Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (36): 5856-5863.doi: 10.12307/2023.776
Previous Articles Next Articles
Measurement and clinical significance of acetabular parameters in the Guizhou population
Li Qizhe1, Kong Yao2, Fan Jiannan1, Wu Yeting3, Yang Hua1, Xiao Yinlong1, Sun Hong1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, 3Department of Infectious Disease, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Third Department of Orthopedics, Taihe Hospital, Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2022-10-18Accepted:2022-12-14Online:2023-12-28Published:2023-03-25 -
Contact:Sun Hong, Doctoral candidate, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Li Qizhe, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China Kong Yao, Master, Attending physician, Third Department of Orthopedics, Taihe Hospital, Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Fund of Guizhou Provincial Health Commission, Nos. gzwjkj2020-1-120 (to SH), gzwjkj2021-074 (to WYT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Qizhe, Kong Yao, Fan Jiannan, Wu Yeting, Yang Hua, Xiao Yinlong, Sun Hong. Measurement and clinical significance of acetabular parameters in the Guizhou population[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5856-5863.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

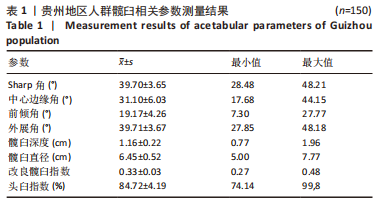
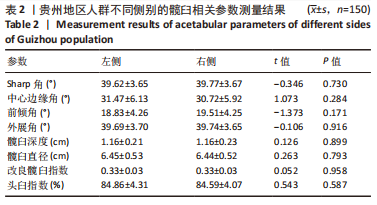
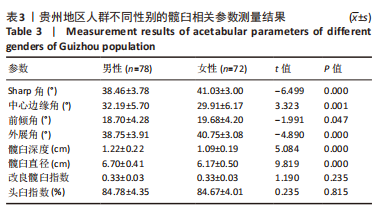
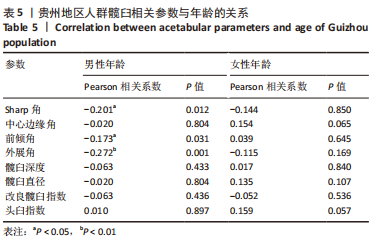
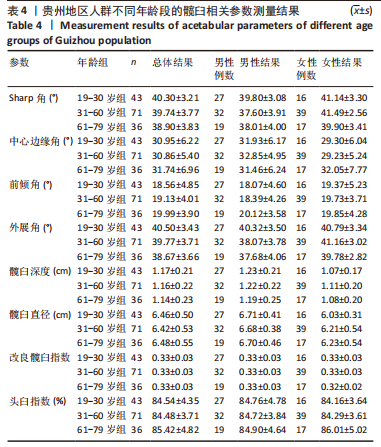
2.2 不同年龄、不同性别髋臼参数比较 贵州成年人不同年龄、不同性别的髋臼角度参数结果如表4所示,此次研究为了更好地分析髋臼相关参数的特征,将测量的参数按年龄特征分为3组的基础上,对各项参数分为不同年龄组、不同性别组进行比较。其中在不同年龄组间髋臼参数比较中,男性的Sharp角(P=0.040)及外展角(P=0.040)有统计学差异,女性的Sharp角(P=0.034)有统计学差异。在各年龄组内男女不同性别比较中发现19-30岁组中的髋臼深度(P=0.000)、髋臼直径(P=0.000)有统计学差异,31-60岁组中的Sharp角(P=0.000)、中心边缘角(P=0.000)、前倾角(P=0.048)、外展角(P=0.000)、髋臼深度(P=0.002)、髋臼直径(P=0.000)有统计学差异,61-79岁组中的髋臼直径(P=0.000)有统计学差异。进一步分析年龄与髋臼影像学相关参数的相关性见表5,男性的Sharp角、前倾角、外展角与年龄相关(P < 0.05),且都与年龄呈负相关;女性的髋臼影像学相关参数与年龄未见明显相关性。"

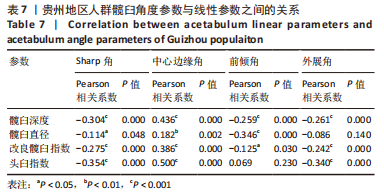
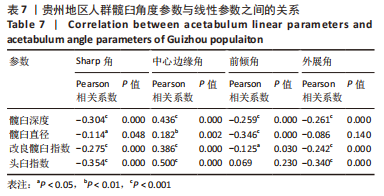
2.3 髋臼参数之间相关性分析 贵州成年人髋臼线性参数之间的相关性分析如表6,髋臼深度与髋臼直径、AAI、AHI存在正相关性(Pearson系数均为正,P < 0.05),AAI与AHI存在正相关性(Pearson系数=0.239,P < 0.05)。髋臼角度参数与线性参数的相关性分析如表7,其中Sharp角与髋臼深度、髋臼直径、AAI、AHI存在负相关性(Pearson系数均为负,P < 0.05),而中心边缘角与髋臼深度、髋臼、AAI、AHI存在正相关性(Pearson系数均为正,P < 0.05);前倾角与髋臼深度、髋臼直径、AAI存在负相关性(Pearson系数均为负,P < 0.05),外展角与髋臼深度、AAI、AHI存在负相关性(Pearson系数均为负,P < 0.05)。"

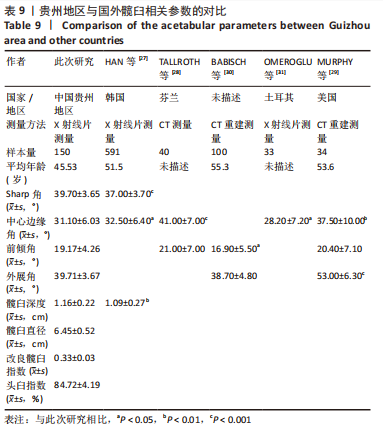
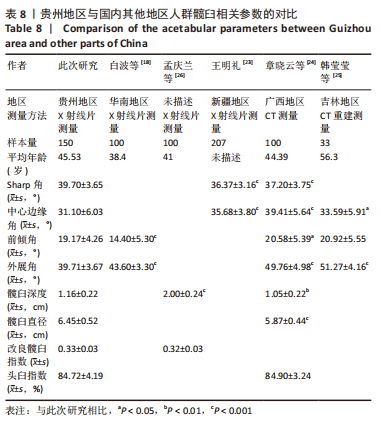
2.4 贵州地区人群与国内外其他地区人群的髋臼相关参数对比 贵州地区人群与国内部分地区人群髋臼影像学参数对比见表8。国内其他地区的X射线片及CT测量的成年人髋臼相关参数结果与此次研究所得数据均有不同。其中Sharp角、中心边缘角与王明礼[23]测量的新疆地区及章晓云等[24]测量的广西地区的结果差异较大,前倾角与白波等[18]测量的华南地区的结果差异较大,外展角与白波等[18]测量的华南地区、章晓云测量的广西地区、韩莹莹等[25]测量的吉林地区结果差异较大,髋臼深度与孟庆兰等[26]测量的结果差异较大,髋臼直径与章晓云测量的广西地区结果差异较大,AAI、AHI与上述学者测量地区的结果无明显差异。"
| [1] QUICKE JG, CONAGHAN PG, CORP N, et al. Osteoarthritis year in review 2021: epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022; 30(2):196-206. [2] 金进宝,肖德明.中国正常成人髋关节解剖参数研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2013,34(6):418-419,423. [3] 朱诗白,张啸天,陈曦,等.股骨头坏死的保髋治疗[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2020,14(6):741-746. [4] ZHOU M, WANG H, ZENG X, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2019;394(10204):1145-1158. [5] 陈俊文,钟昌恒,江宜松,等.发育性髋关节发育不良早期诊断的研究进展[J].