Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (6): 970-976.doi: 10.12307/2023.286
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of the value of exosomal miRNA for the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
Chen Guanting1, Zhang Linqi2, Li Qingru1
- 1First Clinical Medical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-04-08Accepted:2022-05-21Online:2023-02-28Published:2022-08-12 -
Contact:Zhang Linqi, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China -
About author:Chen Guanting, Doctoral candidate, First Clinical Medical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the Special Project of Scientific Research on Traditional Chinese Medicine in Henan Province, No. 2019ZYZD05 (to ZLQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Li Qingru. Meta-analysis of the value of exosomal miRNA for the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 970-976.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

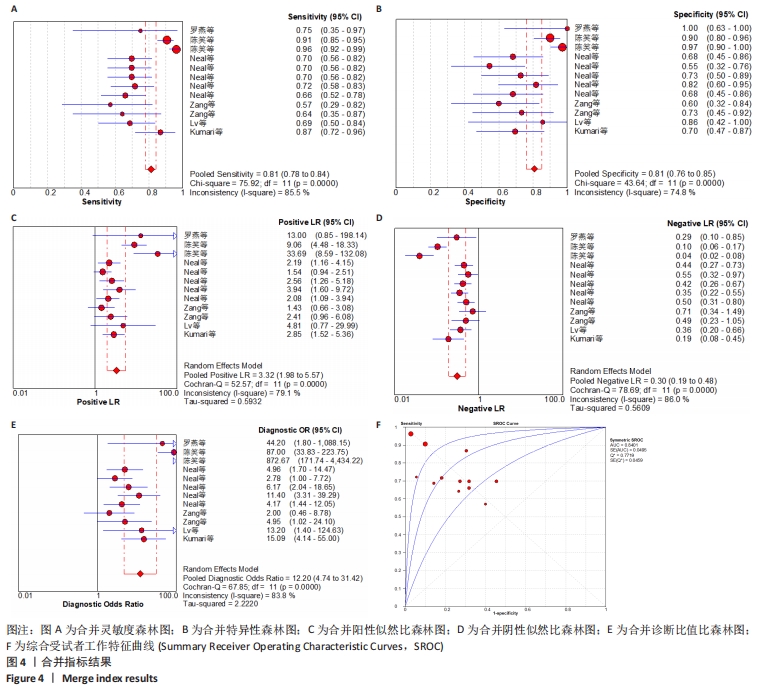
2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 异质性检验 通过Meta DiSc软件对此研究所纳入数据进行分析,得出灵敏度对数与1-特异度对数之间的Spearman相关系数为-0.603,P=0.038 < 0.05,意味着此次研究存在阈值效应。以诊断比值比为效应量,Cochran-Q检验结果为67.85,P < 0.001,且灵敏度、特异性、阳性似然比、阴性似然比、诊断比值比的I2均> 50%,提示此次研究存在非阈值效应引起的异质性,因此采用随机效应模型进行以上5个效应量的合并。 2.3.2 合并指标分析 合并灵敏度为0.81(95%CI:0.78-0.84),合并特异性为0.81(95%CI:0.76-0.85),合并阳性似然比为3.32(95%CI:1.98-5.57),合并阴性似然比为0.30(95%CI:0.19-0.48),合并曲线下面积为0.840 1,Q指数为0.771 9;合并诊断比值比为12.20(95%CI:4.74-31.42),结果见图4。"

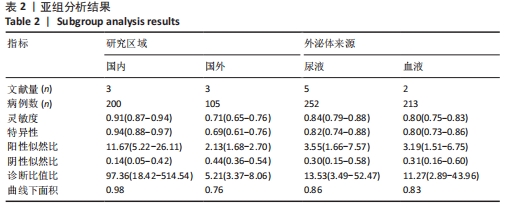
2.4 亚组分析及回归分析 关于纳入文献的研究区域,国内3项研究共计纳入病例200例,国外3项研究共计纳入病例105例,结果显示国内研究灵敏度与特异性明显高于国外研究(0.91 vs. 0.71,0.94 vs. 0.69)。根据外泌体来源不同进行对比分析,检测尿液来源外泌体相关5项研究纳入病例252例,检测血液来源外泌体相关2项研究纳入病例213例,二者灵敏度与特异性基本相当(0.84 vs. 0.80,0.82 vs. 0.80)。此次研究以研究区域、外泌体来源为协变量,采用Meta回归分析探讨非阈值效应异质性来源,结果显示:研究区域P=0.001 4 < 0.05,可能为异质性来源,外泌体来源P=0.316 8 > 0.05,并非异质性主要来源。亚组分析结果见表2。"
| [1] Chapter 1: Definition and classification of CKD. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2013;3(1):19-62. [2] NATIONAL KIDNEY FOUNDATION. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39 (2 Suppl 1):S1-S266. [3] EKNOYAN G, LAMEIRE N, ECKARDT KU, et al. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Foreword. Kidney international supplements. 2013;3(1):1-150. [4] LEVEY AS, INKER LA, CORESH J. GFR estimation: from physiology to public health. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;63(5):820-834. [5] WASUNG ME, CHAWLA LS, MADERO M. Biomarkers of renal function, which and when? Clin Chim Acta. 2015;438:350-357. [6] 朱梦梅,林佳莉,王楚棋,等.治疗性外泌体的研究进展[J].药学学报,2022, 57(3):627-637. [7] PARK SJ, KIM JM, KIM J, et al. Molecular mechanisms of biogenesis of apoptotic exosome-like vesicles and their roles as damage-associated molecular patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(50): E11721-E11730. [8] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. [9] BARILE L, VASSALLI G. Exosomes: Therapy delivery tools and biomarkers of diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;174:63-78. [10] 邢昊楠,陆梅,刘瑛琪,等.基于外泌体的抗肿瘤药物靶向递送的研究进展[J].药学学报,2022,57(1):150-158, 277. [11] HARRILL AH, SANDERS AP. Urinary MicroRNAs in Environmental Health: Biomarkers of Emergent Kidney Injury and Disease. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2020;7(2): 101-108. [12] LV W, FAN F, WANG Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of microRNAs for the treatment of renal fibrosis and CKD. Physiol Genomics. 2018;50(1):20-34. [13] ICHII O, HORINO T. MicroRNAs associated with the development of kidney diseases in humans and animals. J Toxicol Pathol. 2018;31(1):23-34. [14] KATARIA Y. