Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (19): 3084-3089.doi: 10.12307/2024.149
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects and problems of growth differentiation factor 5-induced multidirectional differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
Li Feifei, Deng Jiang
- Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (The First People’s Hospital of Zunyi), Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-07Accepted:2023-05-10Online:2024-07-08Published:2023-09-26 -
Contact:Deng Jiang, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (The First People’s Hospital of Zunyi), Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Li Feifei, Master, Physician, Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (The First People’s Hospital of Zunyi), Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81660367 (to DJ); Guizhou Provincial Health Commission Science and Technology Fund, No. gzwkj2021-236 (to DJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Feifei, Deng Jiang. Effects and problems of growth differentiation factor 5-induced multidirectional differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 3084-3089.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
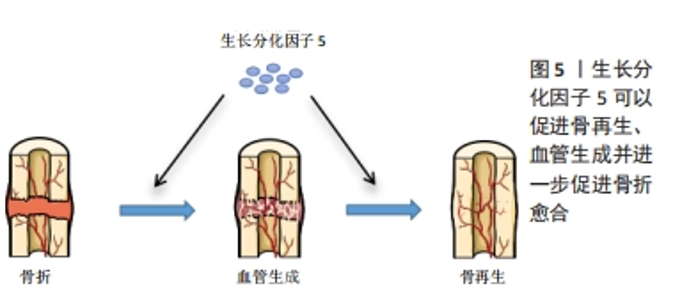
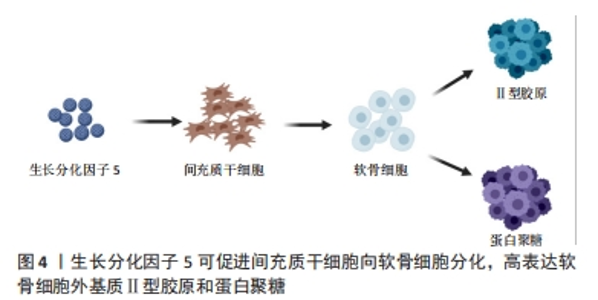
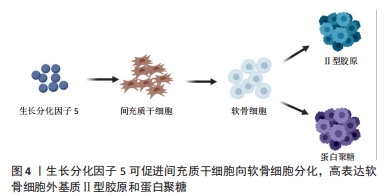
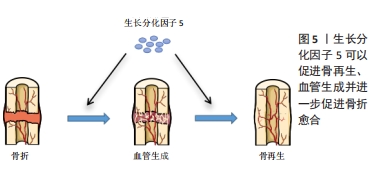
软骨形成始于间充质干细胞的凝结,而GDF5在软骨形成前的凝聚中具有重要作用。GDF5过表达可促进软骨形成,促进间充质干细胞的黏附和软骨细胞增殖[7]。COLEMAN等[8]用GDF5处理间充质干细胞,发现GDF5可促进间充质干细胞的软骨形成,增加了细胞外基质(Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白聚糖)的表达,在后期增加了软骨细胞肥大标志物的表达,如Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅹ型胶原、碱性磷酸酶。HAN等[9]研究认为100 ng/mL GDF5诱导脂肪间充质干细胞软骨分化是有效且经济的,Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白聚糖在14 d高表达,Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅹ型胶原在21 d和28 d达到峰值,结果均表明GDF5在早期促进软骨细胞形成,后期促进软骨细胞向肥大细胞分化。软骨细胞肥大分化被认为是软骨修复的一大阻碍,如何在后期抑制软骨细胞向肥大细胞分化是需要去探索的问题。上述这些文献报道均是体外研究,而在相关的体内研究中,将间充质干细胞植入关节软骨缺损,自发促进了软骨修复[8],表达Ⅱ型胶原,而不表达Ⅹ型胶原,这也是需要思考的一个问题,体内与体外是完全不同的环境,在体内可能与复杂的信号分子及生物力学刺激有关,而不表达肥大标志物Ⅰ型胶原。 GDF5作为多功能诱导因子,在未来可能作为一种候选药物治疗骨关节炎。然而,GDF5的半衰期短、容易失活、降解速度快,可能会限制其临床应用。有研究者通过基因疗法将外源性GDF5基因转入间充质干细胞[10-11],从而解决GDF5作用时间短等问题。虽然GDF5过表达显著增加了软骨分化标志物的表达,但是GDF5基因转染的生物安全性仍有待进一步探讨。 软骨细胞通过平衡自身的合成代谢和分解代谢来调节关节软骨的稳态。研究表明,GDF5与骨关节炎之间存在相关性,GDF5缺乏可导致骨关节炎的发生,外源性给予GDF5对骨关节炎有保护作用[12]。DAANS等[13]发现GDF5基因缺陷小鼠通过不同的机制促进了骨关节炎的发展。另一方面,PARRISH等[14]通过内侧半月板切除术建立小鼠骨关节炎模型,每周向关节腔内注射不同剂量(30,100 μg)的重组人GDF5,研究结果发现,每2周注射2次(100 μg/次)可阻止软骨损伤的进展。而每2周注射3次(100 μg/次)显著刺激了软骨的修复,说明关节内补充重组人GDF5且以剂量依赖方式预防骨关节炎疾病的进展,有望作为治疗骨关节炎的候选药物。 综上,GDF5可诱导间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化,促进软骨损伤的修复。然而,许多文献认为GDF5诱导软骨分化的最适质量浓度是100 ng/mL[15],也有认为50 ng/mL是最适合质量浓度[16],这可能与细胞类型不同或细胞生长微环境有关。最早有研究报道,低浓度GDF5主要是促进成软骨分化,而高浓度GDF5促进成骨分化[17]。目前,对于不同浓度GDF5诱导成软骨分化和成骨分化的报道较少,是否高浓度GDF5完全促进骨形成,这还需进一步研究。 2.2 GDF5诱导骨形成 骨折不愈合或延迟愈合已经成为骨折修复的一大挑战。据报道,有5%-10%的骨折愈合不良,导致骨折畸形愈合或不愈合[18]。骨折愈合是一个复杂、有序的再生过程。骨折和骨退行性疾病导致骨缺损,需要骨再生来替代受损组织[19]。在过去20年里,骨组织工程已经取得了重大进展,大量研究探讨了如何将生物支架材料、细胞和生物活性因子结合起来设计骨组织结构[20-22]。这些技术通过控制模式和仿生结构促进了骨再生,其中生物活性因子在骨组织工程中占据重要地位。骨组织工程的出现为骨折损伤修复带来了希望,生长因子被认为是强烈的骨诱导剂可促进骨形成。 GDF5可促进间充质干细胞向成骨分化。ZENG等[23]探讨了GDF5和BMP2对脂肪间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响,研究发现GDF5可促进小鼠脂肪间充质干细胞向成骨分化。此外,也发现GDF5显著促进了血管内皮生长因子的表达。然而,经BMP2处理的脂肪间充质干细胞中未见血管内皮生长因子的表达,表明GDF5与BMP2之间可能存在协同作用。