Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (3): 373-379.doi: 10.12307/2023.981
Previous Articles Next Articles
Growth differentiation factor-5 modified by bisphosphonate promotes osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells
Li Lisi1, 2, 3, Zhang Chengdong2, Li Xiaolong2, Ye Ziyu3, Pu Chao2, Yang Zaijun1, 3, Shi Feng1, 3, Xiao Dongqin2
- 1Organization and Repair Materials Engineering Technology Collaborative Innovation Center, West China Normal University, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Second Clinical College of North Sichuan Medical College·Institute of Tissue Engineering and Stem Cells of Nanchong Central Hospital, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China; 3College of Life Sciences, West China Normal University, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2022-12-19Accepted:2023-02-11Online:2024-01-28Published:2023-07-10 -
Contact:Yang Zaijun, PhD, Professor, Organization and Repair Materials Engineering Technology Collaborative Innovation Center, West China Normal University, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China; College of Life Sciences, West China Normal University, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China Shi Feng, PhD, Associate professor, Organization and Repair Materials Engineering Technology Collaborative Innovation Center, West China Normal University, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China; College of Life Sciences, West China Normal University, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China Xiao Dongqin, PhD, Associate researcher, Second Clinical College of North Sichuan Medical College·Institute of Tissue Engineering and Stem Cells of Nanchong Central Hospital, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Li Lisi, Master candidate, Organization and Repair Materials Engineering Technology Collaborative Innovation Center, West China Normal University, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China; Second Clinical College of North Sichuan Medical College·Institute of Tissue Engineering and Stem Cells of Nanchong Central Hospital, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China; College of Life Sciences, West China Normal University, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82002289 (to XDQ); Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province, No. 2022NSFSC0685 (to XDQ); Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province, No. 23NSFSC3371 (to ZCD); Nanchong City-School Cooperative Scientific Research Project. No. 22SXJCQN0002 (to XDQ); Nanchong City-School Cooperative Scientific Research Project. No. 22SXQT0385 (to PC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Lisi, Zhang Chengdong, Li Xiaolong, Ye Ziyu, Pu Chao, Yang Zaijun, Shi Feng, Xiao Dongqin. Growth differentiation factor-5 modified by bisphosphonate promotes osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 373-379.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
