MCLAUGHLIN JP, et al. Wound Dressings for Hip and Knee Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Narrative Review. JBJS Rev. 2021;9(7). doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.20.00301. [46] SCHWARTZ J, GOSS S, FACCHIN F, et al. A prospective two-armed trial assessing the efficacy and performance of a silver dressing used postoperatively on high-risk, clean surgical wounds. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2014;60(4):30-40. [47] 胡晓慧,顾蓥璇,黄林峰,等.亲水性纤维含银敷料改善全髋、膝关节置换术后伤口恢复效果的Meta分析[J].护理研究,2021,35(5):802-807. |
| [1] | Min Meipeng, Wu Jin, URBA RAFI, Zhang Wenjie, Gao Jia, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Fan Lei. Role and significance of artificial intelligence preoperative planning in total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1372-1377. |
| [2] | Shan Jiaxin, Zhang Yilong, Wu Hongtao, Zhang Jiayuan, Li Anan, Liu Wengang, Xu Xuemeng, Zhao Chuanxi. Changes in muscle strength and pain in patients receiving Jianpi Yiqi Huoxue Formula after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1378-1382. |
| [3] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [4] | Li Xiaoqiang, Chen Wei, Li Mingyue, Shan Tianchi, Shen Wen. Value of preoperative quantitative ultrasound analysis of quadriceps femoris in predicting chronic post-surgical pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1388-1393. |
| [5] | Zhong Jun, Wang Wen. Network meta-analysis of different anatomical repair strategies to improve chronic lateral ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1470-1476. |
| [6] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [7] | Wang Tihui, Wang Xu, Wu Jinqing, Chen Jiliang, Wang Xiaolu, Miao Juan. Application of three-dimensional simulated osteotomy of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 905-910. |
| [8] | Chen Zan, Lei Fei, Ye Fei, Zhou Qingzhong, Yuan Hao, Zheng Lipeng, Zha Xian, Feng Daxiong. Relationship between drainage time and early efficacy after short-segment lumbar fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 927-933. |
| [9] | Yang Yifeng, Huang Jian, Ye Nan, Wang Lin. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 955-960. |
| [10] | Zhang Zeyi, Yang Yimin, Li Wenyan, Zhang Meizhen. Effect of foot progression angle on lower extremity kinetics of knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 968-975. |
| [11] | Hu Zhixing, Li Qun, Yang Chao, Wang Xiaoxiao, Fang Luochangting, Hou Wuqiong, Lin Na, Chen Weiheng, Liu Chunfang, Lin Ya. Network meta-analysis of the modeling effects of different factors on rabbit models of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 976-984. |
| [12] | Yu Zhaoyu, Tan Lixin, Sun Kai, Lu Yao, Li Yong. Meta-analysis of cement-augmented pedicle screw for thoracolumbar degenerative diseases with osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 813-820. |
| [13] | Zhang Ya, Mu Qiuju, Wang Zilin, Liu Hongjie, Zhu Lili. Hydrogel loaded with platelet-rich plasma promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 690-696. |
| [14] | Xing Hao, Meng Qingfeng, Chang Zhengqi. Mechanism of negative pressure wound therapy in the auxiliary treatment of bone and soft tissue infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 621-626. |
| [15] | Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Alimujiang·Yusufu, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Maimaitimin·Abulimiti, Tuerhongjiang·Abudurexiti. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of terlipatide and bisphosphate in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 639-645. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||