Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (10): 1634-1640.doi: 10.12307/2023.306
Neuroprotective effect of stem cell transplantation on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: a systematic review
Li Ruixin1, 2, Su Gang3, Liu Jifei1, Xu Dan2, Gao Xin1, 2, Ma Tianfei1, 2, Zhang Zhenchang1
- 1Department of Neurology, Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China; 2Second Clinical Medical School, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 3Institute of Genetics, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2022-04-12Accepted:2022-06-02Online:2023-04-08Published:2022-09-09 -
Contact:Zhang Zhenchang, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Neurology, Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Li Ruixin, Master candidate, Department of Neurology, Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China; Second Clinical Medical School, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 31870335 (to ZZC); Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, No. 20JR5RA344 (to ZZC); Gansu Health Industry Research Program, No. GSWSKY2021-017 (to ZZC); “Cuiying Science and Technology Innovation” Project of Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, No. CY2021-MS-B01 (to ZZC); Cuiying Graduate Supervisor Training Program of Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, No. 201802 (to ZZC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Ruixin, Su Gang, Liu Jifei, Xu Dan, Gao Xin, Ma Tianfei, Zhang Zhenchang. Neuroprotective effect of stem cell transplantation on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: a systematic review[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1634-1640.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
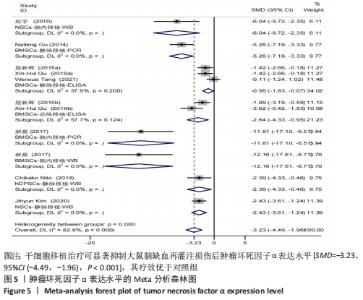
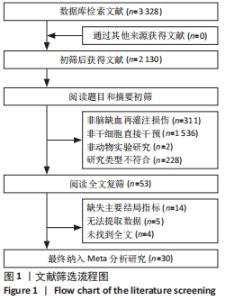
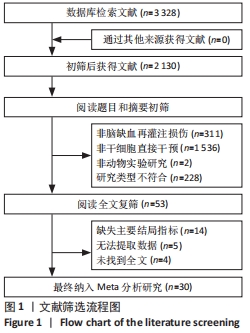
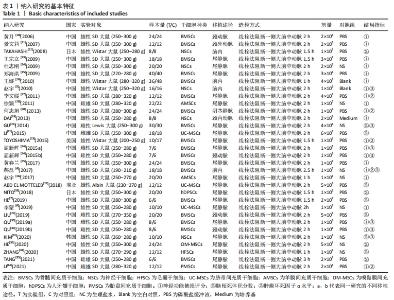
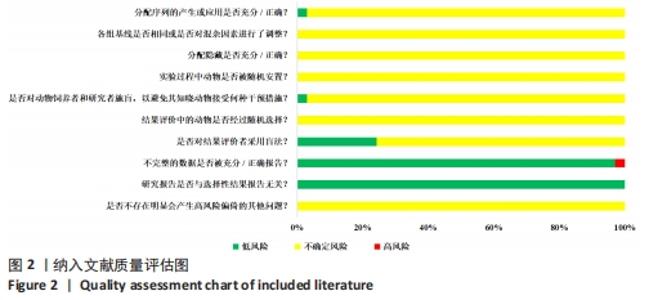
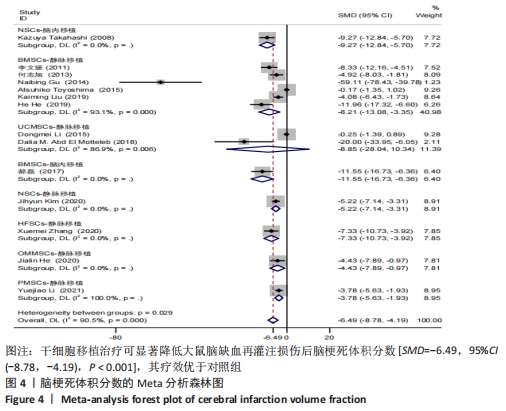
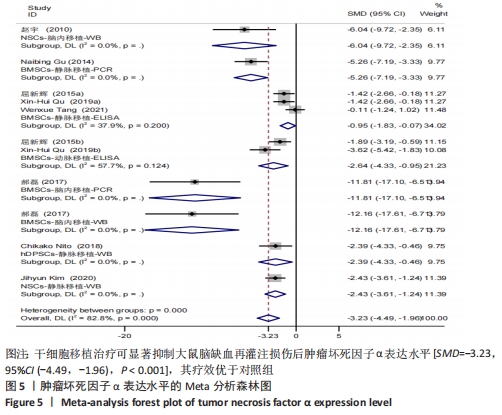
2.4.3 肿瘤坏死因子α表达水平的Meta分析结果 纳入有8篇文献报告了肿瘤坏死因子α表达水平[4-5,21,24,28,30,32,35],其中有1篇文献采用PCR技术,3篇文献采用Western blot技术,3篇文献采用ELISA技术,1篇文献同时采用PCR和Western blot技术。在采用ELISA技术中,其中又有2篇文献同时报告了2种干细胞移植途径,共11个研究。基于随机效应模型的Meta分析表明干细胞移植能够有效抑制肿瘤坏死因子α表达水平[SMD=-3.23,95%CI(-4.49,-1.96)]。有1个研究中肿瘤坏死因子α表达水平与对照组比较[35],差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。亚组分析结果显示骨髓间充质干细胞-静脉移植-ELISA组和骨髓间充质干细胞-动脉移植-ELISA组显著优于对照组,差异有显著性意义,且骨髓间充质干细胞-动脉移植的疗效优于骨髓间充质干细胞-静脉移植,见图5。"
| [1] HUANG Z, GUO L, HUANG L, et al. Baicalin-loaded macrophage-derived exosomes ameliorate ischemic brain injury via the antioxidative pathway. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;126:112123. [2] BARZEGAR M, KAUR G, GAVINS FNE, et al. Potential therapeutic roles of stem cells in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2019;37:101421. [3] 王晓平,倪京满.脑缺血再灌注损伤的研究及药物治疗进展[J].中国新药杂志, 2016,25(6):659-663,691. [4] 郝磊,刘磊,董岸莺,等.大鼠缺血再灌注损伤脑内骨髓间充质干细胞移植抑制TNF-α表达的上调促进TGFβ1表达的上调[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志, 2017,26(4):327-335. [5] 赵宇,谢鹏,朱晓峰,等.神经干细胞移植抑制缺血再灌注大鼠脑内星形胶质细胞的激活和炎症反应[J].第二军医大学学报,2010,31(6):678-681. [6] 李蒙,李传文,孙俊启,等.人脐血间充质干细胞移植对脑缺血再灌注大鼠SIRT1-P53通路的影响[J].安徽医科大学学报,2019,54(4):534-538. [7] HE H, ZENG Q, HUANG G, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation exerts neuroprotective effects following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Brain Res. 2019; 1707:124-132. [8] BONCORAGLIO GB, RANIERI M, BERSANO A, et al. Stem cell transplantation for ischemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019; 5(5):CD007231. [9] HOOIJMANS CR, INTHOUT J, RITSKES-HOITINGA M, et al. Meta-analyses of animal studies: an introduction of a valuable instrument to further improve healthcare. ILAR J. 2014;55(3):418-426. [10] 黄月,许予明,宋波,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对缺血再灌注大鼠脑神经细胞凋亡及Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表达的影响[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2006,41(5):862-864. [11] 景文莉,闫凤霞. 