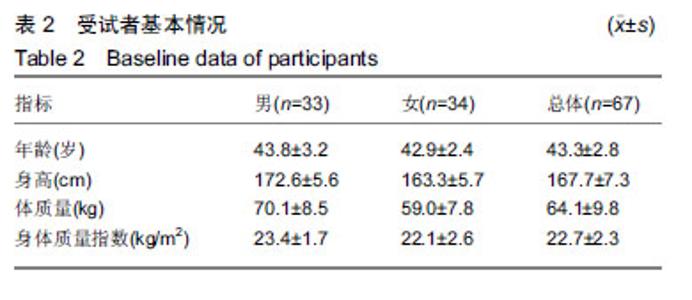
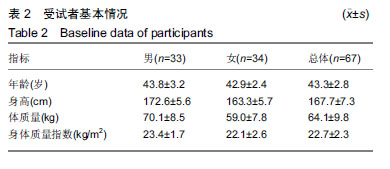
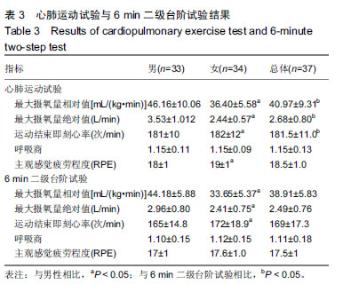
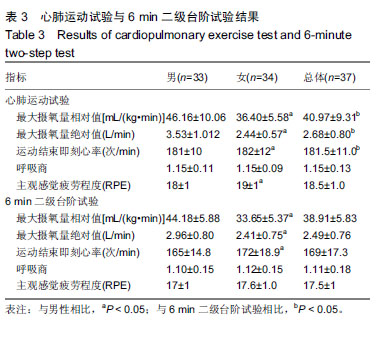
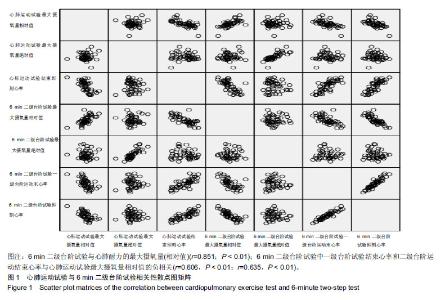
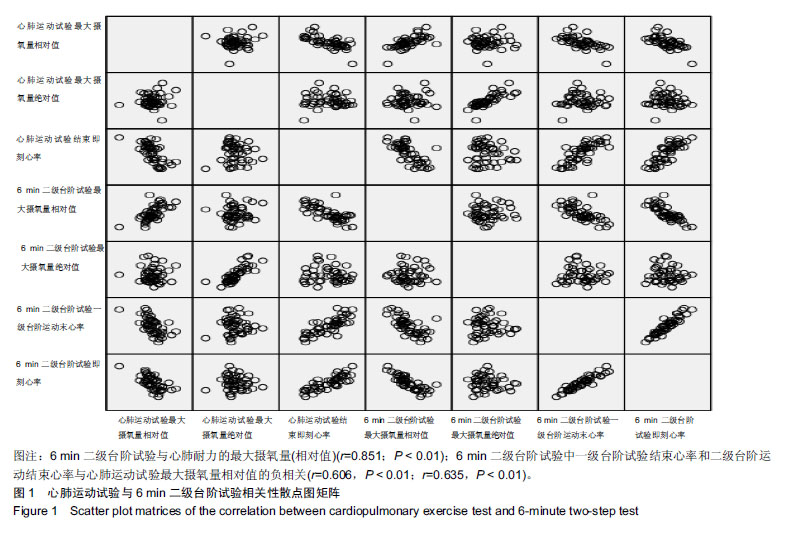
| [1]AMERICAN COLLEGA OF SPORTS MEDICINE. ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription.Tenth Edition. Wolters Kluwer. 2016:45-49.[2]Laukkanen JA, Kurl S, Salonen R,et al. The predictive value of cardiorespiratory fitness for cardiovascular events in men with various risk profiles: a prospective population-based cohort study. Eur Heart J. 2004;25:1428–1437.[3]America Heart Association. Importance of Assessing Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Clinical Practice: A Case for Fitness as a Clinical Vital Sign: A Scientific statement from the American Heart Association.Circulation. 2016:e1-e48.[4]宁亮,孙兴国.心肺运动试验在医学领域的临床应用[J].中国全科医学,2013,16(33):3898-3902.[5]AMERICAN COLLEGA OF SPORTS MEDICINE. ACSM’s Health-Related Physical Fitness Assessment Manual Fourth Edition. Baltimore: Wolters Kluwer. 2014:111.[6]刘爱华.运动心肺功能试验的应用进展[J].医学综述, 2013,19(22): 4125-4128.[7]杨甜. 20-MST评价20-39岁成年人心肺耐力方法及速查表的研究[D].北京:北京体育大学,2016.[8]李萍. 12分钟跑推测大学生最大有氧工作能力方法的研究[D]. 北京:北京体育大学,2012.[9]郭辉,孙景权,张一民.六分钟上下楼梯试验与摄氧量的相关性研究[J].成都体育学院学报,2016,42(3):14-18.[10]Brouha L, Health CW, Graybiel A, Step test simple method of measuring physical fitness for hard muscular work in adult men. Rev Canadian Biol. 1943;(2): 86-89[11]王健, 邓树勋.台阶试验质疑[J].中国体育科技, 2003,39(2): 62-65.[12]蔡广,陆大江,沈勋章,等. 两种台阶实验间接推算和直接测试最大摄氧量的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(15): 2918-2921[13]Jetté M, Campbell J, Mongeon J, et al.The Canadian Home Fitness Test as a predictor for aerobic capacity. Can Med Assoc J.1976; 114(8): 680-682.[14]Bland J, Pfeiffer K, Eisenmann JC. The PWC170: comparison of different stage lengths in 11–16. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(5): 1955-1961.[15]邱少霖,敖运忠,向宗明.Pwc(170)台阶实验、15min跑和12min跑与间接推算VO2max的研究[J].北京体育大学学报, 2001,24(1):52-53.[16]AMERICAN COLLEGA OF SPORTS MEDICINE. ACSM’S Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. Eighth Edition. Wolters Kluwer.2010:65-66.[17]中华人民共和国建设部.《住宅建筑规范》GB 50368—2005[B].北京:中国建筑工业出版社2006.[18]杨文兰.运动心肺试验的安全性及注意事项[J].中国实用内科杂志,2014,34(S1):27-29.[19]Astrand PO, Ryhming I. A Nomogram for Calculation of Aerobic Capacity (Physical Fitness) From Pulse Rate During Submaximal Work. J Appl Physiol. 1954;7(2):218-221.[20]郭辉. 成年人心肺耐力自评价方法的研制与参考等级的建立[D].北京:北京体育大学,2016.[21]王正珍.ACSM运动测试与运动处方指南[M].9版.