中国医药,2020,15(12):1963-1966. [6] HARSANYI S, ZAMBORSKY R, KRAJCIOVA L, et al. Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Review of Etiopathogenesis, Risk Factors, and Genetic Aspects. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020;56(4):153. [7] Paton RW. Screening in Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH). Surgeon. 2017;15(5):290-296. [8] 刘君艳,潘诗农.儿童发育性髋关节发育不良解剖学改变与影像学表现[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(30):4875-4881. [9] GADEMAN MG, HOFSTEDE SN, VLIET VLIELAND TP, et al. Indication criteria for total hip or knee arthroplasty in osteoarthritis: a state-of-the-science overview. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):463. [10] VARACALLO M, LUO TD, JOHANSON NA. Total Hip Arthroplasty Techniques. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2022. [11] 严亮,夏军,黄钢勇,等.成人髋关节发育不良患者股骨近端的解剖形态学特征[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(9):941-947. [12] RONEN D, EVYATAR S, ORNIT C, et al. Acetabular cup orientation and postoperative leg length discrepancy in patients undergoing elective total hip arthroplasty via a direct anterior and anterolateral approaches. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2018;19(1):188. [13] SEAGRAVE K G, TROELSEN A, MALCHAU H, et al. Acetabular cup position and risk of dislocation in primary total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review of the literature. Acta Orthopaedica. 2017;88(1):10-17. [14] D’LIMA DD, URQUHART AG, BUEHLER KO, et al. The effect of the orientation of the acetabular and femoral components on the range of motion of the hip at different head-neck ratios. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(3):315-321. [15] GURNEY B, MERMIER C, ROBERGS R, et al. Effects of limb-length discrepancy on gait economy and lower-extremity muscle activity in older adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83(6):907-915. [16] SCULCO PK, COTTINO U, ABDEL MP, et al. Avoiding Hip Instability and Limb Length Discrepancy After Total Hip Arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2016;47(2):327-334. [17] 许杰,马若凡,丁悦,等.全髋置换术中臼杯置放角度对关节屈伸活动安全性的影响[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2007,25(4):453-457. [18] 白波,董伟强.中国华南地区髋关节的测量参数及临床意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2004,22(6):592-595. [19] 石永言. 2000余例正常国人骨盆正位片常用指标的测量与观察[D]. 沈阳:中国医科大学,2010. [20] 单涛, 刘芙蓉, 王子轩. 与关节置换相关的国人髋关节结构测量[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(13):2497-2500. [21] 石永言,刘天婧,赵群,等.中国人髋关节髋臼指数和Sharp角正常值的测量[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,30(8):748-753. [22] MCLAREN RH. Prosthetic hip angulation. Radiology. 1973;107(3): 705-706. [23] 王明礼. 新疆哈汉族髋CEA、Sharp值测量比较及临床意义[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2014. [24] 章晓云, 陈跃平, 曹桢斌, 等. 广西地区壮族人群正常髋关节形态学研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(11):1351-1356. [25] 韩莹莹, 肖成双, 杨麒巍, 等. CT三维重建下髋臼形态的测量及其意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版),2011,37(6):1136-1140. [26] 孟庆兰,姜瑞涛. 成人髋臼X线测量及其临床意义[J]. 青岛医药卫生,1999(6):455. [27] HAN CD, YOO JH, LEE WS, et al. Radiographic parameters of acetabulum for dysplasia in Korean adults. Yonsei Med J. 1998;39(5):404-408. [28] TALLROTH K, LEPISTO J. Computed tomography measurement of acetabular dimensions: normal values for correction of dysplasia. Acta Orthop. 