Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (27): 4349-4355.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2801
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism and progress of exosomes in the treatment of nonunion
Lai Yu1, Han Jie2
- 1Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Joint and Sports Medicine, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2019-12-30Revised:2020-01-07Accepted:2020-02-26Online:2020-09-28Published:2020-09-09 -
Contact:Han Jie, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Joint and Sports Medicine, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Lai Yu, Master candidate, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760796, 81960803; the Basic Ability Improvement Project of Young Teachers from Guangxi Universities, No. 2019KY0352; the School-Level Scientific Research Project of Guangxi University of Chinese medicine in 2019, No. 2019QN027; the First-Class Discipline Project of Guangxi University of Chinese medicine, No. 2019XK029
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lai Yu, Han Jie. Mechanism and progress of exosomes in the treatment of nonunion[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4349-4355.
share this article
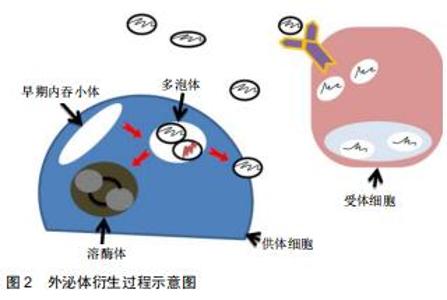
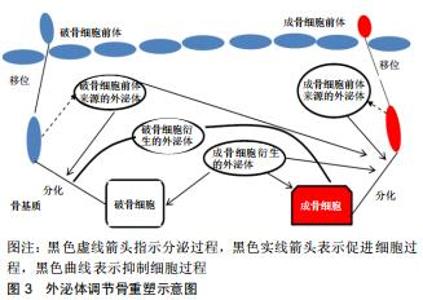
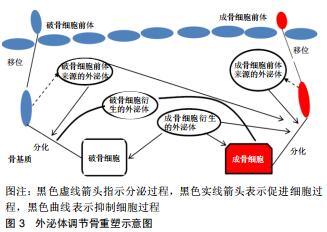
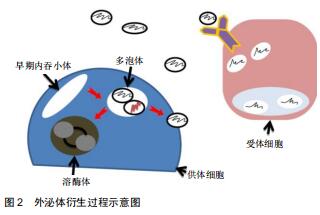
2.2.1 外泌体的来源 外泌体是细胞外囊泡小体,直径为40-100 nm[4],由不同类型的细胞释放,如巨噬细胞、肿瘤细胞、神经细胞、T细胞等,同时最近研究表明,骨相关细胞,包括破骨细胞、成骨细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞等细胞也分泌外体[5]。除此之外,在体液如尿液、血液、羊水、恶性腹水、支气管肺泡灌洗液、滑液和母乳中也发现了外泌体[6]。外泌体的形成和传递是由供体细胞的质膜内化产生的内吞小体(Endosomes)开始,然后蛋白质和RNA(包括lncRNA、circRNA、mRNA和miRNA)通过转运所需的内体分选复合物依赖性或内体分选复合物非依赖性机制选择性地被装入多泡体内。随后,多泡体或者融合到溶酶体上进行降解,或者通过与质膜融合释放到细胞外空间以产生外泌体。随后,外泌体通过特异性识别进入受体细胞,将转运物质释放,其具体传递过程见图2[7-8]。外泌体的成分中含有一些根据供体细胞类型而改变的生物活性分子,同时外泌体富含一些来自于分泌细胞的成分,如mRNAs、IncRNAs、circRNAs、脂质、蛋白质、DNA等,它们在信息传递过程中起到了重要作用。 "
|
[1] CALORI GM. Non-unions. Clinical Cases in Mineral & Bone Metabolism the Official Journal of the Italian Society of Osteoporosis Mineral Metabolism & Skeletal Diseases, 2017;14(2):186-188.
[2] 骆永锋,龚劲纯,吴俊,等.带锁髓内钉治疗四肢创伤骨折后骨不连的临床研究[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2017,38(2):193-195.
