Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (8): 1286-1291.doi: 10.12307/2023.090
Previous Articles Next Articles
The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury
Nie Chenchen1, Su Kaiqi1, Gao Jing1, 2, Fan Yongfu1, Ruan Xiaodi1, Yuan Jie1, Duan Zhaoyuan1, Feng Xiaodong1, 2
- 1Medical College of Rehabilitation, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2Rehabilitation Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-21Accepted:2022-05-06Online:2023-03-18Published:2022-07-29 -
Contact:Feng Xiaodong, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Medical College of Rehabilitation, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; Rehabilitation Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Nie Chenchen, Master candidate, Medical College of Rehabilitation, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82174473 (to FXD); National Natural Science Joint Fund Project, No. U2004131 (to FXD); Henan Provincial Key Laboratory of Neurorestoration Open Project, No. HNSJXF-2021-005 (to FXD); Henan Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Special Project, No. 2018JDZX011 (to FXD); Henan Provincial Science and Technology Research Plan, No. 202102310167 (to FXD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
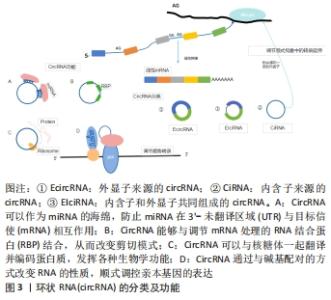
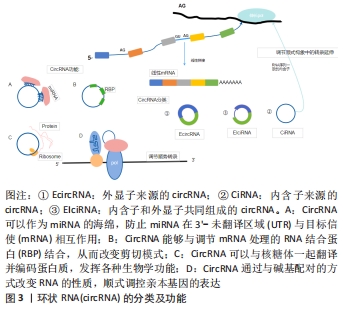
2.1 circRNA的分子概述 circRNA主要来自蛋白质编码基因的外显子,部分来自内含子区域、非翻译区域。根据来源可将circRNA分为3类[8]:①外显子来源的circRNA(EcircRNA);②内含子来源的circRNA(CiRNA);③内含子和外显子共同组成的circRNA(EIciRNA),它们是由RNA聚合酶从前mRNA序列转录而来(通过背部剪接过程的混合物组成)。 目前研究认为,circRNA具有以下几种功能[9]:①miRNA海绵吸附作用;②通过与碱基配对的方式改变RNA性质顺式调控亲本基因的表达;③与蛋白之间的相互作用从而调节细胞的各种功能;④编码蛋白质并发挥各种生物学功能,见图3。近年来研究发现,circRNA因其独特的闭环结构在脑组织中具有高度稳定性和进化保守性[10],它们作为竞争性内源性RNA,在细胞基因表达中扮演miRNA分子海绵的角色,大部分可在转录和转录后参与基因调控,少部分可编码为多肽,具有调节功能,在神经系统中高度富集[11],其基因的外显子通过替代mRNA剪接产生,并通过调节神经炎症参与缺血性脑卒中发病机制的生理病理过程。 "
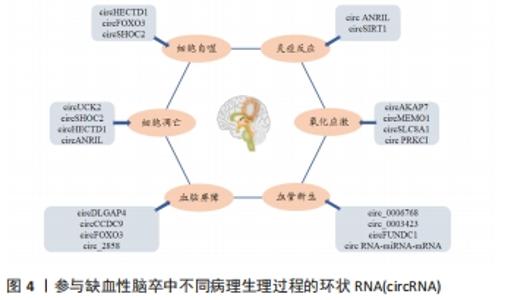
2.2.1 细胞凋亡 细胞凋亡是一种程序性细胞死亡形式。随着脑缺血后神经元坏死,细胞凋亡是缺血性脑卒中后迟发性神经元死亡的一种重要形式[14],也是脑缺血半暗带内细胞的主要死亡方式。一方面,由于缺血缺氧刺激凋亡相关基因的表达;另一方面,细胞内钙超载、氧自由基的过量和兴奋性毒性等也会通过不同的机制诱导神经细胞凋亡。近年来相关研究表明,一些circRNA参与缺血性脑卒中后的细胞凋亡[15]。这些研究提示circRNA在细胞凋亡过程中具有十分重要的作用。 部分circRNA可抑制脑缺血后细胞凋亡。先前已有研究证实Smad3信号通路与细胞凋亡密切相关[16-17],生长分化因子11(GDF11)作为TGF-β超家族的成员在脑卒中中具有神经保护作用。CHEN等[18]在氧-葡萄糖剥夺/再灌注HT-22细胞模型中发现,circRNA尿苷-胞苷激酶2 (circUCK2)一方面可以通过调节TGF-β/Smad3信号通路,减少氧-葡萄糖剥夺诱导的细胞凋亡,另一方面也可作为内源性miR-125b-5p的海绵,通过抑制其活性促进生长分化因子11的表达,从而抑制细胞凋亡。随后该团队通过建立体内外氧-葡萄糖剥夺缺血模型,发现星形细胞源性外泌体(IPAS-EXOs)中circSHOC2的表达显著上调,其作为miR-7670-3p的海绵,可通过调节自噬促进去乙酰化酶1 (Sirtuin 1,SIRT1)的表达来抑制细胞凋亡,改善神经元损伤[19]。因此,缺血性脑卒中后,circRNA不仅能够通过调节信号通路来减少细胞凋亡,而且也能够通过调节miRNA参与细胞的凋亡。 然而,另一部分circRNA也可促进脑缺血后的细胞凋亡。