经颈动脉移植骨髓间充质干细胞治疗局灶性大鼠脑缺血损伤[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007, 11(24):4747-4751. [12] TAKAHASHI K, YASUHARA T, SHINGO T, et al. Embryonic neural stem cells transplanted in middle cerebral artery occlusion model of rats demonstrated potent therapeutic effects, compared to adult neural stem cells. Brain Res. 2008;1234:172-182. [13] 王宗立,范红杰,庞超健,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对缺血再灌注大鼠脑神经细胞凋亡及survivin、caspase-3蛋白表达的影响[J].中国医科大学学报,2009, 38(11):834-837. [14] 杜志刚,伊红丽,王艳玲,等.人脂肪神经干细胞移植对大鼠脑缺血后血管新生和细胞因子的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(10):1823-1828. [15] 郑海洪,冯念苹,梁松岚,等.骨髓间质干细胞移植对大鼠脑缺血再灌注凋亡蛋白Caspase-3的影响[J].中国比较医学杂志,2009,19(4):27-30,51,封3. [16] 王娜.骨髓间充质干细胞移植及生长相关蛋白43表达在脑修复中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(40): 7474-7478. [17] 李文嫒,王莹,孙平,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤Livin和Caspase-3表达的影响[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2011,20(6):554-558. [18] 徐颖,凌伟华,陆士奇,等.尾静脉移植羊膜间充质干细胞治疗大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(49):9198-9201. [19] DAI J, LI SQ, QIU YM, et al. Migration of neural stem cells to ischemic brain regions in ischemic stroke in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2013;552:124-128. [20] 何志旭,严虎,刘俊峰,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗缺血再灌注脑损伤[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志,2013,28(6):435-439. [21] GU N, RAO C, TIAN Y, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic effects of mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in rat brain with cerebral ischemia. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014;23(10):2598-2606. [22] LI D, ZHANG M, ZHANG Q, et al. Functional recovery after acute intravenous administration of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2015;4(2):98-104. [23] TOYOSHIMA A, YASUHARA T, KAMEDA M, et al. Intra-Arterial Transplantation of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Mounts Neuroprotective Effects in a Transient Ischemic Stroke Model in Rats: Analyses of Therapeutic Time Window and Its Mechanisms. PLoS One. 2015;10(6): e0127302. [24] 屈新辉,王万松,吴凌峰,等.动、静脉移植骨髓间充质干细胞治疗急性期缺血再灌注大鼠模型的比较[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(24):6965-6969. [25] 黄春兰,唐艳,汤永红.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对缺血再灌注脑组织miR-34a、miR-21表达的影响[J].实用医学杂志, 2017,33(23):3871-3875. [26] 赵宇.尾静脉移植羊膜间充质干细胞对缺血再灌注损伤后神经功能恢复的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,38(5):707-712. [27] ABD EL MOTTELEB DM, HUSSEIN S, HASAN MM, et al. Comparison between the effect of human Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells and levetiracetam on brain infarcts in rats. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(12):9790-9800. [28] NITO C, SOWA K, NAKAJIMA M, et al. Transplantation of human dental pulp stem cells ameliorates brain damage following acute cerebral ischemia. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:1005-1014. [29] LIU K, GUO L, ZHOU Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells transfer mitochondria into cerebral microvasculature and promote recovery from ischemic stroke. Microvasc Res. 2019;123:74-80. [30] QU XH, WANG WS, LIU SM, et al. A Study on Acute Ischemia-Reperfusion Models in Rats Treated by Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Grafting via Arteries and Veins. J Hard Tissue Biol. 2019;28(4):323-328. [31] HE J, LIU J, HUANG Y, et al. Olfactory Mucosa Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Via Golgi Apparatus Secretory Pathway Ca2+ -ATPase Isoform1. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020; 8:586541. [32] KIM J, SHIN K, CHA Y, et al. Neuroprotective effects of human neural stem cells over-expressing choline acetyltransferase in a middle cerebral artery occlusion model. J Chem Neuroanat. 2020;103:101730. [33] ZHANG X, TANG H, MAO S, et al. Transplanted hair follicle stem cells migrate to the penumbra and express neural markers in a rat model of cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):413. [34] LI Y, DONG Y, RAN Y, et al. Three-dimensional cultured mesenchymal stem cells enhance repair of ischemic stroke through inhibition of microglia. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):358. [35] TANG W, LV X, HUANG J, et al. Neuroprotective effect of stroke pretreated MSCs against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. World Neurosurg. 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.04.114. [36] 崔煦然,刘钊,张志斌,等.大鼠局灶性脑缺血模型评价方法间关联性分析[J].中国实验动物学报,2015,23(5):506-508,512. [37] ZHENG Y, HE R, WANG P, et al. Exosomes from LPS-stimulated macrophages induce neuroprotection and functional improvement after ischemic stroke by modulating microglial polarization. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(5):2037-2049. [38] SOWMITHRA S, JAIN NK, BHONDE R, et al. Recovery of Human Embryonic Stem Cells-Derived Neural Progenitors Exposed to Hypoxic-Ischemic-Reperfusion Injury by Indirect Exposure to Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through Phosphatidyl-inositol-3-Kinase Pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022;42(4):1167-1188. [39] Zhang Y, Yu S, Tuazon JP, et al. Neuroprotective effects of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells against cerebral ischemia are mediated in part by an anti-apoptotic mechanism. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(4):597-604. [40] TEO GS, ANKRUM JA, MARTINELLI R, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells transmigrate between and directly through tumor necrosis factor-α-activated endothelial cells via both leukocyte-like and novel mechanisms. Stem Cells. 2012;30(11):2472-2486. [41] STEINGEN C, BRENIG F, BAUMGARTNER L, et al. Characterization of key mechanisms in transmigration and invasion of mesenchymal stem cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;44(6):1072-1084. [42] VAHIDINIA Z, AZAMI TAMEH A, NEJATI M, et al. The protective effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of ischemic stroke via reducing the C-Jun N-terminal kinase expression. Pathol Res Pract. 2019;215(9):152519. [43] BOND AM, MING GL, SONG H. Adult Mammalian Neural Stem Cells and Neurogenesis: Five Decades Later. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17(4):385-395. [44] JIANG XC, XIANG JJ, WU HH, et al. Neural Stem Cells Transfected with Reactive Oxygen Species-Responsive Polyplexes for Effective Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Adv Mater. 2019;31(10):e1807591. [45] WANG G, WU HL, LIU YP, et al. Pre-clinical study of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for the treatment of traumatic brain injury: safety evaluation from immunogenic and oncogenic perspectives. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(2):354-361. [46] 张培培,刘慧纯,阎晓玲,等.脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠尾静脉移植脐带间充质干细胞的安全性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(14):2581-2584. [47] LIAU LL, LOOI QH, CHIA WC, et al. Treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:112. [48] SHIN DA, KIM JM, KIM HI, et al. Comparison of functional and histological outcomes after intralesional, intracisternal, and intravenous transplantation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2013;155(10):1943-1950. [49] TATOR CH. Review of treatment trials in human spinal cord injury: issues, difficulties, and recommendations. Neurosurgery. 2006; 59(5):957-982. [50] EL-FTESI S, CHANG EI, LONGAKER MT, et al. Aging and diabetes impair the neovascular potential of adipose-derived stromal cells. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009; 123(2):475-485. [51] DRUKKER M, BENVENISTY N. The immunogenicity of human embryonic stem-derived cells. Trends Biotechnol. 2004;22(3): 136-141. |