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill children and young adults. Ann Clin Biochem. 2017;54(3):416. [15] RAMACHANDRAN K, SAIKUMAR J, BIJOL V, et al. Human miRNome profiling identifies microRNAs differentially present in the urine after kidney injury. Clin Chem. 2013; 59(12):1742-1752. [16] YU Y, BAI F, QIN N, et al. Non-Proximal Renal Tubule-Derived Urinary Exosomal miR-200b as a Biomarker of Renal Fibrosis. Nephron. 2018;139(3):269-282. [17] LV CY, DING WJ, WANG YL, et al. A PEG-based method for the isolation of urinary exosomes and its application in renal fibrosis diagnostics using cargo miR-29c and miR-21 analysis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018;50(5):973-982. [18] BERINGER PM, HIDAYAT L, HEED A, et al. GFR estimates using cystatin C are superior to serum creatinine in adult patients with cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 2009;8(1):19-25. [19] SOLÉ C, CORTÉS-HERNÁNDEZ J, FELIP ML, et al. miR-29c in urinary exosomes as predictor of early renal fibrosis in lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015;30(9): 1488-1496. [20] LV LL, CAO YH, NI HF, et al. MicroRNA-29c in urinary exosome/microvesicle as a biomarker of renal fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013;305(8):F1220-1227. [21] 陈笑,石嘉琪,聂安琪,等.外泌体miR-93-5p在慢性肾脏病患者中的表达及临床意义[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2021,37(10): 835-838. [22] BELTRAMI C, CLAYTON A, NEWBURY LJ, et al. Stabilization of Urinary MicroRNAs by Association with Exosomes and Argonaute 2 Protein. Noncoding RNA. 2015;1(2):151-166. [23] WHITING PF, RUTJES AW, WESTWOOD ME, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(8):529-536. [24] ZAMORA J, ABRAIRA V, MURIEL A, et al. Meta-DiSc: a software for meta-analysis of test accuracy data. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2006;6:31. [25] BOSTON RC, SUMNER AE. STATA: a statistical analysis system for examining biomedical data. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003; 537:353-369. [26] 罗艳,胡桂英. 2型糖尿病肾病患者尿液外泌体中miRNA的表达谱分析研究[J]. 检验医学与临床,2017,14(9):1271-1274. [27] NEAL CS, MICHAEL MZ, PIMLOTT LK, et al. Circulating microRNA expression is reduced in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(11):3794-3802. [28] ZANG J, MAXWELL AP, SIMPSON DA, et al. Differential Expression of Urinary Exosomal MicroRNAs miR-21-5p and miR-30b-5p in Individuals with Diabetic Kidney Disease. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):10900. [29] KUMARI M, MOHAN A, ECELBARGER CM, et al. Corrigendum: miR-451 Loaded Exosomes Are Released by the Renal Cells in Response to Injury and Associated With Reduced Kidney Function in Human. Front Physiol. 2020;11:844. [30] ZHANG L, WANG F, WANG L, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet. 2012;379(9818):815-822. [31] 谢院生,李清刚.肾脏病学临床研究新进展[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2020, 21(6):471-473. [32] 崔帅帅,杨晓红. miRNA在骨髓间充质干细胞自我更新、多向分化及命运和功能调控中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2022,26(1):101-105. [33] FICHTLSCHERER S, DE ROSA S, FOX H, et al. Circulating microRNAs in patients with coronary artery disease. Circ Res. 2010; 107(5):677-684. [34] GANTIER MP, MCCOY CE, RUSINOVA I, et al. Analysis of microRNA turnover in mammalian cells following Dicer1 ablation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39(13): 5692-5703. [35] 季康寿,杨茗茜,陈文娜,等.外泌体miRNA与中医理论关联及在冠心病中的机制研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊, 2021, 39(5):48-52. [36] 鲍博艺,李卫萍.外泌体miRNA在急性心肌梗死中的研究进展[J].首都医科大学学报,2022,43(2):199-204. [37] NIK MOHAMED KAMAL NNSB, SHAHIDAN WNS. Non-Exosomal and Exosomal Circulatory MicroRNAs: Which Are More Valid as Biomarkers. Front Pharmacol. 