Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (10): 1626-1633.doi: 10.12307/2023.304
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulation of Sema3A on oral mesenchymal stem cell function
Xing Guoyi1, 2, Sun Legang1, 2, Ma Xiangrui1, Wang Wenlong1
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical College, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; 2School of Stomatology, Binzhou Medical College, Yantai 264003, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2022-04-29Accepted:2022-06-02Online:2023-04-08Published:2022-09-09 -
Contact:Sun Legang, Master, Associate professor, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical College, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; School of Stomatology, Binzhou Medical College, Yantai 264003, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Xing Guoyi, Master candidate, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical College, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; School of Stomatology, Binzhou Medical College, Yantai 264003, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Doctoral Fund of Shandong Natural Science Foundation, No. ZR2018BH026 (to MXR); General Project of Shandong Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Plan, No. 2017WS231 (to MXR); Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, No. ZR2019PH075 (to WWL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xing Guoyi, Sun Legang, Ma Xiangrui, Wang Wenlong. Regulation of Sema3A on oral mesenchymal stem cell function[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1626-1633.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
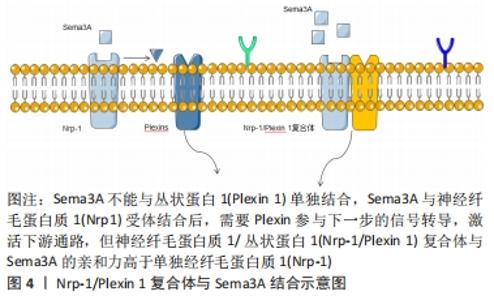
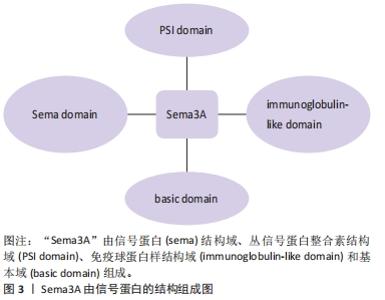
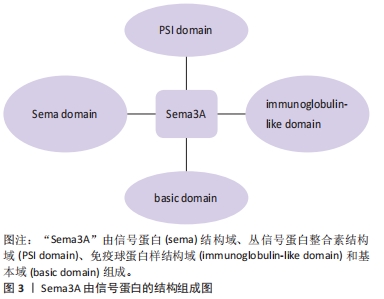
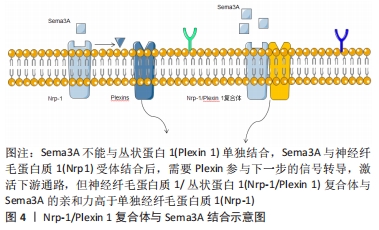
GHERARDI等[6]用隐马尔科夫模型证明“Sema”结构域是由4个二硫键将7个叶状的β螺旋拓扑结构相互连接并环绕分布,其中β-螺旋拓扑结构是“Sema”结构域的主要功能区,是特异性受体的主要结合位点,识别特异性受体后发挥主要的调控功能。早期研究发现神经纤毛蛋白质1(Nrp1)是Sema3A主要的特异性受体,Nrp1跨膜糖蛋白包括2个a1/a2CUB结构域、2个同源因子b1/b2结构域及一个MAM结构域组成的胞外结构,其中a1/a2/b1结构域是Sema3A结合的主要区域[7-8]。研究发现Nrp1不能单独发挥转导信号的作用,需要与其他膜受体结合后才能完成信号转导。丛状蛋白(Plexins)是一类跨膜蛋白,参与该信号传导过程,发挥调节细胞活性、形态等作用[9]。Sema3A与Nrp1受体结合后,需要Plexins参与下一步的信号转导,激活下游通路。而Plexin 1单独不能结合Sema3A,但Nrp-1/Plexin 1复合体与Sema3A的亲和力高于单独Nrp-1,从而发挥调节轴突的定向引导和神经细胞的迁移和聚集作用,见图4。 "
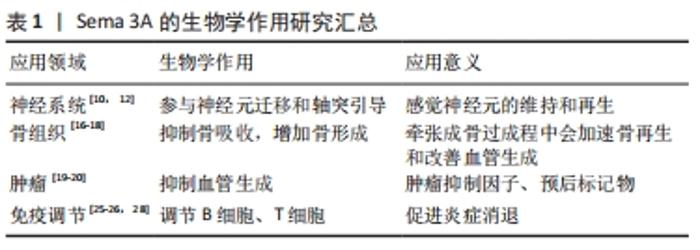
2.2 Sema3A的生物学功能 2.2.1 Sema3A参与神经系统发育中的神经元迁移和轴突引导 1993年,Sema3A首先在鸡脑中发现,并发现其诱导神经元生长锥的塌陷和瘫痪[10]。早期研究表明,Sema3A基因存在于成人中枢神经元和周围神经元的几个离散区域并持续表达[11]。进一步研究发现Sema3A在成人感觉神经元的维持和再生中发挥重要作用[12]。2004年,FENSTERMAKER等[13]培养来自Sema3A无效突变小鼠的新皮质切片,并用绿色荧光蛋白转染神经元,重建神经元,并与来自野生型和杂合子同窝仔猪的神经元进行比较,神经元的形态分析显示这些小鼠的树突长度和分支减少;此外,在野生型神经元中加入外源性Sema3A后,树突长度和分支增加。在培养的皮质神经元中,Sema3A诱导突触后密度95蛋白(PSD-95)和突触前突触蛋白Ⅰ的聚集;当Sema3A处理时,突触后密度95蛋白的簇大小增加,并观察到突触后密度95蛋白和Nrp1的广泛共存或富含肌动蛋白的突起。这些结果表明,Sema3A信号通路在促进树突状分支和脊椎成熟中起重要作用。肌萎缩侧索硬化症是一种以上下运动神经元细胞死亡为特征的神经退行性疾病。BIRGER等[14]测试了人类皮质神经元和脊髓运动神经元对Sema3A的反应,发现Sema3A提高了脊髓运动神经元的存活率;相反,Sema3A降低了皮质神经元的存活率。最终认为肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者皮质中Sema3A的上调或脊髓中的下调都可能直接导致肌萎缩侧索硬化症患者的运动神经元丢失。 2.2.2 Sema3A与骨骼的发育及形成有着密切联系 早期研究发现通过同源重组产生Sema3A缺陷小鼠,发现被敲除Sema3A基因的大鼠出现骨骼发育异常[15]。骨组织在人类一生中不断更新,这一过程称为骨重建,它主要发生在骨表面,包括成骨细胞性骨形成和破骨细胞性骨吸收,这种重建不仅是正常骨量和强度的平衡,也是矿物质动态平衡的平衡。如果骨形成和骨吸收之间的平衡被破坏,就会导致骨质疏松症、骨化症、骨坏死等骨病。随后有研究表明,Sema3A可同步调控骨吸收和骨形成,抑制骨吸收,增加骨形成,发挥骨保护作用,还可通过调节破骨细胞活性参与小鼠牙齿萌出[16]。