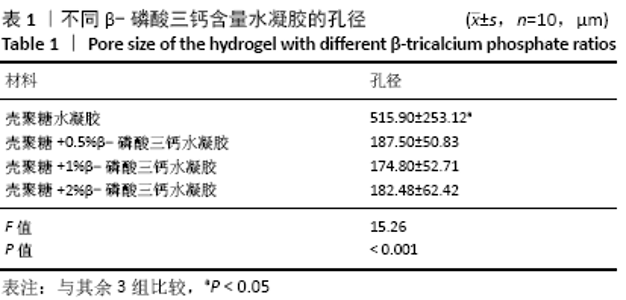
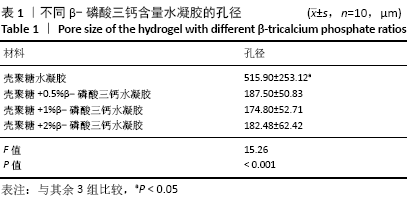
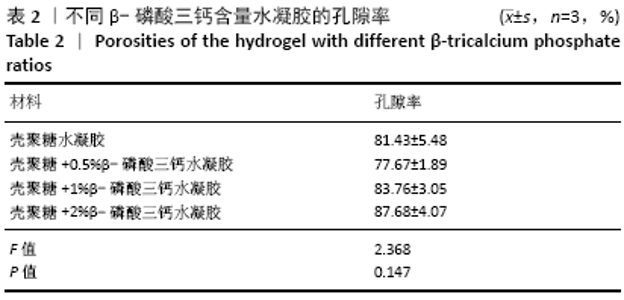
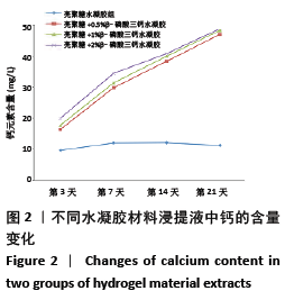
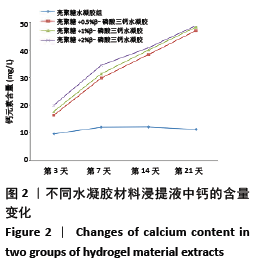
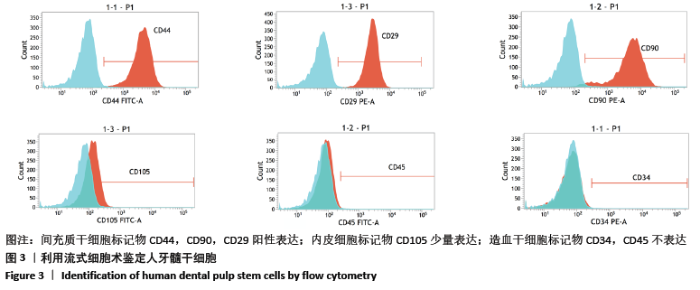
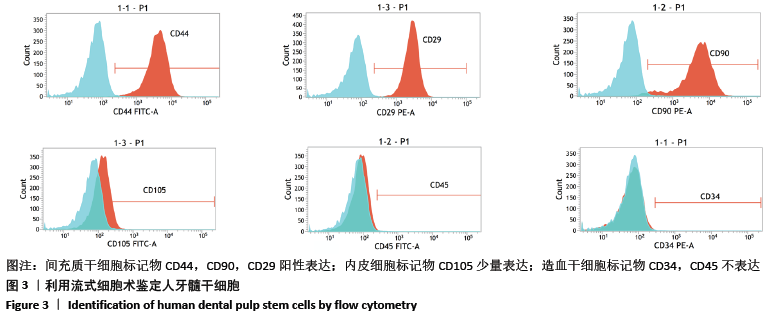
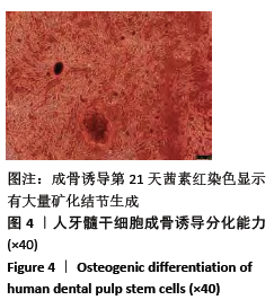
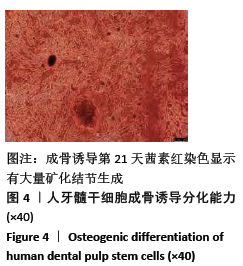
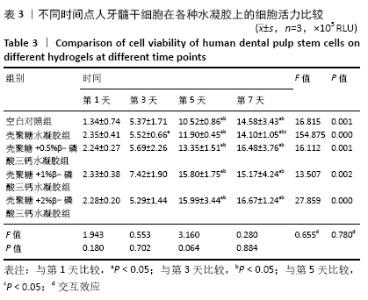
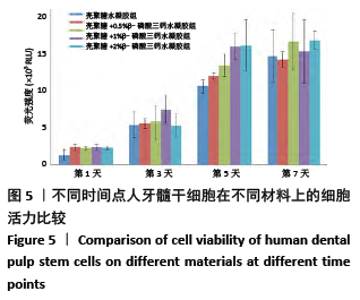
[1] HOLLINGER JO, LEONG K. Poly(alpha-hydroxy acids): carriers for bone morphogenetic proteins. Biomaterials. 1996;17(2):187-194.
