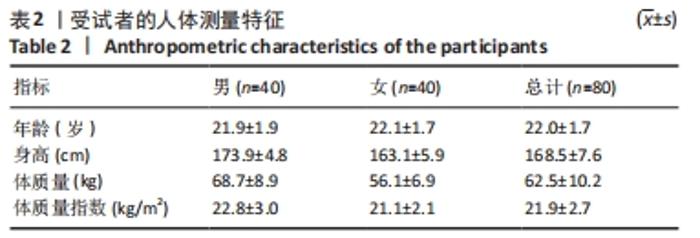
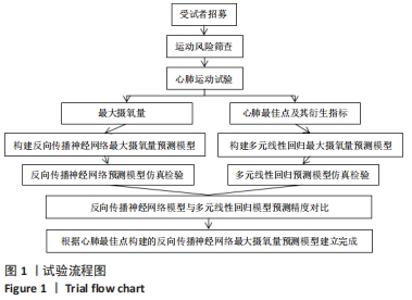
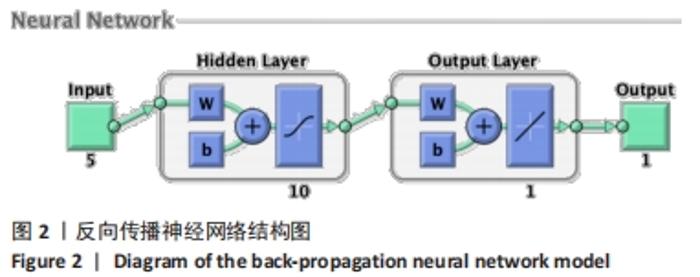
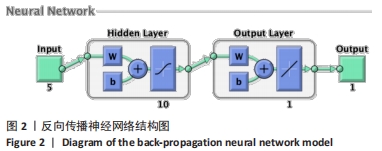
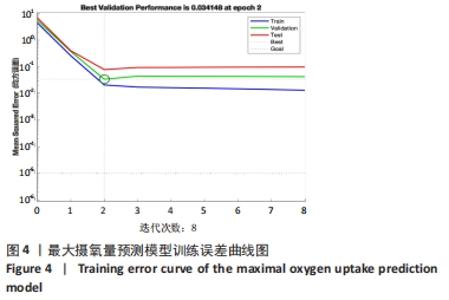
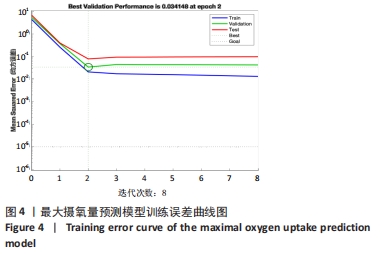
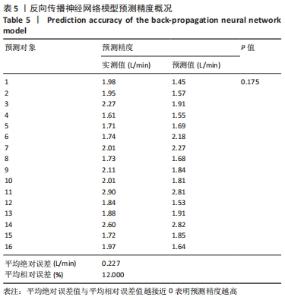
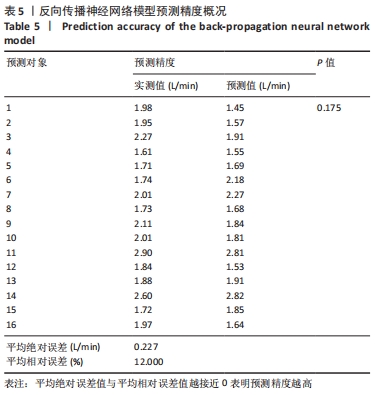
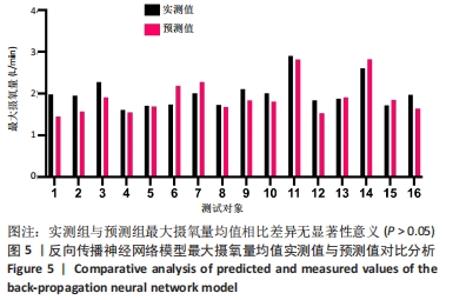
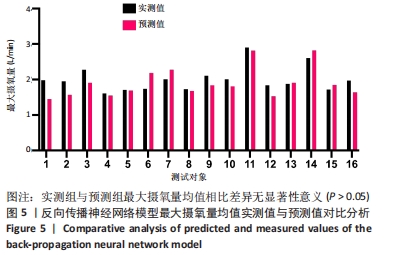
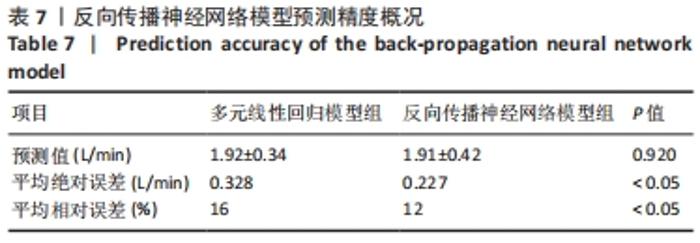
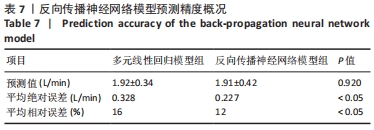
[1] 程宙明, 卢健, 牛俊茹, 等. 最大耗氧量与安静时心输出量和肺呼吸功能相关性研究——以非运动专业的青年女大学生为例[J]. 体育科学,2015,35(8):30-39.