Dai等[20]在大脑中动脉闭塞模型和氧-葡萄糖剥夺处理的HT22细胞中发现,circRNA HECTD1 (circHECTD1)和肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3 (tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3,TRAF3)的表达明显上调,circHECTD1可以通过海绵miR-133b抑制其活性,进一步促进TRAF3的表达,从而起到促进细胞凋亡的作用。JIANG等[21]在体外实验中发现,通过沉默circANRIL,miR-622的表达上调,抑制了NF-κB通路激活,从而抑制细胞凋亡。上述结果表明,circRNA在脑缺血后调控细胞凋亡时,部分circRNA有抑制细胞凋亡改善神经元损伤的作用,此外,也有另一部分circRNA有促进细胞凋亡进而加重神经元损伤的作用。对于其具体调控方式而言,除了通过调节下游靶点的细胞凋亡之外,也可通过调节miRNA参与细胞凋亡。 2.2.2 细胞自噬 自噬也称Ⅱ型程序性细胞死亡,是细胞死亡的一种形式,已被证明参与脑缺血损伤的发生发展过程[22],在维持细胞质稳态中起着重要作用。自噬在脑缺血损伤过程中是一把双刃剑,一方面适度激活自噬可在一定程度上防止缺血性神经元损伤,而另一方面过度激活自噬则可致正常细胞凋亡,并致使神经元损伤[23]。近年来,circRNA在调控细胞自噬中的作用逐渐受到重视。 部分circRNA可促进脑缺血后的细胞自噬。HAN等[24]在短暂性大脑中动脉阻塞小鼠及缺血性脑卒中患者血浆样本中发现circHECTD1显著增加,其可作为miR-142的海绵,通过抑制TCDD诱导的多聚[ADP-核糖]聚合酶(TIPARP)的表达,促进细胞自噬,而致神经元损伤加重。YANG等[25]在缺血性脑卒中患者的脑微血管内皮细胞(HBMECs)和缺血再灌注损伤小鼠模型中检测到circRNA FOXO3(circFOXO3)和自噬通量的上调,同时体内和体外研究均已证明circFOXO3通过抑制雷帕霉素靶基因1 (mammalian target of rapamycin 1,mTORC1)的活性以促进自噬来清除细胞毒性聚集。由上可知,circRNA调控自噬的功能既可通过miRNA的海绵起作用,也可通过抑制mTORC1的活性来调节。另有研究显示,由缺血预处理诱导的星形细胞通过外泌体将circSHOC2转移至神经元,并对其产生保护作用,而自噬抑制剂可以消除circSHOC2对神经元的保护[19],这表明circSHOC2的作用可以通过促进自噬来实现。 2.2.3 氧化应激 氧化应激(OxS)是指生物体活性氧(ROS)过度产生和/或抗氧化能力减弱的病理过程,导致活性氧产生与清除之间的失衡。神经组织对氧化应激较为敏感,因此氧化应激是急性缺血性脑卒中后神经元损伤和死亡的主要机制之一[26-27]。核因子红系2相关因子2(Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2,Nrf2)是一种调节抗氧化反应的转录因子,其通过Nrf2相关通路驱动多种解毒和抗氧化因子的表达[28-29],从而在与神经元损伤及其相关的氧化应激中发挥神经保护作用。 越来越多的证据表明,circRNA参与氧化应激的过程,并且可能是将氧化应激诱导的病理因素与神经系统疾病相关病理状况联系起来的重要机制[30]。一项高通量circRNA微阵列研究显示,circAKAP7在大脑中动脉闭塞小鼠中受到了抑制[31]。随后XU等[32]在体内实验中发现,exo-circAKAP7可以逆转大脑中动脉闭塞组中活性氧和丙二醛的高表达,在细胞实验中用exo-circAKAP7治疗后,氧化应激相关基因Nrf2可通过海绵miR-155-5p来减弱氧-葡萄糖剥夺诱导的细胞损伤,并抑制Nrf2介导的氧化应激。此外,另有临床研究表明,缺血性卒中患者血液中circMEMO1 的表达增加,沉默circMEMO1使细胞活力增强,并抑制ERK/NF-κB信号通路的激活,从而减少氧化应激和炎症反应[33]。circSLC8A1是由钠钙交换基因SLC8A1产生的circRNA[34],在氧化应激中,氧化本身可能增加神经元中circSLC8A1的表达,减少circRNA的降解,最终降低SLC8A1蛋白的表达。相反,在使用他汀类药物治疗的人神经母细胞瘤SH-SY5Y细胞(具有抗氧化潜力的药物)中,circSLC8A1和SLC8A1蛋白均被还原[35]。CHENG等[36]通过实验发现,过氧化氢(H2O2)下调circPRKCI(蛋白激酶Ciota)的表达,并通过circPRKCI-miR-545/589-E2F2轴诱导神经元损伤,circPRKCI的过表达缓解了H2O2诱导的细胞毒性。因此,保护神经元免受氧化应激可从靶向这种新型级联反应考虑,但目前对于circRNA在神经系统氧化应激中的作用机制仍需进一步阐明。 2.2.4 炎症反应 炎症反应是脑缺血的关键致病机制之一,其在脑缺血损伤的各个阶段发挥重要作用,脑缺血时可能会激活小胶质细胞、趋化白细胞、释放炎症因子,从而加重大脑神经功能损伤。而circRNA可以通过调控基因表达或信号通路参与缺血性脑卒中相关的炎性反应。 有研究发现在氧-葡萄糖剥夺/再灌注处理的脑微血管内皮细胞中circANRIL的表达显著上调,circANRIL的过表达进一步增加了脑微血管内皮细胞中炎性细胞因子(白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α)和单核细胞化学抑制剂蛋白1的分泌[21]。此外,circANRIL对miR-622的表达进行负调节,沉默circANRIL可发挥抗凋亡和抗炎作用。此外,脑缺血再灌注所致的炎性损伤加重部分归因于NF-κB的激活[37]。据报道沉默circANRIL通过抑制NF-κB和C-JUM N-末端激酶(JNK)/P38途径的活化来保护细胞免受脂多糖诱导的炎症损伤[38]。