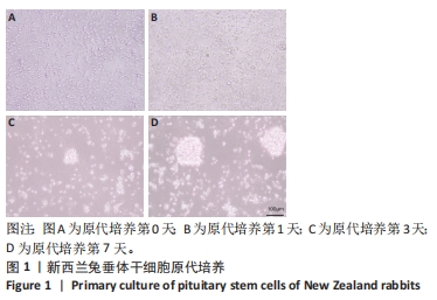
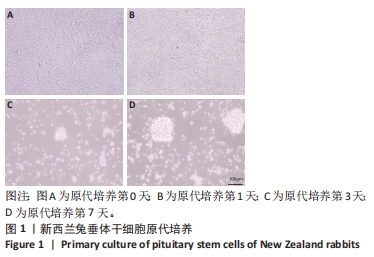
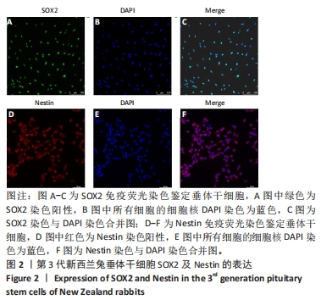
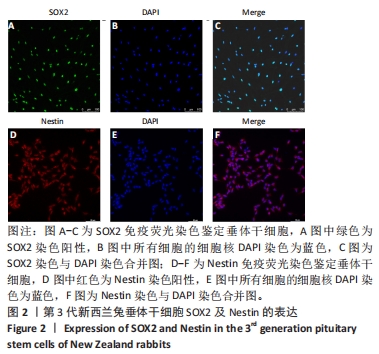
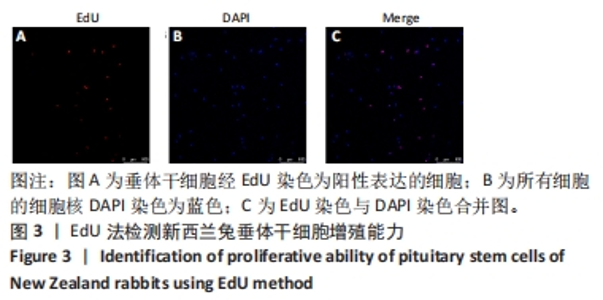
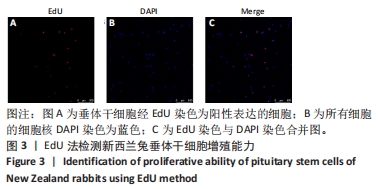
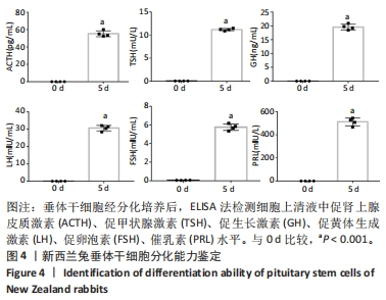
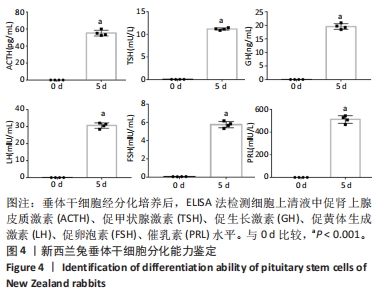
[1] ALATZOGLOU KS, GREGORY LC, DATTANI MT. Development of the Pituitary Gland. Compr Physiol. 2020;10(2):389-413.
[2] LAPORTE E, VENNEKENS A, VANKELECOM H. Pituitary Remodeling Throughout Life: Are Resident Stem Cells Involved? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;11:604519.
[3] SANTIAGO-ANDRES Y, GOLAN M, FIORDELISIO T. Functional Pituitary Networks in Vertebrates. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;11:619352.
[4] FLETCHER PA, SHERMAN A, STOJILKOVIC SS. Common and diverse elements of ion channels and receptors underlying electrical activity in endocrine pituitary cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018;463:23-36.
[5] BROWN CH. Magnocellular Neurons and Posterior Pituitary Function. Compr Physiol. 2016;6(4):1701-1741.
[6] PETERSENN S, HEANEY AP. Targeted systemic and peptide radio-ligand therapy for aggressive pituitary tumors and carcinomas. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2020;21(2):277-286.
[7] LANGLOIS F, VARLAMOV EV, FLESERIU M. Hypophysitis, the Growing Spectrum of a Rare Pituitary Disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022; 107(1):10-28.
[8] MEHTA GU, LONSER RR. Management of hormone-secreting pituitary adenomas. Neuro Oncol. 2017;19(6):762-773.
[9] YU N, DUAN L, HU F, et al. Clinical features and therapeutic outcomes of GH/TSH cosecreting pituitary adenomas: experience of a single pituitary center. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1197244.