[3] WU KJ, LI SH, YEH KT, et al. The risk factors of nonunion after intramedullary nailing fixation of femur shaft fracture in middle age patients. Medicine(Baltimore). 2019;98:e16559.
[4] YANEZ-MO M, SIJANDER PR, ANDREU Z, et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015; 4(1):27066.
[5] 李晓晔,周潇逸,张子程,等.外泌体中miRNA对骨重建过程影响研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(18):1683-1686.
[6] 赵濛,刘志红,李金泉.外泌体组成特征及其作为细胞通讯和分子标记的生物学作用[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2016, 32(6):612-619.
[7] LU J,WANG QY,SHENG JG, et al. Exosomes in the repair of bone defects: next-generation therapeutic tools for the treatment of nonunion. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019: 1983131.
[8] 寿崟,马宇航,虎力,等.外泌体在糖尿病及其并发症的发生、发展和诊治中的作用[J].生理学报,2019,71(6):917-934.
[9] LU Z, ZUO B, JING R, et al. Dendritic cell-derived exosomes elicit tumor regression in autochthonous hepatocellular carcinoma mouse models. J Hepatol. 2017;67: 739-748.
[10] EL-SAGHIR J, NASSAR F, TAWIL N, et al. ATL-derived exosomes modulate mesenchymal stem cells: potential role in leukemia progression. Retrovirology. 2016; 13: 73.
[11] BRAICU C, TOMULEASA C, MONROIG P, et al. Exosomes as divine messengers: are they the Hermes of modern molecular oncology? Cell Death Differ. 2015;22: 34-45.
[12] POURAKBARI R, KHODADADI M, AGHEBATI-MALEKI A, et al. The potential of exosomes in the therapy of the cartilage and bone complications; emphasis on osteoarthritis. Life Sci. 2019;236: 116861.
[13] YAN Z, GUO Y, WANG Y, et al. MicroRNA profiles of BMSCs induced into osteoblasts with osteoinductive medium. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15: 2589-2596.
[14] HAMMOND SM. Dicing and slicing: the core machinery of the RNA interference pathway. FEBS Lett. 2005;579: 5822-5829.
[15] HUTVAGNER G. Small RNA asymmetry in RNAi: Function in RISC assembly and gene regulation. Febs Lett. 2005;579(26): 5850-5857.
[16] WEILNER S, SCHRAML E, REDL H, et al. Secretion of microvesicular miRNAs in cellular and organismal aging. Exp Gerontol. 2013;48(7):626-633.
[17] ZHANG Y, XIE RL, CROCE CM, et al. A program of microRNAs controls osteogenic lineage progression by targeting transcription factor Runx2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(24):9863-9868.
[18] LI Z, HASSAN MQ, VOLINIA S, et al. A microRNA signature for a BMP2-induced osteoblast lineage commitment program. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(37): 13906-13911.
[19] LIU Y, MA Y, ZHANG J, et al. Exosomes: a novel therapeutic agent for cartilage and bone tissue regeneration. Dose Response. 2019;17: 1559325819892702.
[20] XU JF, YANG GH, PAN XH, et al. Altered microrna expression profile in exosomes during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(12):e114627.
[21] GE M, KE R, CAI T, et al. Identification and proteomic analysis of osteoblast-derived exosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;467(1):27-32.
[22] SHRESTHA N, BAHNAN W, WILEY DJ, et al. Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 (eIF2) signaling regulates proinflammatory cytokine expression and bacterial invasion. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287(34):28738-28744.
[23] AKTAS BH, BORDELOIS P, PEKER S, et al. Depletion of eIF2·GTP·Met-tRNAi translation initiation complex up-regulates BRCA1 expression in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 2015;6:6902-6914.
[24] JOHNSON ME, DELIARD S, ZHU F, et al. A ChIP-seq-defined genome-wide map of MEF2C binding reveals inflammatory pathways associated with its role in bone density determination. Calcif Tissue Int. 2014;94(4):396-402.
