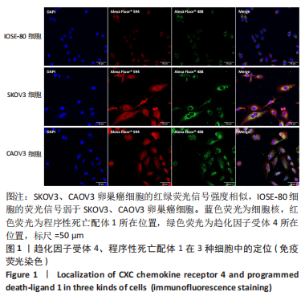
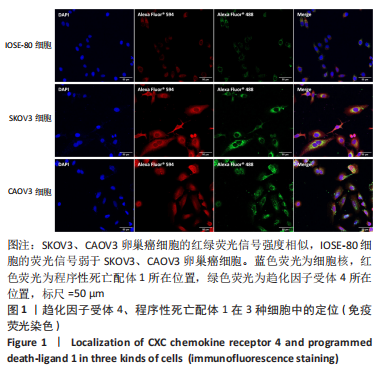
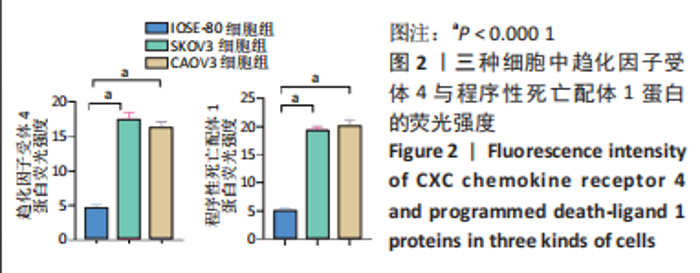
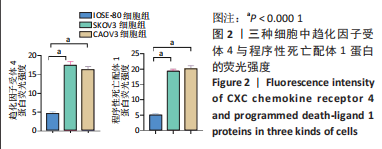
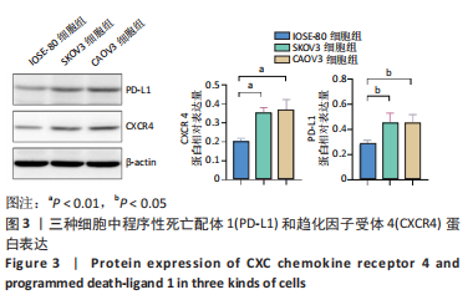
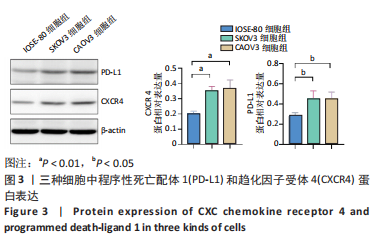
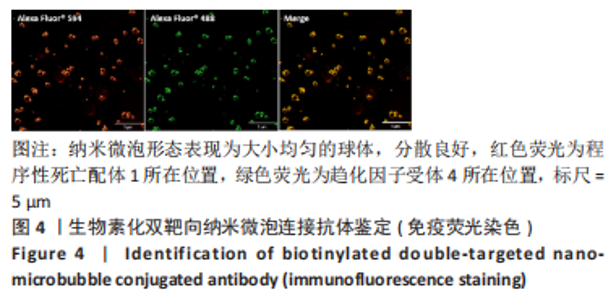
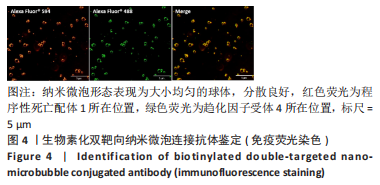
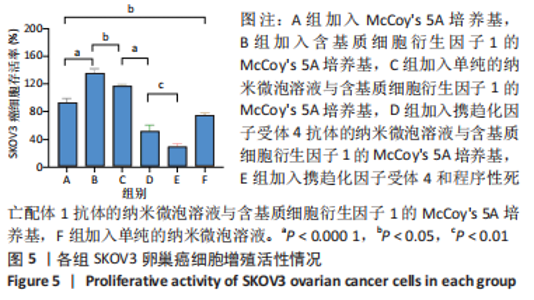
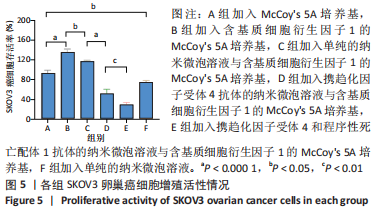
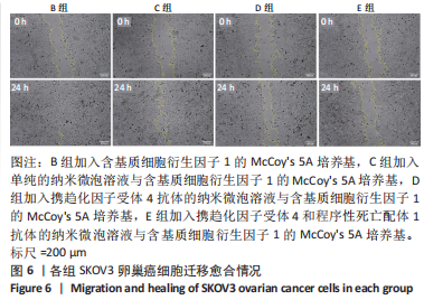
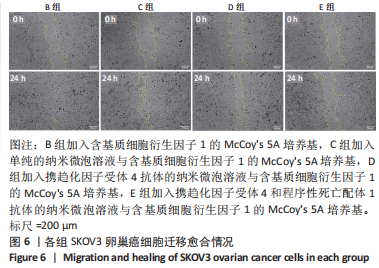
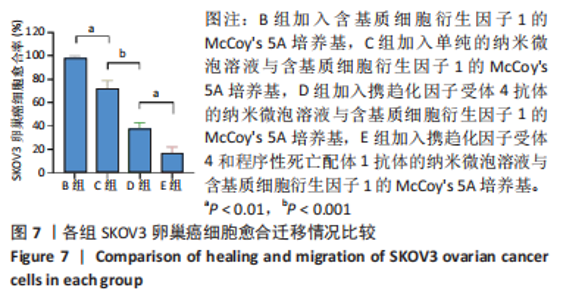
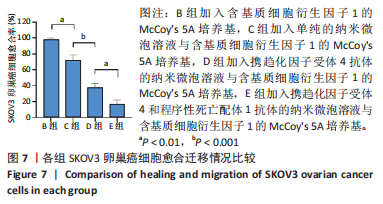
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (3): 341-346.doi: 10.12307/2023.974
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of nanobubbles carrying double antibodies on the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells
Wu Tian, Zhao Yue, Hu Rong
- Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Ultrasound Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Ultrasound, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-11-30Accepted:2023-01-10Online:2024-01-28Published:2023-07-08 -
Contact:Hu Rong, MD, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Ultrasound Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Ultrasound, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wu Tian, Master candidate, Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Ultrasound Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Ultrasound, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81660288 (to HR); Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project for Postgraduates of Xinjiang Medical University, No. CXCY2022008 (to WT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Tian, Zhao Yue, Hu Rong. Effect of nanobubbles carrying double antibodies on the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 341-346.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] ARMSTRONG D, ALVAREZ R, BAKKUM-GAMEZ J, et al. Ovarian Cancer, Version 2.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2021;19(2): 191-226. [2] SUN Q, BAI X, SOFIAS A, et al. Cancer nanomedicine meets immunotherapy: opportunities and challenges. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41(7):954-958. [3] YANG C, XIA B, ZHANG Z, et al. Immunotherapy for Ovarian Cancer: Adjuvant, Combination, and Neoadjuvant. Front Immunol. 2020;11:577869. [4] BANTA K, XU X, CHITRE A, et al. Mechanistic convergence of the TIGIT and PD-1 inhibitory pathways necessitates co-blockade to optimize anti-tumor CD8 T cell responses. Immunity. 2022;55(3):512-526.e519. [5] WEISS S, DJUREINOVIC D, JESSEL S, et al. A Phase I Study of APX005M and Cabiralizumab with or without Nivolumab in Patients with Melanoma, Kidney Cancer, or Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Resistant to Anti-PD-1/PD-L1. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(17):4757-4767. [6] WU M, HUANG Q, XIE Y, et al. Improvement of the anticancer efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade via combination therapy and PD-L1 regulation. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15(1):24. [7] SAXENA R, WANG Y, MIER J. CXCR4 inhibition modulates the tumor microenvironment and retards the growth of B16-OVA melanoma and Renca tumors. Melanoma Res. 2020;30(1):14-25. [8] LI Z, WANG Y, SHEN Y, et al. Targeting pulmonary tumor microenvironment with CXCR4-inhibiting nanocomplex to enhance anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy. Sci Adv. 2020;6(20):eaaz9240. [9] 徐桂兰,宋建生,杨世疆.