有研究发现,清除骨髓内造血干细胞会导致骨髓内皮细胞上调Sema3A的表达,其受体Nrp1和Sema3A-Nrp1信号促进骨髓内皮细胞凋亡和延缓骨髓血管再生。通过基因或药物抑制Sema3A-Nrp1信号可增加骨髓内皮细胞存活,加速去髓小鼠骨髓血管再生,并协同驱动造血干细胞再生和早期造血重建[17]。有研究发现在牵张成骨过成程中Sema3A会加速骨再生和改善血管生成[18]。因此,在Sema3A在生物组织工程骨修复及再生领域可以扮演极其重要的角色。 2.2.3 Sema3A在肿瘤治疗和预后检测方面有着不错的前景 血管生成对于肿瘤的发展和进展至关重要,并受血管内皮生长因子和信号素的调节,特别是Sema3A通过影响内皮生长因子信号传导来抑制血管生成。Sema3A表达和血管内皮生长因子/Sema3A比率被证明是受皮肤黑色素瘤影响患者的有价值的预后生物标志物。Sema3A可能作为皮肤黑色素瘤治疗中的候选肿瘤抑制因子[19]。不仅如此,HUANG等[20]发现Sema3A是一种有效的肿瘤血管生成抑制剂,其试验将构建LentiSema3A-EGFP转导至舌鳞状细胞癌细胞系SSC-9,用内皮细胞管形成和绒膜尿囊膜实验进行血管生成测定,并使用肿瘤异种移植模型评估Sema3A对肿瘤生长的影响,最终在体外和体内实验发现,尿囊绒膜实验分析显示Sema3A显著抑制了内皮细胞管形成并减少了血管生成,进而有效表明Sema3A可以显著抑制肿瘤的生长。此外,TIAN等[21]通过提取《癌症基因组图集-头颈部鳞状细胞癌(TCGA-HNSC)》中的第3级舌鳞状细胞癌细胞数据,与邻近的正常组织相比,发现在被检查的20个Sema基因中,舌鳞状细胞癌组织中有7个显著上调,而8个则显著减少,然后进一步就无复发生存率在多变量分析中得出,Sema3A是惟一具有独立预后价值的基因,其外显子9在复发方面与总的Sema3A表达和单独表达相比具有更好的预后价值 (HR=2.193,95% CI:1.463-3.290,P < 0.001),因此,Sema3A的外显子9表达可以成为舌鳞状细胞癌患者无复发生存率不利的潜在预后标志物。另外,Sema3A还可作为潜在的尿路上皮癌非侵入性标志物。有研究人员发现尿路上皮癌患者尿液中的Sema3A水平升高,通过进一步实验发现,在正常膀胱组织中,黏膜基底层呈现非常浅的Sema3A染色,而在顶端层完全消失;在低级别肿瘤样本中,黏膜基底层的细胞也被Sema3A轻微染色,但 Sema3A 表达在顶端移动时增强,在顶端细胞脱落到尿液中时达到最高水平;在高级别尿路上皮肿瘤中,Sema 3A染色在整个黏膜厚度中都很强烈[22]。最近有研究人员发现Sema3A表达与鼻咽癌患者的不良预后相关,可能促进鼻咽癌的肿瘤进展[23];另外,YAMADA等[24]发现,在小鼠肺癌干细胞中,敲除Sema3A可显著降低干细胞标志物的表达,并完全消除致瘤性和自我更新能力。 2.2.4 Sema3A具有一定的免疫调控和促进炎症消退的作用 AVOUAC等[25]研究发现,3类信号素在类风湿关节炎内皮细胞中有明显的差异表达,在类风湿关节炎患者的血清中观察到Sema4A和Sema3E分别增加1.30倍和1.54倍,以及Sema3A减少24%。目前,越来越多的研究证实Sema3A参与免疫调节。有实验表明,当将Sema3A加入到树突状细胞和T细胞的共培养时,它显著抑制同种异体T细胞的增殖。此外,通过直接作用于T细胞,Sema3A阻断了抗CD3/CD28诱导的T细胞增殖;相反,当内源性Sema3A被封闭抗体中和时,可以看到T细胞增殖的逆转,表明了Sema3A对T细胞增殖起抑制作用[26]。另外,Sema3A也被发现参与人类胸腺细胞迁移的调节,并被证明抑制CXCL12触发的趋化性[27]。同样,在免疫应答中Sema3A对B细胞有调节作用。Sema3A通常与B细胞结合后下调CD100的表达,上调CD72的表达。当与Sema3A共同培养时,CD19+CD25高表达的调节性B细胞中白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β的表达增强;Sema3A通过上调B细胞上CD72的表达来增强调节性B细胞的特性。调节性B细胞可通过细胞间直接接触和分泌白细胞介素10等方式下调免疫应答[28]。RIENKS等[29]比较心肌梗死后Sema3A杂合子和野生型小鼠,发现与野生型小鼠相比,Sema3A杂合子小鼠心脏组织中白细胞的存在增加,其余未有明显差异,然后在体外实验中发现,重组Sema3A蛋白能够影响培养的骨髓源性巨噬细胞的促炎状态,进而表明Sema3A可以通过促进炎症消退来减少心肌炎症,改善心肌梗死后的心功能。此外,ADI等[30]将Sema3A注射在哮喘小鼠模型中,发现在这种哮喘模型中,Sema3A可以有效抑制哮喘相关的炎症。 Sema3A在生物学多个领域发挥重要作用。在神经系统领域参与神经元迁移和轴突引导,可以应用于感觉神经元的维持和再生;在骨再生领域抑制骨吸收,增加骨形成,牵张成骨过成程中会加速骨再生和改善血管生成;在肿瘤领域发挥抑制血管生成作用,可以应用于肿瘤抑制因子、预后标记物;在免疫调节领域,发挥调节B细胞、T细胞作用, 从而促进炎症消退,见表1。 "
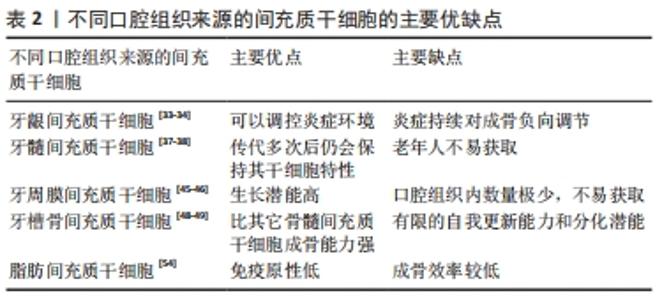
2.3 典型的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在促进间充质干细胞成骨分化中起重要作用 因为Wnt信号通路也是Sema3A调控的成骨细胞的通路,所以,Sema3A可能在调控间充质干细胞分化中发挥重要作用[31]。由此进一步推断Sema3A在调控口腔组织来源的间充质干细胞中可能发挥重要作用。口腔组织来源的间充质干细胞包括牙龈、牙髓、牙周膜、牙槽骨骨髓和脂肪间充质干细胞等。 2.3.1 牙龈间充质干细胞 研究表明,在牙龈的固有层中有细胞表达一组间充质干细胞表面标志物,如CD44,CD73,CD90和CD105,不表达造血干细胞标志物CD14,CD34和CD45[32]。牙龈间充质干细胞具有易于获取,增殖率高等优点,与其他干细胞相比,扩增周期显著较短,可在短时间内大量扩增获得应用于临床治疗的细胞数量。牙龈间充质干细胞自身具有一定的加速组织修复和抑炎作用。HONG等[33]研究报告指出牙龈间充质干细胞可抑制高脂血症相关性牙周炎小鼠模型中M1巨噬细胞的活化,调节脂质代谢,降低炎症反应,促进骨骼再生,表明牙龈间充质干细胞可以调控炎症环境。前期研究发现,在炎症的早期阶段可以刺激牙龈间充质干细胞的增殖,但随着炎症的持续,这种积极正调节作用消失,随之而来的是对成骨的负向调节[34]。另有研究报告表明,抗坏血酸可以增强牙龈间充质干细胞的增殖和分化特性,而抗坏血酸促进诱导细胞增殖和分化需要一个无炎症的微环境[35]。由上可知,如果在炎症环境下能依旧增强牙龈间充质干细胞的增殖和分化特性,将显著提高用于临床的可行性。 2.3.2 牙髓间充质干细胞 在2000年,GRONTHOS等[36]首次在牙髓中分离出牙髓间充质干细胞,并且证实该细胞符合关于间充质干细胞的所有标准。有研究发现牙髓间充质干细胞增殖能力十分显著,传代多次后仍会保持其干细胞特性[37]。牙髓间充质干细胞具备高度的分化增殖能力,与生物材料间存在积极的相互作用,获取简单高效,但除智齿或正畸牙齿外,为牙髓间充质干细胞提取各自的健全牙齿是不现实和不符合临床伦理的。具体而言,在老年患者中,由于生理性2次牙本质生成和病理性3次牙本质生成以及矿化(包括牙列和牙髓结石)导致的与年龄相关的牙髓组织收缩限制了牙髓间充质干细胞的获得,除了数量减少外,分化和再生能力也受到不利干扰[38]。