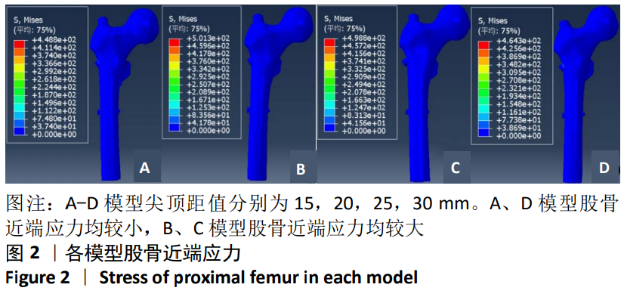
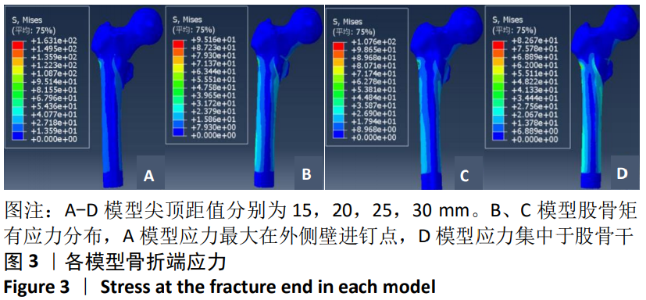
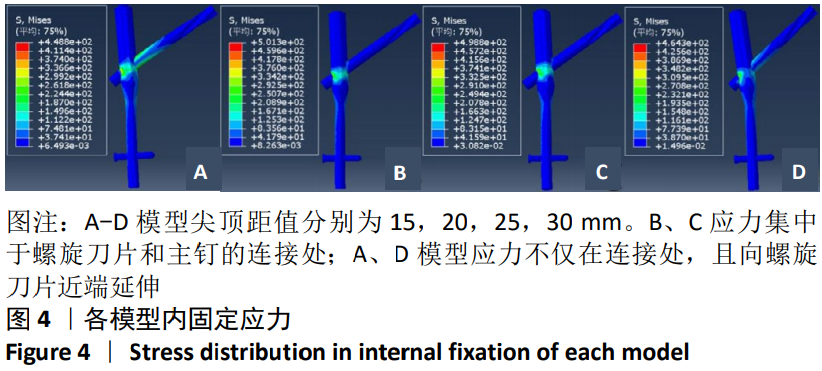
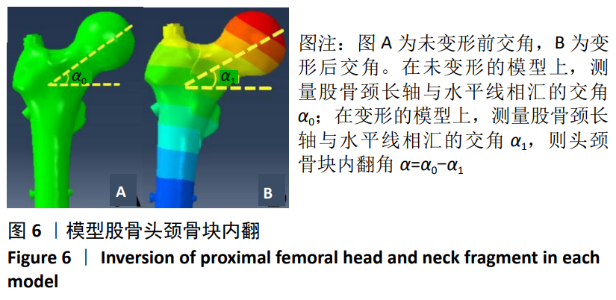
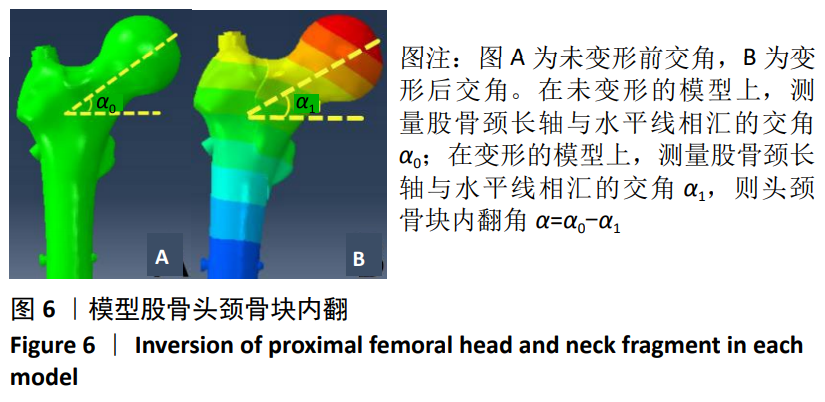
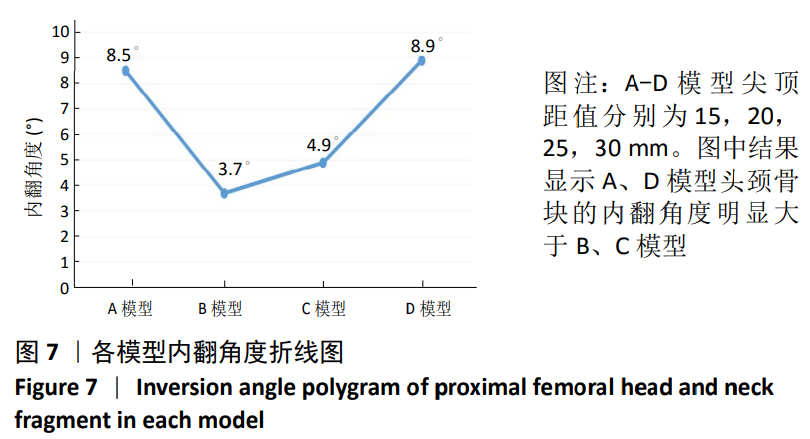
[1] GUO Y, YANG HP, DOU QJ, et al. Efficacy of femoral nail anti-rotation of helical blade in unstable intertrochanteric fracture. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(3 Suppl):6-11.
[2] WANG J, MA JX, LU B, et al. Comparative finite element analysis of three implants fixing stable and unstable subtrochanteric femoral fractures: Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA), Proximal Femoral Locking Plate (PFLP), and Reverse Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(1):95-101.
[3] VÉLEZ M, PALACIOS-BARAHONA U, ARANGO-POSADA MM, et al. Functional results and complications of the use of the proximal femoral nail in the treatment of intertrochanteric hip fractures. Acta Ortop Mex. 2018;32(3): 126-130.
[4] XU R, RU J, JI F, et al. Comparison of efficacy, complications and TGF-β2 expression between DHS and PFNA in elderly patients with osteoporotic femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Exp Ther Med. 2018; 16(1): 394-399.
[5] BUYUKDOGAN K, CAGLAR O, ISIK S, et al. Risk factors for cut-out of double lag screw fixation in proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 2017; 48(2): 414-418.
[6] FUJII T, NAKAYAMA S, HARA M, et al. Tip-Apex Distance Is Most Important of Six Predictors of Screw Cutout After Internal Fixation of Intertrochanteric Fractures in Women. JBJS Open Access. 2017;2(4): e0022.
