Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (19): 3069-3075.doi: 10.12307/2024.163
Previous Articles Next Articles
Photobiomodulation-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
Song Yue1, 2, Shu Qing2, Jia Shaohui1, Tian Jun1, 2
- 1College of Sports Medicine, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2023-04-28Accepted:2023-06-15Online:2024-07-08Published:2023-09-26 -
Contact:Tian Jun, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, College of Sports Medicine, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China; Department of Rehabilitation, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Song Yue, Master candidate, College of Sports Medicine, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China; Department of Rehabilitation, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82174494 (to TJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Yue, Shu Qing, Jia Shaohui, Tian Jun. Photobiomodulation-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 3069-3075.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
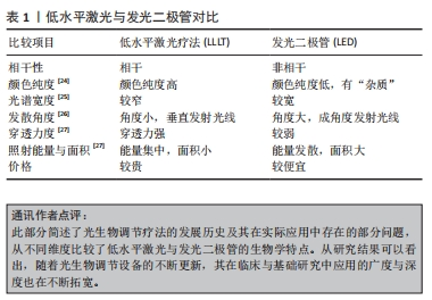
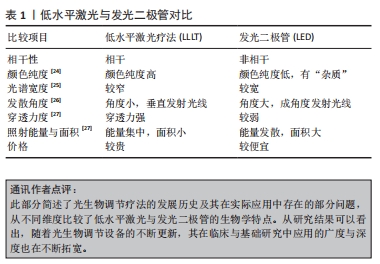
2.1 光生物调节疗法概述及其分类 2.1.1 概述 21世纪前,所有涉及光生物调节疗法的研究均是以低水平激光作为光源,学者们普遍认为可见光及近红外光波段对细胞和组织能够产生有益的生理效应,且激光的治疗作用均是基于其具有单色性、相干性等特征。近年来,发光二极管和宽带光等非相干性光源也普遍应用于光生物疗法中。和许多生物现象一样,光生物调节作用于间充质干细胞时也存在双相剂量反应,若能量密度不足或照射太短可能导致治疗效果不明显,反之则可能产生抑制作用,甚至使情况进一步恶化[16]。此外,有研究利用低水平激光修复大鼠胫骨皮质时发现,碱性磷酸酶与钙沉积在干预后9-15 d达到峰值效应,启示研究者们光生物刺激作用会在固定时间段内达到效应高峰,超过这个时间段后,刺激作用会逐步衰减[17]。如何找到能量密度与照射时间之间的平衡点,采用最佳剂量干预靶向组织,避免出现毒物兴奋效应?对此,研究者们还无从得知。也正是因为光生物调节的标准化治疗参数难以达成共识,治疗方案的推广受到了限制,疗效缺乏可比性[18]。 2.1.2 低水平激光 此疗法是将细胞与组织暴露于可见光及近红外光下进行治疗,输出功率多为毫瓦级,一般不超过250 mW,相较于用以切割、消融治疗的激光,低水平激光的能量密度较低,因而称之为“低水平”[19]。若干研究探讨了低水平激光作用的分子机制,结果发现其光子在线粒体中被细胞色素c氧化酶吸收后,提高了一氧化氮、ATP、钙离子和活性氧等分子的活性[20]。低水平激光干预细胞和组织时能够产生一系列生物刺激作用,因而被广泛地应用于临床研究与基础研究中[21]。 2.1.3 发光二极管 发光二极管(light-emitting diode,LED)是一种半导体光源,属于不相干单色光源,早期的LED多为电子产品的配件,虽能发出较弱的红光,但并无显著的生物活性。随后有研究团队开发了用于基础研究的Nasa LED,在过去的15年里,LED技术不断改进,并形成了自身独特的生物学特点,除去是否具有相干性外,LED光与低水平激光在光谱宽度、颜色纯度等均有明显差异[22]。此外,LED光还具有不良反应小、使用寿命长、转化效能高、携带方便及花费少等优点[23]。如今,LED在医疗保健领域的应用已经相当成熟,其疗效也在众多研究中得到证实。但部分学者对于发光二极管能否作为光生物调节光源这一问题依旧持怀疑态度,或许研究者们可以略过激光特性造成的系列束缚,更多关注低水平激光与发光二极管的参数设置及疾病应用,从而促进光生物调节临床应用指南形成。文章基于激光的各种特性对光生物调节加以界定[24-27],见表1。"
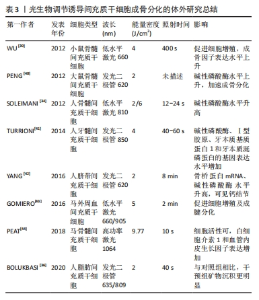
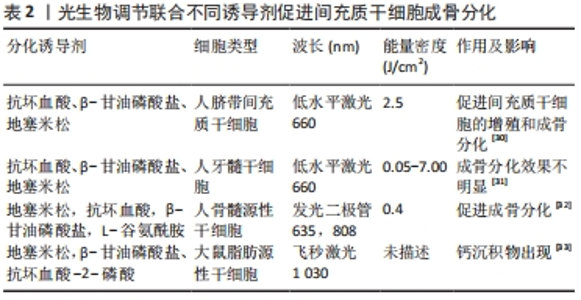
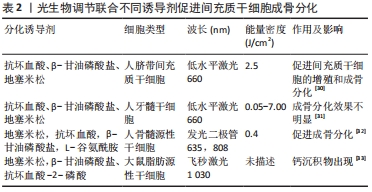
光生物调节作为一种外部刺激,直接照射间充质干细胞能否增强其活性,并促进成骨分化呢?国内外学者对此均给出了肯定答复。SOLEIMANI等[34]应用两种不同能量密度的低水平激光照射骨髓来源间充质干细胞,初步阐明了低水平激光对骨髓来源间充质干细胞增殖的影响及干细胞分化为成骨细胞的潜力。适宜强度的低水平激光还可提高衰老牙周膜干细胞的增殖能力和成骨分化能力[35]。另外,经低水平激光处理后的人脐带间充质干细胞表现出更高水平的增殖速率和分化潜力[30]。尽管有学者不赞成将LED光等非相干性光源纳入光生物调节疗法,但研究者们不能否认LED光对间充质干细胞的增殖与分化产生了一系列积极的影响。 BOLUKBASI等 [36]利用不同波长和不同能量密度的LED光照射脂肪来源间充质干细胞后,在显微镜中观察到数量不等的钙沉积。有研究对比了不同剂量的LED光对大鼠骨髓来源间充质干细胞的影响,单剂量LED光照射能够促进间充质干细胞的生长与增殖,双剂量照射使得间充质干细胞中碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素表达显著增加[37]。AMAROLI等[38]利用不同通量的LED光照射骨髓间充质干细胞,结果显示普通量LED光增加了成骨分化早期标志物-Runt相关转录因子2的表达,而高通量LED光抑制了成骨分化关键转录因子-过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ的合成,说明光生物调节诱导干细胞成骨分化还有光照通量相关联,利用不同通量的LED光干预会呈现出截然相反的效果。因此,无论是低水平激光,还是发光二极管,在促进间充质干细胞生长、诱导其分化方面均具有积极作用,然而部分研究也报告了阴性结果,可能与激光参数设置及成骨诱导液配制有关,后续需要开展更多的随机实验进行验证[34-44],体外研究具体成果见表3。"
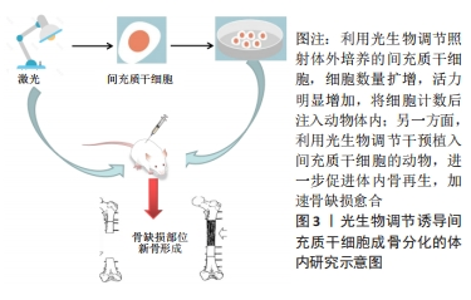
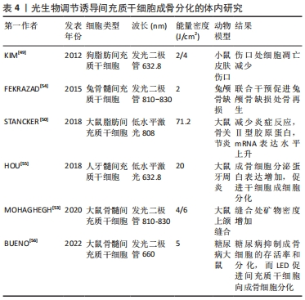
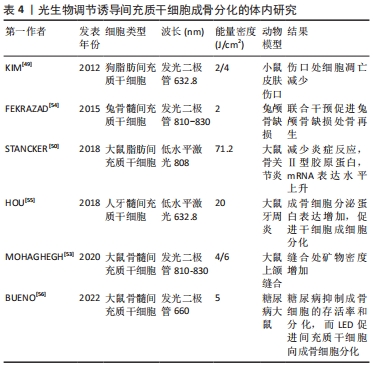