2020; 10:1500. [38] MANIER S, LIU CJ, AVET-LOISEAU H, et al. Prognostic role of circulating exosomal miRNAs in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2017; 129(17):2429-2436. [39] SHAO L, ZHANG Y, LAN B, et al. MiRNA-Sequence Indicates That Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Exosomes Have Similar Mechanism to Enhance Cardiac Repair. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4150705. [40] 宋现静,吕文山.miR-16-5p下调ACE对高糖作用的肾小管上皮细胞增殖、凋亡的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(9): 1908-1913. [41] 郭汉城,丘昭文,凌毅生,等.人血白蛋白对近端肾小管上皮细胞ACE2表达的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2009, 25(10):2050-2052. [42] MCCLELLAND AD, HERMAN-EDELSTEIN M, KOMERS R, et al. miR-21 promotes renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by targeting PTEN and SMAD7. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015;129(12):1237-1249. [43] 朱柄铭,陈文璟,苏运钦,等.血清miR-21在糖尿病肾病中的诊断价值.中国病理生理杂志,2013,29(12):2160-2166. [44] 王彦哲,王筱霞,汪年松.miR-30b/Snail调控糖尿病肾病肾小管上皮细胞EMT[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2017,18(4): 288-291,377-378. [45] 王婷,刘宗明.lncRNA XIST靶向miR-30b-5p调控高糖条件下肾小管上皮细胞损伤的机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2022, 42(2):438-442. |
| [1] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [2] | Wang Yanjin, Zhou Yingjie, Chai Xubin, Zhuo Hanjie. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of 3D printed porous titanium alloy fusion cage in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1434-1440. |
| [3] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [4] | Yu Wenqiang, Ren Fuchao, Shi Guohong, Xu Yuanjing, Liu Tongyou, Xie Youzhuan, Wang Jinwu, . Methods and application of gait analysis of lower limbs after stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1257-1263. |
| [5] | Song Hehua, Wei Zairong. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: research and therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1278-1285. |
| [6] | Li Wenjie, You Aijia, Zhou Junli, Fang Sujuan, Li Chun. Effects of different dressings in the treatment of burn wounds: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1141-1148. |
| [7] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [8] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [9] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [10] | Zhang Houjun, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid exosomes derived from cerebral palsy children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 903-908. |
| [11] | Gao Ting, Ma Xiaohong, Li Xiaorong. Extraction and identification of exosomes from three different sources of ovarian granulosa cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 860-865. |
| [12] | Yuan Bo, Xie Lide, Fu Xiumei. Schwann cell-derived exosomes promote the repair and regeneration of injured peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| [13] | Qin Yuxing, Ren Qiangui, Li Zilong, Quan Jiaxing, Shen Peifeng, Sun Tao, Wang Haoyu. Action mechanism and prospect of bone microvascular endothelial cells for treating femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 955-961. |
| [14] | Xu Qijing, Yang Yichun, Lei Wei, Yang Ying, Yu Jiang, Xia Tingting, Zhang Meng, Zhang Tao, Zhang Qian. Advances and problems in cell-free treatment of diabetic skin chronic wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 962-969. |
| [15] | Yan Le, Zhang Huiping, Dai Lintong. Mesenchymal stem cells for allergic rhinitis: a meta-analysis based on animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 977-984. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||