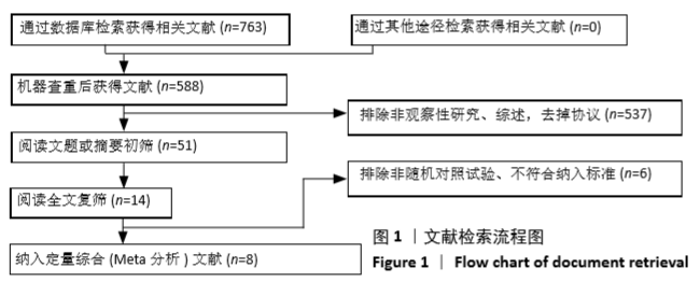
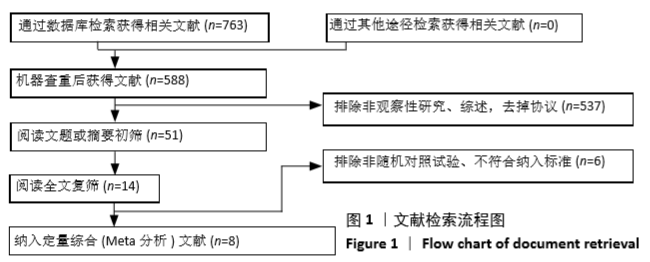
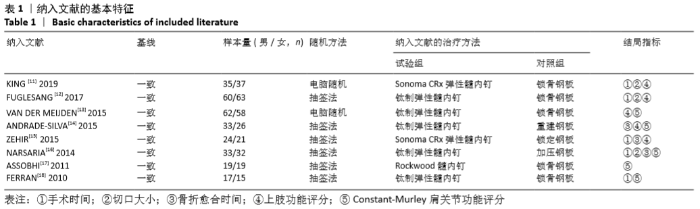
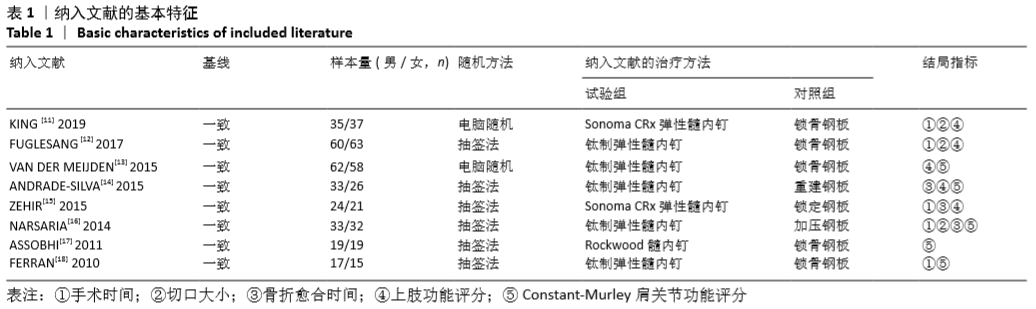
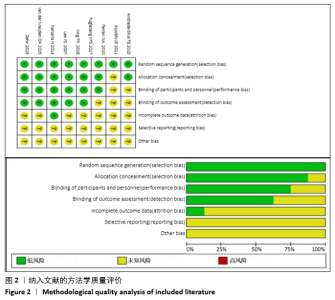
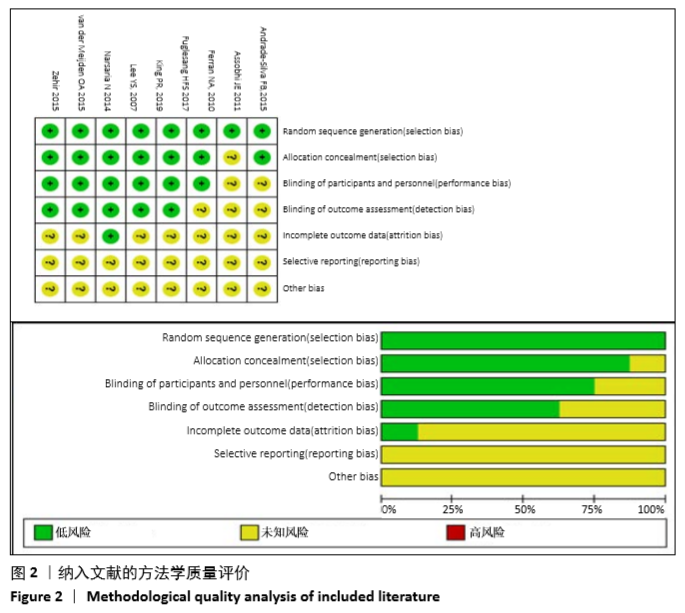
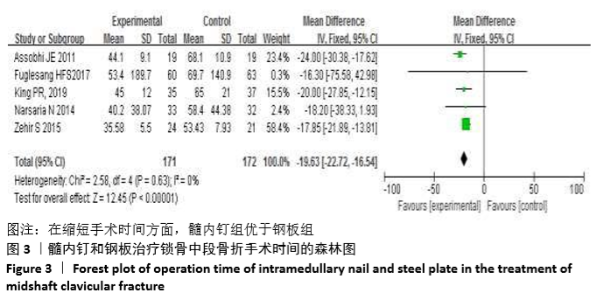
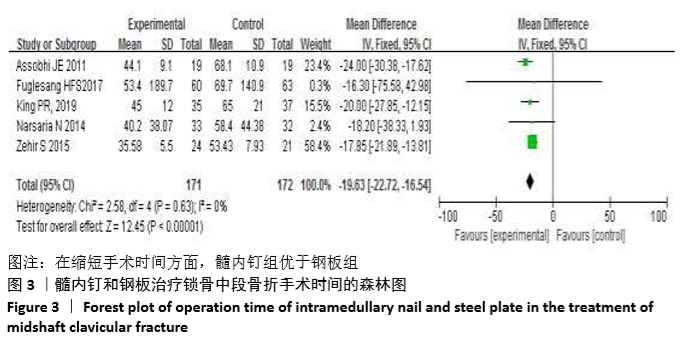
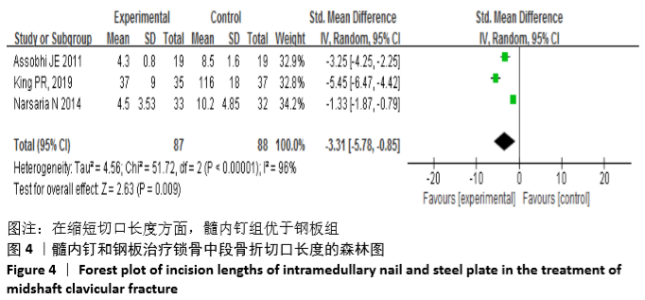
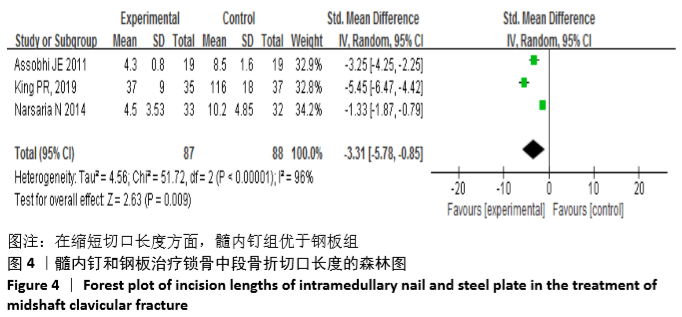
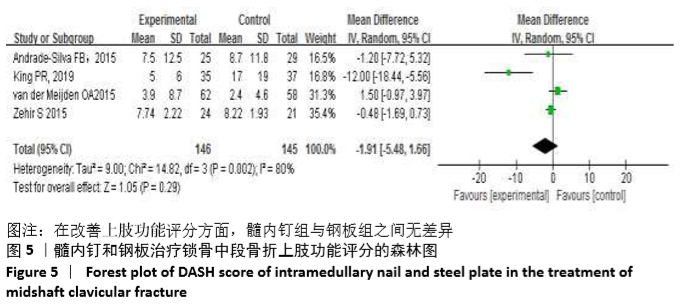
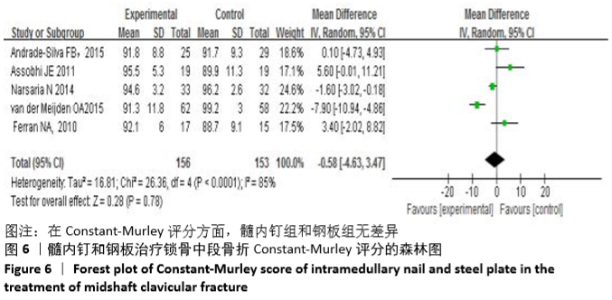
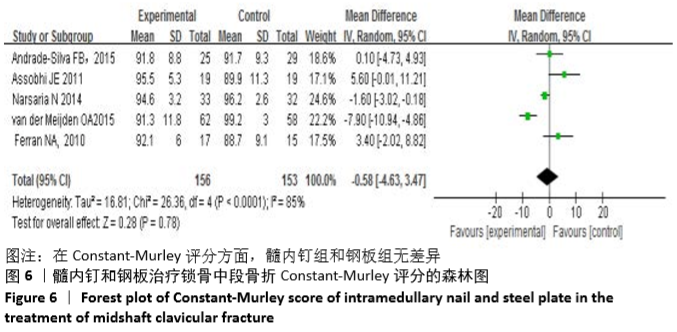
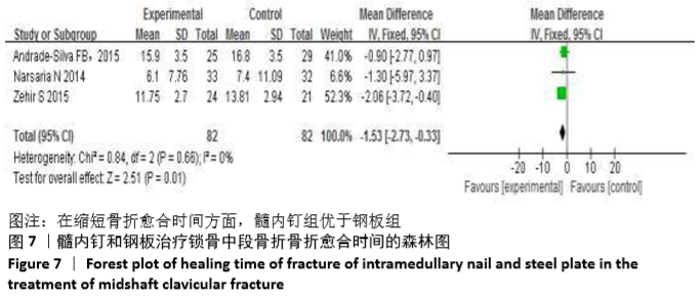
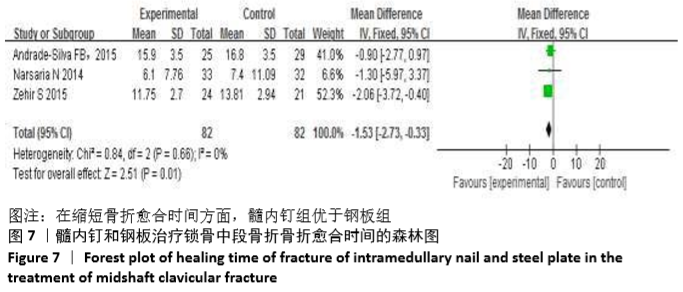
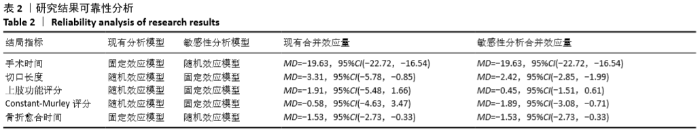
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 471-476.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2949
Previous Articles Next Articles
Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis
Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang
- Shandong Wendeng Osteopathic Hospital, Weihai 264400, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2020-02-13Revised:2020-02-22Accepted:2020-03-20Online:2021-01-28Published:2020-11-19 -
Contact:Jiang Hongjiang, Chief physician, Shandong Wendeng Osteopathic Hospital , Weihai 264400, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Li Yanle, Master, Physician, Shandong Wendeng Osteopathic Hospital, Weihai 264400, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Specialty Construction of Science and Technology Bureau-Orthopedics Department of Weihai, No. 2017GNS13
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] CHEN W, ZHU Y, LIU S, et al. Demographic and socioeconomic factors influencing the incidence of clavicle fractures, a national population-based survey of five hundred and twelve thousand, one hundred and eighty seven individuals. Int Orthop. 2018; 42(3): 651-658. [2] HUSSAIN N, SERMER C, PRUSICK PJ, et al. Intramedullary nailing versus plate fixation for the treatment displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34912. [3] BHATTACHARYYA R, JAYARAM PR, HOLLIDAY R, et al. The virtual fracture clinic: Reducing unnecessary review of clavicle fractures. Injury. 