2006;77(4):598-602. [29] MURPHY SB, KIJEWSKI PK, MILLIS MB, et al. Acetabular dysplasia in the adolescent and young adult. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;(261):214-223. [30] BABISCH JW, LAYHER F, AMIOT LP. The rationale for tilt-adjusted acetabular cup navigation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(2):357-365. [31] OMEROGLU H, BIIMOGLU A, AGU H, et al. Measurement of center-edge angle in developmental dysplasia of the hip: a comparison of two methods in patients under 20years of age. Skeletal Radiol. 2002; 31(1):25-29. [32] WIBERG G. Shelf operation in congenital dysplasia of the acetabulum and in subluxation and dislocation of the hip J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1953;35-A(1):65-80. [33] KLAUE K, DURNIN CW, GANZ R. The acetabular rim syndrome. A clinical presentation of dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73(3):423-429. [34] YANG S, ZUSMAN N, LIEBERMAN E, et al. Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. Pediatrics. 2019;143(1):e20181147. [35] KAHLENBERG CA, NWACHUKWU BU, SCHAIRER WW, et al. Patient Satisfaction Reporting After Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. Orthopedics. 2017;40(3):e400-e404. [36] 赵建军, 张艳艳. 成人髋臼发育不良的诊断与治疗[J]. 中国医药指南,2012,10(10):449-451. [37] 吴尽言,陈晓东.青少年及成人发育性髋关节发育不良保髋治疗最新研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(12):1513-1518. [38] ZHANG S, DOUDOULAKIS KJ, KHURWAL A, et al. Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2020;81(7):1-8. [39] 杨建松. 成人髋臼发育不良的临床影像学诊断分析[J]. 中国社区医师,2014(14):95-95,97. [40] ELLSWORTH BK, SINK EL, DOYLE SM. Adolescent hip dysplasia: what are the symptoms and how to diagnose it. Curr Opinion Pediatr. 2021; 33(1):65-73. [41] TÖNNIS D. Normal values of the hip joint for the evaluation of X-rays in children and adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;119(119):39-47. [42] 张洋, 王健, 李郅涵, 等. 与关节置换相关的华南地区健康成人髋关节形态测量[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(13):1328-1333. [43] OMEROGLU H, BICIMOGLU A, AGUS H, et al. Measurement of center-edge angle in developmental dysplasia of the hip: a comparison of two methods in patients under 20 years of age. Skeletal Radiol. 2002; 31(1):25-29. [44] SHARP IK. Acetabular dysplasia: The acetabular angle. J Bone Joint Surg. 1961;43(2):268-272. [45] 严亮,王彭,汤春平,等. 发育性髋关节发育不良髋臼旋转角对髋臼角度的影响研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2017,31(6):647-652. [46] THIEME WT, THIERSCH JB. Translation: Hilgenreiner on Congenital Hip Dislocation. J Pediatric Orthop. 1986;6(2):202-214. [47] 李晓光, 张明. 实用骨与关节X线测量[M]. 济南:山东科学技术出版社,1996. [48] 王滋润, 王跃, 吕波, 等. 265例发育性髋关节脱位治疗分析[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2013,19(12):1070-1074. [49] 邓方,陈琦. 影响全髋关节置换术患者并发髋关节脱位的多因素分析[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2020,41(18):2265-2266. [50] 张纪,郭卫,周一新. 髋关节置换术后失败原因分析[J]. 中国骨与关节外科,2012,5(3):217-219. [51] WIDMER KH, ZURFLUH B. Compliant positioning of total hip components for optimal range of motion. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(4): 815-821. [52] MURTHA PE, HAFEZ MA, JARAMAZ B, et al. Variations in acetabular anatomy with reference to total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(3):308-313. [53] 蔡碰德, 胡懿郃, 文霆, 等. 人工全髋关节置换术后髋臼假体初始不稳定原因分析及处理[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(12): 1418-1421. |