CHENG等[24]进行了GDF5过表达诱导人间充质干细胞成骨分化的体内和体外研究。在体外,将携带GDF5的腺病毒(Ad-GDF5)转染至人骨髓间充质干细胞,在诱导7,14 d后,与对照组比较,Ad-GDF5组显著增加了Ⅰ型胶原、碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素的表达;Von Kossa染色显示,Ad-GDF5组较对照组有明显的钙沉积;Ⅰ型胶原免疫荧光染色也显示,Ad-GDF5组增加了Ⅰ型胶原的表达。同时在体内实验中,将不同条件培养的细胞注射到裸鼠背部,与对照组比较,Ad-GDF5组也显著增加了Ⅰ型胶原、碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素的表达。以上结果均表明,GDF5在体内和体外均能诱导间充质干细胞向成骨方向分化,这对于骨缺损修复可能具有重要作用。此外,GDF5对软骨下骨也有一定作用。研究报道,GDF5基因敲除小鼠软骨下骨密度降低,骨组织中胶原纤维排列紊乱[13]。MENDES等[25]研究表明GDF5可诱导人骨膜来源干细胞在体外生成骨软骨样组织,在体内实验中,皮下植入诱导后的人骨膜来源干细胞能够生成骨和软骨(异位);植入骨软骨缺损模型,能在缺损处生成骨软骨组织(原位)。这些研究表明将GDF5应用于骨软骨损伤修复可能具有较好的作用,见图5。"
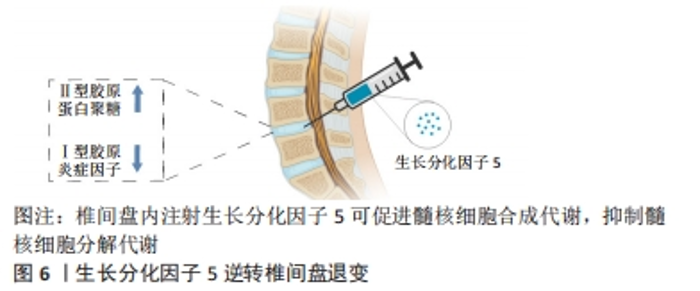
相关研究报道,骨折部位骨组织中GDF5基因的表达水平显著增加,表明GDF5与骨折损伤修复有密切关系。CHHABRA等[26]研究证实BMP14缺失小鼠骨折愈合延迟,相反,这可能说明加入GDF5可促进骨折愈合。COLEMAN等[19]初步研究也认为,GDF5基因缺失小鼠骨折愈合延迟,但是在56 d后骨折愈合与对照组比较无差异,表明GDF5更多的是在骨折修复早期发挥作用。因此,在未来有必要进一步研究GDF5在正常骨折愈合中的作用及其可能的作用机制。在多发性骨关节炎综合征2(SYNS2)中,GDF5促进了骨缺损的愈合[27]。HASENBEIN等[28]研究表明局部低剂量(< 100 μg)的GDF5结合纳米羟基磷灰石诱导了长期的骨形成。然而,在其他研究中,GDF5诱导成骨分化呈剂量依赖性。 KAKUDO等[17]将不同剂量的GDF5与Ⅰ型胶原支架混合植入大鼠腿部肌肉,结果表明,在低剂量组(0 μg和100 μg)无骨和软骨组织出现,在300 μg组可见部分软骨和骨组织聚集,而在500 μg组只有骨组织,表明GDF5诱导成骨的剂量依赖性。在体外研究中,有研究者探讨了不同质量浓度GDF5促进脂肪间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响,结果提示GDF5促进成骨分化的最适质量浓度为100 ng/mL,显著增加了碱性磷酸酶活性和钙结节的形成[29]。然而,这与前者研究存在矛盾,到底多少剂量GDF5适宜骨生成仍有待进一步研究,是否GDF5诱导成骨分化呈剂量依赖性?骨折的愈合离不开良好的血液供应。GDF5不仅促进了骨形成,而且还促进血管生成[30-33]。总之,GDF5无论是对软骨还是骨缺损修复均有积极作用。 2.3 GDF5诱导髓核样细胞分化 髓核变性是椎间盘退行性变的主要原因。椎间盘由髓核、纤维环和软骨终板组成[34]。椎间盘无血管结构,自我修复能力较差,发生退行性变后常不可逆转[35]。髓核的主要成分是蛋白多糖,髓核中的蛋白多糖在髓核内提供高含水量,进而有助于承受施加于椎体的负荷,负荷通过静水压力均匀分布到纤维环上。椎间盘退行性变的主要特征是髓核中蛋白多糖和Ⅱ型胶原的丢失[36]。椎间盘退行性变被认为是椎间盘中心部分细胞外基质的细胞驱动变性引起,最终导致结构损伤,如纤维环破裂、髓核突出。同时血管和痛觉神经纤维进入椎间盘,从而导致疼痛发生[37]。此外,任何合成代谢因子和分解代谢因子之间的平衡失调都会导致椎间盘退行性变。运用传统的开放或微创手术不能很好的治疗椎间盘退行性变,目前治疗主要以缓解症状为主,而不是逆转椎间盘结构的退行性变。目前治疗椎间盘退行性变的一个策略是促进合成代谢和抑制分解代谢。许多研究表明,生长因子可以将分解代谢转为合成代谢状态进而治疗椎间盘退行性变。因此,生长因子逆转椎间盘退行性变有望作为一种有希望的方法,见图6。"
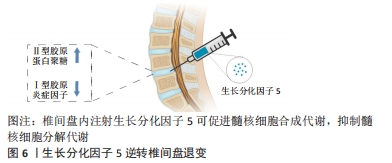
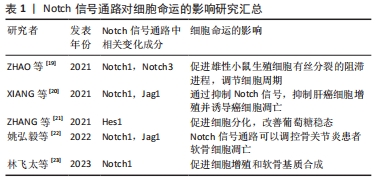
近年来,注射生长因子和间充质干细胞移植对于治疗椎间盘退行性变是一种有希望的生物疗法,生长因子可刺激椎间盘细胞外基质的合成,使退行性椎间盘再生[38-39]。研究表明,GDF5可诱导间充质干细胞向髓核样细胞表型分化。YANG等[40]用GDF5处理髓核样细胞,可促进Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白多糖的合成,表明GDF5对椎间盘退行性变是有利的。相反,GDF5基因敲除小鼠椎间盘中蛋白多糖、Ⅱ型胶原显著降低,组织学显示椎间盘纤维环丧失正常结构,髓核结构紊乱,证明GDF5基因缺失促进了椎间盘退行性变的发生发展。另一方面,分离培养小鼠沉默GDF5基因的椎间盘细胞,加入GDF5诱导培养,增加了蛋白多糖、Ⅱ型胶原的表达[41]。研究表明,多种炎症因子与椎间盘退行性变相关,如白细胞介素1α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6等,而GDF5在体外可抑制炎症因子的表达[42]。体内研究也表明,GDF5干预兔椎间盘退行性变模型,发现炎症因子处于更低的表达水平[43]。XU等[44]通过电喷涂方法合成了一种可注射的甲基丙烯酰凝胶微球,其上负载有脂肪间充质干细胞和GDF5,具有良好的生物相容性和力学性能,促进脂肪间充质干细胞向髓核样细胞分化。 髓核样细胞属于一种类软骨细胞,表达Ⅱ型胶原、蛋白多糖,而在软骨细胞中也同样表达这2种基因[45]。如何证明间充质干细胞向髓核样细胞分化呢?有研究者发现KRT8、KRT18、KRT19是髓核样细胞特异性标记物,在髓核样细胞各个阶段均有表达[46],因此,通过检测这些特异性标志物的表达可证明诱导间充质干细胞向髓核样细胞分化。ZHU等[11]将GDF5基因转染至骨髓间充质干细胞,结果提示KRT8、KRT18、KRT19基因和蛋白的表达显著上调,表明GDF5促进了骨髓间充质干细胞向髓核样细胞分化。除此之外,GDF5可恢复椎间盘的高度,增加髓核样细胞中蛋白多糖的含量[47]。动物相关实验研究发现,在GDF5基因敲除小鼠中发现椎间盘的纤维环正常结构消失,髓核组织萎缩、紊乱,Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白多糖表达也下降,表明GDF5基因缺失与椎间盘退行性变密切相关[38]。反之,也说明外源性加入GDF5对椎间盘退行性变有治疗作用。在体内相关研究中,将转染GDF5基因的人诱导多能干细胞和水凝胶一起注入大鼠尾椎椎间盘退行性变模型中,结果表明其可以改善椎间盘退行性变[48]。ZHU等[49]制备了由肝素和合成的聚阳离子组成的生长因子载体用来维持GDF5的释放,将聚阳离子/肝素/GDF5和人脂肪间充质干细胞一起注入到大鼠尾椎(Co)的椎间隙Co7/Co8和Co8/Co9,研究结果表明,与GDF5联合人脂肪间充质干细胞相比,聚阳离子/肝素/GDF5联合人脂肪间充质干细胞能更有效地减缓椎间盘退行性变。 由于GDF5在体内作用时间短等问题,因此希望GDF5在体内能够持续释放达到治疗目的,大多数实验研究均是通过基因转染或缓释微球等方式达到延长作用时间的目的。