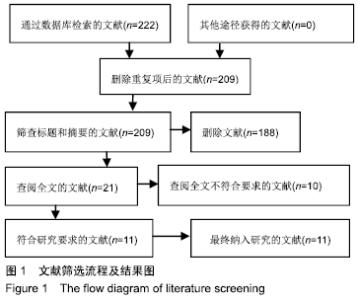
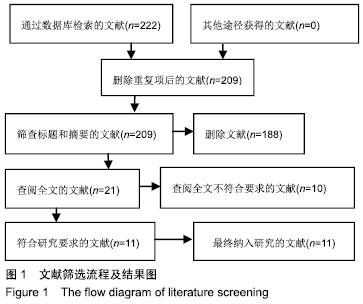
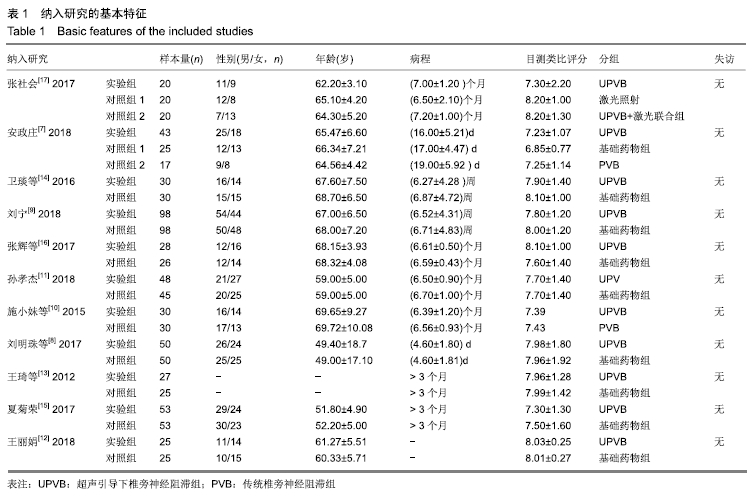
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (11): 1797-1804.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2503
Ultrasound-guided paravertebral nerve block for zoster-associated pain: a Meta-analysis
Song Xudong, He Yunwu, Li Yonglin, Chen Jing, Hu Junlan
- Department of Pain, Second Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2019-07-10Revised:2019-07-12Accepted:2019-08-21Online:2020-04-18Published:2020-02-29 -
Contact:He Yunwu, Master, Associate professor, Associate chief physician, Department of Pain, Second Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Song Xudong, Master candidate, Department of Pain, Second Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Xudong, He Yunwu, Li Yonglin, Chen Jing, Hu Junlan. Ultrasound-guided paravertebral nerve block for zoster-associated pain: a Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(11): 1797-1804.
share this article
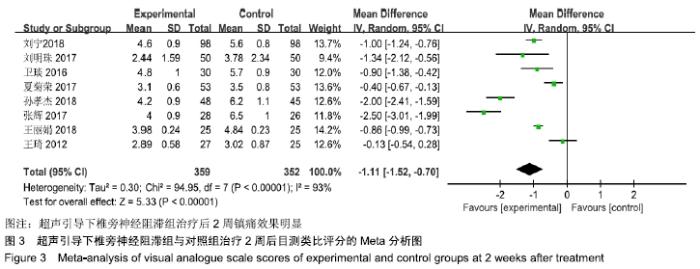
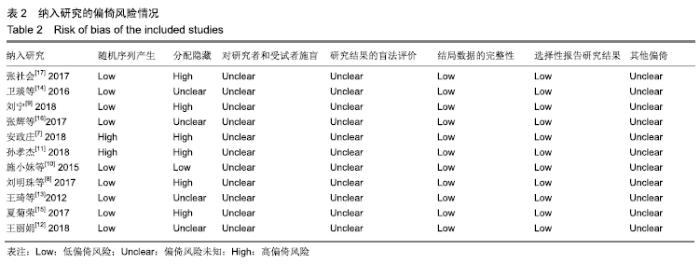
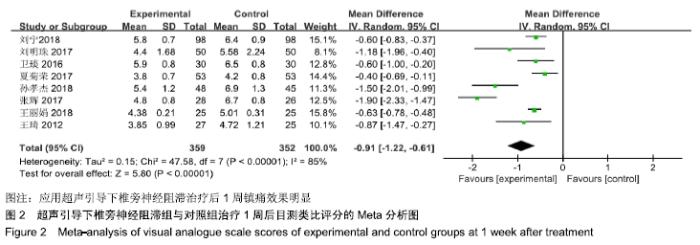
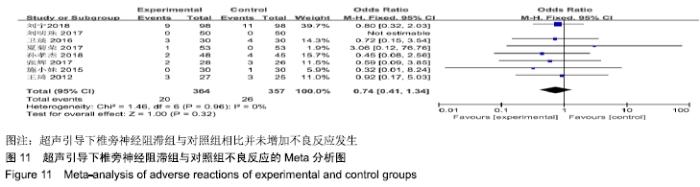
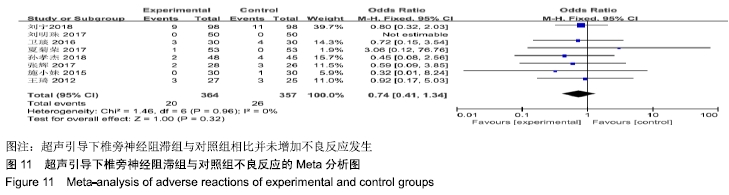
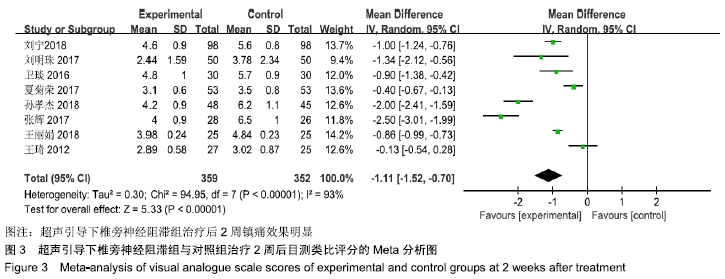
基于对照组基础药物使用的不同,分为非普瑞巴林组和普瑞巴林组进行亚组分析。非普瑞巴林组异质性检验P < 0.000 01,I2=89%,异质性较未分组前增加,说明异质性可能来源于实验组。根据实验组是否联合肋间神经阻滞治疗进行亚组分析,分为单纯椎旁神经阻滞组和联合肋间神经阻滞组。联合肋间神经阻滞组异质性检验P=0.24,I2= 28%,异质性较未分组前明显减少,异质性主要可能来源于实验组联合肋间神经阻滞,分析显示[MD=-1.73,95%CI (-2.11,-1.34),P < 0.000 01]。 (2)治疗后2周目测类比评分:有8项RCT分析了治疗后2周目测类比评分变化[8-9,11-16]。该8项研究异质性检验P < 0.000 01,I2=93%。采用随机效应模型下分析[MD= -1.11,95%CI(-1.52,-0.70),P < 0.000 01]。Meta分析结果显示,超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组与对照组相比,差异存在统计学意义,超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组治疗后2周镇痛效果明显(图3)。 "
