Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (8): 1278-1285.doi: 10.12307/2023.066
Previous Articles Next Articles
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: research and therapy
Song Hehua, Wei Zairong
- Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, The Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-02-08Accepted:2022-04-18Online:2023-03-18Published:2022-07-29 -
Contact:Wei Zairong, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, The Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Song Hehua, Master candidate, Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, The Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Provincial and Ministerial Co-Construction Collaborative Innovation Center Project, No. [2020]39 (to WZR); Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project, No. [2020]5012 (to WZR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Hehua, Wei Zairong. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: research and therapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1278-1285.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
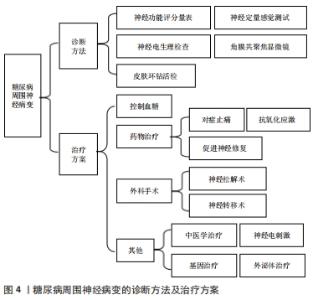
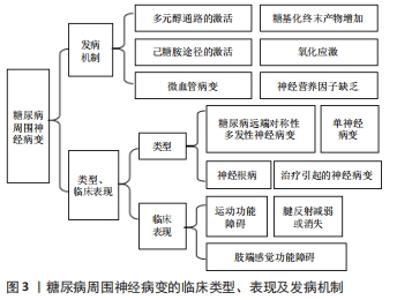
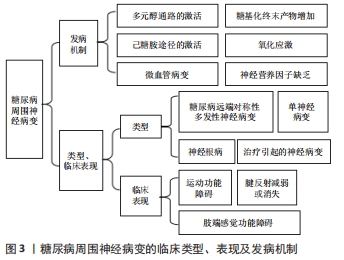
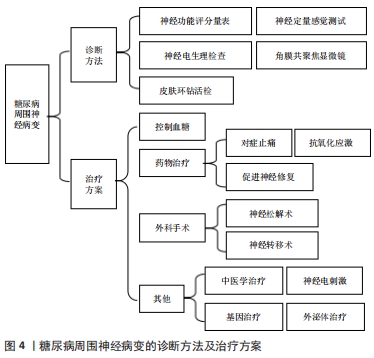
2.1.1 多元醇通路的激活 人体在高糖状态时,葡萄糖的旁路代谢激活,Na+-K+-ATP活性降低,但酶醛糖还原酶活性增强,大量葡萄糖还原成山梨醇,又通过山梨醇脱氢酶转化成果糖,最后神经组织内蓄积了大量的山梨醇和果糖,细胞膜透过困难,导致细胞内渗透压增加,并且竞争性抑制细胞摄取肌醇,引起神经细胞肿胀、变性、坏死[6],神经传导速度减低、轴突变性。同时,醛糖还原酶活性增加降低了还原型辅酶Ⅱ的量,机体活性氧基团产生增多,氧化和抗氧化之间的动态平衡被打破,对神经细胞和组织造成氧化损伤[7]。此外,血糖升高产生的大量二酰甘油会激活蛋白激酶C途径,蛋白激酶C的持续和过度激活会引发组织损伤,造成神经血管损伤及闭塞,最终导致神经变性[8-9],引起糖尿病周围神经病变。 2.1.2 糖基化终末产物途径 糖基化终末产物是指体内过量的糖和蛋白质共价结合形成的产物。在高糖状态下机体糖化过程加快,过多糖基化终末产物蓄积,促发氧化应激,加重周围神经损伤,并且其与神经和神经外膜中的胶原结合,导致周围神经的弹性降低,在通过神经解剖狭窄部位时易加重肿胀神经的卡压[10],导致神经细胞缺血缺氧,再生功能减弱,周围神经损伤不断加重。 2.1.3 己糖胺途径的激活 在生理条件下,己糖胺途径是糖酵解途径的一个小分支。然而在高血糖情况下,线粒体活性氧的增加会抑制糖酵解酶活性,从而更多的葡萄糖通过己糖胺途径代谢,进一步产生二磷酸鸟苷葡萄糖醛酸,修饰包括转录因子、转化生长因子β等多种蛋白质,最终引起糖尿病周围神经病变相关的神经炎症[11]。 2.1.4 氧化应激 氧化应激是由活性氧产生和抗氧化系统之间的不平衡引起的。在糖尿病状态下,受损的葡萄糖代谢将葡萄糖或糖酵解中间体分流到其他代谢和非代谢途径,导致线粒体损伤,从而将氧气转化为超氧自由基,且能量产生减少。神经元无法解毒过量的活性氧以及能量生产不足,使轴突更容易受到活性氧介导的高血糖损伤,进而导致轴突变性。 2.1.5 微血管病变 在长期高血糖的基础上,多元醇-氧化应激、糖基化终末产物、代谢异常等多种因素相互影响,微小血管的血管内皮细胞受损、一氧化氮产生减少、血管内膜增厚、管腔狭窄甚至堵塞,最终造成微循环血管阻力增加,同时血管壁增厚使得氧弥散功能下降,导致周围神经缺血、缺氧而变性、坏死[10]。 2.1.6 神经营养因子缺乏 神经营养因子起着维持神经元和神经纤维功能的作用,神经营养因子缺乏即可损伤神经的生理功能和自愈能力,其中神经生长因子、脑源性神经营养因子和胰岛素样神经生长因子均参与糖尿病周围神经病变的发生和发展。因此神经营养因子缺乏也是诱发糖尿病周围神经病变的一个重要因素[12]。 2.1.7 免疫相关机制 在糖尿病周围神经病变的发病机制中,不能忽视具有调节性T淋巴细胞亚群的细胞免疫机制,它参与了免疫介导炎症的负调节机制[13-14]。CD8+T细胞在糖尿病周围神经组织中的浸润增加,此外CD8+T细胞对许旺细胞具有毒性作用,可诱导其凋亡,因此CD8+T细胞在糖尿病周围神经病变的发生发展中起重要作用[13]。小胶质细胞作为先天免疫细胞,可以清除细胞碎片和异物,发挥免疫监测的关键作用。高血糖和活性氧影响脊髓局部微环境,激活小胶质细胞。反过来,活化的小胶质细胞合成并释放炎性细胞因子和神经活性分子,从而诱导脊髓损伤敏感神经元,引起痛性糖尿病周围神经病变。巨噬细胞有2种极化状态:M1和M2巨噬细胞。在高糖作用下,M1巨噬细胞等免疫细胞被激活,表达大量炎症因子,导致许旺细胞凋亡和痛性糖尿病周围神经病变的发生。研究表明抑制肿瘤坏死因子α,促进M1型巨噬细胞向M2巨噬细胞转化,可使糖尿病大鼠神经传导速度、神经血流量和轴突形态逐渐恢复[15]。 2.2 糖尿病周围神经病变的类型和临床表现以及诊断 2.2.1 类型和临床表现 糖尿病远端对称性多发性神经病变是临床上最常见的糖尿病周围神经病变类型,可分为小纤维神经病变、大纤维神经病变或混合大小纤维神经病变,约70%的糖尿病周围神经病变患者均表现为糖尿病远端对称性多发性神经病变[16],会导致10%-30%的患者出现神经性疼痛症状[17]。典型的糖尿病周围神经病变症状呈缓慢进展,具有长度依赖性,因此通常患者的下肢最远端首先受累,随着时间的推移逐渐向近端发展,并影响上肢[18]。患者常以神经感觉功能异常就诊,感觉功能异常表现为对称性肢端针刺样、烧灼样或电击样疼痛,夜间加重,可能导致失眠,同时伴有袖套-袜子样感觉丧失、麻木,有痛觉过敏或减弱,触觉、温度觉、两点辨别觉、振动觉减退等表现。随着糖尿病周围神经病变的进展,运动功能异常变得明显,表现为肌肉无力、萎缩、足畸形、共济失调、步态不稳,查体部分患者存在腱反射减弱或消失。 非典型形式的糖尿病周围神经病变包括单神经病(即多发性单神经炎)、神经根病或多发性神经根病和治疗引起的神经病变[3]。单神经病与糖尿病密切相关,往往会影响正中神经、尺神经、桡神经或腓总神经[19]。极少累及颅神经,通常表现为影响颅神经Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅵ或Ⅶ的急性单神经病[19]。糖尿病神经根病通常累及腰骶丛,主要表现为单侧大腿疼痛和体质量减轻,随后出现运动无力[3]。治疗引起的神经病变是一种罕见的医源性事件[20],发生在患者出现极端代谢失调(即酮症酸中毒)或血糖控制发生突然变化(即胰岛素神经炎)后。每种非典型糖尿病周围神经病变在很大程度上都是自限性的,通过足部护理、医疗管理及物理治疗将在几个月内消退[19]。 2.2.2 诊断 糖尿病周围神经病变发病率高、起病隐匿,尽早发现有助于缓解病情的加重,改善患者生活质量,目前筛查、评估和诊断糖尿病周围神经病变的方法包括神经功能评分系统、神经电生理检查、皮肤活检、神经定量感觉测试和角膜共聚焦显微镜等,见图4。 "
