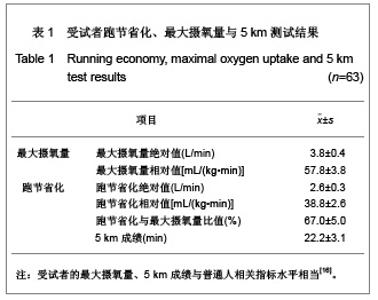
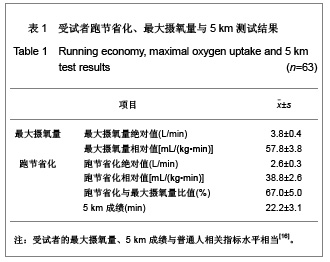
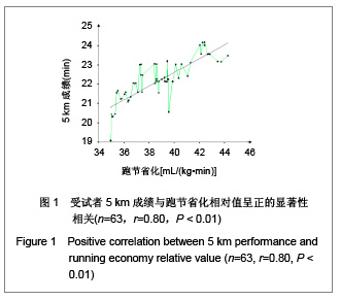
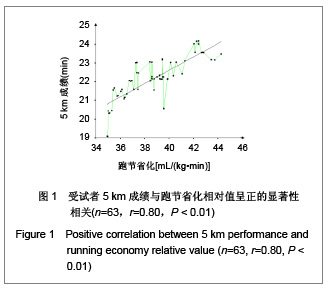
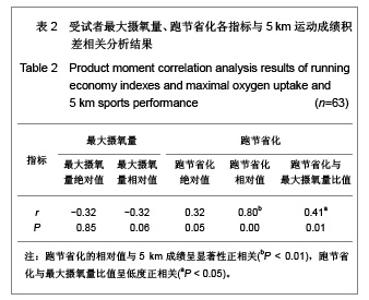
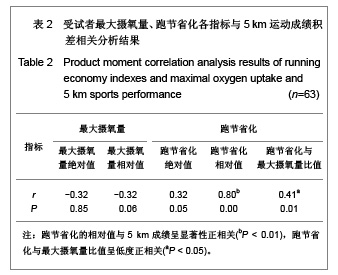
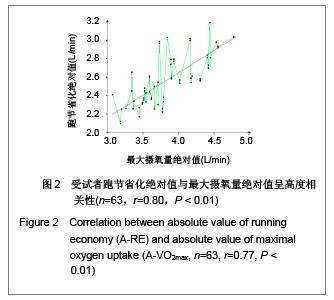
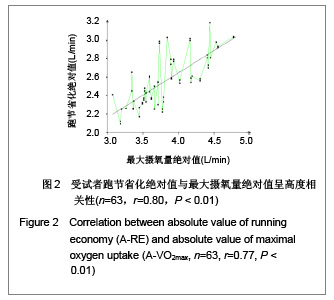
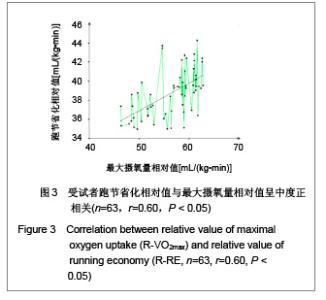
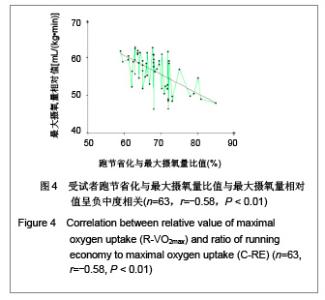
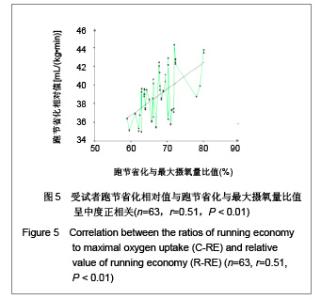
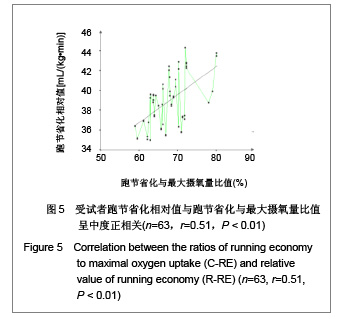
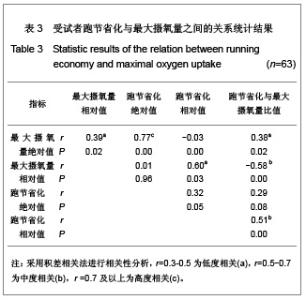
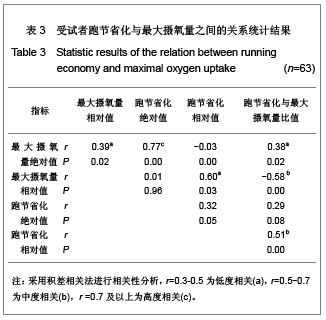
| [1] Wilber RL, Pitsiladis YP. Kenyan and Ethiopian distance runners: what makes them so good? Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2012;7(2):92-102.[2] Ziogas GG, Patras KN, Stergiou N, et al. Velocity at lactate threshold and running economy must also be considered along with maximal oxygen uptake when testing elite soccer players during preseason. J Strength Cond Res. 2011;25(2): 414-419.[3] Sjodin B, Svedenhag J. Applied physiology of marathon running. Sports Med. 1985;2(2):83-99.[4] Krahenbuhl GS, Williams TJ. Running economy: changes with age during childhood and adolescence. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1992;24(4):462-466.[5] Daniels J. Physiological characteristics of champion male athletes. Res Q. 1974;45(4):342-348.[6] di Prampero PE, Salvadego D, Fusi S, et al. A simple method for assessing the energy cost of running during incremental tests. J Appl Physiol. 2009;107(4):1068-1075.[7] Thomas DQ, Fernhall BO, Granat H. Changes in running economy during a 5-km run in trained men and women runners. JSCR. 1999;13(2):162-167.[8] Morgan DW, Baldini FD, Martin PE, et al. Ten kilometer performance and predicted velocity at VO2max among well-trained male runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1989; 21(1):78-83.[9] Beis LY, Polyviou T, Malkova D, et al. The effects of creatine and glycerol hyperhydration on running economy in well trained endurance runners. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2011; 8(1): 24.[10] Xi Y, Wang GJ, Wen L, et al. Zhongguo Yundong Yixue Zhazhi. 2007;(1):39-44. 席翼,王国军,文立,等.5000米跑耐力训练对新兵有氧耐力及左心室结构和功能的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2007,(1):39-44.[11] Ren ZB. Tiyu Kexue. 2010,30(1):86-96. 任占兵.影响跑步经济性的人体下肢肌肉做功研究[J].体育科学, 2010,30(1):86-96.[12] Xi Y, Zhang DB, Wang GJ, et al. Zhongguo Yundong Yixue Zazhi. 