[7] 武政,刘向栋,常宝生. PFNA治疗高龄不稳定性股骨转子间骨折内固定失败的危险因素分析[J]. 局解手术学杂志, 2017, 26(8): 616-619.
[8] 段志斌. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉术后螺旋刀片穿出股骨头的影响因素分析[D].南昌:南昌大学,2018.
[9] BAUMGAERTNER MR, CURTIN SL, LINDSKOG DM, et al. The value of the tip-apex distance in predicting failure of fixation of peritrochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77(7):1058-1064.
[10] NIKOLOSKI AN, OSBROUGH AL, YATES PJ. Should the tip-apex distance (TAD) rule be modified for the proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA)? A retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2013;8:35.
[11] ZHOU JQ, CHANG SM. Failure of PFNA: helical blade perforation and tip-apex distance. Injury. 2012; 43(7): 1227-1228.
[12] 李海丰, 王华, 张英琪, 等. 头髓钉治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折的尖顶距与螺旋刀片移位的关系[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2019, 33(10): 1234-1238.
[13] 郭团茂, 翟红兵, 陈文恒, 等. 采用三种手术方法治疗老年骨质疏松性股骨粗隆间骨折疗效比较[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2020, 48(2): 205-207.
[14] 张扬宁, 陈文杰, 陈海南. 动力髋螺钉与股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年股骨近端骨折的疗效比较[J]. 山西医药杂志, 2020, 49(4): 436-438.
[15] 任德新. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定治疗累及外侧壁的股骨转子间骨折有限元分析[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2018.
[16] 郑利钦, 陈心敏, 张彪, 等. 股骨转子间骨折股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定切割失效的有限元仿真[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(36): 5794-5799.