超声微泡沉默S100A4基因对胃癌干细胞干性和上皮间质转化的调控[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(25):4025-4031. [10] BARZEGAR-FALLAH A, GANDHI K, RIZWAN S, et al. Harnessing Ultrasound for Targeting Drug Delivery to the Brain and Breaching the Blood-Brain Tumour Barrier. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(10):2231. [11] OMATA D, UNGA J, SUZUKI R, et al. Lipid-based microbubbles and ultrasound for therapeutic application. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;154-155:236-244. [12] XUE V, CHUNG J, TANG P, et al. USMB-shMincle: a virus-free gene therapy for blocking M1/M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021;23:26-37. [13] LI N, TANG J, YANG J, et al. Tumor perfusion enhancement by ultrasound stimulated microbubbles potentiates PD-L1 blockade of MC38 colon cancer in mice. Cancer Lett. 2021;498:121-129. [14] ILOVITSH T, FENG Y, FOIRET J, et al. Low-frequency ultrasound-mediated cytokine transfection enhances T cell recruitment at local and distant tumor sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(23):12674-12685. [15] TAN X, YI C, ZHANG Y, et al. Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction Alleviates Immunosuppression Induced by CD71 Erythroid Progenitor Cells and Promotes PDL-1 Blockade Immunotherapy in the Lewis Lung Cancer Model. Front Oncol. 2021;11: 768222. [16] MA Y, HAN J, JIANG J, et al. Ultrasound targeting of microbubble-bound anti PD-L1 mAb to enhance anti-tumor effect of cisplatin in cervical cancer xenografts treatment. Life Sci. 2020;262:118565. [17] YAMAGUCHI K, MATSUMOTO Y, SUZUKI R, et al. Enhanced antitumor activity of combined lipid bubble ultrasound and anticancer drugs in gynecological cervical cancers. Cancer Sci. 2021;112(6):2493-2503. [18] DONG L, LI N, WEI X, et al. A Gambogic Acid-Loaded Delivery System Mediated by Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction: A Promising Therapy Method for Malignant Cerebral Glioma. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:2001-2017. [19] 李翠仙,黄备建,陆清,等.靶向血管内皮生长因子受体2/整合素α_vβ_3微泡体内评价肾细胞癌血管生成的实验研究[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2022,31(4): 338-344. [20] 关丽娜,魏圆圆,窦静,等.优化靶向载基因超声纳米泡效能:实验研究[J].中国医学影像技术,2022,38(9):1281-1285. [21] BONIFÁCIO V. Ovarian Cancer Biomarkers: Moving Forward in Early Detection. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1219:355-363. [22] HAN Y, SUN J, WEI H, et al. Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction: Modulation in the Tumor Microenvironment and Application in Tumor Immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2022;13:937344. [23] YANG Y, LI Q, GUO X, et al. Mechanisms underlying sonoporation: Interaction between microbubbles and cells. Ultrason Sonochem. 2020;67:105096. [24] 曾宏兴,郑德俊,苑伟,等. 超声靶向爆破载藤黄酸微泡对人结肠癌HCT116细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2021,38(11):2163-2166. [25] SHI D, GUO L, SUN X, et al. UTMD inhibit EMT of breast cancer through the ROS/miR-200c/ZEB1 axis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):6657. [26] DAASSI D, MAHONEY KM, FREEMAN GJ. The importance of exosomal PDL1 in tumour immune evasion. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20:209-215. [27] SHI Y, RIESE DJ,SHEN J. The Role of the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 Chemokine Axis in Cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:574667. [28] HAO S, XU S, LI L, et al. Tumour inhibitory activity on pancreatic cancer by bispecific nanobody targeting PD-L1 and CXCR4. BMC Cancer. 2022;22(1):1092. [29] BIASCI D, SMORAGIEWICZ M, CONNELL C, et al. CXCR4 inhibition in human pancreatic and colorectal cancers induces an integrated immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(46):28960-28970. [30] 邓海怡,王李强,杨伊霖,等.