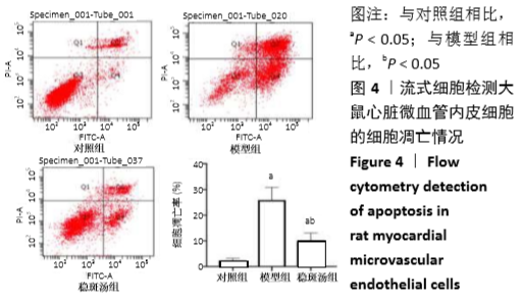
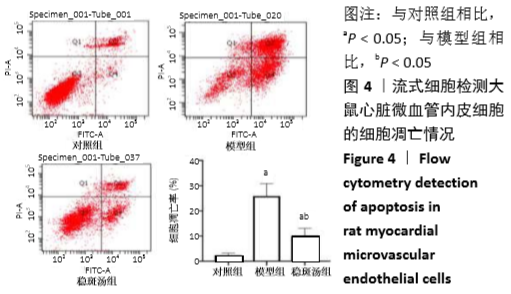
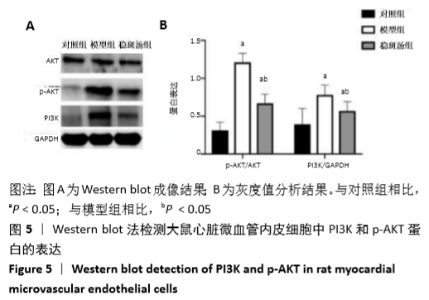
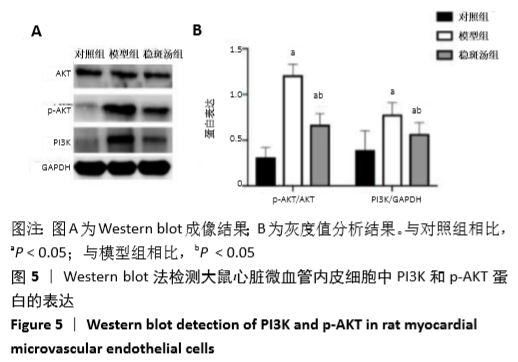
[1] BAO MH, XIAO Y, ZHANG QS, et al. Meta-Analysis of miR-146a Polymorphisms Association with Coronary Artery Diseases and Ischemic Stroke.Int J Mol Sci.2015;16(7):14305-14317.
[2] 王海燕.脑心通胶囊对缺糖缺氧损伤脑微血管内皮细胞的保护作用及其机制[J].中草药,2018, 49(14):3318-3325.
[3] 姜明贺,宫丽鸿.稳斑汤对AopE基因敲除动脉粥样硬化小鼠不稳定斑块TLR4的影响[J].中医杂志,2015, 56(7):598-601.
[4] WANG X, LIU K, LI B, et al. Macrophages Aggravate Hypoxia-Induced Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cell Injury via Peroxynitrite: Protection by Tongxinluo.Cell Communication & Adhesion.2015; 22(2-6):39-47.
[5] 王瑞梅,潘宇清.复方稳斑汤辅助治疗冠心病不稳定型心绞痛临床疗效及对患者血管内皮功能和血脂的影响[J].四川中医,2019, 37(3):80-82.
[6] Qi XF, Li YJ, Chen ZY, et al. Involvement of the FoxO3a pathway in the ischemia/reperfusion injury of cardiac microvascular endothelial cells.Exp Mol Pathol.2013;95 (2): 242-247.
[7] 穆金兴,李雪霞,李延鑫,等.比伐卢定对行经皮冠状动脉介入治疗病人疗效及心肌梗死溶栓试验、心肌灌注评分、心脏主要不良事件的影响分析[J].安徽医药,2019,23(4):700-702.
[8] 陈洪娜,李军,王福文.Diplacone通过抑制氧化应激作用及NF-κB信号通路活性降低Hcy诱导的血管内皮细胞损伤[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2018,19(10):999-1005.
[9] 孙晓晶,徐灿.人参皂苷素Rb1对缺血脑卒中大鼠PI3K/Akt信号通路的影响[J].解剖科学进展,2018,24(5):538-541.
[10] Ma SX, Bai ZF, Wang W, et al. Effects of Microrna-93 on Mouse Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells Injury and Inflammatory Response by Mediating SPP1 Through the NF-ΚB Pathway.Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2018;120(3):2847-2858.
[11] 颜晓睿,宫丽鸿.复方稳斑汤对ApoE基因敲除小鼠主动脉粥样硬化不稳定斑块HSP70和PPAR-γ表达的影响[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2014,9(12):1285-1288.
[12] 马玉东,宋君,张海波.神经干细胞移植对脑外伤大鼠神经功能及脑组织Bcl-2与Bax表达的影响[J].解剖科学进展,2018,24(1):19-25.
[13] Hu SN, Wu YL, Zhao B, et al. Panax notoginseng Saponins Protect Cerebral Microvascular Endothelial Cells against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reperfusion-Induced Barrier Dysfunction via Activation of PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 Antioxidant Signaling Pathway.Molecules.2018;23(11): 2781.
[14] 李轶男,王萍,陈晖.同型半胱氨酸与冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病关系的研究进展[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2019,18(10):792-795.
[15] Singhal AK, Symons JD, Boudina S, et al. Role of Endothelial Cells in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Vasc Dis Prev.2010;7:1-14.
[16] 宋梦莹,蒙健军.厄贝沙坦对高血压合并冠心病患者的疗效及血管内皮功能的影响[J].中国医刊,2019,54(3):266-269.
[17] 姜丹,宫丽鸿.稳斑汤联合体外反搏治疗冠心病经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后患者的临床疗效及对血清血栓素A2、前列腺素I2、TNF-α、单核细胞趋化蛋白-1的影响[J].世界中医药,2018,13(6): 1439-1443.
[18] 陈用贵,宫丽鸿,杨柏松,等.稳斑汤联合增强型体外反搏治疗冠心病不稳定型心绞痛临床研究[J].临床军医杂志,2018,46(10): 1169-1171.
[19] Chen XB, Zhao XY, Cai H, et al. The role of sodium hydrosulfide in attenuating the aging process via PI3K/AKT and CaMKKβ/AMPK pathways. Redox Biol.2017;12:987-1003.
[20] 孔燕茹.血同型半胱氨酸在冠心病危险程度及SYNTAX评分的意义[D].济南:山东大学,2018.
[21] 邵帅,洪乐鹏,邓雪华,等.抑制PI3 K/AKt信号通路对帕金森病炎症细胞模型反应的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2019,39(9):2200-2203.
[22] 唐亚,廖日斌,薛力玮,等.炎症介导的PI3K/Akt/Sp1信号通路激活及内源性H2 S生成加剧重症急性胰腺炎肠道损伤[J].中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(8):1475-1482. |