[2] 赵安娜. 普通高校大学生最大摄氧量非运动在线测量方法的甄选研究[D].杭州:杭州师范大学,2020.
[3] 程宙明. 抗阻和有氧训练对大学生最大摄氧量的影响及其运动适应机制的研究[D]. 上海:华东师范大学,2017.
[4] 范超群, 徐凯, 聂明剑, 等. 心肺耐力的科学测评:心肺运动试验与6 min二级台阶试验的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(23): 3686-3691.
[5] MAHER JP, HEVEL DJ, REIFSTECK EJ, et al. Physical activity is positively associated with college students’ positive affect regardless of stressful life events during the COVID-19 pandemic. Psychol Sport Exerc. 2021; 52:101826.
[6] ARAÚJO CG, PINTO VL. Maximal heart rate in exercise tests on treadmill and in a cycloergometer of lower limbs. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2005;85(1):45-50.
[7] NEDER JA, STEIN R. A simplified strategy for the estimation of the exercise ventilatory thresholds. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006;38(5):1007-1013.
[8] YEH MP, GARDNER RM, ADAMS TD, et al. “Anaerobic threshold”: problems of determination and validation. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983;55(4):1178-1186.
[9] BALADY GJ, ARENA R, SIETSEMA K, et al. Clinician’s Guide to cardiopulmonary exercise testing in adults: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;122(2):191-225.
[10] RAMOS PS, RICARDO DR, ARAÚJO CG. Cardiorespiratory optimal point: a submaximal variable of the cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2012;99(5):988-996.
[11] LAUKKANEN JA. Is Cardiorespiratory Optimal Point Measured During the Maximal Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test a Relevant Indicator of Sports Performance? Int J Cardiovasc Sci. 2018;31(4):320-322.
[12] RAMOS PS, ARAÚJO CG. Cardiorespiratory optimal point during exercise testing as a predictor of all-cause mortality. Rev Port Cardiol. 2017;36(4):261-269.
[13] RAMOS PS, SARDINHA A, NARDI AE, et al. Cardiorespiratory optimal point: a submaximal exercise variable to assess panic disorder patients. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e104932.
[14] SILVA CGND SE, CASTRO CLB, FRANCA JOF, et al. Cardiorespiratory Optimal Point in Professional Soccer Players: A Novel Submaximal Variable During Exercise,2018.
[15] LAUKKANEN JA, SAVONEN K, HUPIN D, et al. Cardiorespiratory optimal point during exercise testing and sudden cardiac death: A prospective cohort study. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2021;68:12-18.
[16] LAUKKANEN JA, KUNUTSOR SK, ARAÚJO CG, et al. Cardiorespiratory optimal point during exercise testing is related to cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021;31(10):1949-1961.
[17] CHARITONIDIS K, KOUTLIANOS N, ANAGNOSTARAS K, et al. Combination of novel and traditional cardiorespiratory indices for the evaluation of adolescent volleyball players. Hippokratia. 2019;23(2):70-74.
[18] BUSCEMA M. Back propagation neural networks. Subst Use Misuse. 1998;33(2):233-270.
[19] WANG X, WANG K, DING J, et al. Predicting water quality during urbanization based on a causality-based input variable selection method modified back-propagation neural network. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021;28(1):960-973.
[20] 刘天舒. BP神经网络的改进研究及应用[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学, 2011.
[21] 石庆焱. 一个基于神经网络——Logistic回归的混合两阶段个人信用评分模型研究[J]. 统计研究,2005(5):45-49.
[22] 张晓瑞, 方创琳, 王振波, 等. 基于RBF神经网络的城市建成区面积预测研究——兼与BP神经网络和线性回归对比分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2013,22(6):691-697.
[23] 张景阳, 潘光友. 多元线性回归与BP神经网络预测模型对比与运用研究[J]. 昆明理工大学学报(自然科学版),2013,38(6):61-67.
