Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (6): 970-976.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2968
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis
Hua Haotian1, Zhao Wenyu1, Zhang Lei2, Bai Wenbo3, Wang Xinwei2
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2Henan Provincial Orthopedic Hospital, Luoyang 471002, Henan Province, China; 3Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712046, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2020-04-03Revised:2020-04-14Accepted:2020-05-13Online:2021-02-28Published:2020-12-05 -
Contact:Wang Xinwei, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Henan Provincial Orthopedic Hospital, Luoyang 471002, Henan Province, China -
About author:Hua Haotian, Master candidate, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Project of Henan Province, No. 182102310487
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
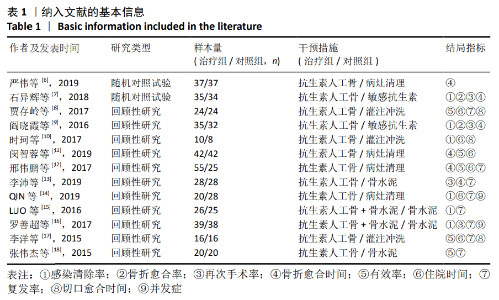
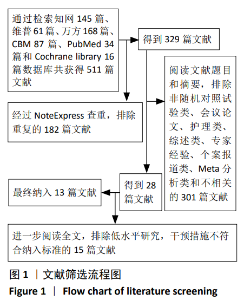
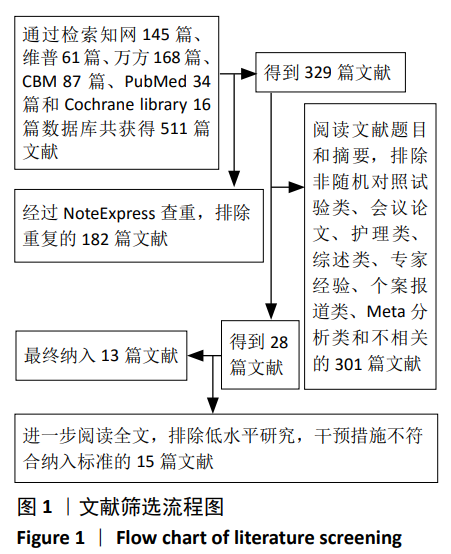
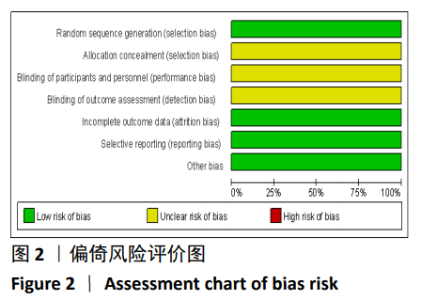
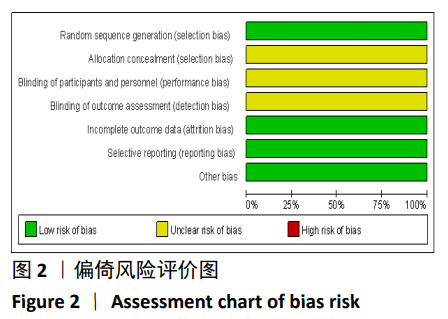
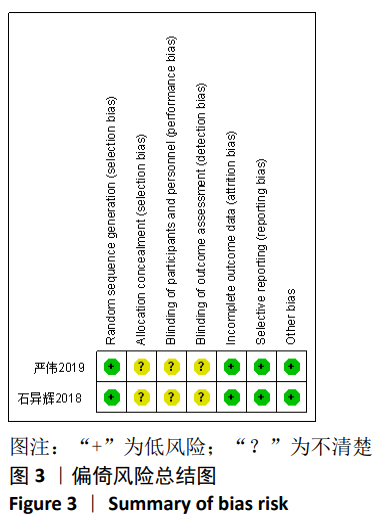
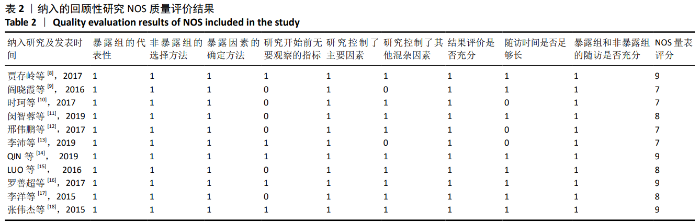
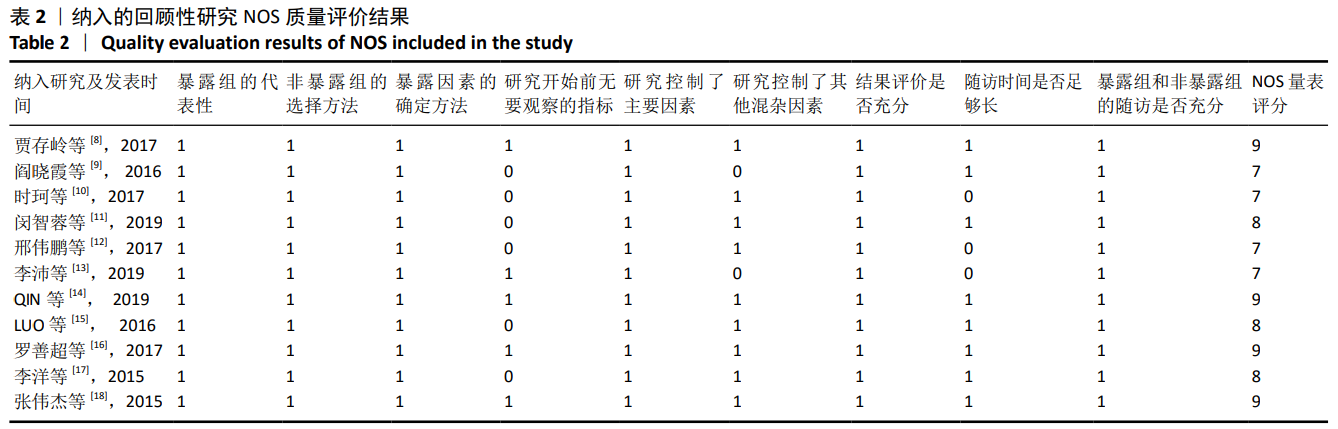
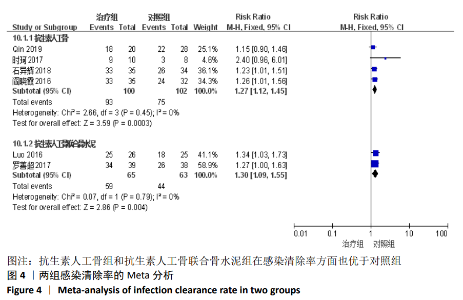
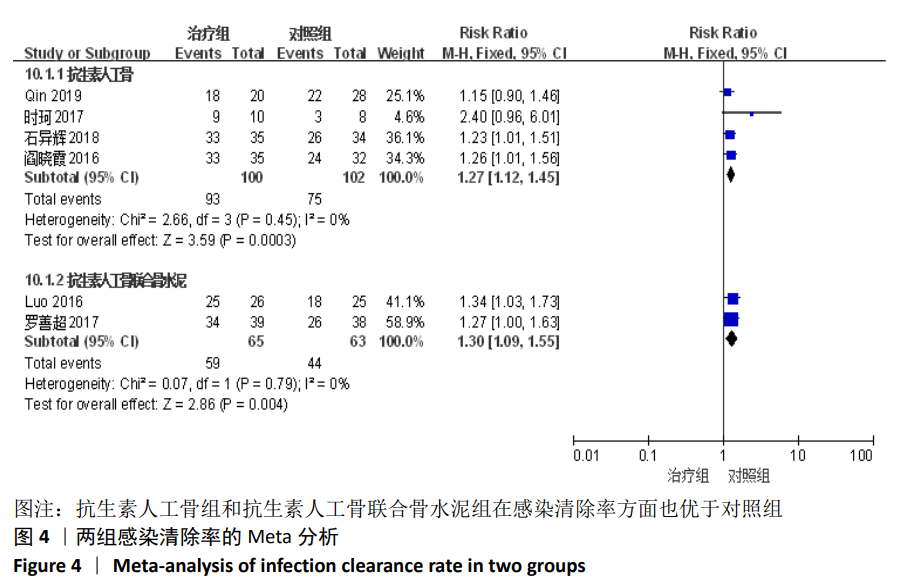
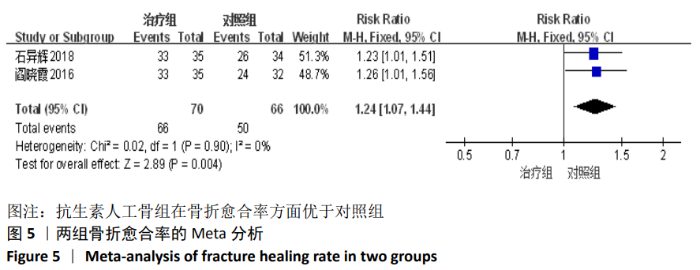
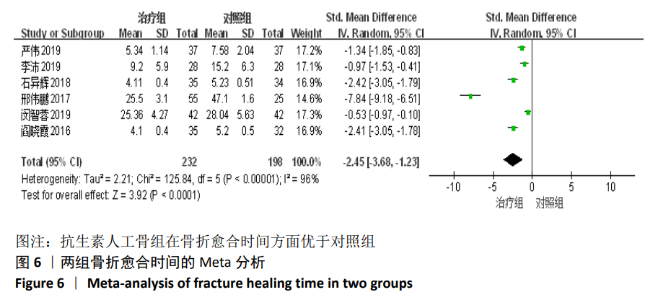
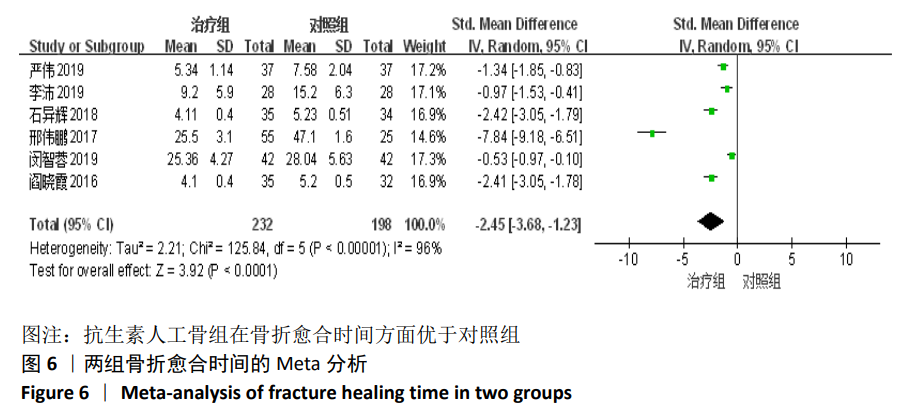
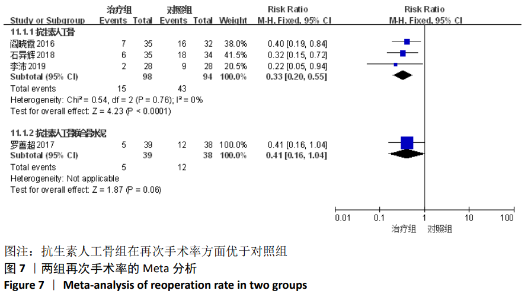
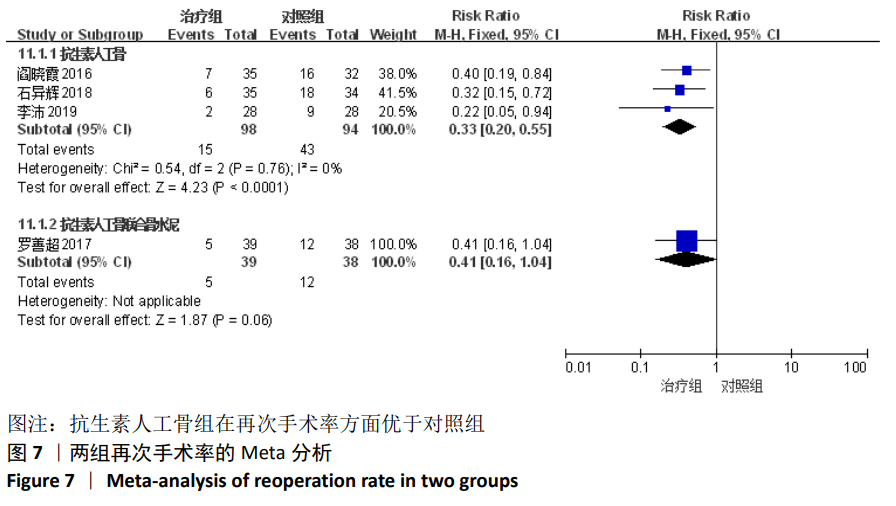
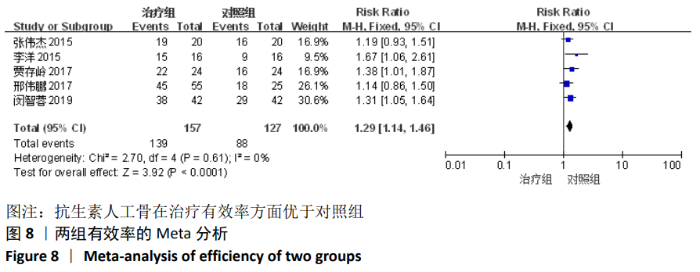
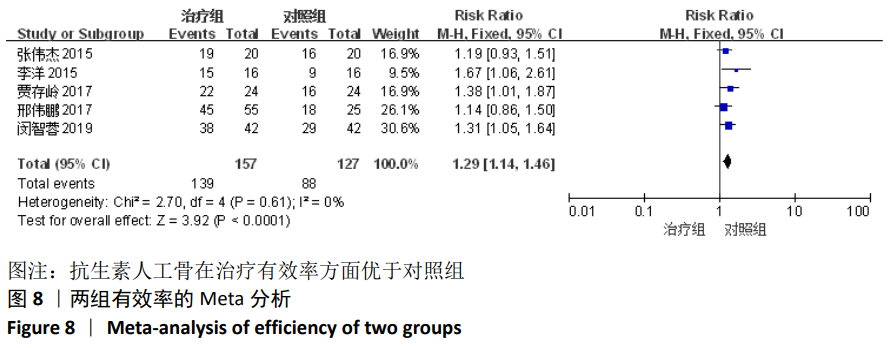
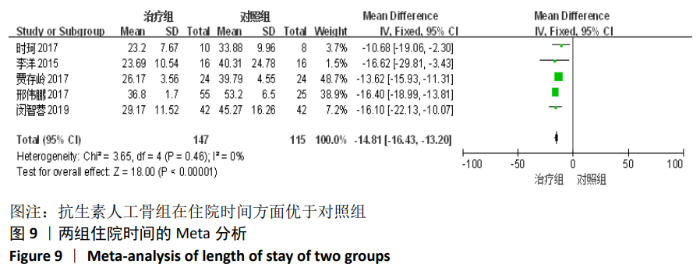
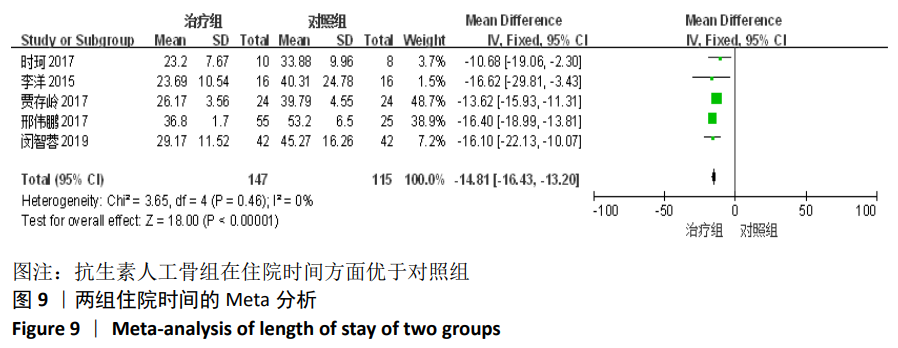
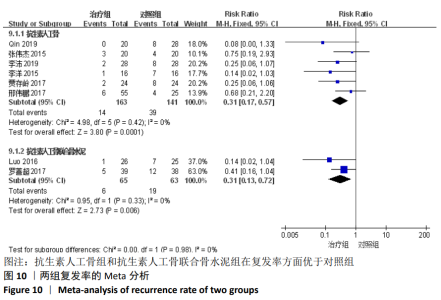
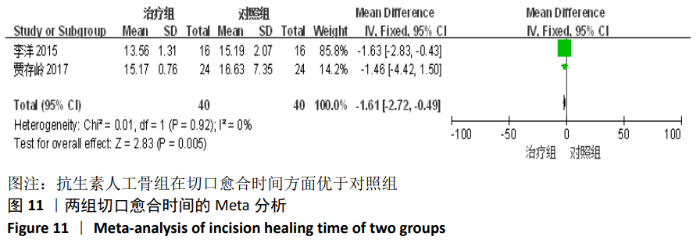
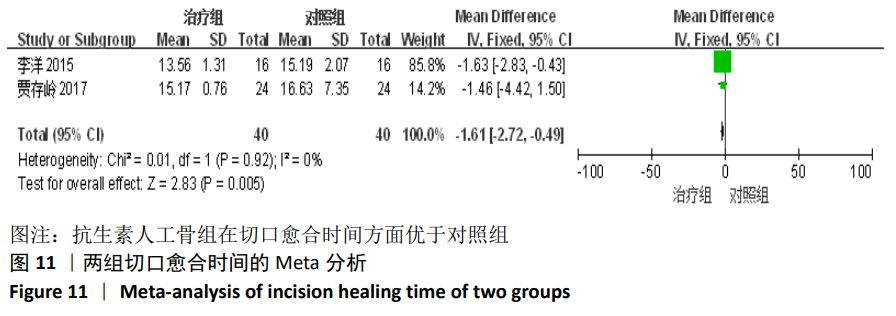
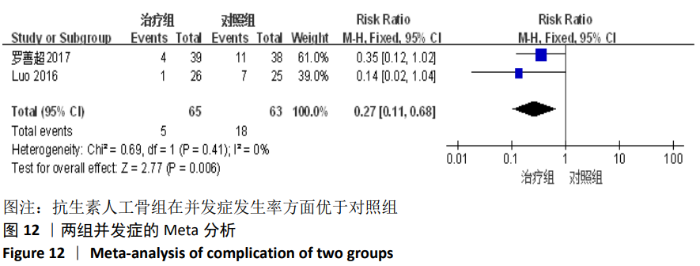
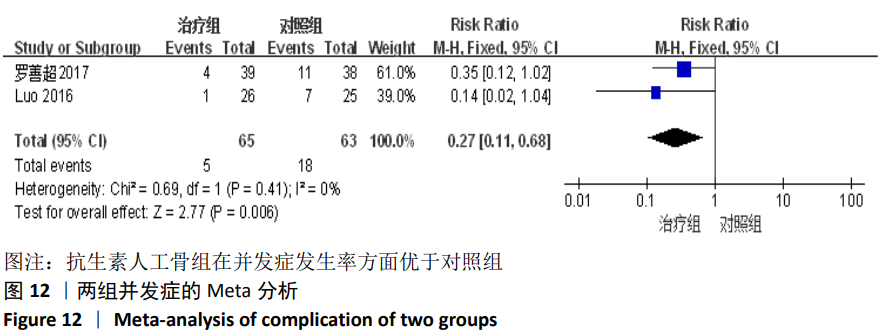