[17] ADIB HAJBAGHERY M, ABBASINIA M. Quality of life of the elderly after hip fracture surgery: a case-control study. J Caring Sci. 2013; 2(1): 53-59.
[18] CLOSE JD, SWARTZ K, DEU R. Hip fracture in older patients: tips and tools to speed recovery. J Fam Pract. 2013; 62(9): 484-492.
[19] 张世民, 马卓, 杜守超. 股骨近端外侧壁的解剖学研究及其对转子间骨折内固定的意义[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 2016, 34(1):39-42.
[20] 李鹏飞, 吕扬, 周方. 合并内侧壁骨折块的股骨粗隆间骨折的研究进展[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2020, 20(1):70-73.
[21] 杨林, 杨浩, 谭科, 等. PFLCP与PFNA治疗老年不稳定型粗隆间骨折在不同时期的疗效对比分析[J]. 四川医学, 2019, 40(12): 1227-1231.
[22] KUZYK PR, LOBO J, WHELAN D, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of extramedullary versus intramedullary fixation for reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(1): 31-38.
[23] KOKOROGHIANNIS C, AKTSELIS I, DELIGEORGIS A, et al. Evolving concepts of stability and intramedullary fixation of intertrochanteric fractures--a review. Injury. 2012;43(6): 686-693.
[24] 徐杨俊, 郑卫平, 刘又生, 等. 3种内固定治疗老年骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2019,22(6):727-730.
[25] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972; 43(5): 301-317.
[26] 何祥鑫, 李鹏飞, 林梓凌, 等. 基于有限元分析法的老年粗隆间骨折建模仿真[J]. 中国医药导报,2017,14(24): 88-91+195.
[27] 孙文涛, 李鹏飞, 林梓凌, 等. 基于断裂力学模拟3种不同跌倒状态下股骨近端骨折的有限元分析[J]. 新疆医科大学学报,2017, 40(12):1529-1532.
[28] 孙文涛, 林梓凌, 李凡, 等. 基于Hypermesh/LS-DYNA仿真股骨干中上1/3骨折的断裂分析[J]. 广东医学,2017,38(16): 2481-2483.
[29] 郑利钦, 林梓凌, 何祥鑫, 等. 动态载荷下股骨转子间区域皮质骨厚度对骨折类型影响的有限元分析[J]. 医学研究生学报, 2018, 31(10):1043-1046.
[30] 李辰, 李建涛, 周坚锋, 等. 短与长髓内钉治疗不稳定粗隆下骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2019, 27(4): 361-366.
[31] 杜守超, 张世民, 张英琪, 等. 不稳定股骨转子间骨折前内侧皮质支撑复位的影像学研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2018, 26(18): 1633-1638.
[32] THOMAS CD, MAYHEW PM, POWER J, et al. Femoral neck trabecular bone: loss with aging and role in preventing fracture. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(11):1808-1818.
[33] BORN CT, KARICH B, BAUER C, et al. Hip screw migration testing: first results for hip screws and helical blades utilizing a new oscillating test method. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(5):760-766.
[34] FLORES SA, WOOLRIDGE A, CAROOM C, et al. The utility of the tip-apex distance in predicting axial migration and cutout with the trochanteric fixation nail system helical blade. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30(6): e207-211.
[35] LENZ M, SCHWINN J, HOFMANN-FLIRI L, et al. Influence of reduced tip-apex distance on helical blade fixation-a biomechanical study. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(3): 649-654.
[36] 付豪. 非均匀材料股骨骨折有限元分析[C]. 中国力学学会、浙江大学.中国力学大会论文集(CCTAM 2019).中国力学学会、浙江大学:中国力学学会,2019:2497-2502.
[37] 何祥鑫. 内收肌主动响应对脾虚型老年髋部骨折断裂行为影响的有限元研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2018.
[38] 孙文涛. 臀中肌主动响应对脾肾阳虚型老年股骨颈骨折的有限元断裂力学分析[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2018.
[39] 王炜昌, 王荣生, 石裕明, 等. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年股骨转子间不稳定骨折内固定失效的危险因素[J]. 临床骨科杂志, 2019, 22(4): 477-481. |