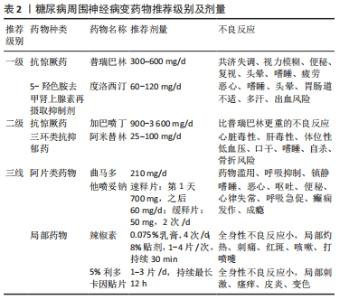
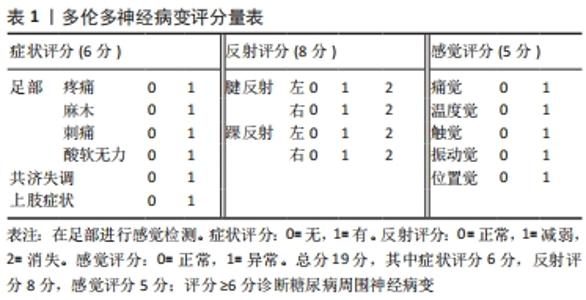
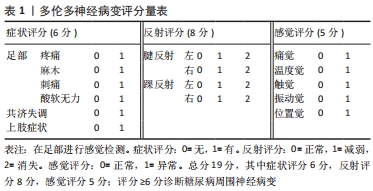
糖尿病周围神经病变公认的诊断标准是神经电生理检查[21-22],对于症状和体征不典型确诊糖尿病周围神经病变困难的患者,通过神经电生理检查可以明确诊断以便下一步治疗。神经电生理检查可以评估周围神经传导电信号的能力,糖尿病周围神经病变患者可记录到神经传导速度的延迟和神经动作电位的幅度降低,提示周围神经脱髓鞘改变,并且常伴有轴索变性。但该检查不仅耗时、昂贵,在检查过程中有明显不适感,且仅对大有髓神经纤维病变较可靠,对糖尿病周围神经病变患者早期小神经纤维病变敏感性差。 通过皮肤环钻活检可早期诊断小神经纤维病变的糖尿病周围神经病变患者。首先在腓肠神经区域,于外踝10 cm处作3 mm孔进行皮肤活检获得样本,然后通过免疫荧光染色进行表皮内神经纤维密度计数[23-24],健康人的范围在(15.0±5.0)根/mm到(12.4±4.6)根/mm,减少健康人神经纤维密度的5%即可诊断糖尿病周围神经病变[24]。但由于皮肤活检属于有创性检查,在临床上患者不易接受,可操作性差。 神经定量感觉测试是通过特定仪器设备量化轻触觉、振动觉、温度觉、痛觉的阈值,定量评价感觉神经功能的一种无创性神经检测技术,有较好的重复性和准确性。10 g单丝压力感觉测试因其可用性和便利性已广泛用于糖尿病周围神经病变的临床筛查,通过测量足部某个点触觉的敏感性,评估足部是否存在保护性感觉,若施加压力使10 g的单丝弯曲但患者感觉不到,则该点被认为是无感觉的[25]。其简单易行,特异性高,敏感性低,临床上感觉缺失明显的患者可采用该方法,通过早期发现预防患者的腿部溃疡和截肢等并发症。 角膜共聚显微镜可以观察并定量分析角膜神经组织的结果和形态改变,在糖尿病周围神经病变患者中可观察到角膜神经纤维密度、长度和分支密度显著降低,可用于诊断及预测糖尿病周围神经病变的发展[26],但其价格昂贵,需要眼科专科医师的参与,在临床上应用受限。 2.3 治疗方案 2.3.1 控制血糖 糖尿病周围神经病变的病程进展是进行性的和不可逆转的,治疗方式侧重于优化血糖管理和缓解症状。加强控制血糖是治疗糖尿病周围神经病变最基础也是最重要的一步,可显著降低糖尿病周围神经病变的发病率及疾病发展[27]。糖尿病控制及并发症研究小组将1 400例糖尿病患者随机分为高血糖强化治疗组和常规治疗组,在大约6.5年的随访期后,强化治疗组中糖尿病周围神经病变发生的频率显著降低,已患有糖尿病周围神经病变的患者病情发展较慢[28]。 2.3.2 药物治疗 (1)对症止痛:糖尿病周围神经病变是周围神经疼痛中最常见的类型,其常见的症状是中至重度的疼痛。在临床实践中,对某种药物而言,患者下肢疼痛减轻30%-50%即认为该药物治疗是有效的,疼痛减轻50%以上为效果良好。用于缓解糖尿病周围神经病变疼痛的药物包括抗惊厥药、5-羟色胺去甲肾上腺素再摄取抑制剂、三环类抗抑郁药、阿片类药物及局部用药,药物推荐级别及剂量见表2[29-34]。 "
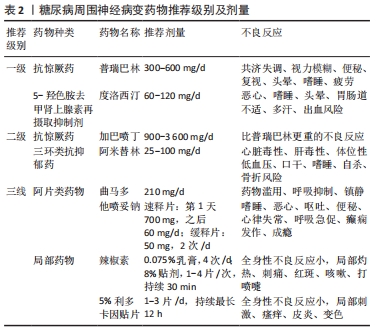
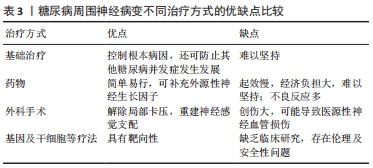
抗惊厥药物已用于多种原因引起的神经病理性疼痛,在治疗神经病理性疼痛方面有不同程度的疗效。但在缓解糖尿病周围神经病变疼痛方面,γ-氨基丁酸类似物效果更佳,如加巴喷丁和普瑞巴林,激活突触前γ-氨基丁酸的受体亚体,使其结构发生改变,降低兴奋性神经递质的释放;另外通过与α2-δ上的电压门控钙通道结合,减少去甲肾上腺素和P物质的释放发挥镇痛作用。此外,两者也可以改善糖尿病周围神经病变患者的情绪和睡眠。加巴喷丁和普瑞巴林药物最终由肾脏代谢,当存在药物间相互作用时可选用。普瑞巴林被推荐为糖尿病周围神经病变的一线药物,推荐剂量300-600 mg/d,常见不良反应包括共济失调、视力模糊、便秘、复视、头晕、嗜睡、疲劳等;加巴喷丁的不良反应较普瑞巴林更严重,为糖尿病周围神经病变的二线推荐药物,推荐剂量900-3 600 mg/d。 5-羟色胺去甲肾上腺素再摄取抑制剂,如度洛西汀,是通过抑制5-羟色胺和去甲肾上腺素再摄取来调节疼痛的下行抑制通路。度洛西汀也可用于治疗抑郁症和焦虑症。对于合并心脏病患者而言是安全的,但可能会导致恶心等胃肠道不良反应。 三环类抗抑郁药,如阿米替林,是通过抑制突触前末梢的单胺类神经递质(5-羟色胺和去甲肾上腺素)的再摄取和离子通道的阻断来发挥镇痛作用,与抗抑郁作用的途径不同。不良反应有体位性低血压、尿潴留、口干和嗜睡。此外,阿米替林禁忌在心律失常患者中使用,在心血管疾病患者中应谨慎使用[34]。 由于阿片类药物的不良反应和滥用的可能性,仅在患者对一级药物和二线药物治疗无效的情况下推荐使用。曲马多是阿片受体的激动剂,也能抑制5-羟色胺和去甲肾上腺素的再摄取,可发挥快速止痛的作用,推荐剂量为210 mg/d,不良反应包括药物滥用、呼吸抑制、镇静。他喷妥钠是一种双效阿片激动剂和去甲肾上腺素拮抗剂,是糖尿病周围神经病变的有效止痛剂,速释片推荐第1天700 mg,之后60 mg/d,缓释片推荐50 mg,2次/d,不良反应有嗜睡、恶心、呕吐、便秘、心律失常、呼吸急促、癫痫发作、成瘾。 当患者无法持续口服药物或承受全身不良反应时,可选用药物局部外用止痛,其全身不良反应小。0.075%辣椒素乳膏外用,4次/d;8%辣椒素贴剂,1-4片/次,每次持续30 min,可导致刺激性咳嗽、喷嚏,局部皮肤灼热、刺痛、红斑。另外可选择5%利多卡因贴片1-3片/d,持续最长12 h,可能引起局部皮肤刺激、瘙痒、皮炎、变色。 (2)抗氧化应激:氧化应激在糖尿病神经病变的发病机制中起关键作用,降低氧化应激的强效药物比其他针对特定高血糖破坏致病途径的药物对糖尿病周围神经病变患者更有益。α-硫辛酸是一种有效的抗氧化剂,已被证明可以改善糖尿病神经病变大鼠模型的神经血流量、减少氧化应激和改善远端神经传导[35]。此外,一项前瞻性研究表示,用600 mg/d的α-硫辛酸连续口服40 d后患者的神经病理性症状显著减轻、生活质量整体改善[36]。 多元醇途径的活化导致大量氧自由基的产生,从而使氧化应激增强。醛糖还原酶是多元醇途径的限速酶,SOLTESOVA PRNOVA等[37]发现糖尿病大鼠经过2个月的醛糖还原酶抑制剂治疗后神经症状恢复正常,山梨醇在红细胞和坐骨神经中的蓄积明显减少。依帕司他作为醛糖还原酶的特异性抑制剂通过阻断多元醇途径来减轻氧化应激,其很容易被神经组织吸收并抑制醛糖还原酶,几乎没有不良反应[38]。此外,与单用α-硫辛酸或依帕司他单药治疗相比,α-硫辛酸与依帕司他联合治疗显著提高了临床疗效并加速了神经传导[39]。 (3)促进神经修复:糖尿病周围神经病变的发病机制尚不明确,临床除上述药物外也采用促进神经修复的药物进行治疗。甲钴胺为内源性B族维生素,是临床上常用的抗周围神经病药物,其对神经组织有特异性的亲和力,具有良好的促进神经纤维修复、改善临床症状的作用。甲钴胺已被中国食品药品监督管理总局批准用于治疗周围神经病变,并在中国2型糖尿病治疗指南中推荐使用[40]。甲钴胺的作用机制包括[41-43]:①甲钴胺的活性甲基可以参与到神经系统中的转甲基过程,向神经组织内转移容易,增强神经细胞内核酸和蛋白质的生成;②促进轴索内输送和轴索的再生;③提高蛋氨酸合成酶的活性,促进髓鞘的主要结构磷脂酰胆碱合成,从而促进髓鞘的形成;④恢复神经冲动的传达延迟和神经递质的减少;⑤减少氧化应激和晚期糖基化产物,抑制蛋白激酶C途径的激活。甲钴胺单一治疗或与其他治疗联合使用均安全有效,推荐口服1 500 mg/d、肌肉注射或静脉注射500 mg/d。DIDANGELOS等[44]研究显示44例口服甲钴胺治疗12个月后的糖尿病周围神经病变患者神经传导速度、动作电位波幅、震动觉阈值、神经病变评分、生活质量评分较安慰剂组均显著改善。袁志新等[45]检测经甲钴胺治疗6周后的60例糖尿病周围神经病变患者感觉及运动神经传导速度、震动觉阈值及同型半胱氨酸水平的相关指标,结果提示较治疗前均有显著改善。 此外,神经生长因子同样作为中国2型糖尿病治疗指南推荐使用的神经修复药物,其是一种经过深入研究的神经营养因子,对周围神经发育和再生过程中的神经元存活、血管生成、许旺细胞活力和增殖具有积极作用[46]。长期高血糖会引起人体内神经生长因子及其受体减少,且与糖尿病周围神经病变的严重程度呈负相关,同时逆向轴突运输及神经生长因子依赖性感觉神经元的支持减少[47],此过程被认为是糖尿病周围神经病变的重要发病机制之一[48]。