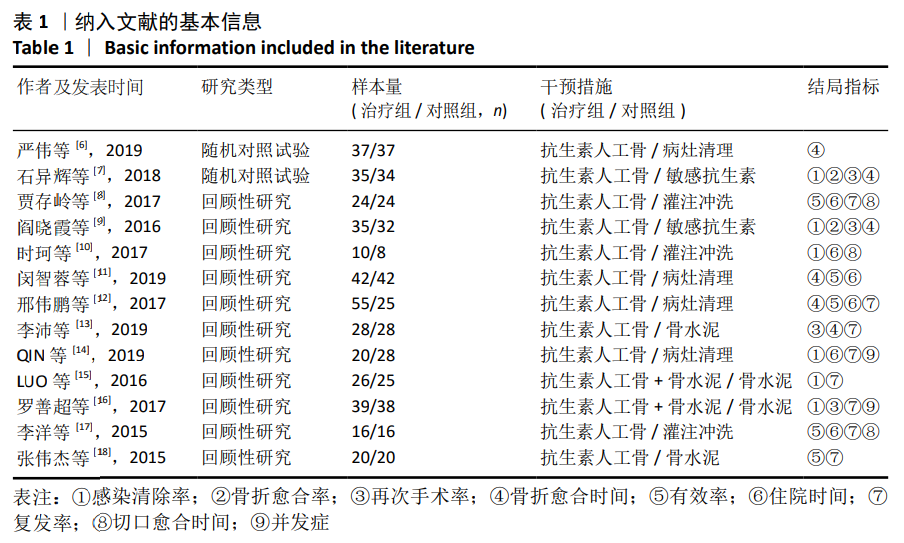
2.2 纳入文献基本情况 纳入研究的13篇文献中包含2篇随机临床对照试验和11篇回顾性研究,共有744例患者,治疗组387例,对照组357例,治疗组使用抗生素人工骨(万古霉素硫酸钙)治疗或在此基础上联合骨水泥,对照组使用敏感抗生素、灌注冲洗及骨水泥等一种方法进行治疗,纳入文献的基本信息见表1。在纳入的13篇文献中,有6篇文献报道了感染清除率[7,9-10,14-16],有2篇报道了骨折愈合率[7,9],有4篇文献报道了再次手术率[7,9,13,16],有6篇文献报道了骨折愈合时间[6-7,9,11-13],有5篇文献报道了治疗有效率[8,11-12,17-18], 有6篇文献报道了住院时间[8,10-12,14,17],有8篇文献报道了复发率[8,12-18],有3篇文献报道了切口愈合时间[8, 10, 17],有2篇文献报道了并发症发生率[15-16]。"
| [1] TSCHUDIN-SUTTER S, FREI R, DANGEL M, et al. Validation of a treatment algorithm for orthopaedic implant-related infections with device-retention-results from a prospective observational cohort study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016;22(5):451-457. [2] DYM H, ZEIDAN J. Microbiology of Acute and Chronic Osteomyelitis and Antibiotic Treatment. Dent Clin North Am. 2017; 61(2):271-282. [3] 张震,魏屹东,季明华,等.胫骨慢性骨髓炎治疗进展[J].