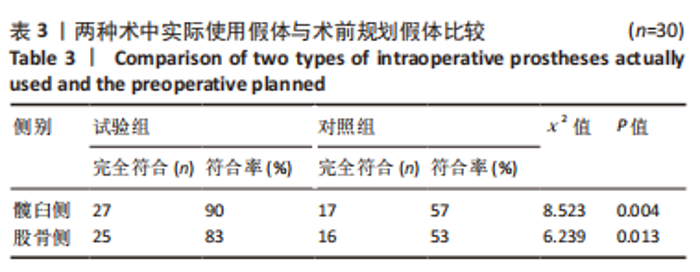
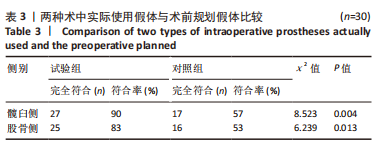
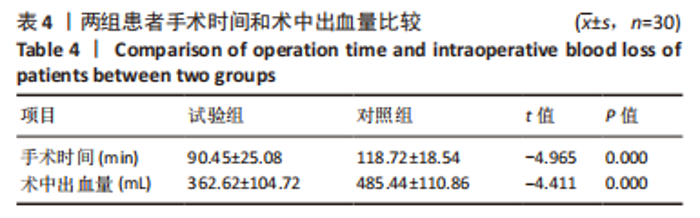
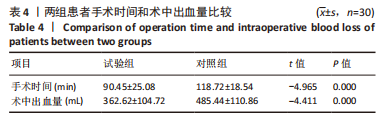
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (9): 1372-1377.doi: 10.12307/2023.798
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and significance of artificial intelligence preoperative planning in total hip arthroplasty
Min Meipeng, Wu Jin, URBA RAFI, Zhang Wenjie, Gao Jia, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Fan Lei
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210011, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-23Accepted:2023-01-04Online:2024-03-28Published:2023-07-25 -
Contact:Fan Lei, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210011, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Min Meipeng, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210011, Jiangsu Province, China Wu Jin, Associate chief nurse, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210011, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Geriatric Health Research Project of Jiangsu Health Commission in 2022, No. LKM2022008 (to FL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Min Meipeng, Wu Jin, URBA RAFI, Zhang Wenjie, Gao Jia, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Fan Lei. Role and significance of artificial intelligence preoperative planning in total hip arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1372-1377.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] 张英泽. 临床创伤骨科流行病学[M].3版. 北京:人民卫生出版社, 2018:703. [2] ZHANG S, CHEN JY, PANG HN, et al. Development and internal validation of machine learning algorithms to predict patient satisfaction after total hip arthroplasty. Arthroplasty. 2021;3(1):33. [3] SHAH AA, DEVANA SK, LEE C, et al. Development of a Novel, Potentially Universal Machine Learning Algorithm for Prediction of Complications After Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(5):1655-1662.e1. [4] TSENG TW, CHEN YP, YEH YC, et al. Automatic prosthetic-parameter estimation from anteroposterior pelvic radiographs after total hip arthroplasty using deep learning-based keypoint detection. Int J Med Robot. 2022;18(4):e2394. [5] LAZIC I, HINTERWIMMER F, LANGER S, et al. Prediction of Complications and Surgery Duration in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Machine Learning: The Necessity of Modified Algorithms and Specific Data. J Clin Med. 2022;11(8):2147. [6] KARNUTA JM, MURPHY MP, LUU BC, et al. Artificial Intelligence for Automated Implant Identification in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Multicenter External Validation Study Exceeding Two Million Plain Radiographs. J Arthroplasty. 2022;S0883-5403(22):272-278. [7] 栗智. AI计算机辅助全髋关节置换术前规划与假体型号选择的研究[D]. 大连:大连医科大学,2021. [8] MURPHY M, KILLEN C, BURNHAM R, et al. Artificial intelligence accurately identifies total hip arthroplasty implants: a tool for revision surgery. Hip Int. 2022;32(6):766-770. [9] BORJALI A, CHEN AF, BEDAIR HS, et al. Comparing the performance of a deep convolutional neural network with orthopedic surgeons on the identification of total hip prosthesis design from plain radiographs. Med Phys. 2021;48(5):2327-2336. [10] KARNUTA JM, HAEBERLE HS, LUU BC, et al. Artificial Intelligence to Identify Arthroplasty Implants From Radiographs of the Hip. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(7S):S290-S294.e1. [11] SINGH JA, YU S, CHEN L, et al. Rates of Total Joint Replacement in the United States: Future Projections to 2020–2040 Using the National Inpatient Sample. J Rheumatol. 2019;46(9):1134-1140. [12] ROUZROKH P, WYLES CC, KURIAN SJ, et al. Deep Learning for Radiographic Measurement of Femoral Component Subsidence Following Total Hip Arthroplasty.Radiol Artif Intell. 2022;4(3):e210206. [13] WEI J, LI D, SING DC, et al. Can images crowdsourced from the internet be used to train generalizable joint dislocation deep learning algorithms? Skeletal radiology. 2022;51(11):2121-2128. [14] WEI J, LI D, SING DC, et al. Detecting total hip arthroplasty dislocations using deep learning: clinical and Internet validation. Emerg Radiol. 2022;29(5):801-808. [15] 方闰, 宁仁德, 吴世桐, 等. 全髋关节置换术后早期Corail股骨柄下沉相关因素分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(6): 595-597. [16] ROWAN FE, BENJAMIN B, PIETRAK JR, et al. Prevention of Dislocation After Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(5):1316-1324. [17] DING X, ZHANG B, LI W, et al. Value of preoperative three-dimensional planning software (AI-HIP) in primary total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective study. J Int Med Res. 2021;49(11): 3000605211058874. [18] HEVESI M, WYLES CC, ROUZROKH P, et al. Redefining the 3D Topography of the Acetabular Safe Zone: A Multivariable Study Evaluating Prosthetic Hip Stability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104(3):239-245. [19] 徐征宇, 杜俊炜, 姜瑶, 等. 三维数字规划和二维胶片模板测量辅助全髋关节置换的效果比较[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2021, 18(2):17-22. [20] 翁文杰, 王锋, 张海林, 等. 全髋关节置换术后双下肢不等长对功能和满意度影响的研究[C]. 