SIRT1基因外显子2-7可共价闭合形成circSIRT1,体外研究发现circSIRT1的表达与SIRT1蛋白的表达成正相关,其可吸附miR-132/212发挥分子海绵效应,从而部分解除miR-132/212与SIRT1 mRNA 3’非翻译区(UTR)的结合,上调SIRT1的表达,后者可通过使p65脱乙酰化失活,进而抑制炎症相关因子表达[39]。此外,过表达的circSIRT1通过与NF-κB p65结合,阻止了T肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的NF-κB核转位,进而抑制炎症相关因子表达。总之,circSIRT1通过两种不同的机制来抑制NF-κB的激活和血管炎症应答:一方面通过抑制胞浆p65核转位激活来抑制炎症因子表达;另一方面,通过上调SIRT1的表达,促进核p65脱乙酰化失活,进而抑制炎性因子表达和血管炎症。这些结果进一步表明,circRNA通过调节炎症因子的表达参与缺血性脑卒中的进展。 2.2.5 血管新生 血管新生是从现有的毛细血管中通过发芽和重塑的方式形成新生血管的生理过程。当缺血性脑卒中后,血流通过新生血管侧支循环的方式改善受损脑组织的缺血缺氧状态,进而改善神经功能障碍[40]。据报道,circRNA是血管新生重要的调控因子,可参与缺血性脑卒中血管生成的病理恢复过程。 研究表明,一些circRNAs参与脑缺血后血管新生的过程。体外实验证明,circ_0006768在氧-葡萄糖剥夺/再灌注诱导的脑微血管内皮细胞中表达下调,circ_0006768过表达可有效恢复脑微血管内皮细胞的血管生成和迁移能力[41]。HANG等[42]通过构建脑微血管内皮细胞损伤模型,发现circ_0003423可通过调节miR-589-5p/TET2轴来缓解脑微血管内皮细胞损伤。另有研究发现,缺血性脑卒中患者外周血中circFUNDC1的表达增加,敲低circFUNDC1减轻了氧-葡萄糖剥夺诱导的细胞凋亡,并促进血管生成[43]。大部分circRNA可以作为miRNA的海绵,并通过竞争性RNA网络调节内源性基因的表达。Li等[3]通过构建circRNA-miRNA-mRNA网络发现circRNA具有miR-122-5p的结合位点,而miR-122-5p作为血管生成因子的上游调节剂,在大脑中动脉闭塞大鼠的血浆和脑脊液中显著下调。此外还发现circRNA-miRNA-mRNA网络中的一些靶基因(如EphB2,Wnt3和Twist1)可参与炎症和血管生成,从而减少神经元损伤。因此,这些circRNA可能是治疗实验性缺血性卒中的靶血管生成因子。 2.2.6 血脑屏障 血脑屏障是由紧密连接结构的大脑血管内皮细胞构成,其具有维持大脑生化环境稳态的重要作用[44]。缺血性脑卒中时,血脑屏障的紧密连接完整性遭到破坏,进而导致细胞旁通透性增加、离子失衡、信号稳态改变和大量的炎症因子进入缺血损伤区,从而使大脑神经元功能障碍甚至细胞凋亡。 circRNA 也参与了缺血性脑卒中后血脑屏障的调控。BAI等[45]通过临床与基础研究发现,circDLGAP4可以充当miR-143的海绵,通过抑制miR-143的活性来调节脑缺血区紧密连接蛋白(Claudin-5、Occludin和ZO-1)和间充质转化标志物(collagenI、collagenIII、α-SMA)的水平,以改善血脑屏障损伤。此外,WU等[46]发现,过表达的circCCDC9可抑制Notch1信号通路,而敲减circCCDC9能够使脑组织亚硝酸盐含量下降、含水量升高,这为circCCDC9保护血脑屏障提供了有力的证据。体内和体外研究表明,circFOXO3主要通过抑制mTORC1促进自噬的作用来改善缺血再灌注下血脑屏障的完整性[47]。后有研究发现,脑膜炎大肠杆菌诱导的脑微血管内皮细胞中 circ_2858 的上调,并证明这种 circRNA 可以通过竞争性海绵 miR-93-5p 促进血管内皮生长因子A(VEGFA)的表达,从而导致紧密连接中断和血脑屏障功能障碍[48]。综上可知,靶向circRNA或利用circRNA分子可能是一种潜在的治疗中枢神经系统血脑屏障损伤的有效策略。 circRNA调控脑缺血发病的作用与机制汇总,见表1。 "

| [1] LI JY, LI QQ, SHENG R. The role and therapeutic potential of exosomes in ischemic stroke. Neurochem Int. 2021;151:105194. [2] 张毅,冯康倪,陈鉴涛,等.非编码RNA在脑缺血再灌注损伤中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2021,37(2):347-355. [3] LI F, LI C, LI X, et al. Altered circular RNA expression profiles in the non-ischemic thalamus in focal cortical infarction mice. Aging. 2020; 12(13):13206-13219. [4] JIANG Q, SU DY, WANG ZZ, et al. Retina as a window to cerebral dysfunction following studies with circRNA signature during neurodegeneration. Theranostics. 2021;11(4):1814-1827. [5] DONG Z, DENG L, PENG Q, et al. CircRNA expression profiles and function prediction in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(3):2609-2618. [6] ZUO L, ZHANG L, ZU J, et al. Circulating Circular RNAs as Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Prediction of Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke. 2020;51(1):319-323. [7] LI S, CHEN L, XU C, et al. Expression profile and bioinformatics analysis of circular RNAs in acute ischemic stroke in a South Chinese Han population. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):10138. [8] SALZMAN J, CHEN RE, OLSEN MN, et al. Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(9):e1003777. [9] 黄纪,李瑞曦,徐军发.环状RNA在感染性疾病中的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2020,33(12):1320-1325. [10] WANG Q, LIU X, ZHAO J, et al. Circular RNAs: novel diagnostic and therapeutic targets for ischemic stroke. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2020; 20(10):1039-1049. [11] CHEN JN, ZHANG YN, TIAN LG, et al. Down-regulating Circular RNA Prkcsh suppresses the inflammatory response after spinal cord injury . Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(1):144-151. [12] 卢志刚,杨昌明,孔祥辉,等. 醒脑开窍中药治疗脑缺血再灌注损伤作用机制的研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(24):235-242. [13] BOGUSZEWSKA-CZUBARA A, BUDZYNSKA B, SKALICKA-WOZNIAK K, et al. Perspectives and New Aspects of Metalloproteinases’ Inhibitors in the Therapy of CNS Disorders: From Chemistry to Medicine. Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(18):3208-3224. [14] XU N, ZHANG Y, DOYCHEVA DM, et al. Adiponectin attenuates neuronal apoptosis induced by hypoxia-ischemia via the activation of AdipoR1/APPL1/LKB1/AMPK pathway in neonatal rats. Neuropharmacology. 2018;133:415-428. [15] WANG H, LI Z, GAO J, et al. Circular RNA circPTK2 regulates oxygen-glucose deprivation-activated microglia-induced hippocampal neuronal apoptosis via miR-29b-SOCS-1-JAK2/STAT3-IL-1β signaling. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;129:488-496. [16] OHSHIRO K, CHEN J, SRIVASTAV J, et al. Alterations in TGF-β signaling leads to high HMGA2 levels potentially through modulation of PJA1/SMAD3 in HCC cells. Genes Cancer. 2020;11(1-2):43-52. [17] CHE F, DU H, WEI J, et al. MicroRNA-323 suppresses nerve cell toxicity in cerebral infarction via the transforming growth factor-β1/SMAD3 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(2):993-1002. [18] CHEN W, WANG H, FENG J, et al. Overexpression of circRNA circUCK2 Attenuates Cell Apoptosis in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via miR-125b-5p/GDF11 Signaling. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;22:673-683. [19] CHEN W, WANG H, ZHU Z, et al. Exosome-Shuttled circSHOC2 from IPASs Regulates Neuronal Autophagy and Ameliorates Ischemic Brain Injury via the miR-7670-3p/SIRT1 Axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;22:657-672. [20] DAI Q, MA Y, XU Z, et al. Downregulation of circular RNA HECTD1 induces neuroprotection against ischemic stroke through the microRNA-133b/TRAF3 pathway. Life Sci. 2021;264:118626. [21] JIANG S, ZHAO G, LU J, et al. Silencing of circular RNA ANRIL attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation-induced injury in human brain microvascular endothelial cells by sponging miR-622. Biol Res. 2020;53(1):27. [22] ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, WEI Q, et al. Activation of Sigma-1 Receptor Enhanced Pericyte Survival via the Interplay Between Apoptosis and Autophagy: Implications for Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity in Stroke. Transl Stroke Res. 2020;11(2):267-287. [23] CHEN W, SUN Y, LIU K, et al. Autophagy: a double-edged sword for neuronal survival after cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen Res. 2014; 9(12):1210-1216. [24] HAN B, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Novel insight into circular RNA HECTD1 in astrocyte activation via autophagy by targeting MIR142-TIPARP: implications for cerebral ischemic stroke. Autophagy. 2018;14(7):1164-1184. [25] YANG Z, HUANG C, WEN X, et al. Circular RNA circ-FoxO3 attenuates blood-brain barrier damage by inducing autophagy during ischemia/reperfusion. Mol Ther. 2022;30(3):1275-1287. [26] MANZANERO S, SANTRO T, ARUMUGAM TV. Neuronal oxidative stress in acute ischemic stroke: sources and contribution to cell injury. Neurochem Int. 2013;62(5):712-718. [27] FUMOTO T, NARAOKA M, KATAGAI T, et al. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Microvascular Disturbances after Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res. 2019;10(6):684-694. [28] SYKIOTIS GP, BOHMANN D. Stress-activated cap’n’collar transcription factors in aging and human disease. Sci Signal. 2010;3(112):re3. [29] YANG JH, ZHANG RJ, LIN JJ, et al. The Differentially Expressed Circular RNAs in the Substantia Nigra and Corpus Striatum of Nrf2-Knockout Mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(3):936-951. [30] FUSCHI P, MAIMONE B, GAETANO C, et al. Noncoding RNAs in the Vascular System Response to Oxidative Stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019;30(7):992-1010. [31] MEHTA SL, PANDI G, VEMUGANTI R. Circular RNA Expression Profiles Alter Significantly in Mouse Brain After Transient Focal Ischemia. Stroke. 2017;48(9):2541-2548. [32] XU L, JI H, JIANG Y, et al. Exosomes Derived From CircAkap7-Modified Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Against Cerebral Ischemic Injury. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:569977. [33] REN X, JING YX, ZHOU ZW, et al. Knockdown of circRNA-Memo1 Reduces Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury in Human Brain Endothelial Cells Through miRNA-17-5p/SOS1 Axis. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(4):2085-2097. [34] JAHN C, BäR C, THUM T. CircSlc8a1, breaking a vicious circle in cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res. 2019;115(14):1946-1947. [35] HANAN M, SIMCHOVITZ A, YAYON N, et al. A Parkinson’s disease CircRNAs Resource reveals a link between circSLC8A1 and oxidative stress. EMBO Mol Med. 2020;12(11):e13551. [36] CHENG Q, CAO X, XUE L, et al. CircPRKCI-miR-545/589-E2F7 axis dysregulation mediates hydrogen peroxide-induced neuronal cell injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;514(2):428-435. [37] ZHAO H, CHEN Z, XIE LJ, et al. Suppression of TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway Improves Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(5):4311-4319. [38] DENG W, CHEN K, LIU S, et al. Silencing circular ANRIL protects HK-2 cells from lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury through up-regulating microRNA-9. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1): 3478-3484. [39] 韩梅. 非编码环RNA与血管疾病[C].中国生物化学与分子生物学会2019年全国学术会议暨学会成立四十周年, 中国山西太原, F, 2019:40 [40] TIAN DS, QIN C, ZHOU LQ, et al. FSAP aggravated endothelial dysfunction and neurological deficits in acute ischemic stroke due to large vessel occlusion. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):6. [41] LI J, WANG J, WANG Z. Circ_0006768 upregulation attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced human brain microvascular endothelial cell injuries by upregulating VEZF1 via miR-222-3p inhibition. Metab Brain Dis. 2021;36(8):2521-2534. [42] YU H, PAN Y, DAI M, et al. Circ_0003423 Alleviates ox-LDL-Induced Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell Injury via the miR-589-5p/TET2 Network. Neurochem Res. 2021;46(11):2885-2896. [43] BAI X, LIU X, WU H, et al. CircFUNDC1 knockdown alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced human brain microvascular endothelial cell injuries by inhibiting PTEN via miR-375. Neurosci Lett. 2022;770: 136381. [44] NIAN K, HARDING IC, HERMAN IM, et al. Blood-Brain Barrier Damage in Ischemic Stroke and Its Regulation by Endothelial Mechanotransduction. Front Physiol. 2020;11:605398. [45] BAI Y, ZHANG Y, HAN B, et al. Circular RNA DLGAP4 Ameliorates Ischemic Stroke Outcomes by Targeting miR-143 to Regulate Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition Associated with Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity. J Neurosci. 