实用骨科杂志, 2019, 25(2):146-149. [4] THABIT AK, FATANI DF, BAMAKHRAMA MS, et al. Antibiotic penetration into bone and joints: An updated review. Int J Infect Dis. 2019;81:128-136. [5] BOYLE KK, SOSA B, OSAGIE L, et al. Vancomycin-laden calcium phosphate-calcium sulfate composite allows bone formation in a rat infection model. PLoS One. 2019;14(9):e222034. [6] 严伟.万古霉素硫酸钙联合负压封闭引流对慢性骨髓炎患者红细胞沉降率、C反应蛋白的影响[J].医疗装备, 2019, 32(14):115-116. [7] 石异辉.抗生素缓释系统治疗创伤后及内固定相关骨感染的临床疗效[J].临床合理用药杂志,2018,11(24):54-56. [8] 贾存岭,贾代良,吕琳,等.载抗生素硫酸钙人工骨治疗慢性骨髓炎及其细菌学分析[J].中国病原生物学杂志, 2017, 12(5):464-469. [9] 阎晓霞,李康,朱明喜,等.万古霉素缓释系统与Wright硫酸钙对骨折内固定术后骨感染治愈率的分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2016,26(19):4491-4493. [10] 时珂.万古霉素硫酸钙治疗慢性骨髓炎临床疗效分析[D].沈阳:中国医科大学, 2017. [11] 闵智蓉.万古霉素与硫酸钙人工骨对跟骨骨折患者术后感染的疗效及其对骨折愈合的影响[J].抗感染药学, 2019,16(8):1468-1469. [12] 邢伟鹏,李无阴,田涛涛,等.抗生素硫酸钙在胫骨慢性骨髓炎中的应用[J].皖南医学院学报,2017,36(1):58-60. [13] 李沛,侯柯楠,唐锴,等.载万古霉素硫酸钙在慢性骨髓炎中的应用[J].