上海:股骨头坏死修复与重建国际研讨会暨辉瑞骨科镇痛高峰论坛论文集,2010:77-79. [21] IWAKIRI K, OHTA Y, FUJII T, et al. Changes in patient-perceived leg length discrepancy following total hip arthroplasty. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021;31(7):1355-1361. [22] XIA T, LIU X, LIU J, et al.Artificial intelligence assisted total hip arthroplasty for patients with Crowe type Ⅳ developmental dysplasia of the hip.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;35(10): 1265-1272. [23] GALEA VP, INGELSRUD LH, FLORISSI I, et al. Patient-acceptable symptom state for the Oxford Hip Score and Forgotten Joint Score at 3 months, 1 year, and 2 years following total hip arthroplasty: a registry-based study of 597 cases. Acta Orthop. 2020;91(4):372-377. [24] DAMMERER D, KEILER A, HERRNEGGER S, et al.Accuracy of digital templating of uncemented total hip arthroplasty at a certified arthroplasty center: a retrospective comparative study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;142(10):2471-2480. [25] HUO J, HUANG G, HAN D, et al. Value of 3D preoperative planning for primary total hip arthroplasty based on artificial intelligence technology. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):156. [26] HOLLIDAY M, STEWARD A. Pre-operative templating for total hip arthroplasty: How does radiographic technique and calibration marker placement affect image magnification? J Med Radiat Sci. 2021;68(3): 228-236. [27] 丁冉, 王淇, 刘烨,等. 人工智能三维术前规划在全髋关节置换术中的应用和准确性分析[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2022,19(2): 33-38. [28] AMENABAR T, MARIMUTHU K, HAWDON G, et al. Total hip arthroplasty using a short-stem prosthesis: restoration of hip anatomy. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2015;23(1):90-94. [29] CHEN X, LIU X, WANG Y, et al. Development and Validation of an Artificial Intelligence Preoperative Planning System for Total Hip Arthroplasty. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:841202. [30] 吴东, 刘星宇, 张逸凌, 等. 人工智能辅助全髋关节置换术三维规划系统的研发及临床应用研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020, 34(9):1077-1084. |
| [1] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [2] | Wang Tihui, Wang Xu, Wu Jinqing, Chen Jiliang, Wang Xiaolu, Miao Juan. Application of three-dimensional simulated osteotomy of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 905-910. |
| [3] | Ke Yuqi, Chen Changjian, Wu Hao, Zheng Lianjie. Comparison of 12-month follow-up results of primary total hip arthroplasty between modified direct anterior approach and direct anterior approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1377-1382. |
| [4] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [5] | Sun Jiangwei, Wang Junxiang, Baibujiafu·Yellisi, Dai Huijuan, Nijati·Turson. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in different smooth collar implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1004-1011. |
| [6] | Shi Yehong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Early thrombosis and prevention of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [7] | Wei Bo, Yao Qingqiang, Tang Cheng, Li Xuxiang, Xu Yan, Wang Liming. Advantage of medial pivot prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty via medial subvastus approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 552-557. |
| [8] | Xu Xiangjun, Wang Chao, Song Qunshan, Li Bingyan, Zhang Jichao, Wang Guodong, Dong Yuefu. Optimal angle for prosthesis implantation in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 612-618. |
| [9] | Chai Hao, Yang Deyong, Zhang Lei, Shu Li. 3D printing personalized osteotomy guide technology versus conventional total knee arthroplasty on the accuracy of lower limb force alignment: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 646-654. |
| [10] | Yan Ruizhong, Li Jiahui, Lin Shuzhong, Wu Xiaogang, Guo Zhijian, Liu Wenqi, Liu Qiang. Effect of pelvic tilt on the stress at the acetabular side in standing position after total hip arthroplasty: finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5795-5800. |
| [11] | Guo Zhuotao, Zhang Kai, Zha Guochun, Guo Kaijin. A matched controlled trial of lumbar fusion effect on mid-term outcomes after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5801-5805. |
| [12] | Ma Hui, Jia Xiangyuan, Yang Haotian, Yuan Lin, Li Yafeng, Zhao Xueqian, Jia Yusong. Total disc replacement for cervical spondylosis with sympathetic symptoms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5818-5822. |
| [13] | Li Qizhe, Kong Yao, Fan Jiannan, Wu Yeting, Yang Hua, Xiao Yinlong, Sun Hong. Measurement and clinical significance of acetabular parameters in the Guizhou population [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5856-5863. |
| [14] | Li Haoran, Huang Jian. Application of finite element analysis in artificial knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5058-5063. |
| [15] | You Aijia, Li Wenjie, Zhou Junli, Li Chun. Systematic evaluation of six dressings on wound safety following total hip and knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 486-492. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||