在这些研究中,虽然解决了GDF5在体内作用时间短的问题,但并未提及GDF5逆转椎间盘退行性变的最低浓度是多少以及持续释放累积到某一高浓度作用下的结果如何,亦需进一步探究。除此之外,目前大多数研究均是以大鼠尾椎间盘为研究对象,不能很好地模拟人的椎间盘退行性变,这对大型动物的脊椎椎间盘可能存在一定挑战,但也期望在未来能有更多的研究,为临床治疗椎间盘退行性变奠定基础。 在许多研究中,生长因子可能会诱导血管的长入,加速椎间盘退行性变的过程。而在动物实验中,有研究者向小鼠椎间盘内注射GDF5可有效减轻椎间盘退行性变,还可抑制血管的长入,相比于转化生长因子β、成纤维细胞生长因子和胰岛素样生长因子1,GDF5更适合于椎间盘退行性变的治疗[50]。然而,还有一个有趣的现象是,为什么GDF5在治疗椎间盘退行性变过程中没有诱导血管的生长,而在骨折损伤过程中诱导了血管内皮生长因子的表达,这也是值得探索的地方,作者猜想这可能是不同组织中局部微环境的不同,存在某一些受体,导致血管内皮生长因子的表达与否,这仍有待于进一步研究。然而,这些研究大多集中在基础研究,在临床应用方面还很缺乏,且GDF5在体内是如何定向诱导间充质干细胞向髓核样细胞分化,这仍然还未可知,但这在未来将是治疗椎间盘退行性变的一种很有前景的方法。 2.4 GDF5诱导肌腱细胞分化 肌腱作为人体运动系统的组成部分,在剧烈运动中常常发生肌腱损伤,损伤的肌腱愈合缓慢,很难恢复到正常肌腱时候的结构和机械强度。手术治疗和非手术治疗均不能完全恢复肌腱的结构,在损伤部位常形成瘢痕愈合,影响肌腱的韧性。而组织工程可能被用来修复损伤的肌腱。 有研究发现,GDF5可诱导间充质干细胞向肌腱细胞分化,这为肌腱损伤修复提供了希望[51]。刘真等[52]研究了GDF5诱导间充质干细胞向肌腱细胞分化及迁移的作用,加入不同浓度的GDF5诱导间充质干细胞分化,结果显示GDF5显著促进肌腱细胞分化标志物Tenascin-C和Ⅰ型胶原的表达,也发现随着GDF5浓度增加促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖,且呈剂量依赖性。WANG等[53]研究发现,BMP14在体外可诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向肌腱细胞分化。脂肪间充质干细胞结合GDF5在最大程度上促进了横断肌腱的愈合[54]。然而,有文献报道,GDF5联合脂肪间充质干细胞不能改善部分横断肌腱的修复。相反,仅用脂肪间充质干细胞在肌腱损伤修复中更有效[55]。QU等[56]探讨了GDF5对小鼠致密骨间充质干细胞活力和腱调蛋白表达的影响,研究发现GDF5可增加间充质干细胞活性,同时促进腱调蛋白的表达。最早有研究探讨了GDF5包被的缝线对大鼠跟腱愈合的影响,结果表明GDF5包被的缝线促进肌腱修复显示出良好的效果,术后2周抗拉强度也明显提高,在术后4周发现有软骨样细胞巢且Ⅱ型胶原表达阳性,表明GDF5也诱导了软骨样组织生成,而作者认为可以通过改变GDF5剂量和缝合材料来克服[57]。然而具体多少浓度仍然不清楚,是否增加肌腱骨化还需进一步研究,见表1。"
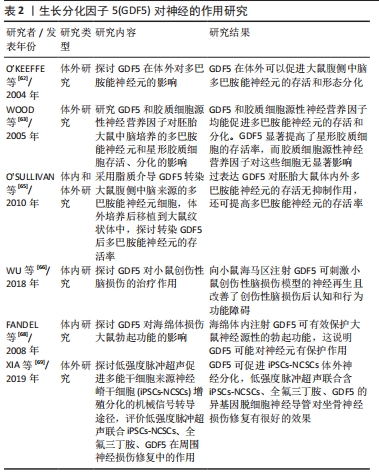
肌腱损伤后发生粘连是一个常见的并发症。术后早期活动是预防肌腱粘连的有效措施之一。有研究报道,GDF5对抑制肌腱粘连有重要作用。HASSLUND等[58]比较了不同剂量GDF5对屈肌腱愈合和粘连的影响,结果表明不同剂量GDF5均可改善关节屈曲功能。而低剂量GDF5对抑制肌腱粘连具有更强的作用,不影响肌腱的修复。因此,表明GDF5在诱导间充质干细胞向肌腱细胞分化、恢复肌腱功能及抑制肌腱粘连方面具有较好的作用。GDF5具有促进间充质干细胞向软骨、骨、肌腱等多向分化,但是如何保证GDF5诱导间充质干细胞向肌腱细胞分化,而不分化为软骨、骨细胞等其他细胞,这还需要进一步研究。有研究报道称,GDF5基因治疗可增加大鼠跟腱的抗张强度,没有诱导愈合肌腱内形成骨或软骨[59],相关的作用机制仍有待进一步阐明。 2.5 GDF5诱导神经发育 帕金森病是世界上最常见的运动障碍,是一种与年龄相关的疾病,60岁以上的人中有1%患有帕金森病,而80岁以上的人中有2%患病率[60]。帕金森病主要的病理表现是含有α-突触核蛋白的路易小体和黑质多巴胺能神经元的缺少[61]。帕金森病有3个主要症状:震颤、僵硬和运动迟缓。胚胎多巴胺能神经元移植被认为是治疗帕金森病有希望的疗法,但是移植的神经元细胞存活率差而受到限制。 有研究发现,GDF5可增强多巴胺能神经元的存活[62-63]。SULLIVAN等[64]研究认为GDF5对帕金森病有潜在的治疗作用,体内和体外实验均证明GDF5对改善黑质纹状体多巴胺能神经元的生存和保护神经元具有重要作用。然而,由于生长因子可在体内快速降解,需要解决长期给药的问题。有研究者通过脂质体介导法将GDF5转染至细胞[65],结果表明,过表达GDF5显著提高了大鼠腹侧中脑培养的多巴胺能神经元的存活率。将转染有GDF5的细胞移植到成年大鼠纹状体内,发现多巴胺能神经元的存活率不受影响,这也表明GDF5治疗帕金森病有着巨大的潜能。WU等[66]通过向创伤性脑损伤小鼠海马直接注射GDF5,发现可刺激神经发生,促进小鼠的功能恢复,表明GDF5对神经元的损伤修复和认知行为改善是一种有希望的治疗方法。研究发现,GDF5增加了多巴胺神经元的数量以及促进神经元轴突的增长,从而促进多巴胺能神经元的发育。GOULDING等[67]也证明GDF5对帕金森病模型大鼠的神经起保护作用。 除此之外,GDF5对周围神经系统也有一定的保护作用。FANDEL 等[68]在大鼠海绵体神经损伤模型中,向海绵体内注射GDF5可以增强勃起功能,表明GDF5对海绵体神经具有营养作用。XIA等[69]体外研究表明,GDF5可诱导多能干细胞来源神经嵴干细胞向神经分化。目前,临床治疗帕金森病更多的是缓解症状,仍不能彻底根治,大多数研究仍处于基础研究,在未来还需更多的理论研究为治疗帕金森病奠定基础。而GDF5的研究现主要集中在骨关节疾病上,GDF5也作为新的神经营养因子,在神经系统方面的研究还很缺乏,未来随着对GDF5的进一步研究,相信GDF5对神经退行性疾病的治疗将是一种很有前景的方法,见表2。"
| [1] LIU H, RUI Y, LIU J, et al. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel encapsulated BMP-14-modified ADSCs accelerate cartilage defect repair in rabbits. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):657. [2] STORM EE, HUYNH TV, COPELAND NG, et al. Limb alterations in brachypodism mice due to mutations in a new member of the TGF beta-superfamily. Nature. 1994;368(6472):639-643. [3] HÖTTEN G, NEIDHARDT H, JACOBOWSKY B, et al. Cloning and expression of recombinant human growth/differentiation factor 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;204(2):646-652. [4] HELDIN CH, MIYAZONO K, TEN DIJKE P. TGF-beta signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins. Nature. 