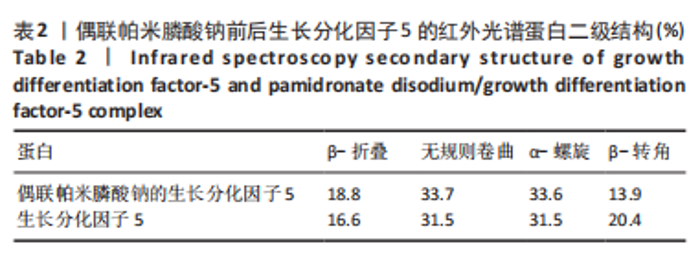
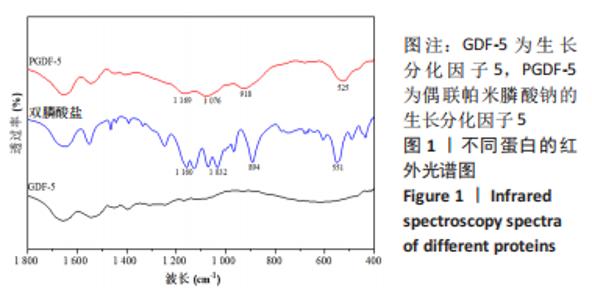
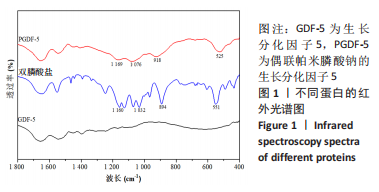
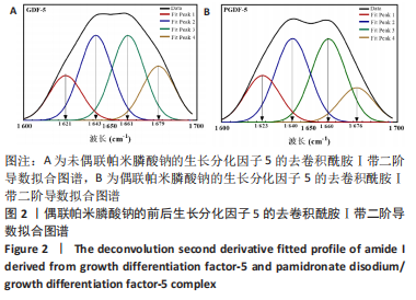
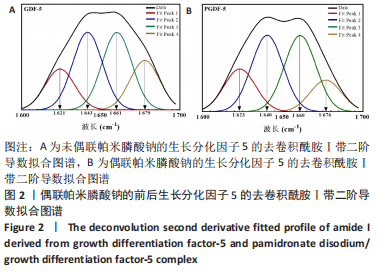
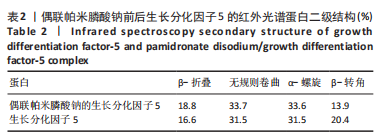
在生长分化因子5的红外图谱中,1 600-1 700 cm-1区域内由4个吸收峰组成,其中心位置分别为1 621,1 643,1 661及1 679 cm-1。类似地,在偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长分化因子5的红外图谱中,1 600-1 700 cm-1区域内由4个吸收峰组成,其中心位置分别为1 623,1 640,1 660及1 676 cm-1。对比酰胺Ⅰ带峰对应蛋白二级结构,可知吸收峰1 621-1 623,1 640-1 643,1 660-1 661,1 676-1 679 cm-1分别归属于β-折叠、无规则卷曲结构、α-螺旋、β-转角。再根据峰面积计算蛋白二级结构比率,结果显示:在生长分化因子5蛋白二级结构中,α-螺旋占比31.5%,无规则卷曲占比31.5%,β-折叠占比16.6%,β-转角占比20.4%;在偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长分化因子5样品中,α-螺旋占比33.6%,无规则卷曲占比33.7%,β-折叠占比18.8%,β-转角占比13.9%,见表2。"
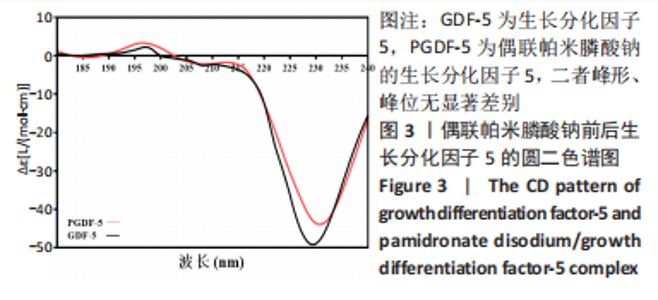
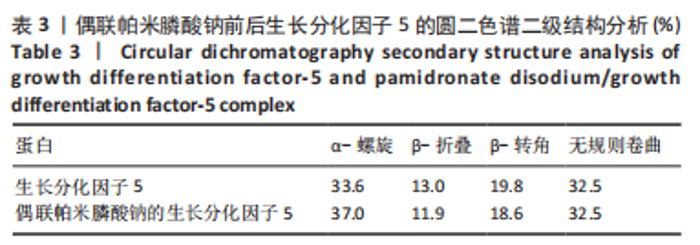
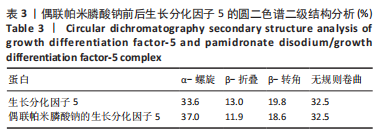
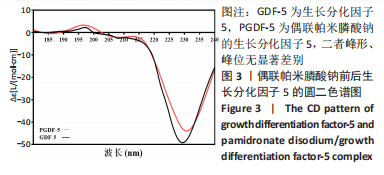
对偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长分化因子5样品和生长分化因子5样品进行圆二色谱测试,结果显示两种蛋白图谱峰形、峰位无显著差别,见图3,蛋白质二级结构数据由CDPro中SELCON3模型计算。计算得到两种蛋白的二级结构各构象单元的百分含量,见表3所示。生长分化因子5蛋白的二级结构中,α-螺旋占比33.6%,无规则卷曲占比32.5%,β-折叠占比13.0%,β-转角占比19.8%;偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长分化因子5样品中,α-螺旋占比37.0%,无规则卷曲占比32.5%,β-折叠占比11.9%,β-转角占比18.6%,实验结果与傅里叶红外光谱结果相符。结合红外光谱数据和圆二色谱数据表明,双膦酸盐改性前后,生长分化因子5蛋白的二级结构无显著变化。"
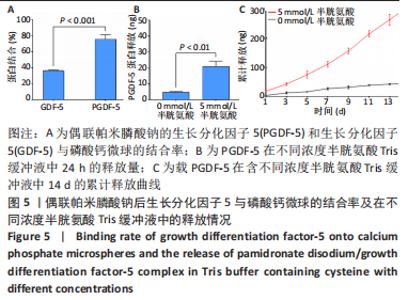
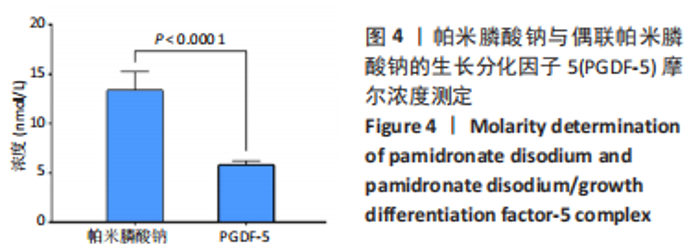
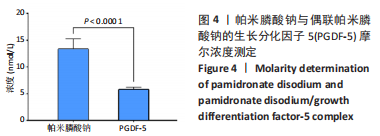
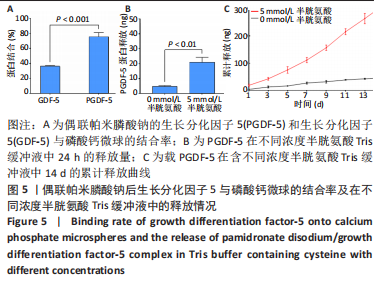
2.3 偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长分化因子5骨靶向性及体外释放表征 利用磷酸钙吸附实验验证改性蛋白的骨靶向性,磷酸钙上偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长分化因子5的吸附量为(1 516.6±14.1) ng,生长分化因子5的吸附量为(728.0±8.2) ng。由此可知,经过双膦酸盐修饰的生长分化因子5蛋白与磷酸钙微球的结合率为(75.8±5.5)%,而生长分化因子5与磷酸钙的结合率仅为(36.4±1.0)%,见图5A,这表明双膦酸盐改性后,生长分化因子5对磷酸钙及骨矿物的亲和力显著提高。 此外,进一步研究了偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长分化因子5在Tris缓冲液及含半胱氨酸Tris缓冲液中的释放情况,蛋白释放结果显示:当溶液中无半光氨酸存在时,24 h后蛋白的释放量仅为(4.6±0.7) ng,而在添加半胱氨酸的溶液中,蛋白的释放量达到(20.8±3.4) ng,见图5B,这表明溶液中半光氨酸的存在有利于蛋白的释放。14 d累计释放结果显示:在含5 mmol/L半胱氨酸Tris缓冲溶液中,偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长因分化因子5的释放速率及释放量显著高于无半胱氨酸的Tris缓冲液,且释放过程中无明显突释现象,见图5C。"
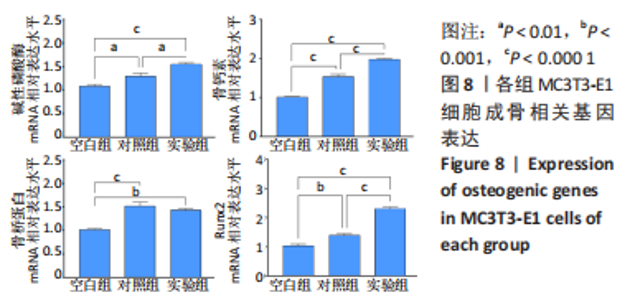
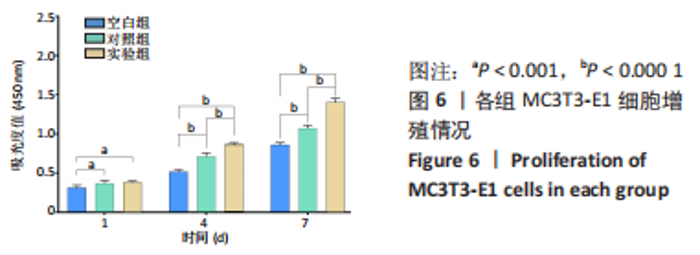
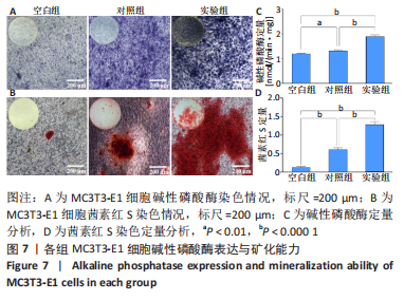
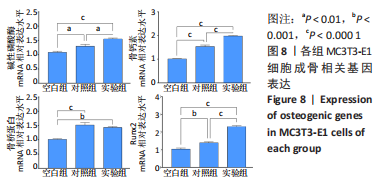
