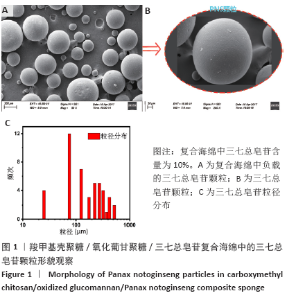
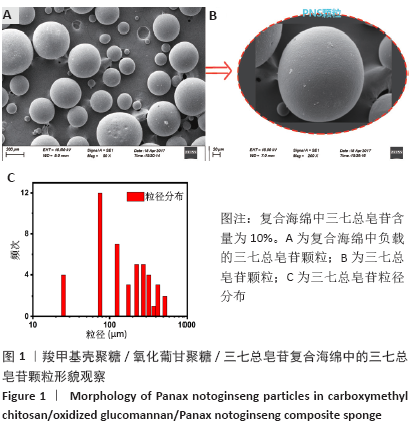
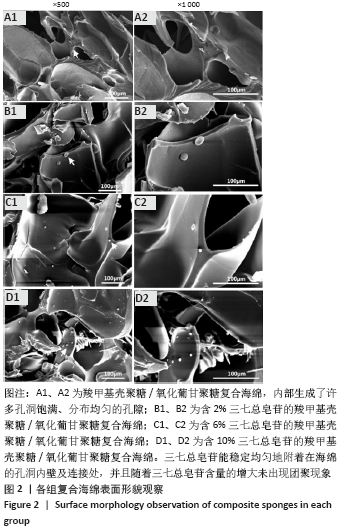
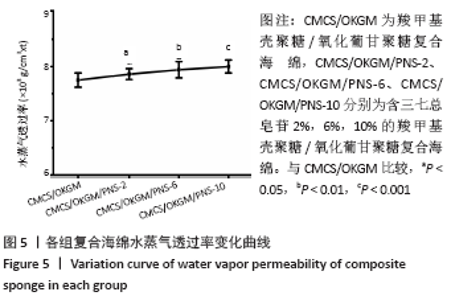
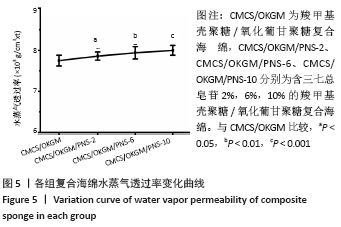
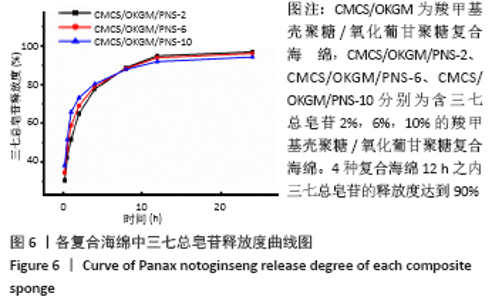
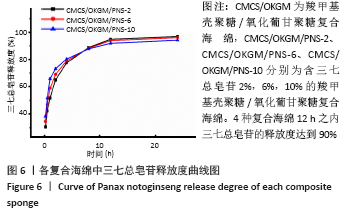
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (16): 2528-2534.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3147
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and performance evaluation of carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized glucomannan/Panax notoginseng compound sponge dressing for chronic wound
Li Jie1, Xu Jianzhen1, Hu Ping1, Lei Qiqi1, Zhang Wenning1, Ao Ningjian1, 2
- 1College of Life Science and Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Biomaterials of Guangdong Education Department, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-04-25Revised:2020-04-27Accepted:2020-05-22Online:2021-06-08Published:2021-01-07 -
Contact:Ao Ningjian, Researcher, Master’s and doctoral supervisor, College of Life Science and Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China; Key Laboratory of Biomaterials of Guangdong Education Department, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:李洁,女,1997年生,云南省西双版纳傣族自治州勐海县人,暨南大学在读硕士,主要从事生物医用材料研发与创伤修复研究。 许楗桢,男,1993年生,广西壮族自治区南宁市人,汉族,暨南大学毕业,硕士,工程师,主要从事新型医用高分子材料与医疗器械产品研发工作。 -
Supported by:a grant from Science and Technology Plan of Guangdong Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. 2017A020211006 (to ANJ); the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 20976068 (to ANJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Jie, Xu Jianzhen, Hu Ping, Lei Qiqi, Zhang Wenning, Ao Ningjian . Preparation and performance evaluation of carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized glucomannan/Panax notoginseng compound sponge dressing for chronic wound[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2528-2534.