2017;48(3):720-723. [4] Guerra E, Previtali D, Tamborini S, et al. Midshaft clavicle fractures: surgery provides better results as compared with nonoperative treatment: a meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47:3541-3551. [5] ROBINSON CM, GOUDIE EB, MURRAY IR, et al. Open reduction and plate fixation versus nonoperative treatment for displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:1576-1584. [6] GUZMÁN-GUEVARA J, LÓPEZ-CÁZARES G, BARRAGÁN-HERVELLA RG, et al. Evaluation of patients with humeral midshaft fractures treated with DCP plate vs. intramedullary nail UHN. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2016;54 Suppl 3:S270-S274. [7] LI Y, HELVIE P, FARLEY FA, et al. Complications after plate fixation of displaced pediatric midshaft clavicle fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2018;38(7):350-353. [8] BALARAMAN R, SATHISH KUMAR R, SRI KRISHNA SANDEEP S, et al. Short term functional outcome of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures treated with TENS nailing. Res J Pharmaceutical Biol Chem Sci. 2015; 6(2):2011-2016. [9] BI H, WANG Y, XIONG Q, et al. Minimally invasive fixation of midclavicular fractures with threaded elastic intramedullary nails. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015; 25(5):833-840. [10] LU CC, LIU PC, HUANG SH, et al. Complications and technical pitfalls of titanium elastic nail fixation for midclavicular fractures. Orthopedics. 2014;37(4):e377-e383. [11] KING PR, IKRAM A, EKEN MM, et al. The effectiveness of a flexible locked intramedullary nail and an anatomically contoured locked plate to treat clavicular shaft fractures: a 1-year randomized control trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101: 628-634. [12] FUGLESANG HFS, FLUGSRUD GB, RANDSBORG PH, et al. Plate fixation intramedullary nailing of completely displaced midshaft fractures of the clavicle: a prospective randomised controlled trial. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(8):1095-1101. [13] VAN DER MEIJDEN OA, HOUWERT RM, HULSMANS M, et al. Operative treatment of dislocated midshaft clavicular fractures: plate or intramedullary nail fixation? A randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97:613-619. [14] ANDRADE-SILVA FB, KOJIMA KE, JOERIS A, et al. Single, superiorly placed reconstruction plate compared with flexible intramedullary nailing for midshaft clavicular fractures: a prospective, randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(8):620-626. [15] ZEHIR S, ZEHIR R, ŞAHIN E, et al. Comparison of novel intramedullary nailing with mini-invasive plating in surgical fixation of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015; 135:339-344. [16] NARSARIA N, SINGH AK, ARUN GR, et al. Surgical fixation of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures: elastic intramedullary nailing versus precontoured plating. J Orthop Traumatol. 2014;15(3): 165-171. [17] ASSOBHI JE. Reconstruction plate versus minimal invasive retrograde titanium elastic nail fixation for displaced midclavicular fractures. J Orthop Traumatol. 2011;12(4): 185-192. [18] FERRAN NA, HODGSON P, VANNET N, et al. Locked intramedullary fixation vs plating for displaced and shortened mid-shaft clavicle fractures: a randomized clinical trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010; 19(6):783-789. [19] 陈浩, 张锦洪, 贺增良. 髓内钉固定与钢板固定治疗锁骨中段骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(13): 2407-2414. [20] 陈敏. 髄内钉与钢板内固定治疗移位型锁骨中段骨折疗效比较的分析[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2014. [21] 熊为, 刘家国, 罗斌, 等.钛制髓内钉与接骨板内固定治疗成人移位型锁骨中段骨折的Meta分析[J].湖北医药学院学报, 2016, 35(3):266-273. [22] ZHANG B, ZHU Y, ZHANG F, et al. Meta-analysis of plate fixation versus intramedullary fixation for the treatment of mid-shaft clavicle fractures. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2015;23:27. [23] HUSSAIN N, SERMER C, PRUSICK PJ, et al. Intramedullary nailing versus plate fixation for the treatment displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2016;6: 34912. [24] DROSDOWECH DS, MANWELL SE, FERREIRA LM, et al. Biomechanical analysis of fixation of middle third fractures of the clavicle. J Orthop Trauma. 2011; 25(1): 39-43. [25] 陈奕,吕建元,陈吉,等.钛制弹性髓内钉微创治疗锁骨中段骨折的生物力学研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011, 19(20):1723-1725. [26] ULLAH K, KHAN S, WANG YQ, et al. Bilaterally threaded, minimal invasive, elastic locking intramedullary nailing (ELIN) for the treatment of clavicle fractures. Orthop Surg. 2020;12: 321-332. [27] 周勤坡, 张峰, 马大年, 等. 钛制髓内钉与重建钢板治疗锁骨中段骨折的疗效比较[J]. 临床骨科杂志, 2019,22(4):462-465. [28] HULSMANS MH, VAN HEIJL M, HOUWERT RM, et al. Surgical fixation of midshaft clavicle fractures: A systematic review of biomechanical studies. Injury. 2018;49(4): 753-765. [29] XIE L, ZHAO Z, ZHANG S, et al. Intramedullary fixation versus plate fixation for displaced mid-shaft clavicle fractures: A systematic review of overlapping meta-analyses. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97: e9752. [30] KEIHAN SHOKOUH H, NADERI MN, KEIHAN SHOKOUH M. Treatment of midshaft clavicular fractures with elastic titanium nails. Trauma Mon. 2014; 19(3): e15623. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [3] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [4] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [5] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [6] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [7] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [8] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [9] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [10] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [11] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [12] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [13] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [14] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [15] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||