外源性神经生长因子给药会影响神经元的可塑性,促进感觉、运动功能的恢复和轴突再生[49-50],还可通过上调神经蛋白水平来减轻糖尿病性神经病变引起的神经再生缺陷[51]。此外,既往研究已经揭示了血管、神经纤维在发育和再生过程中的相互作用关系[52],确定了几种生长因子是指导血管生成和调节轴突末端树枝状化的重要递质。其中,神经生长因子已被证明不仅能促进周围神经的发育和再生,还能促进血管生成[53-54]。鼠神经生长因子是与人神经生长因子高度同源性的小鼠颌下腺提取物,中国2003年已批准在临床上用于治疗周围神经损伤[55-56],未见明显不良反应,是一种安全有效、来源充足的外源性神经生长因子。高血糖导致大量氧自由基在体内蓄积,神经元无法解毒过量的活性氧以及能量生产不足,使轴突更容易受到活性氧介导的高血糖损伤,进而导致轴突变性,研究报道鼠神经生长因子可以提高自由基清除剂的活性,如过氧化物酶、超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽等,继而抑制氧化应激诱导的细胞凋亡,保护并促进神经功能恢复[57]。既往彭俊举等[58-61]研究表明鼠神经生长因子可显著降低糖尿病周围神经病变患者神经病变评分、提高神经传导速度、改善下肢感觉功能,有利于促进神经纤维再生及功能恢复。 2.3.3 外科手术 (1)神经松解术:“双重挤压”假说提出,由于氧化应激和神经内山梨醇积聚的高渗效应,神经内含水量增加、体积增大,顺向轴浆运输活动的减弱加剧神经病变,并且糖基化终末产物蓄积使神经硬化,弹性和滑动性下降,并且神经通行的生理性解剖狭窄部位的纤维结缔组织肥厚、水肿、变硬,最终导致神经受到慢性卡压,又进一步加重神经缺血损伤,此过程共同促成了糖尿病周围神经病变。基于这一致病机制,DELLON等[62]通过解剖学和动物实验研究证明,在高血糖的影响下,周围神经更易受到慢性压迫。1988年DELLON[63]首次提出周围神经松解术可以缓解糖尿病周围神经病变所引起的肢端疼痛和麻木。后续研究证实周围神经松解术可有效防止糖尿病大鼠神经症状的发生[64-65]。1992年DELLON[66]报道了神经松解术治疗症状性糖尿病周围神经病变的良好临床效果,从此国内外多家医疗机构纷纷开展了神经松解术。 DELLON[67]推荐的手术方法是对所有潜在的解剖卡压部位都进行减压,包括正中神经、尺神经、腓总神经、胫神经、腓深神经足背支,这通常涉及5个部位的切口,腕管、肘管、膝外侧腓骨小头处、踝管、足背第一二跖骨间。BALTODANO等[68]报道称875例患者中有91%在神经松解术后疼痛明显减轻。近期一项随机对照研究表示随访1年后手术组患者疼痛较对照组有显著缓解[69]。此外,除了患者主观症状的好转,还有客观证据支持神经松解术。首先,神经松解术有助于显著改善神经功能,ZHANG等[70]将560例糖尿病周围神经病变患者在减压前和双下肢神经松解术后18个月进行了分析,发现神经传导速度、两点辨别觉、感觉定量检测得到改善;其次,神经松解术可减少姿势不平衡和相关的跌倒风险,DUCIC等[71]发现术后患者共济失调显著改善,并且神经松解术可减少溃疡、再发溃疡、感染住院和截肢的风险,一项前瞻性研究报告显示628例患者进行了胫神经松解,术后0.2%的既往无溃疡病史患者出现新的溃疡,3.8%的患者患有既往溃疡复发,1例截肢[72]。ZHANG等[73]对208例既往溃疡史的糖尿病周围神经病变患者接受了双侧神经松解术,18个月的随访中没有患者出现新的溃疡、伤口感染或截肢。 (2)神经转移术:AGARWAL等[74-75]提出了一种针对晚期下肢糖尿病周围神经病变患者新的手术方式,即将患肢隐神经转移到胫后神经感觉束进行足底感觉再支配,术后6个月时随访发现32例患者全都出现了足底保护性感觉,溃疡全部愈合,神经功能有显著改善,且无溃疡出现、再发及截肢。 2.3.4 其他 (1)中医学治疗:从中医学角度来看,糖尿病周围神经病变的根本病因在于气血亏虚、瘀血阻络,治疗方法在于内外并重,内服中药可以气血滋补、通络祛痰,外加针灸、推拿、火罐、中药薰蒸及足浴可以疏经通络、调和气血[76-78]。 (2)神经电刺激:神经电刺激是传统药物治疗无效、或难以承受其毒副作用的痛性糖尿病周围神经病变患者的另一种治疗选择,研究已经证实其安全可行性。神经电刺激主要包括中枢和外周神经刺激,研究最多的中枢神经刺激包括脊髓电刺激和背根神经节电刺激,而经皮神经电刺激是最常见的外周神经刺激,作用原理是通过植入人体内的电极产生电流干扰神经传导环路来调节大脑疼痛感知功能,恢复内源性疼痛通路的平衡,从而减少疼痛。研究显示神经电刺激可以有效减少糖尿病周围神经病变患者的神经性疼痛,无不良反应发生,具备安全可行性[79-80]。除镇痛效果外,神经电刺激也许还能促进神经营养因子的释放、改善循环、促进溃疡愈合及病变神经修复。VAN BEEK等[81]的动物研究显示,糖尿病周围神经病变大鼠在4周脊髓电刺激治疗后疼痛显著缓解,足底皮肤的血液灌注显著增加。此外有研究报道,糖尿病足患者接受了神经电刺激后疼痛缓解、溃疡愈合、经皮氧分压上升、皮肤温度升高[82]。 (3)基因治疗:非病毒基因治疗技术是一种全新且有效的糖尿病周围神经病变治疗方法。肝细胞生长因子是一种多功能蛋白,具有强大的神经营养和血管生成活性,促进感觉、运动神经元的存活和轴突生长,还能诱导糖尿病动物模型侧支血管的形成、增加血流[83]。有研究表明将编码肝细胞生长因子的质粒DNA注射治疗糖尿病周围神经病变患者具有长期有效的镇痛作用[84]。 (4)干细胞疗法:干细胞可以分化成脂肪、骨骼和软骨等组织,具有很强的自我更新能力和多向分化潜能,并能分泌多种细胞因子,它们在糖尿病周围神经病变的治疗中具有良好的应用前景。间充质干细胞移植可促进胰岛细胞增殖,增加胰岛素分泌细胞数量,改善胰岛结构,增加胰岛素合成和分泌,降低血糖浓度,从糖尿病的关键点改善糖尿病患者的血糖水平[13];此外也可通过旁分泌作用及分泌血管生成因子、神经营养因子以及抗炎分子来促进周围神经病变的修复。 (5)外泌体:外泌体是内体来源的膜状纳米囊泡,作为生物活性分子的天然载体在细胞间发挥传递信号的关键作用,其含有功能性mRNA、microRNA(miRNA)、蛋白质和脂质。动物实验证实间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体具有治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的效果[85],通过抑制促炎基因来减轻糖尿病周围神经病变小鼠的神经血管功能障碍并促进功能恢复。MiRNA-146a是一种抗炎miRNA,参与了糖尿病周围神经病变的发病机制[86]。研究表明采用外泌体作为生物载体可以有效介导和增强糖尿病小鼠中间充质干细胞的治疗活性[86],为神经血管重塑和糖尿病周围神经病变功能恢复提供了一种新的治疗策略。 (6)病毒载体技术:病毒载体是最有效的基因传播载体,可通过感染宿主细胞将外源基因整合到染色体中,表现出稳定的基因治疗潜力[87]。慢病毒载体是基于慢病毒基因组的载体,其中去除了与病毒活性相关的多个序列结构,以确保生物安全,然后将外源基因引入基因组骨架。TASYUREK等[88]通过注射携带人胰高血糖素样肽1基因的慢病毒载体,降低了高脂饮食联合链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠的血糖水平,同时三酰甘油水平恢复正常。结果表明慢病毒载体可以有效将潜在的治疗基因转移到胰岛细胞中进行糖尿病周围神经病变的治疗。 综上所述,糖尿病周围神经病变不同治疗方案的作用机制及疗效大不相同,为探索合适的治疗方式,提高糖尿病周围神经病变的疗效,现将不同方法加以总结,见表3。 "