2.2.2 体内研究 众多研究表明,光生物疗法直接照射骨缺损部位时显示出强大的修复能力[45-47]。间充质干细胞移植到研究对象体内后,光生物疗法也扮演了重要的角色。有研究显示经过LED光照射后的脐带来源干细胞在免疫缺陷小鼠体内的植入率显著增强 [48]。亦有研究利用狗脂肪来源干细胞修复无胸腺小鼠的伤口,同时进行低水平激光治疗,结果表明,低水平激光一方面可增强间充质干细胞的存活率,刺激伤口处生长因子的分泌;另一方面又在间充质干细胞促进伤口愈合过程中充当生物刺激剂[49]。在一项骨关节炎的实验中,研究人员将脂肪来源干细胞注射到大鼠膝关节间隙后,利用低水平激光照射患侧膝关节,使得间充质干细胞的生物利用率显著提升[50]。另有研究将体外培养的间充质干细胞移植到大鼠颅骨缺损处,辅以低水平激光干预,结果显示实验组骨缺损处Runt相关转录因子2、骨钙素的表达水平显著增加,骨形成量和形成速率也明显优于对照组[51]。 BAYAT等[52]将低水平激光干预后的间充质干细胞移植到骨质疏松的动物模型中,使得模型组老鼠的骨骼微结构发生了积极变化。此外,另一项研究将间充质干细胞注入大鼠颌间缝合线处,同时利用低水平激光照射,放射线与Micro-CT结果均提示实验组缝合线处矿物密度显著增加,组织学图像中的钙结节较对照组也更加明显[53]。由此可见,越来越多的研究将间充质干细胞与再生医学联系起来,光生物调节作为一种非侵入式的辅助治疗,在促进机体组织结构再生过程中的作用不容小觑,一方面,体外培养的间充质干细胞经光生物调节干预后,细胞活力增加,增殖扩大,碱性磷酸酶等成骨标志物显著上调,另一方面,干细胞注入宿主体内后,光生物调节不仅可以提高干细胞在体存活率,促成归巢效应,缩短骨缺损愈合时间,还可间接消除伤口周围炎症,加速伤后愈 合[49-56]。体内研究机制及汇总分别见图3及表4。"

2.2.3 光生物调节诱导间充质干细胞增殖和分化的作用机制 WANG等[57]指出波长810 nm激光主要通过细胞色素c氧化酶吸收光子来刺激线粒体活性和ATP产生,而波长980 nm激光促进脂肪来源间充质干细成骨分化的过程更多与冷热处理及钙离子通道相关联。此外,相较于红光和近红外光,蓝光和绿光促进脂肪源性干细胞成骨分化的效果似乎更明显,考虑是因为绿光及蓝光能够提升细胞内钙浓度,进而激活钙离子通道[58]。据报道细胞外钙离子浓度增加能够上调间充质干细胞中成纤维细胞生长因子2、转化生长因子β1和骨桥蛋白的表达,并促进间充质干细胞基质矿化,而光生物调节能够改变细胞的生长环境,增加细胞外钙离子浓度 [59],由此可见,钙离子在光生物调节诱导间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中充当双向信号。同时,有研究指出仅通过钙离子激活剂无法上调真核起始因子4E蛋白和β-连环蛋白,然而钙离子动力学经光生物调节干预后能促进间充质干细胞分化为骨祖细胞,其中涉及ERK和Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路的激活[60]。 当骨髓源性间充质干细胞暴露于低水平激光时,骨形态发生蛋白2、碱性磷酸酶和Runt相关转录因子1等基因表达增加,RANKL/OPG比率降低,学者们考虑这一系列生物生理效应可能与骨形态发生蛋白2和胰岛素样生长因子1信号通路相关,低水平激光能够通过上调胰岛素样生长因子1表达诱导分化,并通过上调骨形态发生蛋白2表达进一步强化分化过程[39]。另一项研究使用光生物调节干预口腔颊脂垫来源干细胞,发现干细胞数量与活力增加,碱性磷酸酶和成骨特异性基因表达上调,此外,还观察到胶原蛋白基质产生,研究人员猜测光生物调节可能通过TRPV1离子通道诱导干细胞成骨分化[61]。再者,肌动蛋白细胞结构重组能够调节间充质干细胞的代谢活动,而光生物调节能够促使干细胞肌动蛋白细胞结构重新组合,并影响间充质干细胞的细胞表型。AMAROLI 等[62]还指出肌动蛋白细胞结构分布、干细胞成骨分化与激光照射时间密切相关。已有研究证实了增加核内肌动蛋白能够提高Runt相关转录因子2的活性,进而促进间充质干细胞成骨分化[63],而光生物调节能够促进细胞核中肌动蛋白形成,诱导成骨基因的转录。 此外,ARANY等[64]指出LED光通过剂量依赖性方式诱导活性氧产生,活性氧进一步激活转化生长因子β1,于体外培养扩增的牙髓来源干细胞最终通过转化生长因子β1分化为成牙母细胞。最近一项研究还发现细胞扩增受照射时间的影响较大,照射时间超过72 h后,间充质干细胞便不再继续增殖;而照射时间对成骨分化影响较小,且间充质干细胞的矿化受Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路的调控[65]。因此,间充质干细胞在成骨分化进程中受到多种因素的影响,例如光源波长、能量密度、照射时间及干细胞类型等;在细胞实验与动物实验中,有部分结果不谋而合,具体表现为光生物调节能够上调Runt相关转录因子、碱性磷酸酶及骨形态发生蛋白等成骨标志物水平,进而诱导成骨分化。此外,光生物调节还通过调节干细胞生长的体内外环境创造出干细胞巢,不仅给干细胞提供养分,还调控干细胞的分化方向。"

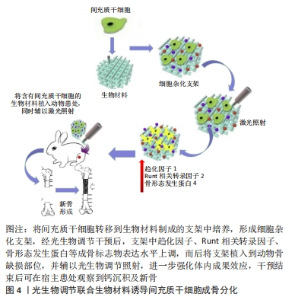
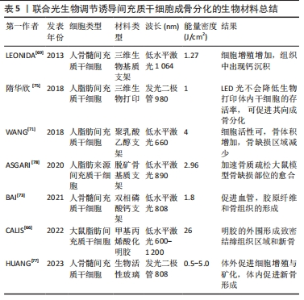
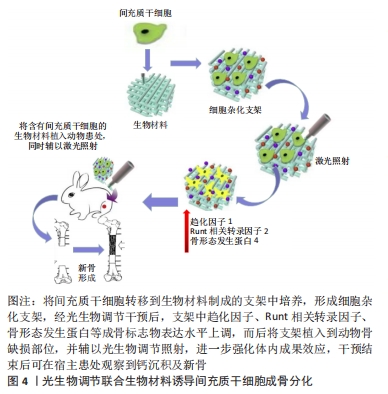
2.3 光生物调节联合生物材料诱导间充质干细胞成骨分化 近年来,生物材料因来源广、加工性能好及组织相容性佳等优点备受研究者的关注,作为组织工程的3大要素之一,生物材料为细胞的黏附、增殖和分化创造了良好的外部环境,其与间充质干细胞联合使用可有效解决骨缺损修复的难题,如果辅助以光生物调节干预,能够获得事半功倍的效果。 甲基丙烯酸化明胶由甲基丙烯酸酯基团和明胶含胺侧基的化学键合形成,因其具备生物学特性的仿生环境及亲水性而用于新骨组织的开发。有研究利用植入脂肪来源干细胞的明胶填充大鼠颅骨缺陷处,光生物调节于患处上方照射,治疗20周后,在组织学标本中可观察到新骨形成和胶原蛋白重组[66]。 脱钙骨基质是骨的提取物,以胶原为主要成分,并含有骨形成蛋白等成骨诱导因子,在骨缺损修复中应用广泛。利用低水平激光预先处理脂肪来源干细胞后,细胞活性显著增强,随后将细胞移入脱钙骨基质支架上,并将支架植入大鼠股骨缺损处,结果显示体内外联合干预促使骨祖细胞数量、骨小梁体积显著增加,并在骨修复的合成代谢阶段显著上调趋化因子1、Runt相关转录因子2和骨形态发生蛋白4的相对mRNA表达[67],这项研究结果与此前GAZOR等[68]的结论相一致。还有研究应用低水平激光照射接种在三维生物基质上的脂肪来源干细胞,干预4周后在组织学检测中发现钙沉积[69]。 聚乳酸乙醇酸是乳酸与乙醇酸经聚合反应而形成的复合物,是一种重要的生物降解材料,具有无毒及生物相容性好等特点[70]。有研究利用聚乳酸乙醇酸制成的支架培养脂肪来源干细胞,并将其植入大鼠颅骨缺损处,结果提示实验组的新生骨量较对照组更加明显,支架上的细胞也更有活力[71]。双相磷酸钙包括羟基磷灰石和磷酸三钙两种成分,由于其化学组成与骨组织的无机成分相似,且具有良好的生物相容性、生物活性和生物安全性,因而被广泛应用于组织工程支架、种植体表面涂层、骨水泥等研究中[72]。有研究将骨髓间充质干细胞接种到双相磷酸钙上制成细胞支架,并将支架植入小鼠颅内,辅以低水平激光照射,在体内植入物中观察到胶原纤维和骨组织血管生成,提示干细胞在植入体宿主血管生成过程中扮演了重要角色,并通过光生物调节进一步上调小鼠血管生成相关因子的表达,特别是血管内皮生长因子和缺氧诱导因子1α,揭示了低水平激光可能是通过耦合血管生成和干细胞成骨分化来提高骨再生能力[73]。 三维生物打印以生物材料、种子细胞、活性分子为基本单位,用三维打印技术构建具有个性化和生物功能的三维生物结构模型,该技术的问世为生物材料、生物医学和组织工程的发展注入了无限生机[74]。研究人员将脂肪来源干细胞 /海藻酸钠/明胶制成三维打印体后,利用低水平激光进行照射,发现低水平激光有望独立于诱导干细胞成骨的培养液之外而单独作为一种促进成骨的方式[75]。 生物活性玻璃是一种具有良好生物活性、生物相容性及骨诱导性的骨移植材料[76],将其植入人体后,能与所处的生物环境发生一系列特殊的反应,并通过与自然组织形成牢固的化学键而获得生物活性。生物活性玻璃与光生物调节联合应用时对增强骨再生具有叠加效应,能够促进间充质干细胞增殖与骨化,并加速体内新骨形成[77]。综上,将间充质干细胞在体外培养扩增后移植到特定的生物材料上,这些材料能够形成一个三维空间,为细胞生存提供所需营养物质,而后将细胞杂化支架植入骨缺损部位,光生物调节、生物材料、间充质干细胞三者的协同作用促进生物材料降解的同时,使得间充质干细胞不断增殖,并诱导新的功能性骨再生。此方法为治疗系列骨疾病提供了更多的方案选择,具有广大的应用前景,具体机制图见图4,相关研究汇总见表5。"