2008;27(1):15-19. 席翼,张得保,王国军,等.跑节省化评价有氧耐力及其训练效果实验研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2008,27(1):15-19.[13] Leng ZY, Yu LZ, Wang GJ, et al. 2008;24(1):47-49. 冷志勇,于林竹,王国军,等.跑节省化(RE)和最大摄氧量评价耐力训练效果的比较研究[J].山东体育学院学报,2008,24(1):47-49.[14] Conley D L, Krahenbuhl G S. Running economy and distance running performance of highly trained athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1980;12(5):357-360.[15] Zhang L. Wuhan Tiyu Xueyuan Xuebao. 1995;29(1):41245. 张立.一种简易监测运动强度和评定运动能力的方法RPE等级值[J].武汉体育学院学报,1995,29(1):41-45.[16] Quanguo Tiyu Yuanxiao Jiaocai Weiyuanhui. Beijing: People Sports Press. 2002. 全国体育院校教材委员会.运动生理学[M].北京:人民体育出版社, 2002.[17] Wang GJ, Xi Y, Wu YQ, et al. Zhongguo Yundong Yixue Zazhi. 2012;31(10):887-891. 王国军,席翼,武雅琼,等.我国18-23岁普通男性跑节省化测试跑速研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2012;31(10):887-891.[18] Fletcher JR, Esau SP, Macintosh BR. Economy of running: beyond the measurement of oxygen uptake. J Appl Physiol. 2009;107(6):1918-1922.[19] Chen TC, Nosaka K, Lin M J, et al. Changes in running economy at different intensities following downhill running. J Sports Sci. 2009;27(11):1137-1144.[20] Wang GJ, Yang Q, Wen H, et al. Shandong Tiyu Xueyuan Xuebao. 2007;23(5):62-65. 王国军,杨谦,温含,等.跑节省化(RE)实验方法及其影响因素的研究进展[J].山东体育学院学报,2007,23(5):62-65.[21] Morgan DW, Martin PE, Baldini FD, et al. Effects of a prolonged maximal run on running economy and running mechanics. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1990;22(6):834-840.[22] Paavolainen L, Hakkinen K, Hamalainen I, et al. Explosive-strength training improves 5-km running time by improving running economy and muscle power. J Appl Physiol. 1999;86(5):1527-1533.[23] Lucia A, Esteve-Lanao J, Olivan J, et al. Physiological characteristics of the best Eritrean runners-exceptional running economy. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2006;31(5): 530-540.[24] Bonacci J, Saunders PU, Alexander M, et al. Neuromuscular control and running economy is preserved in elite international triathletes after cycling. Sports Biomech. 2011; 10(1):59-71.[25] Szabo JA, Parr BB, Holt JA, et al. Effect of the E3 fitness grips on running economy. Int J Exere Sci. 2010;3(2):64-67.[26] Bragada A, Santos J, Maia A, et al. Longitudinal study in 3,000 m male runners: relationship between performance and selected physiological parameters. J Sports Sci Med. 2010; (9):439-444.