share this article
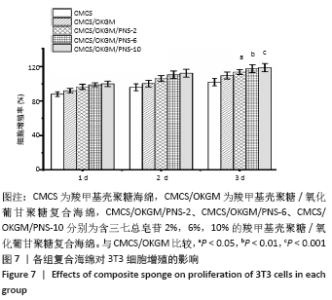
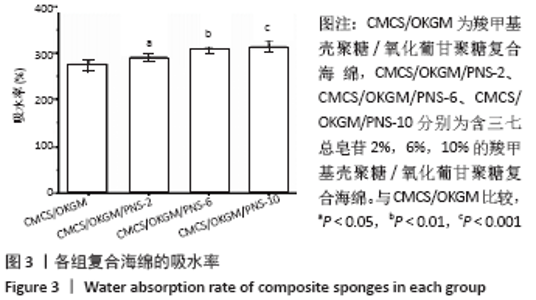
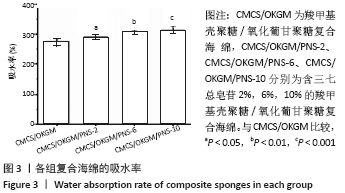
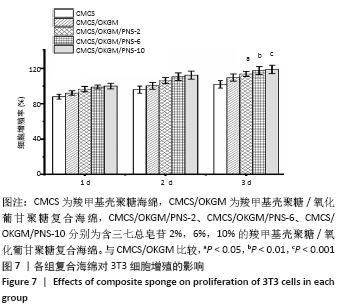
2.6 复合海绵对3T3细胞增殖影响分析 作为慢性伤口敷料必须具备的功能就是可以促进表皮成纤维细胞的生长,以此加速创面的愈合速度,因此通常采用成纤维细胞的增殖情况作为判断伤口敷料有效性依据。图7为各组复合海绵对3T3细胞增殖的影响对比图,可以看到各组复合海绵1,2,3 d的3T3细胞增殖率均超过90%,相比于CMCS海绵,CMCS/OKGM复合海绵可明显促进3T3细胞的增殖;在CMCS/OKGM复合海绵的基础上分别加入2%,6%,10%的PNS,3T3细胞增殖率有显著提升,几乎呈梯度式增长且增殖率均大于95%,说明在CMCS/OKGM复合海绵的基础上加入10%的PNS,能显著提高复合海绵促进3T3细胞增殖的能力,从而对伤口的愈合起到促进作用。"
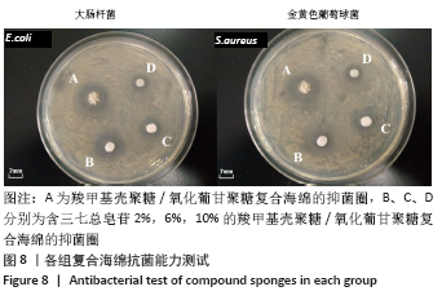
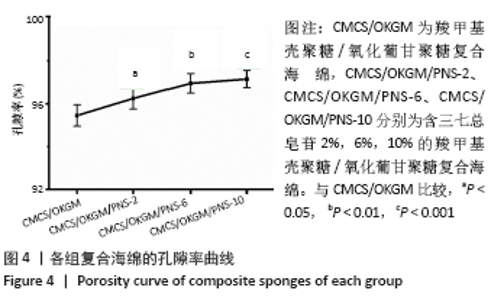
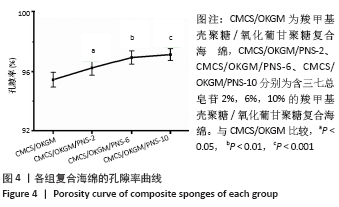
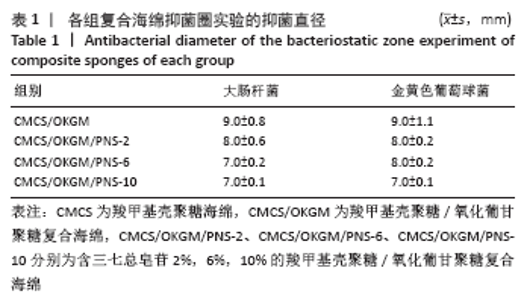
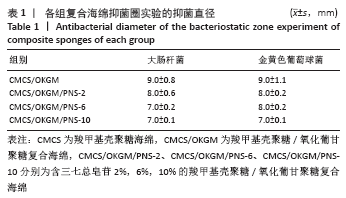
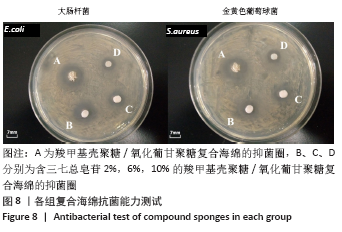
2.7 复合海绵的抑菌效果分析 图8为各组复合海绵抗菌能力测试结果,图中看到所制材料对2种代表性菌种的抑菌圈直径均大于7 mm,表现出明显的抑菌作用,其中CMCS/OKGM是CMCS在体系中所占比例最高的材料,由于CMCS的优良抑菌作用,其对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌均产生超过9 mm的抑菌圈;随着PNS的加入,可以观察到CMCS/OKGM/PNS-2复合海绵对2种代表性菌种的抑菌圈均在8 mm左右,略弱于CMCS/OKGM复合海绵的抑菌效果,该两种复合海绵对大肠杆菌的抑菌性均略强于对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌性;CMCS/OKGM/PNS-6复合海绵对2种代表性菌种的抑菌效果弱于CMCS/OKGM、CMCS/OKGM/PNS-2复合海绵,抑菌圈均略小于8 mm; CMCS/OKGM/PNS-10复合海绵对2种代表性菌种所产生的抑菌圈在7.0-8.0 mm间,并且很清晰,说明其与CMCS/OKGM/PNS-2、CMCS/OKGM/PNS-6复合海绵相比有极佳的抑菌效果,符合医用敷料的抗菌需求。各组复合海绵的抑菌圈直径见表1。 "
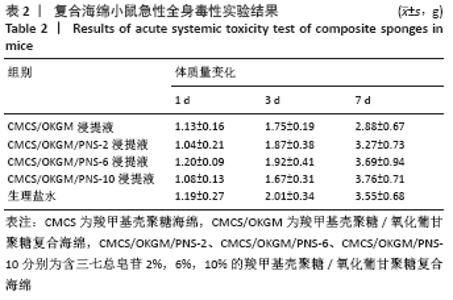
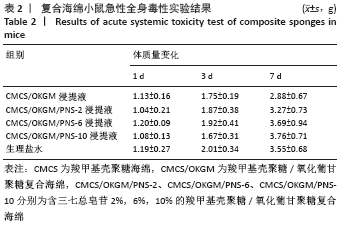
2.8 复合海绵急性全身毒性实验结果 KM小鼠在注射不同材料浸提液1周内生理活动都正常,无中毒或死亡现象发生,且体质量稍有增长,故判定所制材料无急性全身毒性反应,具有生物安全性。 腹腔注射材料浸提液后1,3 ,7 d的KM小鼠体质量变化记录表如表2所示,第1天各组材料浸提液对KM小鼠体质量影响不大;第3,7天时各组KM小鼠体质量日渐增加,生理盐水组与CMCS/OKGM/PNS-2组、CMCS/OKGM/PNS-6组体质量增长结果相似;第7天时,CMCS/OKGM组体质量增长最少;CMCS/OKGM/PNS-10组第3天时体质量增长最少,第7天时体质量增长最多。在复合海绵对3T3细胞增殖影响结果中也表明了CMCS/OKGM/PNS-10复合海绵对3T3细胞的增殖效果最佳,该两项测试结果的高度吻合,证明CMCS/OKGM/PNS-10复合海绵具有极好的生物安全性。 "
| [1] BEHRENS AM, SIKORSKI MJ, KOFINAS P. Hemostatic strategies for traumatic and surgical bleeding. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(11):4182-4194. [2] MCDANIEL JC, BROWNING KK. Smoking, Chronic Wound Healing, and Implications for Evidence-Based Practice. J Wound Ostomy Cont Nurs. 2014; 41(5):415-423. [3] LU Z, GAO J, HE Q, et al. Enhanced antibacterial and wound healing activities of microporous chitosan-Ag/ZnO composite dressing. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;156:460-469. [4] MOROZ A, DEFFUNE E. Platelet-rich plasma and chronic wounds: remaining fibronectin may influence matrix remodeling and regeneration success. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(11):1436-1439. [5] SACCO P, TRAVAN A, BORGOGNA M, et al. Silver-containing antimicrobial membrane based on chitosan-TPP hydrogel for the treatment of wounds. J Mater Sci-Mater Med. 2015;26(3):128. [6] KERSTEIN MD. The non-healing leg ulcer: peripheral vascular disease, chronic venous insufficiency, and ischemic vasculitis. Ostomy Wound Manage. 1996;42(10A Suppl):19S-35S. [7] ANISHA BS, SANKAR D, MOHANDAS A, et al. Chitosan-hyaluronan/nano chondroitin sulfate ternary composite sponges for medical use. Wound Management. 2013;92(2):1470-1476. [8] ONG SY, WU J, MOOCHHALA SM, et al. Development of a chitosan-based wound dressing with improved hemostatic and antimicrobial properties. Biomater. 2008;29(32):4323-4332. [9] YU H, LU J, XIAO C. Preparation and properties of novel hydrogels from oxidized konjac glucomannan cross-linked chitosan for in vitro drug delivery. Macromol Biosci. 2007;7(9-10):1100-1111. [10] 庞杰,林琼.魔芋葡甘聚糖功能材料研究与应用进展[J].结构化学, 2003,22(6):633-642. [11] LIGUI C. Research Progress in the Modification of Konjac Glucomannan. Anhui Nongye Kexue. 2008;36(15):6157-6160. [12] LIU L, WEN H, RAO Z, et al. Preparation and characterization of chitosan -collagen peptide/oxidized konjac glucomannan hydrogel. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;108:376-382. [13] CHEN X G, PARK H J. Chemical characteristics of O-carboxymethyl chitosans related to the preparation conditions. Carbohydr Polym. 2003;53(4): 355-359. [14] NADERI Z, AZIZIAN J. Synthesis and characterization of carboxymethyl chitosan/Fe3O4 and MnFe2O4 nanocomposites hydrogels for loading and release of curcumin. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018;185:206-214. [15] 刘水莲.生物可降解羧甲基壳聚糖—聚乳酸水凝胶的药物释放研究[D].青岛:青岛科技大学,2015. [16] 王莹,禇扬,李伟,等.三七中皂苷成分及其药理作用的研究进展[J].中草药,2015,46(9):1381-1392. [17] 陈社带,陈东波.三七总皂苷对缺血心肌的保护及抗氧化作用的实验研究[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2013,34(4):548-549. [18] 刘慧莲.人参皂甙Rg1对3T3细胞增殖作用的研究[J].潍坊学院学报, 2007,7(4):85-86. [19] YU H, MAO C. Synthesis and properties of novel hydrogels from oxidized konjac glucomannan crosslinked gelatin for in vitro drug delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 2008;72(3):479-489. [20] 许楗桢.