| [1] | Ke Yuqi, Chen Changjian, Wu Hao, Zheng Lianjie. Comparison of 12-month follow-up results of primary total hip arthroplasty between modified direct anterior approach and direct anterior approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Du Xueting, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Yanjun, Wang Mei, Chen Wubiao, Huang Wenhua. Application of compressed sensing technology in two-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of the ankle joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1396-1402. |
| [3] | Xue Ting, Zhang Xinri, Kong Xiaomei. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for pneumoconiosis using nanomaterials combined with multi-modal molecular imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1133-1140. |
| [4] | Li Xiaoyin, Yang Xiaoqing, Chen Shulian, Li Zhengchao, Wang Ziqi, Song Zhen, Zhu Daren, Chen Xuyi. Collagen/silk fibroin scaffold combined with neural stem cells in the treatment of traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 890-896. |
| [5] | Liu Guangluan, Guo Zonglei, Ge Jin, Huang Dong, Wang Yehua. Anatomic risk factors for medial meniscus posterior root tears combined with anterior cruciate ligament injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 663-668. |
| [6] | Pan Weimin, Wang Bing, Han Yabing, Li Ting, Song Jiaqi, Qin Huasheng, Liu Yang. Effects of blood flow restriction training on muscle strength, muscle mass and physical performance in older adults: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 805-812. |
| [7] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [8] | Liu Hao, Yang Hongsheng, Zeng Zhimou, Wang Liping, Yang Kunhai, Hu Yongrong, Qu Bo. Lumbar MRI vertebral bone quality score to evaluate the severity of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 606-611. |
| [9] | Huan Dawei, Yuan Zhaofeng, Dou Weiqiang, Xia Tianwei, Qiu Yue, Zhang Chao, Shen Jirong. Changes in microcirculatory perfusion of femoral head necrosis assessed by dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5864-5869. |
| [10] | Liu Ziwen, Yang Yuming, Xie Hongru, Zhang Zepei, Xu Haoxiang, Miao Jun. Relationship between the degeneration of paraspinal muscle and sagittal alignment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5891-5897. |
| [11] | Yan Ruizhong, Li Jiahui, Lin Shuzhong, Wu Xiaogang, Guo Zhijian, Liu Wenqi, Liu Qiang. Effect of pelvic tilt on the stress at the acetabular side in standing position after total hip arthroplasty: finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5795-5800. |
| [12] | Guo Zhuotao, Zhang Kai, Zha Guochun, Guo Kaijin. A matched controlled trial of lumbar fusion effect on mid-term outcomes after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5801-5805. |
| [13] | Yuan Haibo, Li Dongya, Pan Bin, Guan Kai, Chen Feng, Yuan Feng, Wu Jibin. Sagittal related factors of upper lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4984-4989. |
| [14] | Li Xiaojuan, Zhang Yuanzhi, Yang Xiaoguang, Gao Yang, Wu Qiong. Quantitative evaluation of bone structure changes in femoroacetabular impingement syndrome by magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 4965-4970. |
| [15] | Wu Tong, Yin Caiyun, Zhao Mingzhe, Zhu Yishen. Application of functional peptides for biomedical diagnosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 478-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||