| [1] SAEEDI P, PETERSOHN I, SALPEA P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. [2] LI Y, TENG D, SHI X, et al. Prevalence of diabetes recorded in mainland China using 2018 diagnostic criteria from the American Diabetes Association: national cross sectional study. BMJ. 2020;369:m997. [3] POP-BUSUI R, BOULTON AJ, FELDMAN EL, et al. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(1):136-154. [4] FELDMAN EL, CALLAGHAN BC, POP-BUSUI R, et al. Diabetic neuropathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5(1):42. [5] LIU S, ZHENG H, ZHU X, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;130:90-97. [6] 吴蓝雪,汪四虎,黄大祥,等.2型糖尿病并发痛性糖尿病神经病变的影响因素研究[J].中国全科医学,2021,24(6):658-662. [7] PANG L, LIAN X, LIU H, et al. Understanding Diabetic Neuropathy: Focus on Oxidative Stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:9524635. [8] GERALDES P, KING GL. Activation of protein kinase C isoforms and its impact on diabetic complications. Circ Res. 2010;106(8):1319-1331. [9] SHAKEEL M. Recent advances in understanding the role of oxidative stress in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2015;9(4):373-378. [10] 张文川,钟文翔,廖陈龙,等.周围神经减压改善DPN大鼠神经微循环、促进神经修复的作用机制[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2019, 24(3):130-134. [11] SANDIREDDY R, YERRA VG, ARETI A, et al. Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in diabetic neuropathy: futuristic strategies based on these targets. Int J Endocrinol. 2014;2014:674987. [12] 包秋香.血清脑源性神经营养因子与2型糖尿病周围神经病变中的相关研究[J].内蒙古医科大学学报,2020,42(1):56-58. [13] XUE T, ZHANG X, XING Y, et al. Advances About Immunoinflammatory Pathogenesis and Treatment in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:748193. [14] 黄海伦,吴珊.糖尿病周围神经病相关发病机制研究进展[J].中华脑科疾病与康复杂志(电子版),2019,9(3):176-180. [15] OMI M, HATA M, NAKAMURA N, et al. Transplantation of dental pulp stem cells improves long-term diabetic polyneuropathy together with improvement of nerve morphometrical evaluation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):279. [16] LECHLEITNER M, ABRAHAMIAN H, FRANCESCONI C, et al. Diabetic neuropathy and diabetic foot syndrome (Update 2019). Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2019;131(Suppl 1):141-150. [17] HICKS CW, SELVIN E. Epidemiology of Peripheral Neuropathy and Lower Extremity Disease in Diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2019;19(10):86. [18] ZAKIN E, ABRAMS R, SIMPSON DM. Diabetic Neuropathy. Semin Neurol. 2019;39(5):560-569. [19] SMITH BE. Focal and entrapment neuropathies. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;126:31-43. [20] BOULTON AJ, VINIK AI, AREZZO JC, et al. Diabetic neuropathies: a statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28(4):956-962. [21] IQBAL Z, AZMI S, YADAV R, et al. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Pharmacotherapy. Clin Ther. 2018;40(6): 828-849. [22] TESFAYE S, BOULTON AJ, DYCK PJ, et al. Diabetic neuropathies: update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(10):2285-2293. [23] KÖREI AE, ISTENES I, PAPANAS N, et al. Small-Fiber Neuropathy: A Diabetic Microvascular Complication of Special Clinical, Diagnostic, and Prognostic Importance. Angiology. 2016;67(1):49-57. [24] LAURIA G, BAKKERS M, SCHMITZ C, et al. Intraepidermal nerve fiber density at the distal leg: a worldwide normative reference study. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2010;15(3):202-207. [25] WANG F, ZHANG J, YU J, et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Monofilament Tests for Detecting Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:8787261. [26] PERKINS BA, LOVBLOM LE, LEWIS EJH, et al. Corneal Confocal Microscopy Predicts the Development of Diabetic Neuropathy: A Longitudinal Diagnostic Multinational Consortium Study. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(9):2107-2114. [27] MARTIN CL, ALBERS JW, POP-BUSUI R. Neuropathy and related findings in the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(1):31-38. [28] NATHAN DM, GENUTH S, LACHIN J, et al. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):977-986. [29] KHDOUR MR. Treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a review. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2020;72(7):863-872. [30] BONDAR A, POPA AR, PAPANAS N, et al. Diabetic neuropathy: A narrative review of risk factors, classification, screening and current pathogenic treatment options (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(1):690. [31] AZMI S, ALAM U, BURGESS J, et al. State-of-the-art pharmacotherapy for diabetic neuropathy. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021;22(1):55-68. [32] HUSSAIN N, SAID ASA, JAVAID FA, et al. The efficacy and safety profile of capsaicin 8% patch versus 5% Lidocaine patch in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: a randomized, placebo-controlled study of south Asian male patients. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021;20(1):271-278. [33] 袁丽,白亚菲,杨海波,等.加巴喷丁联合高能红光治疗痛性糖尿病周围神经病变患者的疗效观察[J].广西医学,2019,41(9):1086-1090. [34] SLOAN G, SELVARAJAH D, TESFAYE S. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical management of diabetic sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;17(7):400-420. [35] NAGAMATSU M, NICKANDER KK, SCHMELZER JD, et al. Lipoic acid improves nerve blood flow, reduces oxidative stress, and improves distal nerve conduction in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 1995;18(8):1160-1167. [36] AGATHOS E, TENTOLOURIS A, ELEFTHERIADOU I, et al. Effect of α-lipoic acid on symptoms and quality of life in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. J Int Med Res. 2018;46(5):1779-1790. [37] SOLTESOVA PRNOVA M, SVIK K, BEZEK S, et al. 3-Mercapto-5H-1,2,4-Triazino[5,6-b]Indole-5-Acetic Acid (Cemtirestat) Alleviates Symptoms of Peripheral Diabetic Neuropathy in Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Rats: A Role of Aldose Reductase. Neurochem Res. 2019;44(5):1056-1064. [38] YAMA K, SATO K, MURAO Y, et al. Epalrestat Upregulates Heme Oxygenase-1, Superoxide Dismutase, and Catalase in Cells of the Nervous System. Biol Pharm Bull. 2016;39(9):1523-1530. [39] ZHAO M, CHEN JY, CHU YD, et al. Efficacy of epalrestat plus α-lipoic acid combination therapy versus monotherapy in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a meta-analysis of 20 randomized controlled trials. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(6):1087-1095. [40] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J].国际内分泌代谢杂志,2021,41(5):482-548. [41] SAWANGJIT R, THONGPHUI S, CHAICHOMPU W, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Mecobalamin on Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Altern Complement Med. 2020;26(12):1117-1129. [42] 颜春梅.硫辛酸+甲钴胺联合依帕司他治疗糖尿病周围神经病变对患者震动感觉阈值的影响[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2022, 25(1):26-30. [43] 王鑫. 甲钴胺防治奥沙利铂神经毒性的临床观察[D].青岛:青岛大学,2018. [44] DIDANGELOS T, KARLAFTI E, KOTZAKIOULAFI E, et al. Vitamin B12 Supplementation in Diabetic Neuropathy: A 1-Year, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2021;13(2):395. [45] 袁志新,罗菊红.甲钴胺联合硫辛酸对糖尿病周围神经病变震动感觉阈值及血浆同型半胱氨酸水平的影响[J].糖尿病新世界,2021, 24(23):23-26. [46] LI R, LI DH, ZHANG HY, et al. Growth factors-based therapeutic strategies and their underlying signaling mechanisms for peripheral nerve regeneration. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41(10):1289-1300. [47] HELLWEG R, RAIVICH G, HARTUNG HD, et al. Axonal transport of endogenous nerve growth factor (NGF) and NGF receptor in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Exp Neurol. 1994;130(1):24-30. [48] DEWANJEE S, DAS S, DAS AK, et al. Molecular mechanism of diabetic neuropathy and its pharmacotherapeutic targets. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;833:472-523. [49] KEMP SW, WEBB AA, DHALIWAL S, et al. Dose and duration of nerve growth factor (NGF) administration determine the extent of behavioral recovery following peripheral nerve injury in the rat. Exp Neurol. 2011; 229(2):460-470. [50] WOOD MD, HUNTER D, MACKINNON SE, et al. Heparin-binding-affinity-based delivery systems releasing nerve growth factor enhance sciatic nerve regeneration. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2010;21(6-7):771-787. [51] KARAMOYSOYLI E, BURNAND RC, TOMLINSON DR, et al. Neuritin mediates nerve growth factor-induced axonal regeneration and is deficient in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes. 2008;57(1):181-189. [52] VOGEL G. Developmental biology. The unexpected brains behind blood vessel growth. Science. 2005;307(5710):665-667. [53] DIAO YP, CUI FK, YAN S, et al. Nerve Growth Factor Promotes Angiogenesis and Skeletal Muscle Fiber Remodeling in a Murine Model of Hindlimb Ischemia. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016;129(3):313-319. [54] KARATZAS A, KATSANOS K, LILIS I, et al. NGF promotes hemodynamic recovery in a rabbit hindlimb ischemic model through trkA- and VEGFR2-dependent pathways. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013;62(3):270-277. [55] FAN C, WANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Clinical efficacy of mouse nerve growth factor in treatment of occupational hand-arm vibration disease. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2014;32(12):924-927. [56] 李慧娟.鼠神经生长因子联合α-硫辛酸治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的临床效果观察[J].现代诊断与治疗,2018,29(8):1237-1238. [57] 朱强,胡国良,李全春,等.鼠神经生长因子、亚低温联合甲强龙在急性脊髓损伤中的应用及对氧化应激水平的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2021,31(23):79-83. [58] 彭俊举.鼠神经生长因子联合甲钴胺在重症周围神经损伤患者中的应用及对促炎因子的影响研究[J]. 药品评价,2020,17(12):40-42. [59] 韦莉婷,刘超,商丹.鼠神经生长因子穴位注射治疗周围神经损伤的疗效及对神经传导速度、运动电位潜伏期的影响[J].山西卫生健康职业学院学报,2021,31(1):21-22. [60] 田雄涛,李洁,叶欣,等.注射用鼠神经生长因子治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的临床效果[J].临床医学研究与实践,2021,6(32):40-42. [61] 孔祥娥.鼠神经生长因子在糖尿病周围神经病变临床治疗中的应用效果研究[J].当代医学,2019,25(16):98-100. [62] DELLON AL, MACKINNON SE, SEILER WA 4TH. Susceptibility of the diabetic nerve to chronic compression. Ann Plast Surg. 1988;20(2):117-119. [63] DELLON AL. A cause for optimism in diabetic neuropathy. Ann Plast Surg. 1988;20(2):103-105. [64] DELLON AL, DELLON ES, SEILER WA 4TH. Effect of tarsal tunnel decompression in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Microsurgery. 1994;15(4):265-268. [65] KALE B, YÜKSEL F, CELIKÖZ B, et al. Effect of various nerve decompression procedures on the functions of distal limbs in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: further optimism in diabetic neuropathy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;111(7):2265-2272. [66] DELLON AL. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic neuropathy by surgical decompression of multiple peripheral nerves. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1992;89(4):689-697; discussion 698-699. [67] DELLON AL. Neurosurgical prevention of ulceration and amputation by decompression of lower extremity peripheral nerves in diabetic neuropathy: update 2006. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2007;100:149-151. [68] BALTODANO PA, BASDAG B, BAILEY CR, et al. The Positive Effect of Neurolysis on Diabetic Patients with Compressed Nerves of the Lower Extremities: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2013;1(4):e24. [69] BEST TJ, BEST CA, BEST AA, et al. Surgical peripheral nerve decompression for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy of the foot - A level 1 pragmatic randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;147:149-156. [70] ZHANG W, ZHONG W, YANG M, et al. Evaluation of the clinical efficacy of multiple lower-extremity nerve decompression in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Br J Neurosurg. 