羧甲基壳聚糖/氧化葡甘聚糖/三七复合海绵的制备及评价[D].广州:暨南大学,2018. [21] 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社, 2015. [22] 王超.壳聚糖/海藻酸盐/白芨多糖复合止血材料的制备及其性能研究[D].广州:暨南大学,2017. [23] 由少华.解读GB/T16886《医疗器械生物学评价》系列标准[J].中国医疗器械信息,2005,11(1):20-24. [24] 甘美舍,黄艳,杨斌,等.不同溃疡程度糖尿病足的临床特点及预后分析[J].糖尿病新世界,2020,23(1): 161-162. [25] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J].中国实用内科杂志,2018,38(4):292-344. [26] WANG M, LI H, LIU W, et al. Dammarane-type leads panaxadiol and protopanaxadiol for drug discovery: Biological activity and structural modification. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;189:112087. [27] ANITHA A, MAYA S, DEEPA N, et al. Curcumin-loaded N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles for cancer drug delivery. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2012;23(11):1381-1400. [28] MARZAN AL, TABASSUM R, JAHAN B, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Stable Nanosuspension for Dissolution Rate Enhancement of Furosemide: A Quality by Design (QbD) Approach. Curr Drug Deliv. 2018;15(5):672-685. [29] 陈红艳,陈安,卢芳国,等.三七总皂苷的药理研究进展[J].湖南中医杂志,2019,35(1):154-157. [30] CHEN ZH, LI J, LIU J, et al.Saponins isolated from the root of Panax notoginseng showed significant anti-diabetic effects in KK-Ay mice. Am J Chin Med. 2008;36(5):939-951. [31] 郭爽,张强,田志浩,等.三七总皂苷联用阿司匹林对后者抗血小板凝集作用的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2018,24(9):116-120. [32] 刘文迎,郭亮亮,刘泽员,等.氧化纤维素/壳聚糖复合海绵的制备及性能研究[J].化工新型材料,2019,47(11):162-166. [33] 李治,刘晓非,管云林. O-羧甲基壳聚糖抗菌性的研究[J].日用化学工业,2000,30(3):10-11. [34] WANG L, HUANG Y, YIN G, et al. Antimicrobial activities of Asian ginseng, American ginseng, and notoginseng. Phytother Res. 2020;34(6):1226-1236. [35] 郑立,陈西广,刘万顺,等.羧甲基壳聚糖膜对皮肤成纤维细胞相容性研究[J].生物化学与生物物理进展, 2003,30(2):314-320. |
| [1] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [2] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [3] | Zhang Bin, Sun Lihua, Zhang Junhua, Liu Yusan, Cui Caiyun. A modified flap immediate implant is beneficial to soft tissue reconstruction in maxillary aesthetic area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 707-712. |