2018;38(1):32-50. [46] WU L, XU H, ZHANG W, et al. Circular RNA circCCDC9 alleviates ischaemic stroke ischaemia/reperfusion injury via the Notch pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(24):14152-14159. [47] YANG Z, HUANG C, WEN X, et al. Circular RNA circ-FoxO3 attenuates blood-brain barrier damage by inducing autophagy during ischemia/reperfusion. Mol Ther. 2022;30(3):1275-1287. [48] YANG R, CHEN J, XU B, et al. circ_2858 Helps Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption by Increasing VEGFA via Sponging miR-93-5p during Meningitis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;22:708-721. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [3] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [4] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. A review of physical activity intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [6] | Liang Jiaqi, Liu Hengxu, Yang Jinxin, Yang Yi, Deng Xuhui, Tan Mingjian, Luo Jiong. Health benefit relationship between exercise and intestinal bacteria [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1292-1299. |
| [7] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [8] | Ruan Ling, Wang Guanghua, Wu Rongping, Jin Zhan, Lyu Zhenqing, Zhang Nan, Li Shoubang. Correlation between exercise intensity and lipid metabolism disorder and oxidative stress in a high-diet rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1149-1155. |
| [9] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [10] | Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [11] | Chen Shisong, Liu Xiaohong, Xu Zhiyun. Current status and prospects of bioprosthetic heart valves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1096-1102. |
| [12] | Lu Di, Zhang Cheng, Duan Rongquan, Liu Zongxiang. Osteoinductive properties of calcium phosphate ceramic bone repair materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1103-1109. |
| [13] | Shi Yehong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Early thrombosis and prevention of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [14] | Tang Haotian, Liao Rongdong, Tian Jing. Application and design of piezoelectric materials for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [15] | Wu Yujie, Wan Xiaofang, Wei Mianxing, Peng Shiyuan, Xu Xiaomei. Correlation between autophagy and the Hippo-YAP protein pathway in periodental ligament cells on the pressure side of a mouse model of orthodontic tooth movement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 683-689. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||