北京:北京体育大学出版社, 2014.[22]周誉,王正珍,黄守清,等.不同BMI和心肺耐力水平的中年男性心血管疾病风险因素的特征研究[J].中国体育科技,2017,53(1):56-62.[23]田野. 运动生理学高级教程[M]. 高等教育出版社, 2003:234-235.[24]Vainshelboim B, Lima RM, Edvardsen E, et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness, incidence and mortality of lung cancer in men: A prospective cohort study. J Sci Med Sport. 2019;22(4):403-407.[25]金钟一,皮林,韩海英,胡大一.家庭运动康复对于冠状动脉介入术后患者心肺功能的影响[J].慢性病学杂志, 2018,19(7):838-840+843[26]刘晓丽,刘超能,王人卫,等.心肺功能在健康风险预测中的应用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(2):158-165.[27]Pandey A, Patel M, Gao A, et al. Changes in mid-life fitness predicts heart failure risk at a later age independent of interval development of cardiac and noncardiac risk factors: The Cooper Center Longitudinal Study . Am Heart J. 2015;169(2):290-297.e1. [28]DeFina LF, Radford NB, Leonard D, et al. The association of cardiorespiratory fitness, body mass index, and age with testosterone levels at screening of healthy men undergoing preventive medical examinations: The Cooper Center Longitudinal Study. Maturitas. 2018;118:1-6.[29]石秀廷,尹小俭.20m往返跑用于青少年心肺耐力评价的研究进展[J].中国学校卫生,2017,38(12):1916-1920.[30]Berntsen KS, Tollisen A, Schwartz T,et al.Submaximal Exercise Capacity in Juvenile Dermatomyositis after Longterm Disease: The Contribution of Muscle, Lung, and Heart Involvement. J Rheumatol. 2017;44(6):827-834.[31]张茹斌. 基于智能功率车的心肺耐力测试与训练方法研究[D]. 合肥:中国科学技术大学,2018[32]荆志成.六分钟步行距离试验的临床应用[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2006, 34(4):381-384.[33]陈嵘,王健,杨红春.四种运动负荷试验评价运动心肺功能比较研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2014,(9):917-920.[34]郭辉,孙景权,张一民. 心肺运动试验与6 min上下楼梯试验评价心肺功能的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(2):292-296.[35]Brouha L, Health CW, Graybiel A, Step test simple method of measuring physical fitness for hard muscular work in adult men. Rev Canadian Biol.1943;2: 86.[36]郭辉,孙景权,张一民.74例健康青年志愿者心肺运动试验、六分钟上下楼梯试验结果对比观察[J].山东医药,2016,56(23):52-54.[37]Leone M, Duvergé S, Kalinova É, et al. Comtois Comparison of bioenergetics of walking during a multistage incremental shuttle walk test and a 6-min walk test in active older adults. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2017;29 (2):239-246.[38]张劭夫. 六分钟行走试验: 运动耐力评价的方法及临床意义[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(5): 894-897.[39]闫金辉,张丽华.大学生体力劳动能力和最大摄氧量的关系[J].现代预防医学,2008,35(21):4191-4192.[40]袁林,宋应华,刘心伟,等.不同体重人群爬楼梯过程中能量消耗的测定[J].中国体育科技, 2012, 48 (3) :104-107.[41]刘建华,丸山仁司,胜平纯司.上下台阶方法的生物力学研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2003,9(10):32-33. |