2013;27(6):795-799. [71] DUCIC I, TAYLOR NS, DELLON AL. Relationship between peripheral nerve decompression and gain of pedal sensibility and balance in patients with peripheral neuropathy. Ann Plast Surg. 2006;56(2):145-150. [72] DELLON AL, MUSE VL, NICKERSON DS, et al. Prevention of ulceration, amputation, and reduction of hospitalization: outcomes of a prospective multicenter trial of tibial neurolysis in patients with diabetic neuropathy. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2012;28(4):241-246. [73] ZHANG W, LI S, ZHENG X. Evaluation of the clinical efficacy of multiple lower extremity nerve decompression in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2013;74(2):96-100. [74] AGARWAL P, SHARMA D. Our experience of reinnervation of sole in diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy: A chance to change the natural history of disease. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021;17:25-29. [75] AGARWAL P, SHARMA D, NEBHANI D, et al. Saphenous nerve to posterior tibial nerve transfer: A new approach to restore sensations of sole in diabetic sensory polyneuropathy. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2021;74(9):2110-2119. [76] 方朝晖,吴以岭,赵进东.糖尿病周围神经病变中医临床诊疗指南(2016年版)[J].中医杂志,2017,58(7):625-630. [77] 李冠新.中医治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的现状[J].糖尿病新世界, 2020,23(17):162-163,166. [78] 冯圣钰,杨华,邹冉,等.中医治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的研究进展[J].世界临床药物,2021,42(9):751-756. [79] LEFAUCHEUR JP, ANTAL A, AYACHE SS, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). Clin Neurophysiol. 2017;128(1):56-92. [80] ZENG H, PACHECO-BARRIOS K, CAO Y, et al. Non-invasive neuromodulation effects on painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):19184. [81] VAN BEEK M, HERMES D, HONIG WM, et al. Long-Term Spinal Cord Stimulation Alleviates Mechanical Hypersensitivity and Increases Peripheral Cutaneous Blood Perfusion in Experimental Painful Diabetic Polyneuropathy. Neuromodulation. 2018;21(5):472-479. [82] GAO JB, BAO M. Case report of the treatment of diabetic foot disease using spinal cord stimulation. Brain Stimul. 2019;12(3):792-793. [83] KO KR, LEE J, LEE D, et al. Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) Promotes Peripheral Nerve Regeneration by Activating Repair Schwann Cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):8316. [84] KESSLER JA, SHAIBANI A, SANG CN, et al. Gene therapy for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A randomized, placebo-controlled phase III study of VM202, a plasmid DNA encoding human hepatocyte growth factor. Clin Transl Sci. 2021;14(3):1176-1184. [85] FAN B, LI C, SZALAD A, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes ameliorate peripheral neuropathy in a mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia. 2020;63(2):431-443. [86] FAN B, CHOPP M, ZHANG ZG, et al. Treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy with engineered mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes enriched with microRNA-146a provide amplified therapeutic efficacy. Exp Neurol. 2021;341:113694. [87] LIU X, HUANG H, GAO Y, et al. Visualization of gene therapy with a liver cancer-targeted adeno-associated virus 3 vector. J Cancer. 2020;11(8): 2192-2200. [88] TASYUREK HM, ALTUNBAS HA, BALCI MK, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Lentivirus-Mediated Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Gene Therapy for Diabetes. Hum Gene Ther. 2018;29(7):802-815. |