碱性磷酸酶染色结果显示,实验组被染成蓝紫色的细胞数量明显最多且颜色最深,对照组次之,空白组最浅,见图7A。碱性磷酸酶试剂盒定量测试结果显示,培养7 d后,对照组细胞碱性磷酸酶表达明显高于空白组(P < 0.01),实验组细胞碱性磷酸酶表达明显高于对照组、空白组(P < 0.000 1),见图7C。这说明相比于生长分化因子5,偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长分化因子5更有利于增强细胞的碱性磷酸酶表达。 茜素红S染色结果显示,实验组细胞周围形成的橘红色钙结节含量最多,对照组明显减少,空白组细胞周围几乎看不见橘红色钙结节,见图7B。定量分析结果显示,实验组钙结节含量明显高于对照组、空白组(P < 0.000 1),见图7D。这表明比于生长分化因子5,偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长分化因子5更有利于增强细胞的矿化能力。 综合上述,相比于生长分化因子5,偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长分化因子5更有利于促进细胞的成骨分化能力。 2.4.3 偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长分化因子5对MC3T3-E1细胞成骨相关基因表达的影响 qRT-PCR检测结果显示,在成骨诱导第7天时,相比于空白组,对照组及实验组显著促进细胞碱性磷酸酶、骨桥蛋白、骨钙素及Runx2 mRNA的表达(P < 0.01,P < 0.001,P < 0.000 1);相比于对照组,实验组显著促进细胞碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素及Runx2 mRNA的表达(P < 0.01,P < 0.000 1),见图8。这表明生长分化因子5及偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长分化因子5均有利于上调细胞成骨分化相关基因的表达,而偶联帕米膦酸钠的生长分化因子5促进成骨分化基因表达上调的作用更显著。"
| [1] QU H, FU H, HAN Z, et al. Biomaterials for bone tissue engineering scaffolds: a review. RSC Adv. 2019;9(45):26252-26262. [2] PRADOS B, DEL TORO R, MACGROGAN D, et al. Heterotopic ossification in mice overexpressing Bmp2 in Tie2+ lineages. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(8):729. [3] BARRATT SL, FLOWER VA, PAULING JD, et al. VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) and Fibrotic Lung Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(5):1269. [4] MANG T, KLEINSCHMIDT-DORR K, PLOEGER F, et al. The GDF-5 mutant M1673 exerts robust anabolic and anti-catabolic effects in chondrocytes. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(13):7141-7150. [5] WALDMANN L, LEYHR J, ZHANG H, et al. The role of Gdf5 in the development of the zebrafish fin endoskeleton. Dev Dyn. 2022;251(9):153515-153549. [6] KAUSAR T, NAYEEM SM. Correlating interfacial water dynamics with protein-protein interaction in complex of GDF-5 and BMPRI receptors Biophys Chem. 2018;240:50-62. [7] ZHAO Q, XIAO DQ, LI YW, et al. Repair of rabbit femoral head necrosis by release of alendronate and growth differentiation factor-5 from injectable alginate/calcium phosphate carriers. Mater Today Commun. 2022;33. doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104530 [8] LV B, GAN WK, CHENG ZR, et al. Current Insights Into the Maintenance of Structure and Function of Intervertebral Disc: A Review of the Regulatory Role of Growth and Differentiation Factor-5. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:842525. [9] GUO S, CUI L, XIAO C, et al. The Mechanisms and Functions of GDF-5 in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(3):734-741. [10] LEKNES KN, YANG J, QAHASH M, et al. Alveolar ridge augmentation using implants coated with recombinant human growth/differentiation factor -5 (rhGDF-5). Radiographic observations. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013;24(11):1185-1191. [11] XIAO D, YANG F, ZHAO Q, et al. Fabrication of a Cu/Zn co-incorporated calcium phosphate scaffold-derived GDF-5 sustained release system with enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis properties. RSC Adv. 2018;8(52):29526-29534. [12] ZHANG BG, MYERS DE, WALLACE GG, et al. Bioactive coatings for orthopaedic implants-recent trends in development of implant coatings. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(7): 11878-11921. [13] TEIXEIRA S, BRANCO L, FERNANDES MH, et al. Bisphosphonates and Cancer: A Relationship Beyond the Antiresorptive Effects. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2019;19(12): 988-998. [14] ROMANELLO M, BIVI N, PINES A, et al. Bisphosphonates activate nucleotide receptors signaling and induce the expression of Hsp90 in osteoblast-like cell lines. Bone. 2006;39(4):739-753. [15] CUI Y, ZHU T, LI D, et al. Bisphosphonate-Functionalized Scaffolds for Enhanced Bone Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(23):e1901073. [16] LEGIRET FE, SIEBEN VJ, WOODWARD EM, et al. A high performance microfluidic analyser for phosphate measurements in marine waters using the vanadomolybdate method. Talanta. 2013;116:382-387. [17] 肖东琴,王东微,任俊臣,等.掺铜羟基磷灰石微球的制备及表征[J].无机材料学报,2014,29(7):769-775. [18] 陈硕,肖东琴,李兴平,等.钛植入体表面钽功能涂层制备及性能表征[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):546-552. [19] ZHANG Q, WANG QQ, LV S, et al. Comparison of collagen and gelatin extracted from the skins of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Food Biosci. 2016;13:41-48. [20] SAFARPOUR H, BANADKOKI SB, KESHAVARZI Z, et al. Expression analysis and ATR-FTIR characterization of the secondary structure of recombinant human TNF-alpha from Escherichia coli SHuffle((R)) T7 Express and BL21 (DE3) cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;99:173-178. [21] ZHAO HY, WU J, ZHU JJ, et al. Research Advances in Tissue Engineering Materials for Sustained Release of Growth Factors. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:808202. [22] WRIGHT JE, GITTENS SA, BANSAL G, et al. A comparison of mineral affinity of bisphosphonate-protein conjugates constructed with disulfide and thioether linkages. Biomaterials. 2006;27(5):769-784. [23] MACDONALD B, MCCARLEY S, NOEEN S, et al. Protein-protein interactions affect alpha helix stability in crowded environments. J Phys Chem B. 2015;119(7): 2956-2967. [24] YUTA A, BARANIUK JN. Therapeutic approaches to mucus hypersecretion. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2005;5(3):243-251. [25] PEDONE E, FIORENTINO G, BARTOLUCCI S, et al. Enzymatic Antioxidant Signatures in Hyperthermophilic Archaea. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(8):703. [26] 孟凡青,吕国良,吴鸿雁,等.帕米磷酸钠对大鼠成骨细胞增殖、分化的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2004,10(10):8-9. [27] 李颉颃,苏志飞,白璇,等.唑来膦酸对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及成骨分化的作用研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2019,37(3):242-247. [28] 李公超,任秀智,王延宙,等.帕米磷酸钠对成骨不全成骨细胞和成纤维细胞增殖分化的研究[J].罕少疾病杂志,2011,18(3):1-5. [29] 袁斯远,孔蓓蓓,盛彤,等.葛根素干预小鼠成骨细胞分化相关特征性蛋白mRNA的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(42):6732-6736. |