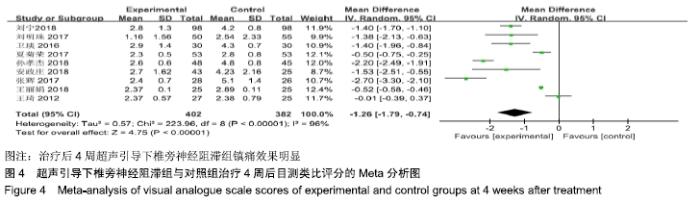
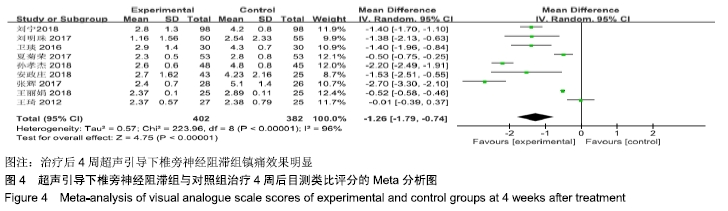
基于对照组基础药物使用的不同进行亚组分析,分为非普瑞巴林组和普瑞巴林组。非普瑞巴林组异质性检验P < 0.000 01,I2=90%,异质性较未分组前未见明显变化,说明异质性可能来源于实验组。基于实验组是否联合肋间神经阻滞治疗进行亚组分析,分为单纯椎旁神经阻滞组和联合肋间神经阻滞组。联合肋间神经阻滞组异质性检验P=0.13,I2=56%,异质性较未分组前明显减少,异质性主要可能来源于实验组联合肋间神经阻滞,随机效应模型下分析显示[MD=-2.23,95%CI(-2.71,-1.74),P < 0.000 01]。 (3)治疗后4周目测类比评分:有9项RCT分析了治疗后4周目测类比评分变化[7-9,11-16]。其异质性检验P < 0.000 01,I2=96%。采用随机效应模型下分析[MD=-1.26,95%CI (-1.79,-0.74),P < 0.000 01]。Meta分析结果显示,超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组与对照组相比,差异存在统计学意义,治疗后4周超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组镇痛效果明显 (图4)。 "
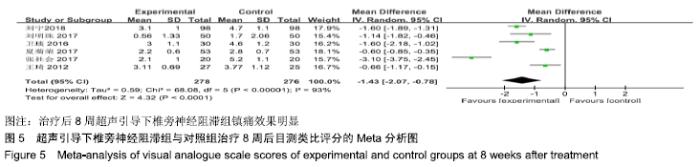
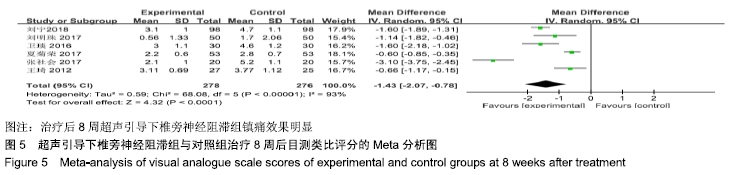
基于对照组基础药物使用的不同分组进行亚组分析。非普瑞巴林组异质性检验P < 0.000 1,I2=81%。普瑞巴林组异质性检验P=0.03,I2=71%。基于实验组是否联合肋间神经阻滞治疗进行亚组分析。单纯椎旁神经阻滞组异质性检验P < 0.000 01,I2=89%。联合肋间神经阻滞组异质性检验P=0.14,I2=54%。 (4)治疗后8周目测类比评分:有6项RCT报道了治疗后8周目测类比评分变化[8-9,13-16]。其异质性检验P < 0.000 01,I2=93%,随机效应模型下分析[MD=-1.43,95%CI (-2.07,-0.78),P < 0.000 1]。Meta分析结果显示,超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组与对照组相比,差异存在统计学意义,治疗后8周超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组镇痛效果明显(图5)。 "

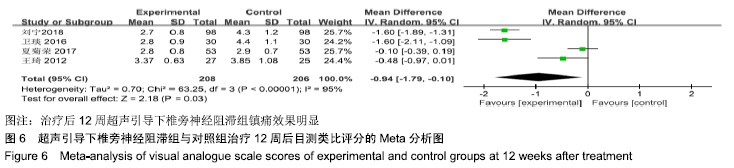
