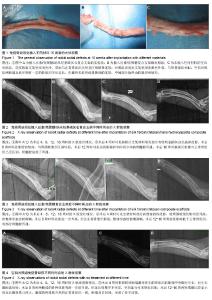
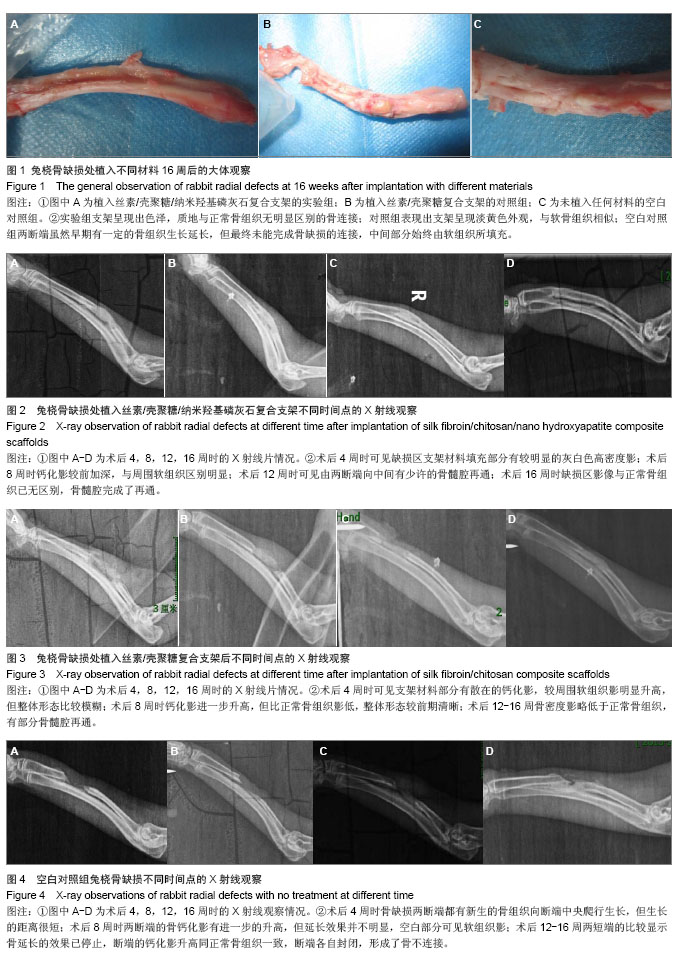
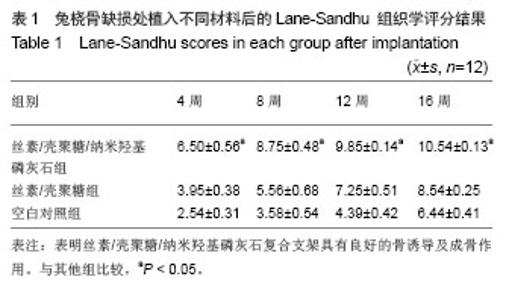
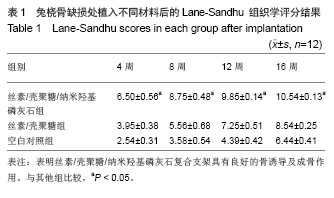
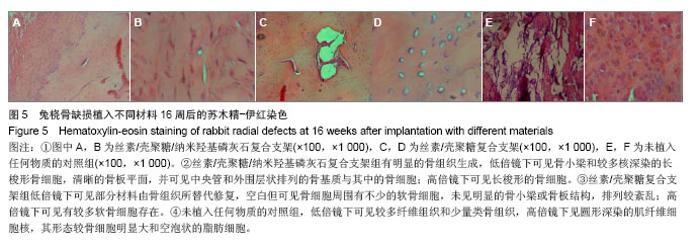
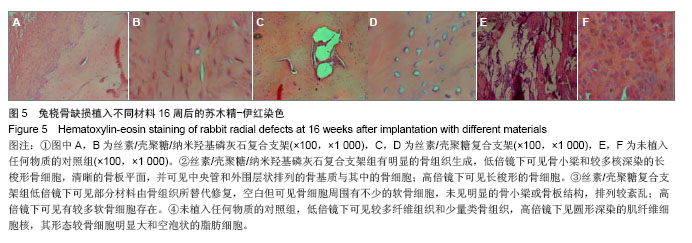
| [1]Puppi D,Chiellini F,Piras AM,et al.Polymeric materials for bone and cartilage repair.Prog Polym Sci.2010;35:403-440. [2]Pan Z,Ding JD.Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) porous scaffolds for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.Interface Focus. 2012;2(3):366-377.[3]Park SH,Park DS,Shin JW,et al.Scaffolds for bone tissue engineering fabricated from two different materials by the rapid prototyping technique: PCL versus PLGA.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2012;23(11):2671-2678.[4]Wang Z,Li M,Yu B,et al.Nanocalcium-deficient hydroxyapatite- poly (e-caprolactone)-polyethylene glycol-poly (e-caprolactone) composite scaffolds.Int J Nanomed.2012; 7:3123-3131.[5]De Santis R,Gloria A,Russo T,et al.A basic approach toward the development of nanocomposite magnetic scaffolds for advanced bonetissue engineering.J Appl Polym Sci.2011; 122(6): 3599-3605.[6]Budiraharjo R,Neoh KG,Kang ET.Hydroxyapatite-coated carboxymethyl chitosan scaffolds for promoting osteoblast and stem cell differentiation.J Colloid Interface Sci.2012; 366(1):224-232.[7]Alves da Silva ML,Crawford A,Mundy JM,et al. Chitosan/polyester-based scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering: assessment of extracellular matrix formation. Acta Biomater.2010;6:1149-1157.[8]邓 江,余荣峰,黄文良,等.丝素蛋白/壳聚糖生物支架复合骨髓间质干细胞修复老年兔软骨缺损[J].中华老年医学杂,2012,31(2): 156-160.[9]Tiyaboonchai W,Chomchalao P,Pongcharoen S,et al.Preparation and characterization of blended Bombyx mori silk fibroin scaffolds. Fiber Polym. 2011; 12:324-333.[10]Murphy CM,Haugh MG,O'Brien FJ.The effect of mean pore size on cell attachment, proliferation andmigration in collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2010;31:461-466.[11]Lu Q,Zhang X,Hu X,et al.Green Process to Prepare Silk Fibroin/Gelatin Biomaterial Scaffolds.Macromol Biosci. 2010; 10:289-298.[12]Zhang HF,Zhao CY, Fan HS.Histological and biomechanical study of repairing rabbit radius segmental bone defect with porous titanium.Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao.2011;43(5):724-729.[13]Rahimzadeh R,Veshkini A,Sharifi D,et al.Value of color Doppler ultrasonography and radiography for the assessment of the cancellous bone scaffold coated with nano-hydroxyapatite in repair of radial bone in rabbit. Acta Cir Bras.2012;27(2):148-154.[14]Hao W,Dong J,Jiang M,et al.Enhanced bone formation in large segmental radial defects by combining adipose-derived stem cells expressing bone morphogenetic protein 2 with nHA/RHLC/PLA scaffold.Int Orthop.2010;34(8):1341-1349.[15]Salerno M,Cenni E,Fotia C,et al.Bone-targeted doxorubicin-loaded nanoparticles as a tool for the treatment of skeletal metastases.Curr Cancer Drug Targets.2010;10(7): 649-659.