| [1] | Wu Tian, Zhao Yue, Hu Rong. Effect of nanobubbles carrying double antibodies on the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 341-346. |
| [2] | Ran Lei, Han Haihui, Xu Bo, Wang Jianye, Shen Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Molecular docking analysis of the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Cibotium barometz and Epimedium for rheumatoid arthritis: animal experiment validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 208-215. |
| [3] | Wang Qian, Lu Ziang, Li Lihe, Lyu Chaoliang, Wang Meng, Zhang Cunxin. Sinomenine effectively inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 224-230. |
| [4] | Yang Ting, Ding Zhibin, Jiang Nan, Han Hongxia, Hou Miaomiao, Ma Cungen, Song Lijuan, Li Xinyi. Astrocytes regulate glial scar formation in cerebral ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 131-138. |
| [5] | Wei Yurou, Tian Jiaqing, He Xianshun, Zhan Zhiwei, Wei Tengfei, Lin Tianye, He Wei, Wei Qiushi. Effect of lentiviral silencing of Piezo1 on osteogenic differentiation and TAZ expression in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 12-19. |
| [6] | Zhang Yuanshu, He Xu, Xue Yuan, Jin Yesheng, Wang Kai, Shi Qin, Rui Yongjun. Irisin alleviates palmitic acid-induced osteogenic inhibition in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 26-31. |
| [7] | Zhou Minghua, Hu Xiaoyu. LncRNA SNHG4 regulates miR-152-3p during osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 38-43. |
| [8] | Sun Jing, Liao Jian, Sun Jiangling, Cheng Ping, Feng Hongchao. Recombinant human growth hormone promotes osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 56-61. |
| [9] | Fan Yongjing, Wang Shu, Jin Wulong. Characteristics, advantages and application of osteogenic differentiation of jaw bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 100-106. |
| [10] | Huang Yongbin, Wang Tao, Lou Yuanyi, Pang Jingqun, Chen Guanghua. Application prospect of mesenchymal stem cells in promoting muscle tissue repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 107-112. |
| [11] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-6. |
| [12] | He Xi, Wan Yu, Tang Yuting, Yang Anning, Wu Kai, Jiao Yun, Bai Zhigang, Jiang Yideng, Shen Jiangyong. Erastin inhibits proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-. |
| [13] | Ke Yuqi, Chen Changjian, Wu Hao, Zheng Lianjie. Comparison of 12-month follow-up results of primary total hip arthroplasty between modified direct anterior approach and direct anterior approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1377-1382. |
| [14] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [15] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||