此外,牙髓干细胞也具有免疫调节功能和具有生成牙本质的能力[39],促进牙本质-牙髓再生。 2.3.3 牙周膜间充质干细胞 牙周膜是围绕牙根的结缔组织,在将牙齿固定在牙槽骨上、调节牙齿的正常稳态、修复和营养方面有着至关重要的作用[40]。起初,牙周膜间充质干细胞被认为是来源于靠近血管和骨内膜的干细胞群中。在2004年,间充质干细胞首次在来自人类牙周韧带组织的细胞中被鉴定出来[41]。此后,许多研究人员成功地从人类和动物身上分离出了牙周膜间充质干细胞,并对其进行了详细地表征。一些研究报告了人牙周膜间充质干细胞高表达的间充质干细胞相关标记,如CD10,CD26,CD29,CD73,CD349/FZD9,CD44,CD73和CD90,而CD146仅在人牙周膜间充质干细胞中强烈表达[42],表明CD146可能是鉴定人牙周膜间充质干细胞的重要细胞表面分子。牙周膜间充质干细胞被认为是一种极有前景的生物工程的干细胞,例如,LEE等[43]研究发现牙周膜间充质干细胞可以转分化为功能性胰岛样细胞,并为胰腺修复提供新的替代细胞群。令人惊讶的是,牙周膜间充质干细胞具有与骨髓间充质干细胞相似的特征,并表现出自我更新能力和多能性[44],但人类牙周膜间充质干细胞显示出比人类骨髓间充质干细胞和人类牙髓干细胞更高的生长潜力[45]。然而,由于个体间牙周膜间充质干细胞的生长和分化潜力不同,从一个患者来源中分离出足够数量的高质量牙周膜间充质干细胞存在技术上的困难,其稀缺性阻碍了基础和临床研究的进展[46]。由于牙周膜间充质干细胞具有在体内生成牙骨质和聚乳酸样组织的能力,将牙周膜间充质干细胞与组织工程技术结合使用,有潜力成为一种极具价值的牙周再生治疗新策略。 2.3.4 牙槽骨骨髓间充质干细胞 骨髓间充质干细胞主要来源于骨髓中非造血干细胞,具有分化为成骨细胞、软骨细胞、脂肪细胞、骨细胞和成肌细胞等多种细胞类型的潜能[47]。随着年龄的增加,骨髓间充质干细胞数量减少、向成骨细胞分化的能力下降及向脂肪细胞分化的能力增强,导致骨量下降,是原发性骨质疏松症的病理机制之一。牙槽骨骨髓间充质干细胞来源于口腔内上下颌牙槽骨中,其表面标志物与其它骨髓间充质干细胞有部分相同,如CD13,CD73,CD44和CD90为阳性。牙槽骨骨髓间充质干细胞与一般骨髓间充质干细胞的基本特性一致:具有自我复制的能力和多向分化的能力,但其具有高度可变和有限的自我更新能力和分化潜能,并且在体外连续繁殖过程中表现出可变的形态和复制衰老[48]。有实验表明体外相同的诱导条件下,牙槽骨骨髓间充质干细胞与其它骨髓间充质干细胞比较,成骨能力更强,在成脂潜能方面相对较差[49],因此,牙槽骨骨髓间充质干细胞帮助牙周炎患者牙槽骨再生修复有着独特的优势。 2.3.5 脂肪间充质干细胞 脂肪间充质干细胞是来源于中胚层的一种成体干细胞,其主要存在于脂肪组织中,尽管口腔内的脂肪组织含量相对较少,但在口腔内依然可以分离出脂肪间充质干细胞。2001年,ZUK等[50]首次在人脂肪组织中分离出具有某种特点的细胞群,经过体外培养后,发现这些细胞的增殖中呈现出倍增效应和低衰老性,并具备多向分化的特性,将其命名为脂肪干细胞。相对于骨髓间充质干细胞表达来说,脂肪间充质干细胞与其表达的表面标志不完全相符,如:脂肪间充质干细胞表达CD49d,不表达CD106,而骨髓间充质干细胞则正好相反;由于脂肪间充质干细胞不表达CD45和CD31,表明其无造血干细胞特性;脂肪间充质干细胞不表达HLA-DR和一类MHC分子,说明其免疫原性低,可进行同种异体移植;除此以外,脂肪间充质干细胞还表达胚胎干细胞的标记物,例如Nanog和REX-1等,这可能成为脂肪间充质干细胞跨胚层分化的分子基础[51]。脂肪间充质干细胞可以从脂肪组织中分离出来,注入或包裹在生物材料中植入伤口,可以提高愈合率,并能直接分化为特定的细胞系,它们是骨髓间充质干细胞的绝佳替代品[52]。在再生牙科中,脂肪间充质干细胞已经在动物模型中被评估其分化牙槽骨、牙周韧带、牙骨质和牙髓的能力[53]。与其它间充质干细胞相比,脂肪干细胞由于其缺乏免疫排斥和具有稳定的多向分化而被大量研究。然而,进一步研究发现脂肪间充质干细胞成骨效率较低,且极具成脂倾向[54]。 口腔组织来源的间充质干细胞有着各自的优点及局限,牙龈间充质干细胞主要优点是可以调控炎症环境,主要缺点是炎症持续会对成骨负向调节;牙髓间充质干细胞主要优点是传代多次后仍会保持其干细胞特性,主要缺点是在老年人中不易获取;牙周膜间充质干细胞主要优点是生长潜能高,主要缺点是口腔组织内数量极少,不易获取;牙槽骨间充质干细胞主要优点是比其它骨髓间充质干细胞成骨能力强,主要缺点是有限的自我更新能力和分化潜能;脂肪间充质干细胞主要优点是免疫原性低,主要缺点是成骨效率较低,如表2。 "


2.4 Sema3A对口腔间充质干细胞的作用 2.4.1 Sema3A可在炎症环境下促进牙龈间充质干细胞增殖及成骨分化 有研究表明,通过病毒转染的方式将Sema3A基因整合到牙龈间充质干细胞的基因组中,发现Sema3A正向促进牙龈间充质干细胞的成骨分化,同时负向调节破骨前体细胞的分化,并且该实验表明在脂多糖诱导的炎症环境中,Sema3A的过表达促进了牙龈间充质干细胞增殖和成骨基因的表达[55]。这表明在Sema3A作用下,对牙龈间充质干细胞应用于临床治疗可行性具有重大意义。虽然目前在炎症刺激下Sema3A对牙龈间充质干细胞的相关作用机制尚未明确,只要进一步深入研究炎症环境下Sema3A对牙龈间充质干细胞生命活动的信号转导机制,发现促进干细胞定向分化的新技术,确定Sema3A临床治疗的作用靶点,将可为牙周炎的治疗提供新依据。 2.4.2 Sema3A可调控牙髓炎并促进牙髓间充质干细胞增殖分化 有研究表明,通过经典的Wnt /β-catenin途径调节牙髓间充质干细胞分化及矿化,NRP1可以作为成牙本质细胞分化的启动子[56]。YOSHIDA等[57]研究发现,在成熟的大鼠牙髓组织和人牙髓干细胞中有表达Sema3A/Nrp1,并证实了Sema3A可以有效诱导牙髓间充质干细胞的细胞迁移、趋化、增殖和成牙细胞分化,并可以强化典型的Wnt/βcatenin信号通路。该实验发现在大鼠牙髓暴露模型中,Sema3A能使牙髓暴露部位形成新的牙本质小管和排列整齐的成牙细胞样细胞层,并且在直接盖髓后4周,新型修复性牙本质几乎完全可以覆盖牙髓暴露组织。此外,有研究发现,肿瘤坏死因子α作用于人牙髓细胞可以产生Sema3A,Sema3A可以有效抑制肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的白细胞介素6和CXCL10的产生,并抑制核转录因子κB的激活。由上提示,Sema3A可能调控牙髓炎症,而根尖周炎是大部分一种来自于牙髓炎症后的继发疾病,伴随根尖区周围的骨质破坏。有学者进一步研究了Sema3A/Nrp1在根尖周炎中的表达及其与骨破坏的相关性,发现Sema3A/Nrp1在根尖周病变中的表达降低,可能参与根尖周区域的骨吸收[58],提示Sema3A/Nrp1可能进一步参与根尖周炎的病理发展。因此有理由认为,Sema3A参与牙髓炎及根尖周炎调控,并且对牙髓干细胞和在牙髓治疗中有着重要的影响,可作为靶点开发牙本质-牙髓复合体再生的新药物,也可成为新一代盖髓治疗的新选择。 2.4.3 Sema3A可以诱导牙周膜细胞分化成牙周膜间充质干细胞并维持其干性 MENICANIN等[59]证明牙周膜间充质干细胞在体内和体外均表现出高的自我更新潜能。有研究证实了Sema3A及其受体在小鼠牙周韧带组织和人牙周韧带细胞中的表达。有趣的是,多潜能人牙周膜细胞株与一个低潜能的人牙周膜细胞系相比,高表达了Sema3A,这表明了Sema3A在调节牙周膜间充质干细胞的干细胞特性方面的重要性。Sema3A基因的诱导可以提高牙周膜细胞系多分化潜能。