Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (25): 3994-3999.doi: 10.12307/2024.186
Previous Articles Next Articles
Neuron-derived extracellular vesicles promote neurogenesis of neural stem cells
Li Zhen1, Sun Xiao1, Xie Yongpeng2, Rong Wang1, Sun Haitao3
- 1Trauma Center, 3Department of Orthopedics, First People’s Hospital of Lianyungang, Lianyungang 222000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, First People’s Hospital of Lianyungang, Institute of Emergency Medicine of Lianyungang, Lianyungang 222000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-21Accepted:2023-08-07Online:2024-09-08Published:2023-11-23 -
Contact:Sun Xiao, Chief physician, Trauma Center, First People’s Hospital of Lianyungang, Lianyungang 222000, Jiangsu Province, China Xie Yongpeng, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, First People’s Hospital of Lianyungang, Institute of Emergency Medicine of Lianyungang, Lianyungang 222000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Li Zhen, Master, Physician, Trauma Center, First People’s Hospital of Lianyungang, Lianyungang 222000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Youth Project of First People’s Hospital of Lianyungang, No. QN2213 (to LZ); Scientific Research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission of China, No. H2019109 (to XYP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zhen, Sun Xiao, Xie Yongpeng, Rong Wang, Sun Haitao. Neuron-derived extracellular vesicles promote neurogenesis of neural stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 3994-3999.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
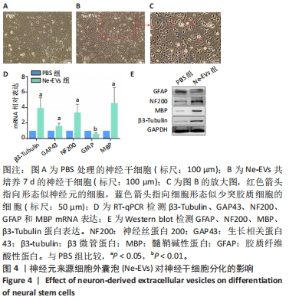
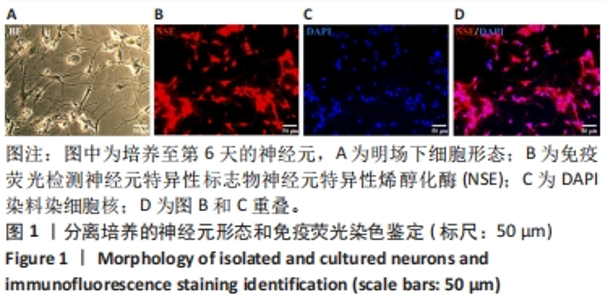
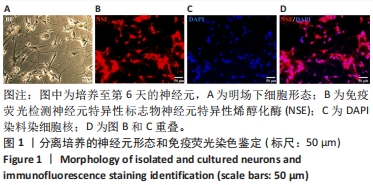
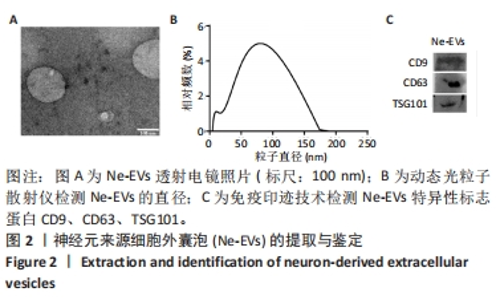
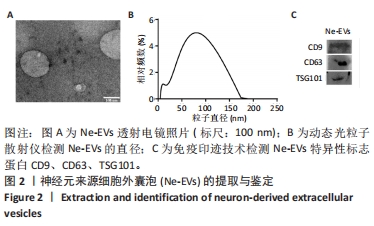
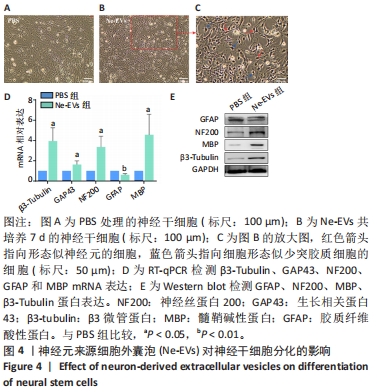
2.4 神经元来源细胞外囊泡对神经干细胞分化的影响 与PBS处理组相比,神经元来源细胞外囊泡处理后神经干细胞形态发生明显改变,细胞突起明显,胞体饱满,部分细胞形态呈神经元样,部分细胞似少突胶质细胞样,见图4A-C。RT-qPCR检测发现,相比于PBS组,神经元来源细胞外囊泡组神经元特异性标志蛋白β3-Tubulin、GAP43、NF200的表达升高,少突胶质细胞的标志蛋白MBP的表达也有升高,见图4D,此外,星形胶质细胞特异性标志蛋白GFAP的表达下降。相应地,免疫印迹技术和免疫荧光检测也发现β3-Tubulin、NF200和MBP蛋白表达升高,而GFAP表达降低,见图4E和图5。这些结果说明,神经元来源细胞外囊泡促进神经干细胞向神经元及少突胶质细胞方向分化,抑制星形胶质细胞分化,有利于神经生成。"
| [1] REYNOLDS BA, WEISS S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1992;255(5052):1707-1710. [2] XU B, YIN M, YANG Y, et al. Transplantation of neural stem progenitor cells from different sources for severe spinal cord injury repair in rat. Bioact Mater. 2022;23:300-313. [3] ASSINCK P, DUNCAN GJ, HILTON BJ, et al. Cell transplantation therapy for spinal cord injury. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20(5):637-647. [4] 陈晓丽, 李少川, 陈久智, 等. 神经干细胞治疗脊髓损伤的研究近况[J].中国医药生物技术,2017,12(5):424-428. [5] 李晓寅, 杨晓青, 陈淑莲,等. 胶原/丝素蛋白支架联合神经干细胞治疗创伤性脊髓损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(6):890-896. [6] LU P, WOODRUFF G, WANG Y, et al. Long-distance axonal growth from human induced pluripotent stem cells after spinal cord injury. Neuron. 2014;83(4):789-796. [7] LU P, WANG Y, GRAHAM L, et al. Long-distance growth and connectivity of neural stem cells after severe spinal cord injury. Cell. 2012;150(6):1264-1273. [8] ROSENZWEIG ES, BROCK JH, LU P, et al. Restorative effects of human neural stem cell grafts on the primate spinal cord. Nat Med. 2018;24(4):484-490. [9] SALEWSKI RP, MITCHELL RA, LI L, et al. Transplantation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neural Stem Cells Mediate Functional Recovery Following Thoracic Spinal Cord Injury Through Remyelination of Axons. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(7):743-754. [10] O’SHEA TM, BURDA JE, SOFRONIEW MV. Cell biology of spinal cord injury and repair. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(9):3259-3270. [11] FITCH MT, SILVER J. CNS injury, glial scars, and inflammation: Inhibitory extracellular matrices and regeneration failure. Exp Neurol. 2008;209(2):294-301. [12] MATHIEU M, MARTIN-JAULAR L, LAVIEU G, et al. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(1):9-17. [13] ZOMER A, MAYNARD C, VERWEIJ FJ, et al. In Vivo imaging reveals extracellular vesicle-mediated phenocopying of metastatic behavior. Cell. 2015;161(5): 1046-1057. [14] VALADI H, EKSTRÖM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659. [15] HUANG CC, NARAYANAN R, ALAPATI S, et al. Exosomes as biomimetic tools for stem cell differentiation: Applications in dental pulp tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2016;111:103-115. [16] SHARMA P, MESCI P, CARROMEU C, et al. Exosomes regulate neurogenesis and circuit assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(32):16086-16094. [17] CHOU CH, FAN HC, HUENG DY. Potential of Neural Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2015;2015:571475. [18] PARMAR M. Towards stem cell based therapies for Parkinson’s disease. Development. 2018;145(1):dev156117. [19] HAYASHI Y, LIN HT, LEE CC, et al. Effects of neural stem cell transplantation in Alzheimer’s disease models. J Biomed Sci. 2020;27(1):29. [20] IM W, LEE ST, CHU K, et al. Stem Cells Transplantation and Huntington’s Disease. Int J Stem Cells. 2009;2(2):102-108. [21] CHOI KA, CHOI Y, HONG S. Stem cell transplantation for Huntington’s diseases. Methods. 2018;133:104-112. [22] ZHANG HA, YUAN CX, LIU KF, et al. Neural stem cell transplantation alleviates functional cognitive deficits in a mouse model of tauopathy. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(1):152-162. [23] GHOBRIAL GM, ANDERSON KD, DIDIDZE M, et al. Human Neural Stem Cell Transplantation in Chronic Cervical Spinal Cord Injury: Functional Outcomes at 12 Months in a Phase II Clinical Trial. Neurosurgery. 2017;64(CN_suppl_1):87-91. [24] CURTIS E, MARTIN JR, GABEL B, et al. A First-in-Human, Phase I Study of Neural Stem Cell Transplantation for Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Stem Cell. 2018; 22(6):941-950. [25] LEVI AD, OKONKWO DO, PARK P, et al. Emerging Safety of Intramedullary Transplantation of Human Neural Stem Cells in Chronic Cervical and Thoracic Spinal Cord Injury. Neurosurgery. 2018;82(4):562-575. [26] LEVI AD, ANDERSON KD, OKONKWO DO, et al. Clinical Outcomes from a Multi-Center Study of Human Neural Stem Cell Transplantation in Chronic Cervical Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2019;36(6):891-902. [27] SHIN JC, KIM KN, YOO J, et al. Clinical Trial of Human Fetal Brain-Derived Neural Stem/Progenitor Cell Transplantation in Patients with Traumatic Cervical Spinal Cord Injury. Neural Plast. 2015;2015:630932. [28] WU CC, LIEN CC, HOU WH, et al. Gain of BDNF Function in Engrafted Neural Stem Cells Promotes the Therapeutic Potential for Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci Rep. 2016;6:27358. [29] MARSH SE, BLURTON-JONES M. Neural stem cell therapy for neurodegenerative disorders: The role of neurotrophic support. Neurochem Int. 2017;106:94-100. [30] CUMMINGS BJ, UCHIDA N, TAMAKI SJ, et al. Human neural stem cell differentiation following transplantation into spinal cord injured mice: association with recovery of locomotor function. Neurol Res. 2006;28(5):474-481. [31] HE N, MAO XJ, DING YM, et al. New insights into the biological roles of immune cells in neural stem cells in post-traumatic injury of the central nervous system. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(9):1908-1916. [32] HANEY MJ, KLYACHKO NL, ZHAO Y, et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J Control Release. 2015;207:18-30. [33] GUO S, PERETS N, BETZER O, et al. Intranasal Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Loaded with Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog siRNA Repairs Complete Spinal Cord Injury. ACS Nano. 2019;13(9):10015-10028. [34] MAROTE A, TEIXEIRA FG, MENDES-PINHEIRO B, et al. MSCs-Derived Exosomes: Cell-Secreted Nanovesicles with Regenerative Potential. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:231. [35] PERETS N, HERTZ S, LONDON M, et al. Intranasal administration of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates autistic-like behaviors of BTBR mice. Mol Autism. 