[10] HAGE C, GAN HW, IBBA A, et al. Advances in differential diagnosis and management of growth hormone deficiency in children. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;17(10):608-624.
[11] HAGE C, GAN HW, IBBA A, et al. Advances in differential diagnosis and management of growth hormone deficiency in children. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;17(10):608-624.
[12] GORADEL NH, HOUR FG, NEGAHDARI B, et al. Stem Cell Therapy: A New Therapeutic Option for Cardiovascular Diseases. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(1):95-104.
[13] CURTIS E, MARTIN JR, GABEL B, et al. A First-in-Human, Phase I Study of Neural Stem Cell Transplantation for Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(6):941-950.
[14] UCCELLI A, MORETTA L, PISTOIA V. Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(9):726-736.
[15] YOUNG RA. Control of the embryonic stem cell state. Cell. 2011;144(6): 940-954.
[16] YU Q, QIAO GH, WANG M, et al. Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:812262.
[17] GENC B, BOZAN HR, GENC S, et al. Stem Cell Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1084:145-174.
[18] ZAKRZEWSKI W, DOBRZYŃSKI M, SZYMONOWICZ M, et al. Stem cells: past, present, and future. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):68.
[19] RIZZOTI K, AKIYAMA H, LOVELL-BADGE R. Mobilized adult pituitary stem cells contribute to endocrine regeneration in response to physiological demand. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;13(4):419-432.
[20] FAUQUIER T, RIZZOTI K, DATTANI M, et al. SOX2-expressing progenitor cells generate all of the major cell types in the adult mouse pituitary gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(8):2907-2912.
[21] WILLIS TL, LODGE EJ, ANDONIADOU CL, et al. Cellular interactions in the pituitary stem cell niche. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(12):612.
[22] FU Q, GREMEAUX L, LUQUE RM, et al. The adult pituitary shows stem/progenitor cell activation in response to injury and is capable of regeneration. Endocrinology. 2012;153(7):3224-3235.
[23] FU Q, VANKELECOM H. Regenerative capacity of the adult pituitary: multiple mechanisms of lactotrope restoration after transgenic ablation. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(18):3245-3257.
[24] WILLEMS C, FU Q, ROOSE H, et al. Regeneration in the Pituitary After Cell-Ablation Injury: Time-Related Aspects and Molecular Analysis. Endocrinology. 2016;157(2):705-721.
[25] ROOSE H, COX B, BORETTO M, et al. Major depletion of SOX2+ stem cells in the adult pituitary is not restored which does not affect hormonal cell homeostasis and remodelling. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16940.
[26] LAPORTE E, NYS C, VANKELECOM H. Development of Organoids from Mouse Pituitary as In Vitro Model to Explore Pituitary Stem Cell Biology. J Vis Exp. 2022;(180). doi: 10.3791/63431.
[27] YOSHIDA S, NISHIMURA N, UEHARU H, et al. Isolation of adult pituitary stem/progenitor cell clusters located in the parenchyma of the rat anterior lobe. Stem Cell Res. 2016;17(2):318-329.
[28] RUSSELL JP, LIM X, SANTAMBROGIO A, et al. Pituitary stem cells produce paracrine WNT signals to control the expansion of their descendant progenitor cells. Elife. 2021;10:e59142.
[29] LAPORTE E, VENNEKENS A, VANKELECOM H. Pituitary Remodeling Throughout Life: Are Resident Stem Cells Involved? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;11:604519.
[30] DE HERDT C, PHILIPSE E, DE BLOCK C. ENDOCRINE TUMOURS: Thyrotropin-secreting pituitary adenoma: a structured review of 535 adult cases. Eur J Endocrinol. 2021;185(2):R65-R74.
[31] SONG S, WANG L, QI Q, et al. Endoscopic vs. microscopic transsphenoidal surgery outcomes in 514 nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma cases. Neurosurg Rev. 2022;45(3):2375-2383.
[32] GASTON-MASSUET C, ANDONIADOU CL, SIGNORE M, et al. Increased Wingless (Wnt) signaling in pituitary progenitor/stem cells gives rise to pituitary tumors in mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(28):11482-11487.
[33] RUSSELL JP, LIM X, SANTAMBROGIO A, et al. Pituitary stem cells produce paracrine WNT signals to control the expansion of their descendant progenitor cells. Elife. 2021;10:e59142.
[34] CHAMBERS TJ, GILES A, BRABANT G, et al. Wnt signalling in pituitary development and tumorigenesis. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013;20(3): R101-R111.
[35] TODA M, TAMURA R, TODA M. Recent Progress in Stem Cell Research of the Pituitary Gland and Pituitary Adenoma. Endocrines. 2020;1(1):49-57. |