基于对照组基础药物使用的不同分组进行亚组分析。普瑞巴林组异质性检验P=0.84,I2=0%,异质性较未分组前明显减少,异质性可能来源于对照组基础药物的差异,固定效应模型下分析[MD=-0.61,95%CI(-0.83,-0.39),P < 0.000 01]。 (5)治疗后12周目测类比评分:4项RCT报道了治疗后12周目测类比评分变化[9,13-15]。其异质性检验P < 0.000 01,I2=95%,随机效应模型下分析[MD=-0.94,95%CI (-1.79,-0.10),P=0.03 < 0.05]。Meta分析结果显示,超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组与对照组相比,差异存在统计学意义,治疗后12周超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组镇痛效果明显(图6)。 "
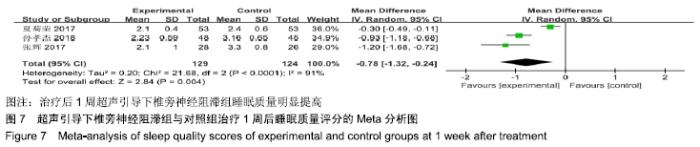
基于对照组基础药物使用的不同分组进行亚组分析。普瑞巴林组异质性检验P=0.19,I2=43%,异质性较未分组前明显减少,异质性可能来源于对照组基础药物的差异,固定效应模型下分析[MD=-0.20,95%CI(-0.44,0.05),P =0.12 > 0.05]。 2.4.2 睡眠质量评分分析结果 (1)治疗后1周睡眠质量评分:共有3项RCT报道了治疗后1周睡眠质量评分变化[11,15- 16]。其异质性检验P < 0.000 1,I2=91%,随机效应模型下分析[MD=-0.78,95%CI (-1.32,-0.24),P=0.004 ]。Meta分析结果显示,超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组与对照组相比,差异存在统计学意义,治疗后1周超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组睡眠质量明显提高(图7)。 "
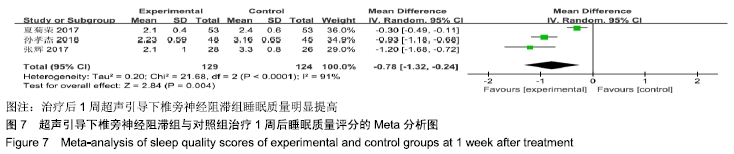
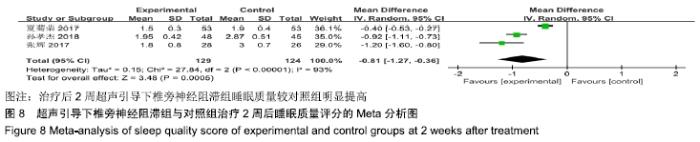
基于实验组是否联合肋间神经阻滞治疗进行亚组分析。联合肋间神经阻滞组异质性检验P=0.33,I2=0%,异质性较未分组前明显减少,异质性主要可能来源于实验组同时合并肋间神经阻滞,固定效应模型下分析示[MD= -0.99,95%CI (-1.21,-0.76),P < 0.000 01]。 (2)治疗后2周睡眠质量评分:3项RCT报道了治疗后2周睡眠质量评分变化[11,15-16]。其异质性检验P < 0.000 01,I2=93%,随机效应模型下分析[MD=-0.81,95%CI(-1.27,-0.36),P=0.000 5]。Meta分析结果显示,超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组与对照组相比,差异存在统计学意义,治疗后2周超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组睡眠质量较对照组明显提高(图8)。 "
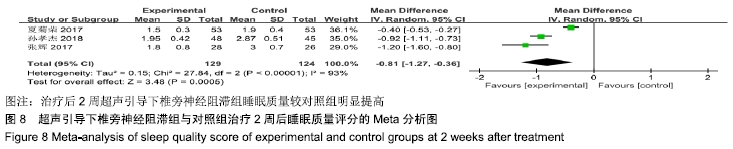

基于实验组是否联合肋间神经阻滞治疗进行亚组分析。联合肋间神经阻滞组异质性检验P=0.22,I2=35%,异质性较未分组前明显减少,异质性主要可能来源于实验组联合肋间神经阻滞,固定效应模型下分析示[MD=-0.97,95%CI (-1.14,-0.80),P < 0.000 01]。 (3)治疗后4周睡眠质量评分:有3项RCT报道了治疗后4周睡眠质量评分变化[11,15-16]。其异质性检验P < 0.000 01,I2=98%,随机效应模型下分析[MD=-0.90,95%CI(-1.57,-0.24),P=0.007]。Meta分析结果显示,超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组与对照组相比,差异存在统计学意义,治疗后2周超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组睡眠质量较对照组明显提高(图9)。 "