| [4] | Fu Shuanhu, Qin Kai, Lu Dahan, Qin Haibiao, Gu Jin, Chen Yongxi, Qin Haoran, Wei Jiading, Wu Liang, Song Quansheng. Lumbar spinal tuberculosis implanted with artificial bone with streptomycin sulfate and percutaneous pedicle screw under transforaminal endoscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 493-498. |
| [5] | Li Wenjing, Li Haobo, Liu Congna, Cheng Dongmei, Chen Huizhen, Zhang Zhiyong. Comparison of different bioactive scaffolds in the treatment of regenerative pulp of young permanent teeth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 499-503. |
| [6] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [7] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [8] | Li Chenjie, Lü Linwei, Song Yang, Liu Jingna, Zhang Chunqiu. Measurement and statistical analysis of trabecular morphological parameters of titanium alloy peri-prosthesis under preload [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 516-520. |
| [9] | Sun Qi, Zhou Yanan, Dong Xin, Li Ning, Yan Jiazhen, Shi Haojiang, Xu Sheng, Zhang Biao. Metal-ceramic interface characteristics of Co-Cr alloy fabricated by selective laser melting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 521-525. |
| [10] | Liu Yang, Gong Yi, Fan Wei. Anti-hepatoma activity of targeted Pluronic F127/formononetin nanocomposite system in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 526-531. |
| [11] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| [12] | Zhang Guomei, Zhu Jun, Hu Yang, Jiao Hongwei. Stress of three-dimensional finite element models of E-MAX porcelain inlay [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 537-541. |
| [13] | Liu Jiangfeng. Nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite filling combined with locking plate in the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of femoral bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
| [14] | Li Quanxi, Shen Yu, Wan Wei, Sun Shanzhi. Changes of abdominal wall mechanics and pain after tension-free inguinal hernia repair with polypropylene mesh [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 548-552. |
| [15] | Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Zhao Qiao, Chen Shuo, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and properties of copper-loaded antibacterial functional film on titanium surface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 553-557. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||