武警后勤学院学报(医学版),2019,9:48-50. [14] QIN CH, ZHOU CH, SONG HJ, et al. Infected bone resection plus adjuvant antibiotic-impregnated calcium sulfate versus infected bone resection alone in the treatment of diabetic forefoot osteomyelitis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):246. [15] LUO S, JIANG T, YANG Y, et al. Combination therapy with vancomycin-loaded calcium sulfate and vancomycin-loaded PMMA in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):502. [16] 罗善超.万古霉素硫酸钙与万古霉素PMMA缓释系统联合治疗慢性创伤性骨髓炎[D].桂林:广西医科大学,2017. [17] 李洋.万古霉素硫酸钙与灌注冲洗治疗慢性骨髓炎的临床分析[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2015. [18] 张伟杰.载万古霉素硫酸钙治疗慢性骨髓炎的临床研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2015. [19] SENNEVILLE E, ROBINEAU O. Treatment options for diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017;18(8):759-765. [20] WU ZQ, ZENG DL, YAO JL, et al. Research Progress on Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Osteomyelitis. Chin Med Sci J. 2019; 34(3): 211-220. [21] 李文波,张超,石杰,等.慢性骨髓炎感染复发诱因的研究进展[J].实用骨科杂志, 2017,23(12):1099-1102. [22] GUPTA P, SARKAR S, DAS B, et al. Biofilm, pathogenesis and prevention--a journey to break the wall: a review. Arch Microbiol. 2016;198(1): 1-15. [23] THADDEUS CA, EMEKA OM. Whole clavicle sequestration from chronic osteomyelitis in a 10 year old boy: a case report and review of the literature. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2016;6:92-95. [24] 王步祥,杨铁翼,赵振群,等.组织工程技术在感染性骨缺损治疗中的应用及优势[J].中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(28):4543-4549. [25] 占华松,陈跃平,章晓云.骨组织工程技术治疗感染性骨缺损:优势与问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(30):4848-4854. [26] SUN PQ, MA Y, ZHANG YC, et al. Application of antibiotic impregnated beads on the patients with tibial chronic osteomyelitis. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2018; 31(6(Special)):2783-2786. [27] MASQUELET AC, KISHI T, BENKO PE. Very long-term results of post-traumatic bone defect reconstruction by the induced membrane technique. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(1):159-166. [28] WENTAO Z, LEI G, LIU Y, et al. Approach to osteomyelitis treatment with antibiotic loaded PMMA. Microb Pathog. 2017;102:42-44. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [5] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [6] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [7] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [8] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [9] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [10] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [11] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [12] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [13] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [14] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [15] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||