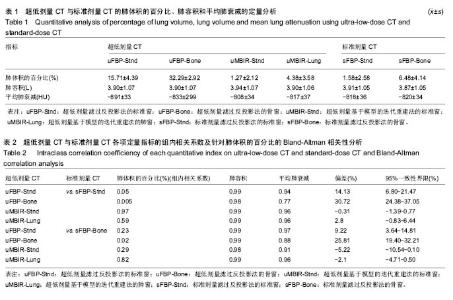
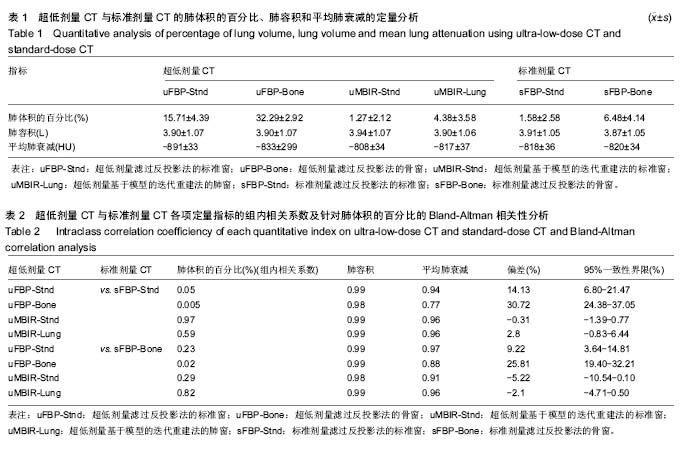
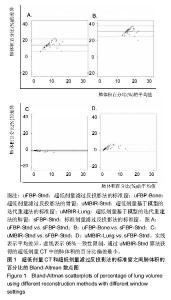
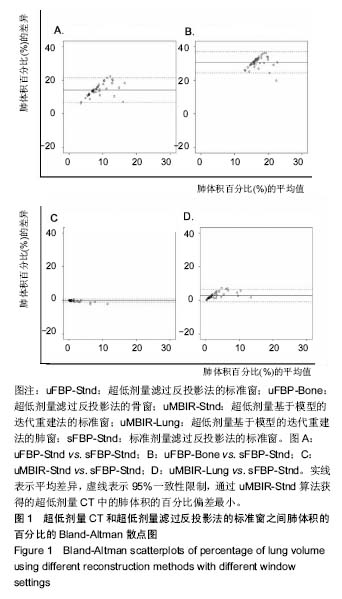
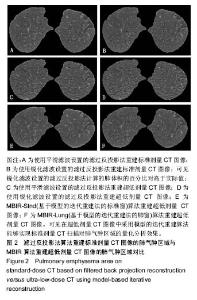
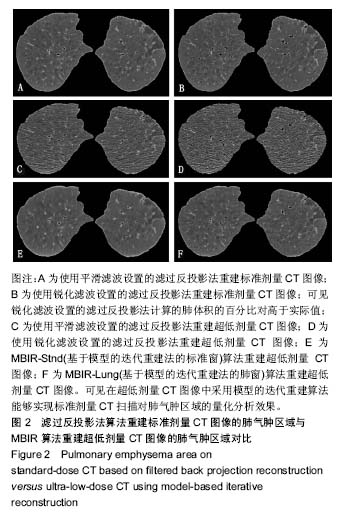
| [1] 李红梅,李平. 多原发恶性肿瘤的病因和发病机制的探讨[J]. 华西医学, 2016(05):991-995.[2] 董继伟. CT迭代重建技术原理及其研究进展[J].中国医学装备, 2016, 13(10):128-133.[3] Padole A, Ali KR, Kalra MK, et al. CT radiation dose and iterative reconstruction techniques. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015;204(4): W384-W392.[4] Yokomachi K, Tatsugami F, Higaki T, et al. Neointimal formation after carotid artery stenting: phantom and clinical evaluation of model-based iterative reconstruction (MBIR). Eur Radiol. 2018 Jun 22.[5] 牟灿,阳明明. 基于CT影像的胸腰椎爆裂骨折治疗临床应用研究[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2018,37(3):1124-1130.[6] Ostridge K, Williams NP, Kim V, et al. Relationship of CT-quantified emphysema, small airways disease and bronchial wall dimensions with physiological, inflammatory and infective measures in COPD. Respir Res.2018;19(1):31.[7] 贾永军,于楠,杨创勃,等. 新一代基于模型的迭代重建中肺特异性设置在提高胸部CT图像质量中的应用价值[J]. 中国中西医结合影像学杂志, 2017,15(5):551-555.[8] Kim C, Lee KY, Shin C, et al. Comparison of Filtered Back Projection, Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction, Model-Based Iterative Reconstruction, and Virtual Monoenergetic Reconstruction Images at Both Low- and Standard-Dose Settings in Measurement of Emphysema Volume and Airway Wall Thickness: A CT Phantom Study. Korean J Radiol.2018; 19(4):809-817.[9] Al-Ekrish AA, Alfadda SA, Tamimi D, et al. Do Ultra-Low Multidetector Computed Tomography Doses and Iterative Reconstruction Techniques Affect Subjective Classification of Bone Type at Dental Implant Sites?. Int J Prosthodont. 2018; 31(5):465-470.[10] 王新莲,贺文. 腹盆部低剂量CT扫描的临床应用进展[J]. 放射学实践, 2017,32(7):761-766.[11] Fujita M, Higaki T, Awaya Y, et al. Lung cancer screening with ultra-low dose CT using full iterative reconstruction. Jpn J Radiol. 2017;35(4): 179-189.[12] Nishio M, Koyama H, Ohno Y, et al. Emphysema Quantification Using Ultralow-Dose CT With Iterative Reconstruction and Filtered Back Projection. AJR Am J Roentgenol.2016;206(6):1184-1192.[13] Kim HJ, Yoo S Y, Jeon T Y, et al. Model-based iterative reconstruction in ultra-low-dose pediatric chest CT: comparison with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction. Clin Imaging. 2016;40(5):1018-1022.[14] Ju YH, Lee G, Lee J W, et al. Ultra-low-dose lung screening CT with model-based iterative reconstruction: an assessment of image quality and lesion conspicuity. Acta Radiol.2018;59(5): 553-559.[15] Messerli M, Ottilinger T, Warschkow R, et al. Emphysema quantification and lung volumetry in chest X-ray equivalent ultralow dose CT - Intra-individual comparison with standard dose CT. Eur J Radiol. 2017,91:1-9. |