2018;9:57. [36] NI H, YANG S, SIAW-DEBRAH F, et al. Exosomes Derived From Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Early Inflammatory Responses Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:14. [37] WILLIAMS AM, DENNAHY IS, BHATTI UF, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Provide Neuroprotection and Improve Long-Term Neurologic Outcomes in a Swine Model of Traumatic Brain Injury and Hemorrhagic Shock. J Neurotrauma. 2019;36(1):54-60. [38] REZA-ZALDIVAR EE, HERNÁNDEZ-SAPIÉNS MA, MINJAREZ B, et al. Potential Effects of MSC-Derived Exosomes in Neuroplasticity in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:317. [39] FÜHRMANN T, ANANDAKUMARAN PN, SHOICHET MS. Combinatorial Therapies After Spinal Cord Injury: How Can Biomaterials Help? Adv Healthc Mater. 2017; 6(10):1601130. [40] XU B, ZHANG Y, DU XF, et al. Neurons secrete miR-132-containing exosomes to regulate brain vascular integrity. Cell Res. 2017;27(7):882-897. [41] YIN Z, HAN Z, HU T, et al. Neuron-derived exosomes with high miR-21-5p expression promoted polarization of M1 microglia in culture. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;83:270-282. |
| [1] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [2] | Feng Ruiqin, Han Na, Zhang Meng, Gu Xinyi, Zhang Fengshi. Combination of 1% platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [3] | Wang Wen, Zheng Pengpeng, Meng Haohao, Liu Hao, Yuan Changyong. Overexpression of Sema3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and MC3T3-E1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 993-999. |
| [4] | Qiu Xiaoyan, Li Bixin, Li Jingdi, Fan Chuiqin, Ma Lian, Wang Hongwu. Differentiation of insulin-producing cells from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells infected by MAFA-PDX1 overexpressed lentivirus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1000-1006. |
| [5] | Li Longyang, Zhang Songjiang, Zhao Xianmin, Zhou Chunguang, Gao Jianfeng. Electroacupuncture intervention on the proliferation and differentiation of hippocampal neurons and oligodendrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1029-1035. |
| [6] | Mu Bingtao, Yu Jingwen, Liu Chunyun, Guo Minfang, Meng Tao, Yang Pengwei, Wei Wenyue, Song Lijuan, Yu Jiezhong, Ma Cungen. Immunomodulatory effect of astragaloside IV on T cells of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1057-1062. |
| [7] | Liu Kexin, Song Lijuan, Wu Yige, Han Guangyuan, Miao Zhuyue, Wei Ruheng, Xiao Baoguo, Ma Cungen, Huang Jianjun. Hydroxysafflor yellow A intervenes astrocyte lipocalin 2 expression after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1063-1069. |
| [8] | Liu Jianhong, Liao Shijie, Li Boxiang, Tang Shengping, Wei Zhendi, Ding Xiaofei. Extracellular vesicles carrying non-coding RNA regulate the activation of osteoclasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1076-1082. |
| [9] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [10] | Liu Hanfeng, Wang Jingjing, Yu Yunsheng. Artificial exosomes in treatment of myocardial infarction: current status and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1118-1123. |
| [11] | Zhuge Xiaoxuan, Li Ce, Bao Guangjie, Kang Hong. Potential value of canonical and non-canonical roles of connexin 43 in disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1130-1136. |
| [12] | Chen Zepeng, Hou Yonghui, Chen Shudong, Hou Yu, Lin Dingkun. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid treats spinal cord injury by reducing apoptosis of spinal cord neurons under glucose and oxygen deprivation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 528-534. |
| [13] | Li Lisi, Zhang Chengdong, Li Xiaolong, Ye Ziyu, Pu Chao, Yang Zaijun, Shi Feng, Xiao Dongqin. Growth differentiation factor-5 modified by bisphosphonate promotes osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 373-379. |
| [14] | Wang Li, Chen Peng, Wei Xiuying, Lu Yangjia, Lai Sijia, Wang Kaihua. Application of MRI-based image navigation and target selection in transcranial magnetic stimulation treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4234-4241. |
| [15] | Yue Tingting, Zhu Ting, Mao Jiannan, Li Wei, Hang Chunhua. Culture, identification, and differentiation of rabbit pituitary stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 3942-3946. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||