1997;390(6659):465-471. [5] PARK A, HOGAN MV, KESTURU GS, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells treated with growth differentiation factor-5 express tendon-specific markers. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(9):2941-2951. [6] JIMI E, FEI H, NAKATOMI C. NF-κB Signaling Regulates Physiological and Pathological Chondrogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6275. [7] MACKAY AM, BECK SC, MURPHY JM, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of cultured human mesenchymal stem cells from marrow. Tissue Eng. 1998; 4(4):415-428. [8] COLEMAN CM, VAUGHAN EE, BROWE DC, et al. Growth differentiation factor-5 enhances in vitro mesenchymal stromal cell chondrogenesis and hypertrophy. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(13):1968-1976. [9] HAN C, REN Y, JIA Y, et al. The effective mode of growth and differentiation factor-5 in promoting the chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2016;17(1):105-115. [10] CUI Y, YAO M, LIU Y, et al. Effects of cartilage-derived morphogenetic protein 1 (CDMP1) transgenic mesenchymal stem cell sheets in repairing rabbit cartilage defects. Genet Mol Res. 2016;15(2). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15028058. [11] ZHU K, ZHAO R, YE Y, et al. Effect of lentivirus-mediated growth and differentiation factor-5 transfection on differentiation of rabbit nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells. Eur J Med Res. 2022;27(1):5. [12] LOUGHLIN J. Genetic contribution to osteoarthritis development: current state of evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27(3):284-288. [13] DAANS M, LUYTEN FP, LORIES RJ. GDF5 deficiency in mice is associated with instability-driven joint damage, gait and subchondral bone changes. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(1):208-213. [14] PARRISH WR, BYERS BA, SU D, et al. Intra-articular therapy with recombinant human GDF5 arrests disease progression and stimulates cartilage repair in the rat medial meniscus transection (MMT) model of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(4):554-560. [15] 李明辉,刘洋,孙凯,等.生长分化因子5诱导脂肪干细胞向软骨细胞的转化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(51):7628-7633. [16] 杨亚军. CDMP1诱导ADSCs修复软骨损伤的实验研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2008. [17] KAKUDO N, WANG YB, MIYAKE S, et al. Analysis of osteochondro-induction using growth and differentiation factor-5 in rat muscle. Life Sci. 2007;81(2): 137-143. [18] MARUYAMA M, RHEE C, UTSUNOMIYA T, et al. Modulation of the Inflammatory Response and Bone Healing. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:386. [19] COLEMAN CM, SCHEREMETA BH, BOYCE AT, et al. Delayed fracture healing in growth differentiation factor 5-deficient mice: a pilot study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(10):2915-2924. [20] DALY AC, FREEMAN FE, GONZALEZ-FERNANDEZ T, et al. 3D Bioprinting for Cartilage and Osteochondral Tissue Engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(22). [21] YANG J, ZHANG YS, YUE K, et al. Cell-laden hydrogels for osteochondral and cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2017;57:1-25. [22] AMINI AR, LAURENCIN CT, NUKAVARAPU SP. Bone tissue engineering: recent advances and challenges. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2012;40(5):363-408. [23] ZENG Q, LI X, BECK G, et al. Growth and differentiation factor-5 (GDF-5) stimulates osteogenic differentiation and increases vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels in fat-derived stromal cells in vitro. Bone. 2007; 40(2):374-381. [24] CHENG X, YANG T, MENG W, et al. Overexpression of GDF5 through an adenovirus vector stimulates osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012;196(1):56-67. [25] MENDES LF, KATAGIRI H, TAM WL, et al. Advancing osteochondral tissue engineering: bone morphogenetic protein, transforming growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor signaling drive ordered differentiation of periosteal cells resulting in stable cartilage and bone formation in vivo. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):42. [26] CHHABRA A, ZIJERDI D, ZHANG J, et al. BMP-14 deficiency inhibits long bone fracture healing: a biochemical, histologic, and radiographic assessment. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19(9):629-634. [27] DEGENKOLBE E, SCHWARZ C, OTT CE, et al. Improved bone defect healing by a superagonistic GDF5 variant derived from a patient with multiple synostoses syndrome. Bone. 2015;73:111-119. [28] HASENBEIN I, SACHSE A, HORTSCHANSKY P, et al. Single Application of Low-Dose, Hydroxyapatite-Bound BMP-2 or GDF-5 Induces Long-Term Bone Formation and Biomechanical Stabilization of a Bone Defect in a Senile Sheep Lumbar Osteopenia Model. Biomedicines. 2022;10(2):513. [29] 张勇.生长分化因子-5诱导人脂肪基质细胞成骨的实验研究[D].北京:解放军医学院,2010. [30] KLEINSCHMIDT K, WAGNER-ECKER M, BARTEK B, et al. Superior angiogenic potential of GDF-5 and GDF-5(V453/V456) compared with BMP-2 in a rabbit long-bone defect model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(20):1699-1707. [31] XIAO D, YANG F, ZHAO Q, et al. Fabrication of a Cu/Zn co-incorporated calcium phosphate scaffold-derived GDF-5 sustained release system with enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis properties. RSC Adv. 2018;8(52): 29526-29534. [32] BUNGARTZ M, KUNISCH E, MAENZ S, et al. GDF5 significantly augments the bone formation induced by an injectable, PLGA fiber-reinforced, brushite-forming cement in a sheep defect model of lumbar osteopenia. Spine J. 2017;17(11):1685-1698. [33] ZHANG C, YANG F, XIAO D, et al. Repair of segmental rabbit radial defects with Cu/Zn co-doped calcium phosphate scaffolds incorporating GDF-5 carrier. RSC Adv. 2020;10(4):1901-1909. [34] WANG H, ZHOU Y, CHU TW, et al. Distinguishing characteristics of stem cells derived from different anatomical regions of human degenerated intervertebral discs. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(9):2691-2704. [35] COLOMBINI A, LOMBARDI G, CORSI MM, et al. Pathophysiology of the human intervertebral disc. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40(5):837-842. [36] PATIL P, NIEDERNHOFER LJ, ROBBINS PD, et al. Cellular senescence in intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. Curr Mol Biol Rep. 2018;4(4): 180-190. [37] LV B, GAN W, CHENG Z, et al. Current Insights Into the Maintenance of Structure and Function of Intervertebral Disc: A Review of the Regulatory Role of Growth and Differentiation Factor-5. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:842525. [38] FENG C, LIU H, YANG Y, et al. Growth and differentiation factor-5 contributes to the structural and functional maintenance of the intervertebral disc. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(1):1-16. [39] LUO XW, LIU K, CHEN Z, et al. Adenovirus-mediated GDF-5 promotes the extracellular matrix expression in degenerative nucleus pulposus cells. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2016;17(1):30-42. [40] YANG Z, GAO XJ, ZHAO X. CDMP1 promotes type II collagen and aggrecan synthesis of nucleus pulposus cell via the mediation of ALK6. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(21):10975-10983. [41] LI X, LEO BM, BECK G, et al. Collagen and proteoglycan abnormalities in the GDF-5-deficient mice and molecular changes when treating disk cells with recombinant growth factor. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(20):2229-2234. [42] SHEN L, WU Y, HAN L, et al. Overexpression of growth and differentiation factor-5 inhibits inflammatory factors released by intervertebral disc cells. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(4):3603-3608. [43] YUAN B, RUDEEN K, LI J, et al. Biodegradable Microspheres and Hydrogel Drug Delivery System of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Inhibitor and Growth Differentiation Factor 5 (GDF5) Reduces Disc Inflammation in the Rabbit Model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2023 Apr 17. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000004686. [44] XU H, SUN M, WANG C, et al. Growth differentiation factor-5-gelatin methacryloyl injectable microspheres laden with adipose-derived stem cells for repair of disc degeneration. Biofabrication. 2020;13(1):015010. [45] STOYANOV JV, GANTENBEIN-RITTER B, BERTOLO A, et al. Role of hypoxia and growth and differentiation factor-5 on differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells towards intervertebral nucleus pulposus-like cells. Eur Cell Mater. 2011;21:533-547. [46] MINOGUE BM, RICHARDSON SM, ZEEF LA, et al. Transcriptional profiling of bovine intervertebral disc cells: implications for identification of normal and degenerate human intervertebral disc cell phenotypes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(1):R22. [47] WANG Z, WU Y, ZHAO Z, et al. Study on Transorgan Regulation of Intervertebral Disc and Extra-Skeletal Organs Through Exosomes Derived From Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 741183. [48] HU A, XING R, JIANG L, et al. Thermosensitive hydrogels loaded with human-induced pluripotent stem cells overexpressing growth differentiation factor-5 ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration in rats. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(5):2005-2016. [49] ZHU J, XIA K, YU W, et al. Sustained release of GDF5 from a designed coacervate attenuates disc degeneration in a rat model. Acta Biomater. 2019;86:300-311. [50] GUO S, CUI L, XIAO C, et al. The Mechanisms and Functions of GDF-5 in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(3):734-741. [51] 侯凯,李梅,李金茹,等.体外诱导大鼠脂肪源间充质干细胞成肌腱潜能的研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2011,21(8):929-933. [52] 刘真,张浩然.生长分化因子-5对间充质干细胞向肌腱细胞分化及迁移潜能影响的相关研究[J].