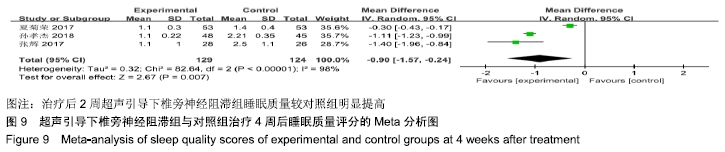
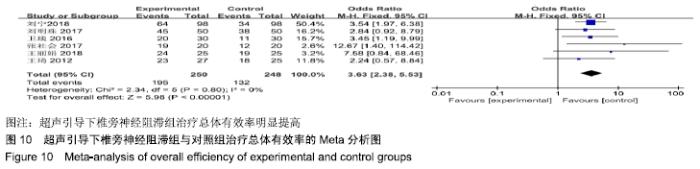
基于实验组是否联合肋间神经阻滞治疗进行亚组分析。联合肋间神经阻滞组异质性检验P=0.32,I2=0%,异质性较未分组前明显减少,异质性主要可能来源于实验组联合肋间神经阻滞,固定效应模型下分析示[MD=-1.12,95%CI(-1.24,-1.01),P < 0.000 01]。 2.4.3 总体有效率分析结果 有6项RCT统计了治疗总体有效率[8- 9,12-14,17]。其异质性检验P=0.80,I2=0%,固定效应模型下分析[OR=3.63,95%CI(2.38,5.53),P < 0.000 01]。Meta分析结果显示,超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组与对照组相比,差异存在统计学意义,超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞组治疗总体有效率明显提高(图10)。 "
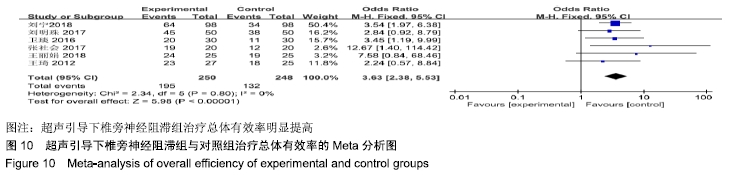
| [1] SCHMADER K. HERPES ZOSTER. Ann Intern Med.2018;169(3): ITC19-ITC31. [2] HONG S, GU L, ZHOU F, et al. Altered functional connectivity density in patients with herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia. J Pain Res. 2018;11:881-888. [3] LI SJ, FENG D.Effect of 2% lidocaine continuous epidural infusion for thoracic or lumbar herpes-zoster-related pain. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(32):e11864. [4] CHOUDHARY S, DHANDE S, KHARAT S, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Different Systemic Treatment Modalities for Acute Pain of Herpes Zoster: A Pilot Study. Indian Dermatol Online J.2018;9(2):101-104. [5] CUNNINGHAM AL, LEVIN MJ.Herpes Zoster Vaccines.J Infect Dis. 2018;218(suppl_2):S127-S133. [6] MAKHARITA MY, AMR YM, EL-BAYOUMY Y. Single paravertebral injection for acute thoracic herpes zoster: a randomized controlled trial.Pain Pract.2015;15(3):229-235. [7] 安政庄.超声引导下胸椎旁神经阻滞治疗43例带状疱疹神经痛的疗效分析[J].重庆医学, 2018,47(31):4067-4069. [8] 刘明珠,李亚洲,刘光东.