| [1] | Zhong Yizheng, Huang Peizhen, Cai Qunbin, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Dong Hang. Microstructural indexes that determine the trabecular bone maximum stress of micro-finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1313-1318. |
| [2] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Correlation of cervical sagittal force line parameters with degenerative segment and Pfirrmann classification in patients with cervical intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1319-1324. |
| [3] | Ke Yuqi, Chen Changjian, Wu Hao, Zheng Lianjie. Comparison of 12-month follow-up results of primary total hip arthroplasty between modified direct anterior approach and direct anterior approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1377-1382. |
| [4] | Zhang Lichuang, Gao Huali, Wang Jingchao, Lin Huijun, Wu Chonggui, Ma Yinghui, Huang Yunfei, Fang Xue, Zhai Weitao. Effect of tendon manipulation with equal emphasis on muscles and bones on accelerating the functional rehabilitation of quadriceps femoris after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1383-1389. |
| [5] | Du Xueting, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Yanjun, Wang Mei, Chen Wubiao, Huang Wenhua. Application of compressed sensing technology in two-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of the ankle joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1396-1402. |
| [6] | You Zhengqiu, Zhang Zhongzu, Wang Qunbo. Early symptomatic intervertebral disc pseudocysts after discectomy detected on MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1403-1409. |
| [7] | Li Chao, Zhang Peipei, Xu Mengting, Li Linlin, Ding Jiangtao, Liu Xihua, Bi Hongyan. Respiratory training improves morphological changes of the multifidus muscle in patients with chronic nonspecific lower back pain assessed by musculoskeletal ultrasound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1417-1421. |
| [8] | He Yinhao, Li Xiaosheng, Chen Hongwen, Chen Tiezhu. 3D printed porous tantalum metal in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: current status and application prospect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1455-1461. |
| [9] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [10] | Wang Yanjin, Zhou Yingjie, Chai Xubin, Zhuo Hanjie. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of 3D printed porous titanium alloy fusion cage in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1434-1440. |
| [11] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [12] | Wu Dongzhe, Gao Xiaolin, Li Chuangtao, Wang Hao. Constructing the prediction model of maximal oxygen uptake by back-propagation neural network based on the cardiorespiratory optimal point [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1224-1231. |
| [13] | Yang Jiujie, Li Zhi, Wang Shujie, Tian Ye, Zhao Wei. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of functional changes following durotomy with decompression for acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [14] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [15] | Bai Yulong, Li Zhonghai, Zhao Yantao, Xia Cencan, Shi Lei. History, current situation and prospect of tissue banks in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1306-1312. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||