有研究表明,Sema3A可能具有将牙周膜细胞转化为间充质干细胞样细胞的功能,并且Sema3A在保持牙周膜相关基因表达的同时诱导牙周膜细胞的干细胞特性,Sema3A过表达的牙周膜细胞表现出增强的分化成功能性成骨细胞和脂肪细胞的能力[60]。因此Sema3A刺激的牙周膜细胞比来自其他细胞系的干细胞群或重编程的干细胞群更适合牙周组织再生。最新研究发现,缺氧环境会导致牙周膜间充质成骨分化减弱,而Sema3A可以提高牙在缺氧环境下牙周膜间充质成骨分化能力[61]。由此,Sema3A可解决牙周膜间充质干细胞来源不足问题,为其在组织工程领域研究提供基础。 2.4.4 Sema3A可能在炎症环境下调控人牙槽骨间充质干细胞成骨分化 现有的大量研究已指出骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化相关信号通路,如Wnt/β-catenin信号通路、BMP/Smad信号通路、PI3K/Akt信号通路等[62]。QIAO等[63]表明Sema3A刺激对骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖或迁移没有影响,但是Sema3A刺激显著增加了成骨相关基因的表达,包括Ⅰ型胶原、碱性磷酸酶、Runt-related转录因子2(RUNX2)、骨形成蛋白和骨钙素,此外,通过Sema3A刺激,骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨能力也增加。另外,LIU等[64]研究发现Sema3A可促进牙槽骨骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。令人惊奇的是,有研究表明,Sema3A通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进炎症环境下中大鼠骨髓间充质的成骨分化[65]。由此可推测,在炎症环境下Sema3A可能具有刺激牙槽骨骨髓间充质干细胞成骨的能力,这将在临床牙槽骨组织再生领域具有重大意义。 2.4.5 Sema3A增强脂肪间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力 LIU等[66]通过体外分析表明,在脂肪间充质干细胞中过表达Sema3A显著增强骨相关基因的表达和细胞外基质钙沉积,同时降低脂肪相关基因的表达。然后将Sema3A修饰的脂肪间充质干细胞移植到聚乳酸-羟基乙酸支架中,修复大鼠模型临界大小的颅骨缺损,进一步研究发现,Sema3A修饰的脂肪间充质干细胞显著促进新骨形成,且骨体积分数和骨密度均较高。此外,文章发现Sema3A可以同时增加多个Wnt相关基因,从而激活Wnt通路,由此可知,Sema3A是成骨表型的关键基因。在口腔种植方面,钛种植体被认为是替换缺失牙齿的最佳选择,但在2型糖尿病患者中仍难以获得足够的骨整合,FANG等[67]将Sema3A改良的脂肪间充质干细胞片包裹在钛植入物周围,随后将其插入胫骨,然后再将大鼠暴露于Sema3A刺激下,此研究表明,Sema3A修饰的脂肪间充质干细胞片可用于改善2型糖尿病条件下的骨整合;另外,将大鼠暴露于Sema3A刺激下发现,脂肪间充质干细胞的形态和增殖能力保持不变,然而,它们的成骨分化能力增加了。因此,Sema3A可提高脂肪间充质干细胞的成骨效率。"

| [1] FU X, LIU G, HALIM A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell migration and tissue repair. Cells. 2019;8(8):784. [2] ZHOU LL, LIU W, WU YM, et al. Oral mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells: the immunomodulatory masters. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020: 1327405. [3] BOTELHO J, CAVACAS MA, MACHADO V, et al. Dental stem cells: recent progresses in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Ann Med. 2017;49(8):644-651. [4] KOLODKIN AL, MATTHES DJ, GOODMAN CS. The semaphorin genes encode a family of transmembrane and secreted growth cone guidance molecules. Cell. 1993;75(7):1389-1399. [5] FIORE R, PUSCHEL AW. The function of semaphorins during nervous system development. Front Biosci. 2003;8:s484-s499. [6] GHERARDI E, YOULES ME, MIGUEL RN, et al. Functional map and domain structure of MET, the product of the c-met protooncogene and receptor for hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(21):12039-12044. [7] KOLODKIN AL, LEVENGOOD DV, ROWE EG, et al. Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell. 1997;90(4):753-762. [8] ROHM B, OTTEMEYER A, LOHRUM M, et al. Plexin/neuropilin complexes mediate repulsion by the axonal guidance signal semaphorin 3A. Mech Dev. 2000;93(1-2):95-104. [9] HOTA PK, BUCK M. Plexin structures are coming: opportunities for multilevel investigations of semaphorin guidance receptors, their cell signaling mechanisms, and functions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012;69(22): 3765-3805. [10] LUO Y, RAIBLE D, RAPER JA. Collapsin: a protein in brain that induces the collapse and paralysis of neuronal growth cones. Cell. 1993;75(2): 217-227. [11] GIGER RJ, WOLFER DP, DE WIT GM, et al. Anatomy of rat semaphorin III/collapsin-1 mRNA expression and relationship to developing nerve tracts during neuroembryogenesis. J Comp Neurol. 