季德胜蛇药片联合超声引导下胸椎椎旁阻滞治疗带状疱疹的临床效果[J].世界中医药, 2017,12(11):2662-2665. [9] 刘宁.超声引导下胸椎旁神经阻滞联合加巴喷丁治疗老年带状疱疹后神经痛的效果[J].国际医药卫生导报, 2018,24(8):1201-1203. [10] 施小妹,傅少雄,陈日,等.超声引导下胸椎旁阻滞治疗带状疱疹后神经痛[J].中国疼痛医学杂志, 2015,21(10):788-790. [11] 孙孝杰.超声引导下胸椎旁神经阻滞治疗带状疱疹的效果分析[J].实用医技杂志, 2018,25(9):1005-1007. [12] 王丽娟.普瑞巴林联合B超引导下胸椎旁神经阻滞治疗带状疱疹后神经痛临床分析[J].药品评价, 2018,15(17):32-34. [13] 王琦,何明伟,倪家骧.普瑞巴林联合B超引导下胸椎旁神经阻滞治疗带状疱疹后神经痛[J].中国新药杂志, 2012,21(24):2932-2935. [14] 卫琰,陈弘,张昕,等.超声引导下胸椎旁神经阻滞对老年带状疱疹后神经痛的疗效分析[J].中国疼痛医学杂志, 2016,22(7):510-513. [15] 夏菊荣.普瑞巴林联合超声引导下椎旁神经阻滞对带状疱疹后遗神经痛治疗效果的临床研究[J].中国医师杂志, 2017,19(10):1570-1572. [16] 张辉,张昕,施海峰. 超声引导下胸椎旁神经阻滞在治疗带状疱疹中的意义[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2017,9(7):89-90. [17] 张社会. 超激光照射联合超声引导下胸椎旁神经阻滞治疗带状疱疹后遗神经痛的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2017,39(10):783-784. [18] KIM YD, PARK SJ, SHIM J, et al. Clinical usefulness of pectoral nerve block for the management of zoster-associated pain: case reports and technical description.J Anesth. 2016;30(6):1074-1077. [19] OXMAN MN.Advances and Controversies in Our Understanding of Herpes Zoster-Introduction. J Infect Dis.2018;218(suppl_2):S55-S56. [20] BOUMAN EAC, SIEBEN JM, BALTHASAR AJR, et al. Boundaries of the thoracic paravertebral space: potential risks and benefits of the thoracic paravertebral block from an anatomical perspective. Surg Radiol Anat.2017;39(10):1117-1125. [21] BERTINI L.Refresher course: Ultrasound guided chronic pain management: Evidence and practice. Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.2015;40(5):e61-e62. [22] ANNELOT C, KREDIET, NIZAR MOAYERI, et al. Different Approaches to Ultrasound-guided Thoracic Paravertebral Block : An Illustrated Review. Anesthesiology.2015;123:459-474. [23] LEE HJ, PARK HS, MOON HI, et al. Effect of Ultrasound-Guided Intercostal Nerve Block Versus Fluoroscopy-Guided Epidural Nerve Block in Patients With Thoracic Herpes Zoster: A Comparative Study. J Ultrasound Med.2019;38(3):725-731. [24] D'ERCOLE F, ARORA H, KUMAR PA. Paravertebral Block for Thoracic Surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2018,32(2):915-27. [25] ONAKPOYA IJ, THOMAS ET, LEE JJ, et al. Benefits and harms of pregabalin in the management of neuropathic pain: a rapid review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials.BMJ open. 2019;9(1): e023600. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [4] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Zeng Zhen, Hu Jingwei, Li Xuan, Tang Linmei, Huang Zhiqiang, Li Mingxing. Quantitative analysis of renal blood flow perfusion using contrast-enhanced ultrasound in rats with hemorrhagic shock during resuscitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1201-1206. |
| [7] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [8] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [9] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [10] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [11] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [12] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [13] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [14] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [15] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||