双免疫联合治疗在晚期非小细胞肺癌中的一线应用[J].中国肺癌杂志,2022,25(2):102-110. [31] LU G, QIU Y, SU X. Targeting CXCL12-CXCR4 Signaling Enhances Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy Against Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021;157: 105606. [32] SCHOEN S, KILINC M, LEE H, et al. Towards controlled drug delivery in brain tumors with microbubble-enhanced focused ultrasound. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;180: 114043. [33] YOO S, MITTELSTEIN D, HURT R, et al. Focused ultrasound excites cortical neurons via mechanosensitive calcium accumulation and ion channel amplification. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):493. |
| [1] | Li Lisi, Zhang Chengdong, Li Xiaolong, Ye Ziyu, Pu Chao, Yang Zaijun, Shi Feng, Xiao Dongqin. Growth differentiation factor-5 modified by bisphosphonate promotes osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 373-379. |
| [2] | Ran Lei, Han Haihui, Xu Bo, Wang Jianye, Shen Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Molecular docking analysis of the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Cibotium barometz and Epimedium for rheumatoid arthritis: animal experiment validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 208-215. |
| [3] | Wang Qian, Lu Ziang, Li Lihe, Lyu Chaoliang, Wang Meng, Zhang Cunxin. Sinomenine effectively inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 224-230. |
| [4] | Yang Ting, Ding Zhibin, Jiang Nan, Han Hongxia, Hou Miaomiao, Ma Cungen, Song Lijuan, Li Xinyi. Astrocytes regulate glial scar formation in cerebral ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 131-138. |
| [5] | Sun Jing, Liao Jian, Sun Jiangling, Cheng Ping, Feng Hongchao. Recombinant human growth hormone promotes osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 56-61. |
| [6] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-6. |
| [7] | He Xi, Wan Yu, Tang Yuting, Yang Anning, Wu Kai, Jiao Yun, Bai Zhigang, Jiang Yideng, Shen Jiangyong. Erastin inhibits proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-. |
| [8] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [9] | Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877. |
| [10] | Hao Liufang, Duan Hongmei, Wang Zijue, Hao Fei, Hao Peng, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Yang Zhaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Spatiotemporal dynamic changes of ependymal cells after spinal cord injury in transgenic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [11] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [12] | Qin Yixiong, Yuan Zijian, Xie Shanzhou, Zhu Yingwen, Chen Minghui, Han Biao, Guo Yong. Effect of tea polyphenols on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts stimulated by lipopolysaccharide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5665-5669. |
| [13] | Huang Qian, Hao Liying, He Longlong, Du Liangzhi. Graphene oxide-chitosan composite coating affects the biological behavior of osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5430-5435. |
| [14] | Zhou Yuebin, Guo Honggang. Construction of tissue-engineered bone composite scaffolds by loading rabbit-derived bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on magnesium-based alloy scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5491-5496. |
| [15] | Wang Yao, Liu Danan, Zhao Guangjian, Zhou Bo, Wang Xiang. Irisin/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha signaling pathway mediates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5320-5326. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||