1996;375(3):378-392. [12] GAVAZZI I. Semaphorin-neuropilin-1 interactions in plasticity and regeneration of adult neurons. Cell Tissue Res. 2001;305(2):275-284. [13] FENSTERMAKER V, CHEN Y, GHOSH A, et al. Regulation of dendritic length and branching by semaphorin 3A. J Neurobiol. 2004;58(3):403-412. [14] BIRGER A, OTTOLENGHI M, PEREZ L, et al. ALS-related human cortical and motor neurons survival is differentially affected bySema3A. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(3):256. [15] BEHAR O, GOLDEN JA, MASHIMO H, et al. Semaphorin III is needed for normal patterning and growth of nerves, bones and heart. Nature. 1996;383(6600):525-528. [16] YU X, ZHENG F, DU Y, et al. Semaphorin 3A gets involved in the establishment of mouse tooth eruptive pathway. J Mol Histol. 2019; 50(5):427-434. [17] TERMINI CM, PANG A, FANG T, et al. Neuropilin 1 regulates bone marrow vascular regeneration and hematopoietic reconstitution. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):6990. [18] ZHANG N, HUA Y, LI Y, et al. Sema3Aaccelerates bone formation during distraction osteogenesis in mice. Connect Tissue Res. 2021:1-11. [19] LUCARINI G, SIMONETTI O, LAZZARINI R, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor/semaphorin-3A ratio andSema3Aexpression in cutaneous malignant melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2020;30(5):433-442. [20] HUANG C, WANG Y, HUANG JH, et al. Sema3A drastically suppresses tumor growth in oral cancer Xenograft model of mice. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017;18(1):55. [21] TIAN T, ZHANG L, TANG K, et al. Sema3A Exon 9 expression is a potential prognostic marker of unfavorable recurrence-free survival in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma. DNA Cell Biol. 2020;39(4):555-562. [22] BEJAR I, RUBINSTEIN J, BEJAR J, et al. Expression of semaphorin 3A in malignant and normal bladder tissue: immunohistochemistry staining and morphometric evaluation. Biology (Basel). 2021;10(2):109. [23] IMOTO T, KONDO S, WAKISAKA N, et al. Overexpression of semaphorin 3A is a marker associated with poor prognosis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Microorganisms. 2020;8(3):423. [24] YAMADA D, TAKAHASHI K, KAWAHARA K, et al. Autocrine Semaphorin3A signaling is essential for the maintenance of stem-like cells in lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;480(3):375-379. [25] AVOUAC J, PEZET S, VANDEBEUQUE E, et al. Semaphorins: from angiogenesis to inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73(9):1579-1588. [26] CATALANO A, CAPRARI P, MORETTI S, et al. Semaphorin-3A is expressed by tumor cells and alters T-cell signal transduction and function. Blood. 2006;107(8):3321-3329. [27] GARCIA F, LEPELLETIER Y, SMANIOTTO S, et al. Inhibitory effect of semaphorin-3A, a known axon guidance molecule, in the human thymocyte migration induced by CXCL12. J Leukoc Biol. 2012;91(1):7-13. [28] VADASZ Z, HAJ T, TOUBI E. The role of B regulatory cells and Semaphorin3A in atopic diseases. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2014; 163(4):245-251. [29] RIENKS M, CARAI P, BITSCH N, et al. Sema3Apromotes the resolution of cardiac inflammation after myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol. 2017;112(4):42. [30] ADI SD, EIZA N, BEJAR J, et al. Semaphorin 3A is effective in reducing both inflammation and angiogenesis in a mouse model of bronchial asthma. Front Immunol. 