[27] Green H, Ros B, Grant S, et al. Increases in submaximal cycling efficiency mediated by altitude acclimatization. J Appl Phycol. 2000;(89):1189-1197.[28] Ohnston R, Quinn T, Kerrtzer R, et al. Strength training in female distance runners:Impact on running economy. J Strength Cond Res. 1997;(11):224-229.[29] Marcinik E, Potts J, Schlabach G, et al. Effects of strength training on lactate threshold and endurance performance. Med Sci Sports Exere. 1991;(23):739-743.[30] Saunders PU, Telford RD, Pyne DB, et al. Improved running economy in elite runners after 20 days of simulated moderate- altitude exposure. J Appl Physiol. 2004;96(3): 931-937.[31] Larsen H. Kenyan dominance in distance running. Comb Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2003;(136):161-170.[32] Allor KM, Pivarnik JM, Sam LJ, et al. Treadmill economy in girls and women matched for height and weight. J Appl Physiol. 2000;89(2):512-516.[33] Krahenbuhl G, Morgan D, Pangrazi R. Longitudinal changes in distance-running performance of young males. Int J Sports Med. 1989;10(2):92-96.[34] Kloyiam S, Breen S, Jakeman P, et al. Soccer-specific endurance and running economy in soccer players with cerebral palsy. Adapt Phys Activ Q. 2011;28(4):354-367.[35] Morgan DW, Martin PE, Krahenbuhl GS. Factors affecting running economy. Sports Med. 1989;7(5):310-330.[36] Davies MJ, Mahar MT, Cunningham LN. Running economy: comparison of body mass adjustment methods. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1997;68(2):177-181.[37] Sjodin B, Svedenhag J. Oxygen uptake during running as related to body mass in circumpubertal boys: a longitudinal study. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1992;65(2):150-157.[38] Sawyer B, Blessinger J, Irving B, et al. Walking and running economy: inverse association with peak oxygen uptake. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(11):2122-2127.[39] Helgerud J, Storen O, Hoff J. Are there differences in running economy at different velocities for well-trained distance runners?. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010;108(6):1099-1105.[40] Li R, Jiang CM, Cai R, et al. Tiyu Kexue. 2012;32(6):81-84. 李然,江崇民,蔡睿,等.运动后恢复期心率对心功能的评价-台阶指数对不同年龄段人群心功能评价的局限性[J].体育科学,2012, 32(6):81-84.[41] Moore IS, Jones AM, Dixon S. Mechanisms for improved running economy in beginner runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012;44(8):1125-1129. |