[16]Yewle JN,Puleo DA,Bachas LG.Enhanced affinity bifunctional bisphosphonates for targeted delivery of therapeutic agents to bone.Bioconjug Chem.2011;22(12):2496-2506.[17]Kelly DJ,Jacobs CR.The Role of Mechanical Signals in Regulating Chondrogenesis and Osteogenesis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2010;90:75-85.[18]Jayasuriya AC,Bhat A.Fabrication and characterization of novel hybrid organic/inorganic microparticles to apply in bone regeneration.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010;93(4):1280-1288.[19]Lee JS,Park WY,Cha JK,et al.Periodontal tissue reaction to customized nano-hydroxyapatite block scaffold in one-wall intrabony defect: a histologic study in dogs.J Periodontal Implant Sci.2012;42:50-58. [20]Martínez-Vázquez FJ,Perera FH,Miranda P,et al.Improving the compressive strength of bioceramic robocast scaffolds by polymer infiltration.Acta Biomater. 2010;6(11):4361-4368.[21]Crouzier T,Sailhan F,Becquart P,et al.The performance of BMP-2 loaded TCP/HAP porous ceramics with a polyelectrolyte multilayer film coating. Biomaterials.2011; 32(30): 7543-7554.[22]van der Pol U,Mathieu L,Zeiter S,et al.Augmentation of bone defect healing using a new biocomposite scaffold: an in vivo study in sheep.Acta Biomater. 2010;6(9):3755-3762.[23]Liao F,Chen Y,Li Z,et al.A novel bioactive three-dimensional beta-tricalcium phosphate/chitosan scaffold for periodontal tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010;21(2): 489-496.[24]朱凌云,王彦平,石宗利.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚磷酸钙纤维/聚乳酸骨组织工程复合支架的特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(3): 431-433.[25]肖海军,薛 锋,何志敏.纳米羟基磷灰石/羧甲基壳聚糖-海藻酸钠复合骨水泥的性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2011,15(38): 7113-7117.[26]叶荣,张晓峰,严怀宁.羟基丁酸-羟基戊酸纳米纤维材料修复胫骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(34):6284-6288.[27]杨 耀,徐卫袁,张 亚.丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石材料复合骨髓间充质干细胞构建组织工程化软骨[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(29):5339-5342.[28]Marelli B,Ghezzi CE,Mohn D.Accelerated mineralization of dense collagen-nano bioactive glass hybrid gels increases scaffold stiffness and regulates osteoblastic function. Biomaterials. 2011;32(34):8915-8926.[29]Lao LH,Wang YJ,Zhu Y,et al.Poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/ hydroxyapatite nanofibrous scaffolds fabricated by electrospinning for bone tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010;22(8):4374-4378. [30]Sun F,Zhou H,Lee J.Various preparation methods of highly porous hydroxyapatite/polymer nanoscale biocomposites for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater.2011;7(11):3813-3828.[31]Zhou H,Lee J.Nanoscale hydroxyapatite particles for bone tissue engineering.Acta Biomater.2011;7(7):2769-2781.[32]Zhang CY,Lu H,Zhuang Z,et al.Nano-hydroxyapatite/poly (l-lactic acid) composite synthesized by a modified in situ precipitation: preparation and properties.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010;21(12):3077-3083. |