2.4 光生物调节联合其他物理因子诱导间充质干细胞成骨分化 电磁场是导电体和交流电产生的电衍生物,能够影响各种生物过程。众多研究报告了电磁场可增强间充质干细胞的活力、增殖及分化[79]。利用电磁场和低水平激光联合干预脂肪来源干细胞,既可促进细胞增殖,又能保存细胞活力,但诱使细胞增殖的机制仍有待阐明[80]。 低能量脉冲超声波,从属于微能量医学,频率0.7-3.0 MHz, 强度多低于3 W/cm2 ,脉冲比1∶4,其机械生物学效应与细胞产生的微生物力学相互作用,能够引发细胞内生物效应。近年来,大量的研究关注低能量超声波对干细胞的影响,尽管其作用机制尚不明确,但是超声波干预干细胞后产生的系列疗效是毋庸置疑的,具体而言其可在体外刺激干细胞、促进干细胞增殖分化和迁移、维持干细胞活性,并规避干细胞移植效率低下、种子细胞来源不足等问题[81]。低能量超声波与低水平激光联合使用时,生物刺激作用将产生叠加效应,在细胞分化前期,二者能够增加干细胞的初始数量,维持细胞活力,而在分化开始后,二者又能够加速成骨分化的进展[82]。 尽管已有研究证明了光生物调节能够联合其他物理因子诱导干细胞成骨分化,但其中的作用机制还不完全清楚,研究者们在分析对比各项研究时,不仅要将前文提及的各种光源参数纳入考虑范围,还应将其他物理因子的治疗参数也纳入考虑范围。因此,亟需进行更合理的实验设计以及更多样本、更高质量的随机对照研究提供有力的证据,以便寻找出最适的参数来更好地辅助治疗。 2.5 光生物调节联合药物诱导间充质干细胞成骨分化 催产素是一种下丘脑神经肽,在大脑中发挥神经调节剂的作用,协调各种动物的感官处理、进食控制、社会认知和情绪等行为。此外,催产素还能够调控间充质干细胞的增殖与分化[83],当低水平激光与催产素联合应用时,能够缓解骨质疏松继发的间充质干细胞活力降低,并诱导干细胞矿化[84]。 维生素D是钙磷代谢的重要调节因子之一,维持正常的血钙和磷水平,参与许多组织细胞的分化和增殖等生命周期。既往研究表明维生素D在促进脂肪来源干细胞成骨分化过程中能够发挥自分泌/旁分泌作用,并通过25-羟基维生素D3和骨化三醇上调胰岛素样生长因子1完成干细胞向成骨细胞的转化[85]。培养牙周韧带干细胞时添加维生素D,辅以发光二极管干预,结果提示LED光与维生素D联合干预显著促进了牙周韧带干细胞的增殖,并使得Runt相关转录因子2,Ⅰ型胶原,碱性磷酸酶和骨粘连蛋白等成骨标志物表达显著上升[86]。 阿仑膦酸钠为氨基二膦酸盐骨吸收抑制剂,与骨内羟磷灰石有强亲和力,能进入骨基质羟磷灰石晶体中,破骨细胞溶解晶体后,药物被释放,能降低破骨细胞活性,抑制骨吸收,多用于预防或治疗绝经后骨质疏松症、类固醇诱导的骨质疏松症、男性骨质疏松[87]。培育干细胞时加入阿伦膦酸盐,并观察其联合低水平激光对骨髓来源间充质干细胞的影响,干预组中可观察到大量钙沉积,细胞活力也明显优于对照组[88]。"

| [1] AIBAR-ALMAZAN A, VOLTES-MARTINEZ A, CASTELLOTE-CABALLERO Y, et al. Current status of the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(16):9465. [2] FLORENCIO-SILVA R, SASSO GR, SASSO-CERRI E, et al. Biology of bone tissue: structure, function, and factors that influence bone cells. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:421746. [3] TSIKLIN IL, SHABUNIN AV, KOLSANOV AV, et al. In vivo bone tissue engineering strategies: advances and prospects. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(15):3222. [4] MUSHAHARY D, SPITTLER A, KASPER C, et al. Isolation, cultivation, and characterization of human mesenchymal stem cells. Cytometry A. 2018;93(1): 19-31. [5] ALMALKI SG, AGRAWAL DK. Key transcription factors in the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Differentiation. 2016;92(1-2):41-51. [6] HU L, YIN C, ZHAO F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: cell fate decision to osteoblast or adipocyte and application in osteoporosis treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):360. [7] LI X, LING W, KHAN S, et al. Therapeutic effects of intrabone and systemic mesenchymal stem cell cytotherapy on myeloma bone disease and tumor growth. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(8):1635-1648. [8] LI F, ZHOU C, XU L, et al. Effect of stem cell therapy on bone mineral density: a meta-analysis of preclinical studies in animal models of osteoporosis. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0149400. [9] JIANG Y, ZHANG P, ZHANG X, et al. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for the treatment of osteoporosis. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(1):e12956. [10] ROSSO MPO, BUCHAIM DV, POMINI KT, et al. Photobiomodulation therapy (pbmt) applied in bone reconstructive surgery using bovine bone grafts: a systematic review. Materials (Basel). 2019;12(24):4051. [11] AILIOAIE LM, LITSCHER G. Photobiomodulation and sports: results of a narrative review. Life (Basel). 2021;11(12):1339. [12] MIN KH, BYUN JH, HEO CY, et al. Effect of low-level laser therapy on human adipose-derived stem cells: in vitro and in vivo studies. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2015;39(5):778-782. [13] EROGLU B, GENOVA E, ZHANG Q, et al. Photobiomodulation has rejuvenating effects on aged bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):13067. [14] MORADI A, ZARE F, MOSTAFAVINIA A, et al. Photobiomodulation plus adipose-derived stem cells improve healing of ischemic infected wounds in type 2 diabetic rats. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):1206. [15] AGAS D, HANNA R, BENEDICENTI S, et al. Photobiomodulation by near-infrared 980-nm wavelengths regulates pre-osteoblast proliferation and viability through the PI3K/Akt/Bcl-2 pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(14):7586. [16] HUANG YY, SHARMA SK, CARROLL J, et al. Biphasic dose response in low level light therapy-an update. Dose Response. 2011;9(4):602-618. [17] YAAKOBI T, MALTZ L, ORON U. Promotion of bone repair in the cortical bone of the tibia in rats by low energy laser (He-Ne) irradiation. Calcif Tissue Int. 1996; 59(4):297-300. [18] MOSCA RC, ONG AA, ALBASHA O, et al. Photobiomodulation therapy for wound care: a potent, noninvasive, photoceutical approach. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2019; 32(4):157-167. [19] CHUNG H, DAI T, SHARMA SK, et al. The nuts and bolts of low-level laser (light) therapy. Ann Biomed Eng. 2012;40(2):516-533. [20] DOMPE C, MONCRIEFF L, MATYS J, et al. Photobiomodulation-underlying mechanism and clinical applications. J Clin Med. 2020;9(6):1724. [21] GUPTA A, KESHRI GK, YADAV A. Non-thermal therapeutic applications of light. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect A Phys Sci. 2018;88(3):473-478. [22] HEISKANEN V, HAMBLIN MR. Photobiomodulation: lasers vs. light emitting diodes? Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2020;17(8):1003-1017. [23] SORBELLINI E, RUCCO M, RINALDI F. Photodynamic and photobiological effects of light-emitting diode (LED) therapy in dermatological disease: an update. Lasers Med Sci. 2018;33(7):1431-1439. [24] HASHMI J T, HUANG YY, OSMANI BZ, et al. Role of low-level laser therapy in neurorehabilitation. PM R. 2010;2(12 Suppl 2):S292-S305. [25] MOSKVIN SV. Only lasers can be used for low level laser therapy. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2017;7(4):22. [26] BROCHETTI RA, LEAL MP, RODRIGUES R, et al. Photobiomodulation therapy improves both inflammatory and fibrotic parameters in experimental model of lung fibrosis in mice. Lasers Med Sci. 2017;32(8):1825-1834. [27] SALEHPOUR F, MAHMOUDI J, KAMARI F, et al. Brain photobiomodulation therapy: a narrative review. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(8):6601-6636. [28] ZHANG X, ZHANG S, WANG T. How the mechanical microenvironment of stem cell growth affects their differentiation: a review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):415. [29] FERREIRA-BAPTISTA C, QUEIROS A, FERREIRA R, et al. The osteogenic potential of falciform ligament-derived stromal cells-a comparative analysis between two osteogenic induction programs. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022;9(12):810. [30] MIRANDA JM, DE ARRUDA J AA, MORENO L MM, et al. Photobiomodulation therapy in the proliferation and differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: an in vitro study. J Lasers Med Sci. 2020;11(4):469-474. [31] PEREIRA LO, LONGO JP, AZEVEDO RB. Laser irradiation did not increase the proliferation or the differentiation of stem cells from normal and inflamed dental pulp. Arch Oral Biol. 2012;57(8):1079-1085. [32] TANI A, CHELLINI F, GIANNELLI M, et al. Red (635 nm), Near-Infrared (808 nm) and Violet-Blue (405 nm) photobiomodulation potentiality on human osteoblasts and mesenchymal stromal cells: a morphological and molecular in vitro study. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):1946. [33] TANG W, WANG H, HE H. Protocol to photoactivate adipose-derived stem cell differentiation using a tightly-focused femtosecond laser. STAR Protoc. 2022;3(3): 101574. [34] SOLEIMANI M, ABBASNIA E, FATHI M, et al. The effects of low-level laser irradiation on differentiation and proliferation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neurons and osteoblasts--an in vitro study. Lasers Med Sci. 2012;27(2):423-430. [35] 邵馨,王爽,郭小梅,等.低能量激光对衰老牙周膜干细胞增殖和成骨分化功能的影响[J].山西医科大学学报,2022,53(11):1452-1457. [36] BOLUKBASI ATES G, AK A, GARIPCAN B, et al. Photobiomodulation effects on osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Cytotechnology. 2020;72(2):247-258. [37] LI WT, LEU YC, WU JL. Red-light light-emitting diode irradiation increases the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Photomed Laser Surg. 2010;28 Suppl 1:S157-S165. [38] AMAROLI A, AGAS D, LAUS F, et al. The effects of photobiomodulation of 808 nm diode laser therapy at higher fluence on the in vitro osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Front Physiol. 2018;9:123. [39] WU JY, WANG YH, WANG GJ, et al. Low-power GaAlAs laser irradiation promotes the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of stem cells via IGF1 and BMP2. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44027. [40] PENG F, WU H, ZHENG Y, et al. The effect of noncoherent red light irradiation on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Lasers Med Sci. 2012;27(3):645-653. [41] TURRIONI AP, BASSO FG, MONTORO LA, et al. Phototherapy up-regulates dentin matrix proteins expression and synthesis by stem cells from human-exfoliated deciduous teeth. J Dent. 2014;42(10):1292-1299. [42] YANG D, YI W, WANG E, et al. Effects of light-emitting diode irradiation on the osteogenesis of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Sci Rep. 2016;6: 37370. [43] GOMIERO C, BERTOLUTTI G, MARTINELLO T, et al. Tenogenic induction of equine mesenchymal stem cells by means of growth factors and low-level laser technology. Vet Res Commun. 2016;40(1):39-48. [44] PEAT FJ, COLBATH AC, BENTSEN LM, et al. In vitro effects of high-intensity laser photobiomodulation on equine bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell viability and cytokine expression. Photomed Laser Surg. 2018;36(2):83-91. [45] DE MARCO AC, TORQUATO LC, GONCALVES PR, et al. The effect of photobiomodulation therapy in different doses on bone repair of critical size defects in rats: a histomorphometric study. J Lasers Med Sci. 2021;12:e53. [46] MAGRI AM, FERNANDES KR, ASSIS L, et al. Photobiomodulation and bone healing in diabetic rats: evaluation of bone response using a tibial defect experimental model. Lasers Med Sci. 2015;30(7):1949-1957. [47] MAGRI A MP, FERNANDES KR, KIDO HW, et al. Photobiomodulation guided healing in a sub-critical bone defect in calvarias of rats. Laser Ther. 2019;28(3):171-179. [48] YANG J, WANG L, WU MX. 830 nm photobiomodulation therapy promotes engraftment of human umbilical cord blood-derived hematopoietic stem cells. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):19671. [49] KIM H, CHOI K, KWEON OK, et al. Enhanced wound healing effect of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells with low-level laser therapy in athymic mice. J Dermatol Sci. 2012;68(3):149-156. [50] STANCKER TG, VIEIRA SS, SERRA AJ, et al. Can photobiomodulation associated with implantation of mesenchymal adipose-derived stem cells attenuate the expression of MMPs and decrease degradation of type II collagen in an experimental model of osteoarthritis? Lasers Med Sci. 2018;33(5):1073-1084. [51] NAGATA MJ, SANTINONI CS, POLA NM, et al. Bone marrow aspirate combined with low-level laser therapy: a new therapeutic approach to enhance bone healing. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2013;121:6-14. [52] BAYAT M, JALALIFIROUZKOUHI A. Presenting a method to improve bone quality through stimulation of osteoporotic mesenchymal stem cells by low-level laser therapy. Photomed Laser Surg. 2017;35(11):622-628. [53] MOHAGHEGH S, MOHAMMAD-RAHIMI H, ESLAMIAN L, et al. Effect of mesenchymal stem cells injection and low-level laser therapy on bone formation after rapid maxillary expansion: an animal study. Am J Stem Cells. 2020;9(5):78-88. [54] FEKRAZAD R, SADEGHI GHUCHANI M, ESLAMINEJAD MB, et al. The effects of combined low level laser therapy and mesenchymal stem cells on bone regeneration in rabbit calvarial defects. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2015;151: 180-185. [55] HOU T, LI S, ZHANG G, et al. High-fluence low-power laser irradiation promotes odontogenesis and inflammation resolution in periodontitis by enhancing stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(4):2107-2119. [56] BUENO NP, KFOURI CC, COPETE IN, et al. Photobiomodulation treatments drive osteogenic versus adipocytic fate of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells reversing the effects of hyperglycemia in diabetes. Lasers Med Sci. 2022; 37(7):2845-2854. [57] WANG Y, HUANG YY, WANG Y, et al. Photobiomodulation of human adipose-derived stem cells using 810 nm and 980 nm lasers operates via different mechanisms of action. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861(2):441-449. [58] WANG Y, HUANG YY, WANG Y, et al. Photobiomodulation (blue and green light) encourages osteoblastic-differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells: role of intracellular calcium and light-gated ion channels. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33719. [59] LEE MN, HWANG HS, OH SH, et al. Elevated extracellular calcium ions promote proliferation and migration of mesenchymal stem cells via increasing osteopontin expression. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50(11):1-16. [60] TANG W, WANG H, ZHAO X, et al. Stem cell differentiation with consistent lineage commitment induced by a flash of ultrafast-laser activation in vitro and in vivo. Cell Rep. 2022;38(10):110486. [61] GHOLAMI L, AFSHAR S, ARKIAN A, et al. NIR irradiation of human buccal fat pad adipose stem cells and its effect on TRP ion channels. Lasers Med Sci. 2022; 37(9):3681-3692. [62] AMAROLI A, SABBIETI MG, MARCHETTI L, et al. The effects of 808-nm near-infrared laser light irradiation on actin cytoskeleton reorganization in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2021;383(3):1003-1016. [63] SEN B, XIE Z, UZER G, et al. Intranuclear actin regulates osteogenesis. Stem Cells. 2015;33(10):3065-3076. [64] ARANY PR, CHO A, HUNT TD, et al. Photoactivation of endogenous latent transforming growth factor-beta1 directs dental stem cell differentiation for regeneration. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(238):238ra69. [65] RUAN Y, KATO H, TAGUCHI Y, et al. Irradiation by high-intensity red light-emitting diode enhances human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation and mineralization through Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Lasers Med Sci. 2021;36(1):55-65. [66] CALIS M, IRMAK G, DEMIRTAS TT, et al. Photobiomodulation combined with adipose-derived stem cells encapsulated in methacrylated gelatin hydrogels enhances in vivo bone regeneration. Lasers Med Sci. 2022;37(1):595-606. [67] KHOSRAVIPOUR A, AMINI A, FARAHANI RM, et al. Evaluation of the effects of preconditioned human stem cells plus a scaffold and photobiomodulation administration on stereological parameters and gene expression levels in a critical size bone defect in rats. Lasers Med Sci. 2022;37(5):2457-2470. [68] GAZOR R, ASGARI M, ABDOLLAJHIFAR MA, et al. Simultaneous treatment of photobiomodulation and demineralized bone matrix with adipose-derived stem cells improve bone healing in an osteoporotic bone defect. J Lasers Med Sci. 2021;12: e41. [69] LEONIDA A, PAIUSCO A, ROSSI G, et al. Effects of low-level laser irradiation on proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells seeded on a three-dimensional biomatrix: in vitro pilot study. Lasers Med Sci. 2013;28(1):125-132. [70] WU W, LIU X, ZHOU Z, et al. Three-dimensional porous poly(propylene fumarate)-co-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffolds for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(9):2507-2517. [71] WANG YH, WU JY, KONG SC, et al. Low power laser irradiation and human adipose-derived stem cell treatments promote bone regeneration in critical-sized calvarial defects in rats. PLoS One. 2018;13(4):e0195337. [72] MOFAKHAMI S, SALAHINEJAD E. Biphasic calcium phosphate microspheres in biomedical applications. J Control Release. 2021;338:527-536. [73] BAI J, LI L, KOU N, et al. Low level laser therapy promotes bone regeneration by coupling angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):432. [74] MATAI I, KAUR G, SEYEDSALEHI A, et al. Progress in 3D bioprinting technology for tissue/organ regenerative engineering. Biomaterials. 2020;226:119536. [75] 隋华欣,吕培军,王勇,等.低能量激光照射对人脂肪来源干细胞/海藻酸钠/明胶三维生物打印体成骨能力的影响[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2018, 50(5):868-875. [76] GERHARDT L C, BOCCACCINI A R. Bioactive glass and glass-ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Materials (Basel). 2010;3(7):3867-3910. [77] HUANG L, GONG W, HUANG G, et al. The additive effects of bioactive glasses and photobiomodulation on enhancing bone regeneration. Regen Biomater. 2023;10:rbad024. [78] ASGARI M, GAZOR R, ABDOLLAHIFAR MA, et al. Combined therapy of adipose-derived stem cells and photobiomodulation on accelerated bone healing of a critical size defect in an osteoporotic rat model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;530(1):173-180. [79] ROSS CL, SIRIWARDANE M, ALMEIDA-PORADA G, et al. The effect of low-frequency electromagnetic field on human bone marrow stem/progenitor cell differentiation. Stem Cell Res. 2015;15(1):96-108. [80] NURKOVIC J, ZALETEL I, NURKOVIC S, et al. Combined effects of electromagnetic field and low-level laser increase proliferation and alter the morphology of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Lasers Med Sci. 2017;32(1): 151-160. [81] TAN Y, GUO Y, REED-MALDONADO A B, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound stimulates proliferation of stem/progenitor cells: what we need to know to translate basic science research into clinical applications. Asian J Androl. 