[24] 杨慧君. 基于心功能、血液、体成分指标预测大学生最大摄氧量的研究[D].北京:国家体育总局体育科学研究所,2020.
[25] 戴敏, 黄亚楼. 基于数据挖掘的运动员体能测试数据分析[J]. 计算机工程与应用,2003(9):38-40+60.
[26] 郭辉, 刘韵婷, 孔振兴, 等. 基于BP神经网络的最大摄氧量预测方法研究[J]. 实验室科学,2020,23(5):44-48.
[27] ATS/ACCP Statement on cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167(2):211-177.
[28] CHRYSOHOOU C. Cardiopulmonary exercise test: more than a simple exercise test, but cautious how to interpret. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2021; 62(2):127-128.
[29] TRAN D. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing. Methods Mol Biol. 2018; 1735:285-295.
[30] GUAZZI M, BANDERA F, OZEMEK C, et al. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing: What Is its Value? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(13):1618-1636.
[31] AGOSTONI P, VIGNATI C, GENTILE P, et al. Reference Values for Peak Exercise Cardiac Output in Healthy Individuals. Chest. 2017;151(6): 1329-1337.
[32] KANG J, RATAMESS NA, FAIGENBAUM AD, et al. Use of Heart Rate Index to Predict Oxygen Uptake - A Validation Study. Int J Exerc Sci. 2020;13(7):1705-1717.
[33] 董莉, 唐缨红, 黄骏, 等. 青少年耐力运动员最大摄氧量与NICOM心排量的相关性分析[J]. 辽宁体育科技,2018,40(5):57-61.
[34] 石羽飞, 罗林, 陈伟. 有氧运动能力与人体VO_2max和躯干去脂软体重的Logistic回归模型 [J]. 当代体育科技,2015,5(26):1+3.
[35] 蔡秋, 王步标, 龚正伟. 12分钟跑与20米往返跑预测最大吸氧量的比较研究[J]. 体育学刊,1997,4(2):37-40.
[36] 李萍, 曾令可, 税安泽, 等. 基于MATLAB的BP神经网络预测系统的设计[J]. 计算机应用与软件,2008,25(4):149-150+184.
[37] 梁红红. 基于心功能、血液、体成分指标预测大学生无氧阈的研究[D].北京:国家体育总局体育科学研究所,2021.
[38] 李莉婕. 台阶试验评价大学生最大有氧能力方法的研究[D].北京:北京体育大学,2012.
[39] 王念辉, 洪平, 苏中军. 基于身高、体重及肺活量的大学一年级男生最大摄氧量推算方法研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(3):202-207.
[40] LI F, CHANG CH, HO CA, et al. The Determination of Step Frequency in 3-min Incremental Step-in-Place Tests for Predicting Maximal Oxygen Uptake from Heart Rate Response in Taiwanese Adults. Int J Environment Res Public Health. 2022;19(1):563.
[41] AANDSTAD A. Estimation of maximal oxygen uptake from the 3,000 m run in adult men and women. J Sports Sci. 2021;39(15):1746-1753.
[42] 米欢, 王正珍. 步行试验推测40-49岁人群最大摄氧量回归方程的研究[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2012,35(5):50-54.
[43] 郭辉, 孙景权, 张一民. 六分钟上下楼梯试验与摄氧量的相关性研究[J]. 成都体育学院学报,2016,42(3):14-18.
[44] 刘笑. 800米、1000米跑及20mSRT与最大摄氧量的相关性研究[D].上海:华东师范大学,2014.
[45] 李楠楠. 推测青少年最大摄氧量回归方程的研究[D].济南:山东体育学院,2017.
[46] 梁华伟, 原颜东, 薛红卫. 基于BP神经网络的体育赛事风险预警模型[J]. 统计与决策,2018,34(16):85-88.
[47] WANG L, QIU K, LI W. Sports Action Recognition Based on GB-BP Neural Network and Big Data Analysis. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021;2021: 1678123.
[48] 夏祥伟, 毛丽娟, 黄金玲, 等. 中国高校研究生体育锻炼与全面健康的相关性——基于BP神经网络的实证研究[J]. 全球教育展望, 2018,47(4):111-128.
[49] 梁美富, 曲淑华. 依据反向传播神经网络建模预测骨骼肌的最佳功率负荷[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(23):3641-3647.
[50] 张雷, 陈小平, 冯连世. 科技助力:新时代引领我国竞技体育高质量发展的主要驱动力[J]. 中国体育科技,2020,56(1):3-11.
|