中国医学创新,2021,18(20):28-32. [53] WANG D, JIANG X, LU A, et al. BMP14 induces tenogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(2): 1165-1174. [54] FITZGERALD MJ, MUSTAPICH T, LIANG H, et al. Tendon Transection Healing Can Be Improved With Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Cultured With Growth Differentiation Factor 5 and Platelet-Derived Growth Factor. Hand (N Y). 2023;18(3):436-445. [55] DE ARO AA, CARNEIRO GD, TEODORO LFR, et al. Injured Achilles Tendons Treated with Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Transplantation and GDF-5. Cells. 2018;7(9):127. [56] QU Y, ZHOU L, LV B, et al. Growth differentiation factor‑5 induces tenomodulin expression via phosphorylation of p38 and promotes viability of murine mesenchymal stem cells from compact bone. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(3):3640-3646. [57] RICKERT M, JUNG M, ADIYAMAN M, et al. A growth and differentiation factor-5 (GDF-5)-coated suture stimulates tendon healing in an Achilles tendon model in rats. Growth Factors. 2001;19(2):115-126. [58] HASSLUND S, DADALI T, ULRICH-VINTHER M, et al. Freeze-dried allograft-mediated gene or protein delivery of growth and differentiation factor 5 reduces reconstructed murine flexor tendon adhesions. J Tissue Eng. 2014;5:2041731414528736. [59] BOLT P, CLERK AN, LUU HH, et al. BMP-14 gene therapy increases tendon tensile strength in a rat model of Achilles tendon injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(6):1315-1320. [60] GOULDING SR, ANANTHA J, COLLINS LM, et al. Growth differentiation factor 5: a neurotrophic factor with neuroprotective potential in Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(1):38-44. [61] TYSNES OB, STORSTEIN A. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2017;124(8):901-905. [62] O’KEEFFE GW, DOCKERY P, SULLIVAN AM. Effects of growth/differentiation factor 5 on the survival and morphology of embryonic rat midbrain dopaminergic neurones in vitro. J Neurocytol. 2004;33(5):479-488. [63] WOOD TK, MCDERMOTT KW, SULLIVAN AM. Differential effects of growth/differentiation factor 5 and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor on dopaminergic neurons and astroglia in cultures of embryonic rat midbrain. J Neurosci Res. 2005;80(6):759-766. [64] SULLIVAN AM, O’KEEFFE GW. The role of growth/differentiation factor 5 (GDF5) in the induction and survival of midbrain dopaminergic neurones: relevance to Parkinson’s disease treatment. J Anat. 2005;207(3):219-226. [65] O’SULLIVAN DB, HARRISON PT, SULLIVAN AM. Effects of GDF5 overexpression on embryonic rat dopaminergic neurones in vitro and in vivo. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2010;117(5):559-572. [66] WU H, LI J, XU D, et al. Growth Differentiation Factor 5 Improves Neurogenesis and Functional Recovery in Adult Mouse Hippocampus Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Front Neurol. 2018;9:592. [67] GOULDING SR, CONCANNON RM, MORALES-PRIETO N, et al. Growth differentiation factor 5 exerts neuroprotection in an α-synuclein rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 20213;144(2):e14. [68] FANDEL TM, BELLA AJ, LIN G, et al. Intracavernous growth differentiation factor-5 therapy enhances the recovery of erectile function in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. J Sex Med. 2008;5(8):1866-1875. [69] XIA B, CHEN G, ZOU Y, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound combination with induced pluripotent stem cells-derived neural crest stem cells and growth differentiation factor 5 promotes sciatic nerve regeneration and functional recovery. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(4):625-636. |
