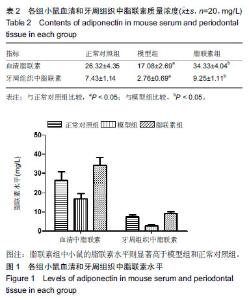
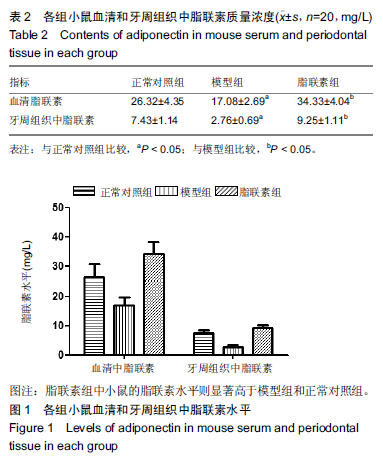
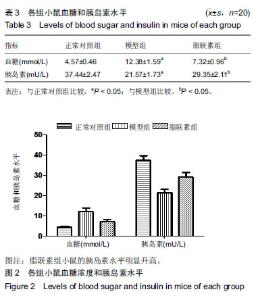
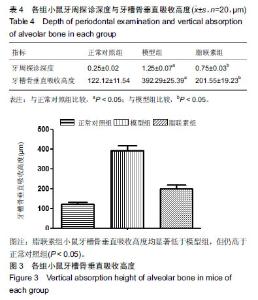
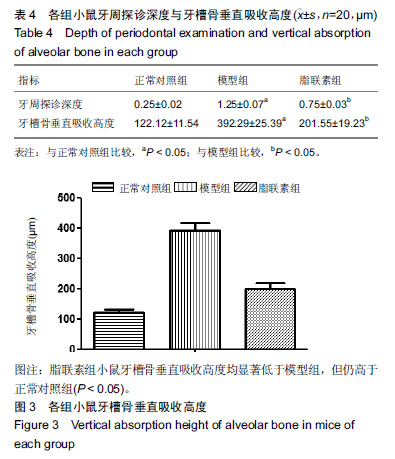
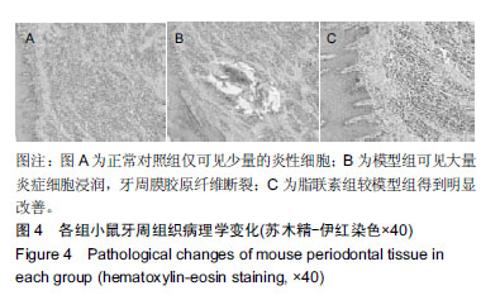
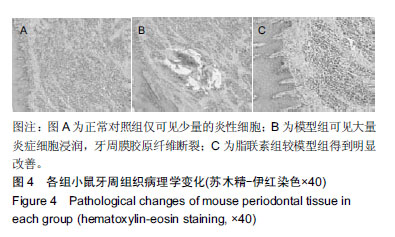
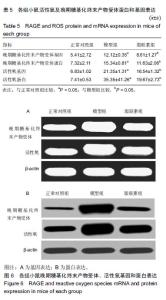
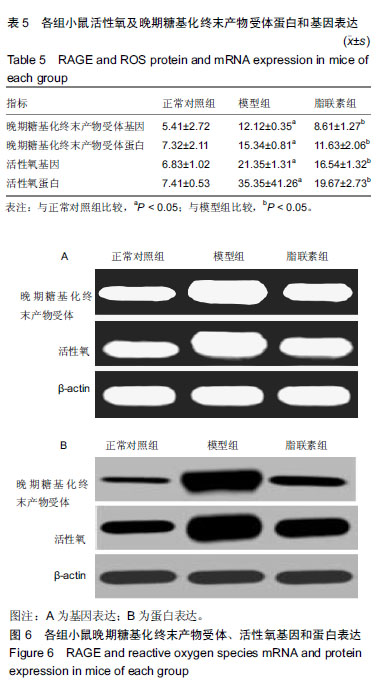
| [1]Oliver RC,Tervonen T.Diabetes--a risk factor for periodontitis in adults?. J Periodontol. 1994;65(5 Suppl):530-538.[2]Daudt LD,Musskopf ML,Mendez M,et al.Association between metabolic syndrome and periodontitis:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Braz Oral Res. 2018;32:e35.[3]康健,李新月.牙周炎与糖尿病关系的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2017,23(18):3670-3674.[4]赵博,王永兰.糖尿病牙周炎昆明系模型小鼠牙周组织中脂联素的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(5):721-726.[5]Kishida K,Funahashi T,Shimomura I.Adiponectin as a routine clinical biomarker. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;28(1):119-130.[6]Lim S,Quon MJ,Koh KK.Modulation of adiponectin as a potential therapeutic strategy. Atherosclerosis. 2014;233(2): 721-728.[7]权善花.2型糖尿病血清脂联素与骨密度变化及其相关因素的研究[D]. 延边:延边大学,2014.[8]陈亮,魏民,刘玉杰.脂联素对骨性关节炎影响的研究进展[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2017,16(8):620-623.[9]刘努,贺涛,张馨艺,等.牙周基础治疗对2型糖尿病伴牙周炎患者疗效的研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2014,22(5):278-280.[10]Taylor JJ,Preshaw PM,Lalla E.A review of the evidence for pathogenic mechanisms that may link periodontitis and diabetes. J Clin Periodontol. 2013;40 Suppl 14:S113-134.[11]Antonoglou G,Knuuttila M,Nieminen P,et al.Serum osteoprotegerin and periodontal destruction in subjects with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Periodontol. 2013;40(8): 765-770.[12]Wang X,Yu S,Hu J P,et al.Streptozotocin-induced diabetes increases amyloid plaque deposition in AD transgenic mice through modulating AGEs/RAGE/NF-κB pathway. Int J Neurosci 2014;124 (8): 601-608.[13]Kay AM, Simpson CL, Stewart JA Jr.The Role of AGE/RAGE Signaling in Diabetes-Mediated Vascular Calcification. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:6809703 [14]Fisman EZ, Tenenbaum A. Adiponectin: a manifold therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and coronary disease?. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014;13:103.[15]Ghoshal K, Bhattacharyya M. Adiponectin: Probe of the molecular paradigm associating diabetes and obesity. World J Diabetes. 2015;6(1):151-166.[16]李渊,房伟,王辉,等.脂联素在炎症疾病中的作用[J].中国医药指南,2016,14(22):32-33.[17]李志高.牙周干预和老年2型糖尿病牙周炎患者脂联素以及炎症因子之间的相互作用机制的研究[J].中国医药科学, 2017,7(8): 234-237.[18]张静隆,朱迪,王贺林,等.脂联素抑制炎症小体NLRP3表达减轻高糖高脂诱导内皮细胞损伤[J].心脏杂志,2016,26(6):634-637.[19]黄焱,郑卫东,修惠平,等.吡哆胺对糖尿病小鼠视皮质AGE-RAGE系统的影响[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志, 2014,23(1):55-59.[20]杨圣菊,孟国梁,顾黎雄,等.糖尿病小鼠皮肤组织中晚期糖基化终末产物的表达及其对胶原纤维的影响[J].中华皮肤科杂志, 2014, 47(11):785-789.[21]Fukami K,Yamagishi S,Okuda S.Role of AGEs-RAGE system in cardiovascular disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(14): 2395-2402.[22]Tesch G,Sourris K C,Summers S A,et al.Deletion of bone-marrow-derived receptor for AGEs (RAGE)improves renal function in an experimental mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia.2014;57(9):1977-1985.[23]Chen J,Jing J,Yu S,et al.Advanced glycation endproducts induce apoptosis of endothelial progenitor cells by activating receptor RAGE and NADPH oxidase/JNK signaling axis. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(5):2169-2178.[24]皇甫长梅.晚期糖基化终产物通过RAGE/ROS通路影响肾小管上皮细胞自噬-溶酶体系统[D]. 广州:暨南大学,2015.[25]Ohtsu A,Shibutani Y,Seno K,et al.Advanced glycation end products and lipopolysaccharides stimulate interleukin-6 secretion via the RAGE/TLR4-NF-κB-ROS pathways and resveratrol attenuates these inflammatory responses in mouse macrophages. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(5):4363-4370.[26]王敏华,邓淑丽,刘云西,等.二甲双胍对牙周致病菌内毒素所致饮食诱导肥胖小鼠高血糖的改善作用[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2018,34(8):945-948.[27]刘海涛.慢性牙周炎患者基础治疗前后血清及龈沟液脂联素检测及临床意义研究[J].贵州医药,2018,42(2): 232-233.[28]颜明,牙周基础治疗对伴2型糖尿病的中、重度牙周炎患者脂联素和代谢水平的影响[J].中国医学创新,2018,15(10):99-102.[29]张杰,梁伯贵,王柏灿,等.牙周治疗对2型糖尿病伴牙周炎患者炎症因子、脂联素及糖化血红蛋白的影响[J].现代实用医学, 2017, 29(4):527-528.[30]刘洋,王国芳, 岳二丽,等.罗格列酮对牙周炎大鼠牙龈脂联素受体表达的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2017,33(1):19-22. |