| [1] | Yang Jiujie, Li Zhi, Wang Shujie, Tian Ye, Zhao Wei. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of functional changes following durotomy with decompression for acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [2] | Wu Tong, Yin Caiyun, Zhao Mingzhe, Zhu Yishen. Application of functional peptides for biomedical diagnosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 478-485. |
| [3] | Zhang Jian, Lin Jianping, Zhou Gang, Wang Benchao, Wu Yongchang. Etiological analysis of discoid meniscus based on whole exome sequencing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 192-199. |
| [4] | Quan Meilin, Liu Qi, Chen Xi, Deng Xiaobo, He Kechen, Liu Yanli. Application of improved geodesic active contour model in kidney CT image segmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 171-176. |
| [5] | Li Mingxiu, Wang Xuan, Yang Jie, Li Yi. An osteoarthritis model in vitro: characteristics and new design idea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 300-306. |
| [6] | Lu Pan, Zhang Chunlin, Wang Yongkui, Yan Xu, Dong Chao, Yue Yisen, Li Long, Zhu Andi. Volume changes of cervical herniated discs after open-door laminoplasty and conservative treatment as assessed by three-dimensional volume method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1395-1401. |
| [7] | Li Jiajun, Xia Tian, Liu Jiamin, Chen Feng, Chen Haote, Zhuo Yinghong, Wu Weifeng. Molecular mechanism by which icariin regulates osteogenic signaling pathways in the treatment of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 780-785. |
| [8] | Lu Qinxue, Xu Ning, Yang Yinglan, Han Qianqian, Duanmu Xianyu, Guo Yuwei, Han Qing. Femoroacetabular impingement: strength trainings for nerve-muscle, peripheral muscle and core muscle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 786-791. |
| [9] | Zheng Zhenquan, Rong Jiesheng. Sarcopenia: age-related muscle mass loss and functional declines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 792-797. |
| [10] | Song Dawei, Yu Hao, Yang Ming, Xie Haifeng, Wu Cenhao, Yan Qi, Wang Yingjie, Yang Huilin, Geng Dechun, Niu Junjie, Wang Jinning. Three approaches of pedicle screw internal fixation for thoracolumbar fractures: spinal function, vertebral height reduction and local Cobb angle recovery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(36): 5844-5848. |
| [11] | Chen Lin, Xu Xiaomei, Zhang Li, Xu Pengfei, Zheng Qian. Finite element study on the effect of canine distal movement on anterior tooth intrusion by clear aligners [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5669-5675. |
| [12] | Zheng Rui, Sun Yong. Effects of alkali-and-heat treatment combined with ultraviolet photofunctionalization pure titanium on osteoblast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5486-5491. |
| [13] | Zhang Jian, Lin Jianping, Zhou Gang, Fang Yehan, Wang Benchao, Wu Yongchang. Semi-quantitative MRI evaluation of cartilage degeneration in early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 425-429. |
| [14] | Liang Haoran, Zhou Xin, Yang Yanfei, Niu Wenjie, Song Wenjie, Ren Zhiyuan, Wang Xueding, Liu Yang, Duan Wangping. Pathogenesis of femoral head necrosis after internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in young adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 456-460. |
| [15] | Li Zhishuai, Zhang Hongqian, Liu Jianquan, Zhang Hankun, Li Li. Visualization analysis of current research hotspots on rehabilitation treatment after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4234-4241. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||