2021; 23(6):602-610. [82] BAYAT M, VIRDI A, REZAEI F, et al. Comparison of the in vitro effects of low-level laser therapy and low-intensity pulsed ultrasound therapy on bony cells and stem cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2018;133:36-48. [83] FOROSTYAK O, BUTENKO O, ANDEROVA M, et al. Specific profiles of ion channels and ionotropic receptors define adipose- and bone marrow derived stromal cells. Stem Cell Res. 2016;16(3):622-634. [84] FALLAHNEZHAD S, JAJARMI V, SHAHNAVAZ S, et al. Improvement in viability and mineralization of osteoporotic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell through combined application of photobiomodulation therapy and oxytocin. Lasers Med Sci. 2020;35(3):557-566. [85] GENG S, ZHOU S, BI Z, et al. Vitamin D metabolism in human bone marrow stromal (mesenchymal stem) cells. Metabolism. 2013;62(6):768-777. [86] ABDELGAWAD LM, ABDELAZIZ AM, SABRY D, et al. Influence of photobiomodulation and vitamin D on osteoblastic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells and bone-like tissue formation through enzymatic activity and gene expression. Biomol Concepts. 2020;11(1):172-181. [87] VERTESICH K, SOSA BR, NIU Y, et al. Alendronate enhances osseointegration in a murine implant model. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(4):719-726. [88] FALLAHNEZHAD S, AMINI A, HAJIHOSSAINLOU B, et al. Combined effects of photobiomodulation and alendronate on viability of osteoporotic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018;182:77-84. |
| [1] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [2] | Bai Chen, Yang Wenqian, Meng Zhichao, Wang Yuze. Strategies for repairing injured anterior cruciate ligament and promoting graft healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1457-1463. |
| [3] | Cheng Jie, Wang Jihong, Zhang Pei. Functional exercise for tendon adhesion in a model of deep flexor tendon II injury of the third toe [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1161-1167. |
| [4] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [5] | Feng Ruiqin, Han Na, Zhang Meng, Gu Xinyi, Zhang Fengshi. Combination of 1% platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [6] | Wang Wen, Zheng Pengpeng, Meng Haohao, Liu Hao, Yuan Changyong. Overexpression of Sema3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and MC3T3-E1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 993-999. |
| [7] | Qiu Xiaoyan, Li Bixin, Li Jingdi, Fan Chuiqin, Ma Lian, Wang Hongwu. Differentiation of insulin-producing cells from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells infected by MAFA-PDX1 overexpressed lentivirus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1000-1006. |
| [8] | Liu Qiwei, Zhang Junhui, Yang Yuan, Wang Jinjuan. Role and mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1015-1020. |
| [9] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [10] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [11] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [12] | Hu Guangzhi, Lu Hongyan. Changes in pulmonary pericytes and tube formation of pulmonary vascular endothelial cells in mouse models of broncho-pulmonary dysplasia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 522-527. |
| [13] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [14] | Lin Feng, Cheng Ling, Gao Yong, Zhou Jianye, Shang Qingqing. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel-encapsulated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote cardiac function in myocardial infarction rats (III) [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 355-359. |
| [15] | Bi Yujie, Ma Dujun, Peng Liping, Zhou Ziqiong, Zhao Jing, Zhu Houjun, Zhong Qiuhui, Yang Yuxin. Strategy and significance of Chinese medicine combined with medical hydrogel for disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 419-425. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||