| [1] | Yang Junliang, Lu Tan, Xu Biao, Jiang Yaqiong, Wang Fucheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of effects of partial anterior cruciate ligament rupture on knee joint stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1347-1353. |
| [2] | Wang Menghan, Qi Han, Zhang Yuan, Chen Yanzhi. Three kinds of 3D printed models assisted in treatment of Robinson type II B2 clavicle fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1403-1408. |
| [3] | Yang Cekai, Cai Zhuoyan, Chen Ming, Liu Hao, Weng Rui, Cui Jianchao, Zhang Shuncong, Yao Zhensong. Relationship between degeneration of paraspinal muscle and refractures in postmenopausal women treated by percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1414-1419. |
| [4] | Weng Rui, Lin Dongxin, Guo Haiwei, Zhang Wensheng, Song Yuke, Lin Hongheng, Li Wenchao, Ye Linqiang. Abnormal types of intervertebral disc structure and related mechanical loading with biomechanical factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1436-1442. |
| [5] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [6] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [7] | Bai Chen, Yang Wenqian, Meng Zhichao, Wang Yuze. Strategies for repairing injured anterior cruciate ligament and promoting graft healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1457-1463. |
| [8] | Lin Zeyu, Xu Lin. Research progress in gout-induced bone destruction mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1295-1300. |
| [9] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Liu Hua, Chai Yuan, Chen Feng, Zeng Hao, Gao Zhengang, Huang Yourong. Effect of Yishen Gushu Formula on bone metabolic markers and clinical efficacyn in patients with osteoporosis of kidney deficiency and blood stasis type [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1155-1160. |
| [10] | Cheng Jie, Wang Jihong, Zhang Pei. Functional exercise for tendon adhesion in a model of deep flexor tendon II injury of the third toe [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1161-1167. |
| [11] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [12] | Dai Yuexing, Zheng Liqin, Wu Minhui, Li Zhihong, Li Shaobin, Zheng Desheng, Lin Ziling. Effect of vessel number on computational fluid dynamics in vascular networks [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1206-1210. |
| [13] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [14] | Zhuang Xinyi, Peng Yuanhao, Yu Ting, Lyu Dongmei, Wen Xiujie, Cheng Qian. Cone-beam CT evaluation of bone mass in the external oblique line of the mandible in adolescents with different cervical vertebral bone ages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1253-1258. |
| [15] | Xiaheida·Yilaerjiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun, Reyila·Kuerban, Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Chen Xin. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the distribution pattern of stress in bone tissues with different characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1277-1282. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||