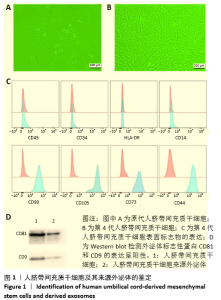
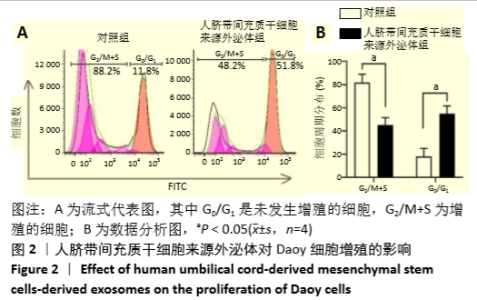
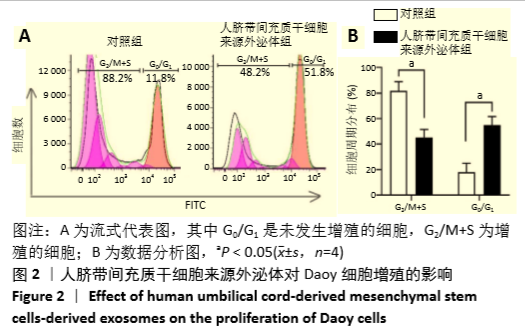
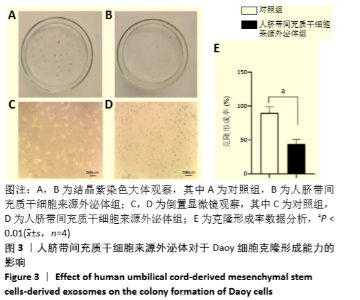
[1] HAN Y, LI X, ZHANG Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine. Cells. 2019;8(8):886.
[2] SCHMELZER E, MCKEEL DT, GERLACH JC. Characterization of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Different Tissues and Their Membrane Encasement for Prospective Transplantation Therapies. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:6376271.
[3] TKACH M, THÉRY C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell. 2016;164(6):1226-1232.
[4] TRAMS EG, LAUTER CJ, SALEM N JR, et al. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981;645(1):63-70.
[5] LUDWIG N, HONG CS, LUDWIG S, et al. Isolation and Analysis of Tumor-Derived Exosomes. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2019;127(1):e91.
[6] ZHANG X, YUAN X, SHI H, et al. Exosomes in cancer: small particle, big player. J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:83.
[7] 李安,方拥军.儿童髓母细胞瘤的治疗研究进展[J].中国小儿血液与肿瘤杂志,2020,25(3):178-181.
[8] QIN Q, HUANG D, JIANG Y. Survival difference between brainstem and cerebellum medulloblastoma: the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results-based study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(41):e22366.
[9] SHI Y, YANG Y, GUO Q, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Differentiation in Inflammatory Environments and Benefit Cardioprotective Effects. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(12):799-811.
[10] 武雪,钱曼青,吴东梁,等.间充质干细胞来源外泌体对肿瘤的调控效应[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(25):4083-4088.
[11] VAKHSHITEH F, ATYABI F, OSTAD SN. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes: a two-edged sword in cancer therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:2847-2859.
[12] 徐竹青,王珠慧,张馨予,等.骨髓间充质干细胞与舌鳞癌细胞:是促进生长还是靶向生物治疗[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(1):128-132.
[13] RYAN D, PAUL BT, KOZIOL J, et al. The pro- and anti-tumor roles of mesenchymal stem cells toward BRCA1-IRIS-overexpressing TNBC cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2019; 21(1):53.
[14] CHEN J, JI T, WU D, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells promote tumor growth via MAPK pathway and metastasis by epithelial mesenchymal transition and integrin alpha5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(6):425.
[15] QI J, ZHOU Y, JIAO Z, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Tumor Growth Through Hedgehog Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(6):2242-2254.
[16] WANG J, HENDRIX A, HERNOT S, et al. Bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomes as communicators in drug resistance in multiple myeloma cells. Blood. 2014;124(4):555-566.
[17] JI R, ZHANG B, ZHANG X, et al. Exosomes derived from human mesenchymal stem cells confer drug resistance in gastric cancer. Cell Cycle. 2015;14(15):2473-2483.
[18] ZHU W, HUANG L, LI Y, et al. Exosomes derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2012;315(1): 28-37.
[19] LIANG X, ZHANG L, WANG S, et al. Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-125a. J Cell Sci. 2016;129(11):2182-2189.
[20] LIN R, WANG S, ZHAO RC. Exosomes from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote migration through Wnt signaling pathway in a breast cancer cell model. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;383(1-2):13-20.
[21] LI X, LI Z. Effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on co-cultured ovarian carcinoma cells. Microsc Res Tech. 2019;82(6):898-902.
[22] PASCUCCI L, COCCÈ V, BONOMI A, et al. Paclitaxel is incorporated by mesenchymal stromal cells and released in exosomes that inhibit in vitro tumor growth: a new approach for drug delivery. J Control Release. 2014;192:262-270.
[23] MUNOZ JL, BLISS SA, GRECO SJ, et al. Delivery of Functional Anti-miR-9 by Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Exosomes to Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells Conferred Chemosensitivity. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2013;2(10):e126.
[24] AMINI S, SHIRALI S, JAFARIRAD S, et al. Are Lipid Profile, Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, and Blood Pressure of Depressed Elderly Patients Different from Healthy Subjects? Int J Prev Med. 2019;10:185.
[25] FAZIO G, GASTON-MASSUET C, BETTINI LR, et al. CyclinD1 Down-Regulation and Increased Apoptosis Are Common Features of Cohesinopathies. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231(3):613-622.
[26] 董雅洁,高维娟. BCL-2、BAX、CASPASE-3在细胞凋亡中的作用及其关系[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(21):4828-4830.
[27] LIU L, HUANG Z, CHEN J, et al. Protein phosphatase 2A activation mechanism contributes to JS-K induced caspase-dependent apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):142.
[28] COSIALLS AM, SÁNCHEZ-VERA I, POMARES H, et al. The BCL-2 family members NOXA and BIM mediate fluorizoline-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;180:114198.
[29] 李昕睿,杨敏.Pim-3蛋白和Bcl-2蛋白生物学特性及在恶性肿瘤中的相关性研究进展[J].海南医学,2020,31(15):2010-2013.
|