2019;10:550. [31] CASE N, RUBIN J. Beta-catenin--a supporting role in the skeleton. J Cell Biochem. 2010;110(3):545-553. [32] EL-SAYED KM, PARIS S, GRAETZ C, et al. Isolation and characterisation of human gingival margin-derived STRO-1/MACS(+) and MACS(-) cell populations. Int J Oral Sci. 2015;7(2):80-88. [33] HONG R, WANG Z, SUI A, et al. Gingival mesenchymal stem cells attenuate pro-inflammatory macrophages stimulated with oxidized low-density lipoprotein and modulate lipid metabolism. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;98:92-98. [34] ZHANG F, SI M, WANG H, et al. IL-1/TNF-alpha inflammatory and anti-inflammatory synchronization affects gingival stem/progenitor cells’ regenerative attributes. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:1349481. [35] FAWZY EL-SAYED KM, NGUYEN N, DöRFER CE. Ascorbic acid, inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β/TNF-α/IFN-γ), or their combination’s effect on stemness, proliferation, and differentiation of gingival mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020: 8897138. [36] GRONTHOS S, MANKANI M, BRAHIM J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630. [37] NUTI N, CORALLO C, CHAN BM, et al. Multipotent differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells: a literature review. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2016;12(5):511-523. [38] TAKEDA T, TEZUKA Y, HORIUCHI M, et al. Characterization of dental pulp stem cells of human tooth germs. J Dent Res. 2008;87(7):676-681. [39] TOMASELLO L, MAUCERI R, COPPOLA A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from inflamed dental pulpal and gingival tissue: a potential application for bone formation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017; 8(1):179. [40] CARNES DL, MAEDER CL, GRAVES DT. Cells with osteoblastic phenotypes can be explanted from human gingiva and periodontal ligament. J Periodontol. 1997;68(7):701-707. [41] SEO BM, MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet. 2004; 364(9429):149-155. [42] IWASAKI K, KOMAKI M, YOKOYAMA N, et al. Periodontal ligament stem cells possess the characteristics of pericytes. J Periodontol. 2013; 84(10):1425-1433. [43] LEE JS, AN SY, KWON IK, et al. Transdifferentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells into pancreatic cell lineage. Cell Biochem Funct. 2014;32(7):605-611. [44] TOMOKIYO A, WADA N, MAEDA H. Periodontal ligament stem cells: regenerative potency in periodontium. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(15): 974-985. [45] ELEUTERIO E, TRUBIANI O, SULPIZIO M, et al. Proteome of human stem cells from periodontal ligament and dental pulp. PLoS One. 2013; 8(8):e71101. [46] HASEGAWA D, HASEGAWA K, KANEKO H, et al. MEST regulates the stemness of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:9672673. [47] LI Y, YANG F, GAO M, et al. miR-149-3p regulates the switch between adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by targeting FTO. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;17:590-600. [48] WAGNER W, HORN P, CASTOLDI M, et al. Replicative senescence of mesenchymal stem cells: a continuous and organized process. PLoS One. 2008;3(5):e2213. [49] HUANG X, CHENG B, SONG W, et al. Superior CKIP-1 sensitivity of orofacial bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells in proliferation and osteogenic differentiation compared to long bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(2):1169-1178. [50] ZUK PA, ZHU M, MIZUNO H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001; 7(2):211-228. [51] CHU DT, NGUYEN THI PHUONG T, TIEN NLB, et al. Adipose tissue stem cells for therapy: an update on the progress of isolation, culture, storage, and clinical application. J Clin Med. 2019;8(7):917. [52] STORTI G, SCIOLI MG, KIM BS, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells in bone tissue engineering: useful tools with new applications. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:3673857. [53] GAUR S, AGNIHOTRI R. Application of adipose tissue stem cells in regenerative dentistry: a systematic review. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2021;11(3):266-271. [54] KANG BJ, RYU HH, PARK SS, et al. Comparing the osteogenic potential of canine mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissues, bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, and Wharton’s jelly for treating bone defects. J Vet Sci. 2012;13(3):299-310. [55] TIAN T, TANG K, WANG A, et al. The effects of Sema3Aoverexpression on the proliferation and differentiation of rat gingival mesenchymal stem cells in the LPS-induced inflammatory environment. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019;12(10):3710-3718. [56] SONG Y, LIU X, FENG X, et al. NRP1 accelerates odontoblast differentiation of dental pulp stem cells through classical Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cell Reprogram. 2017;19(5):324-330. [57] YOSHIDA S, WADA N, HASEGAWA D, et al. Semaphorin 3A induces odontoblastic phenotype in dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 2016; 95(11):1282-1290. [58] LIN Y, XING Q, QIN W, et al. Decreased expression of Semaphorin3A/Neuropilin-1 signaling axis in apical periodontitis. Biomed Res Int. 2017; 2017:8724503. [59] MENICANIN D, BARTOLD PM, ZANNETTINO AC, et al. Identification of a common gene expression signature associated with immature clonal mesenchymal cell populations derived from bone marrow and dental tissues. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(10):1501-1510. [60] WADA N, MAEDA H, HASEGAWA D, et al. Semaphorin 3A induces mesenchymal-stem-like properties in human periodontal ligament cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(18):2225-2236. [61] CHANG X, ZHOU F, BU L, et al. Semaphorin 3A attenuates the hypoxia suppression of osteogenesis in periodontal ligament stem cells. J Periodontal Res. 2022;57(2):425-433. [62] 姜朝阳,谢兴文,徐世红,等.骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化相关信号通路[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2020,13(5):473-478. [63] QIAO Q, XU X, SONG Y, et al. Semaphorin 3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSC from type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. J Mol Histol. 