[2] JIA W, LAU GY, HUANG W, et al. Bioactive Glass for Large Bone Repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(18):2842-2848.
[3] DUMIC-CULE I, PECINA M, JELIC M, et al. Biological aspects of segmental bone defects management. Int Orthop. 2015;39(5): 1005-1011.
[4] MHANNA R, HASAN A. Tissue engineering for artificial organs[M]. Weinheim: WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2017:1-34.
[5] CHAPPARD D, GUILLAUME B, MALLET R, et al. Sinus lift augmentation and beta-TCP: a microCT and histologic analysis on human bone biopsies. Micron. 2010;41(4):321-326.
[6] DURKIN CA, MOCK T, ARMBRUST EV. Chitin in diatoms and its association with the cell wall. Eukaryot Cell. 2009;8(7):1038-1050.
[7] 胡慧婷,于凤麟,赵月萍. 牙髓干细胞生物学特性影响因素的研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2019,27(4):268-272.
[8] GRONTHOS S, MANKANI M, BRAHIM J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.
[9] HUANG GT, YAMAZA T, SHEA LD, et al. Stem/progenitor cell-mediated de novo regeneration of dental pulp with newly deposited continuous layer of dentin in an in vivo model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(2): 605-615.
[10] LINDROOS B, MÄENPÄÄ K, YLIKOMI T, et al. Characterisation of human dental stem cells and buccal mucosa fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;368(2):329-335.
[11] MONTERUBBIANESI R, BENCUN M, PAGELLA P, et al. A comparative in vitro study of the osteogenic and adipogenic potential of human dental pulp stem cells, gingival fibroblasts and foreskin fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1761.
[12] CHING HS, LUDDIN N, RAHMAN IA, et al. Expression of Odontogenic and Osteogenic Markers in DPSCs and SHED: A Review. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(1):71-79.
[13] NAAHIDI S, JAFARI M, LOGAN M, et al. Biocompatibility of hydrogel-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol Adv. 2017;35(5):530-544.
[14] PARK JB. The use of hydrogels in bone-tissue engineering. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011;16(1):e115-118.
[15] DU C, FALINI G, FERMANI S, et al. Supramolecular assembly of amelogenin nanospheres into birefringent microribbons. Science. 2005;307(5714):1450-1454.
[16] REGITSKY AU, KESHAVARZ B, MCKINLEY GH, et al. Rheology as a Mechanoscopic Method to Monitor Mineralization in Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules. 2017;18(12):4067-4074.
[17] DISCHER DE, MOONEY DJ, ZANDSTRA PW. Growth factors, matrices, and forces combine and control stem cells. Science. 2009;324(5935): 1673-1677.
[18] HOLLISTER SJ, FLANAGAN CL, ZOPF DA, et al. Design control for clinical translation of 3D printed modular scaffolds. Ann Biomed Eng. 2015;43(3):774-786.
[19] WATSON BM, VO TN, TATARA AM, et al. Biodegradable, phosphate-containing, dual-gelling macromers for cellular delivery in bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2015;67:286-296.
[20] LAINO G, GRAZIANO A, D’AQUINO R, et al. An approachable human adult stem cell source for hard-tissue engineering. J Cell Physiol. 2006;206(3):693-701.
[21] LEE SK, LEE SK, LEE SI, et al. Effect of calcium phosphate cements on growth and odontoblastic differentiation in human dental pulp cells. J Endod. 2010;36(9):1537-1542.
[22] SHIE MY, DING SJ. Integrin binding and MAPK signal pathways in primary cell responses to surface chemistry of calcium silicate cements. Biomaterials. 2013;34(28):6589-6606. |