2018;49(4):369-376. [64] LIU L, WANG J, SONG X, et al. Semaphorin 3A promotes osteogenic differentiation in human alveolar bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(4):3489-3494. [65] SUN Z, YAN K, LIU S, et al. Semaphorin 3A promotes the osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in inflammatory environments by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Mol Histol. 2021;52(6):1245-1255. [66] LIU X, TAN N, ZHOU Y, et al. Semaphorin 3A shifts adipose mesenchymal stem cells towards osteogenic phenotype and promotes bone regeneration in vivo. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:2545214. [67] FANG K, SONG W, WANG L, et al. Semaphorin 3A-modified adipose-derived stem cell sheet may improve osseointegration in a type 2 diabetes mellitus rat model. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(3):2449-2456. [68] FUKUDA T, TAKEDA S, XU R, et al. Sema3A regulates bone-mass accrual through sensory innervations. Nature. 2013;497(7450):490-493. [69] HAYASHI M, NAKASHIMA T, YOSHIMURA N, et al. Autoregulation of osteocyte Sema3A orchestrates estrogen action and counteracts bone aging. Cell Metab. 2019;29(3):627-637.e625. [70] ŞEN S, LUX CJ, ERBER R. A Potential Role of Semaphorin 3A during Orthodontic Tooth Movement. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8297. |
| [1] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [2] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [3] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [4] | Yang Yitian, Wang Lu, Yao Wei, Zhao Bin. Application of the interaction between biological scaffolds and macrophages in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [5] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [6] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [7] | Li Xinyue, Li Xiheng, Mao Tianjiao, Tang Liang, Li Jiang. Three-dimensional culture affects morphology, activity and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| [8] | Yuan Wei, Liu Jingdong, Xu Guanghui, Kang Jian, Li Fuping, Wang Yingjie, Zhi Zhongzheng, Li Guanwu. Osteogenic differentiation of human perivascular stem cells and its regulation based on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 866-871. |
| [9] | Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877. |
| [10] | Hao Liufang, Duan Hongmei, Wang Zijue, Hao Fei, Hao Peng, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Yang Zhaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Spatiotemporal dynamic changes of ependymal cells after spinal cord injury in transgenic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [11] | Zhang Qijian, Xu Ximing. Acquisition and application of ectodermal mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 928-934. |
| [12] | Yuan Bo, Xie Lide, Fu Xiumei. Schwann cell-derived exosomes promote the repair and regeneration of injured peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| [13] | Lu Huixiu, Cao Haiyu, Lou Dan, Li Jianying, Liu Hongyuan, Sun Jing. Imiquimod combined with photodynamic therapy for hypertrophic scars: immune response and prognosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 690-694. |
| [14] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [15] | Zhang Lichen, Chen Liang, Gu Yong. Inorganic ion bionic periosteum regulates immune microenvironment to promote bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 346-353. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||