[25] TANAKA KI, KAJI H, YAMAGUCHI T, et al. Involvement of the Osteoinductive Factors, Tmem119 and BMP-2, and the ER Stress Response PERK–eIF2α–ATF4 Pathway in the Commitment of Myoblastic into Osteoblastic Cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 2014;94(4):454-464.
[26] YANG X, MATSUDA K, BIALEK P, et al. ATF4 is a substrate of RSK2 and an essential regulator of osteoblast biology; implication for Coffin-Lowry Syndrome. Cell. 2015;117(3): 387-398.
[27] NOJIMA H, TOKUNAGA C, EGUCHI S, et al. The Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Partner, Raptor, Binds the mTOR Substrates p70 S6 Kinase and 4E-BP1 through Their TOR Signaling (TOS) Motif. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(18): 15461-15464.
[28] JACINTO E, LOEWITH R, SCHMIDT A, et al. Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6(11):1122-1128.
[29] LI X, CHANG B, WANG B, et al. Rapamycin promotes osteogenesis under inflammatory conditions. Mol Med Rep. 2017; 16: 8923-8929.
[30] SUN H, KIM JK, MORTENSEN RM, et al. Osteoblast-targeted Suppression of PPARγ Increases Osteogenesis through Activation of mTOR Signaling. Stem Cells. 2013;31: 2183-2192.
[31] LONG H, ZHU Y, LIN Z, et al. miR-381 modulates human bone mesenchymal stromal cells (BMSCs) osteogenesis via suppressing Wnt signaling pathway during atrophic nonunion development. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10: 470.
[32] XIE Y, CHEN Y, ZHANG L, et al. The roles of bone-derived exosomes and exosomal microRNAs in regulating bone remodelling. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21: 1033-1041.
[33] MOHAMMED MK,SHAO C,WANG J,et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling plays an ever-expanding role in stem cell self-renewal, tumorigenesis and cancer chemoresistance. Genes Dis.2016;3(1):11-40.
[34] CUI Y, LUAN J, LI H, et al. Exosomes derived from mineralizing osteoblasts promote ST2 cell osteogenic differentiation by alteration of microRNA expression. FEBS Lett. 2016; 590(1):185-192.
[35] HASSAN MQ, MAEDA Y, TAIPALEENMAKI H, et al. miR-218 directs a Wnt signaling circuit to promote differentiation of osteoblasts and osteomimicry of metastatic cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(50):42084-42092.
[36] NEGISHI-KOGA T, SHINOHARA M, KOMATSU N, et al. Suppression of bone formation by osteoclastic expression of semaphorin 4D. Nature Med. 2011;17(11):1473-1480.
[37] SUN W, ZHAO C, LI Y, et al. Osteoclast-derived microRNA-containing exosomes selectively inhibit osteoblast activity. Cell Discov. 2016; 2:16015. [38] LI D, LIU J, GUO B, et al. Osteoclast-derived exosomal miR-214-3p inhibits osteoblastic bone formation. Nature Commun. 2016;7:10872.
[39] DI LEVA G, CHEUNG DG, BUZZETTI M. miRNAs in bone metastasis. Exp Rev Endocrinol Metabol. 2017: 17446651.2017.1383893.
[40] HUYNH N, VONMOSS L, SMITH D, et al. Characterization of regulatory extracellular vesicles from osteoclasts. J Dent Res. 2016:0022034516633189.
[41] MARTINS M, RIBEIRO D, MARTINS A, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from osteogenically induced human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells can modulate lineage commitment. Stem Cell Rep. 2016; 6(3):284-291.
[42] QIN Y, WANG L, GAO Z, et al. Bone marrow stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles regulate osteoblast activity and differentiation in vitro and promote bone regeneration in vivo. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:21961.
[43] 陈燕,姜胜军,彭友俭.骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体对成骨细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2019,35(4):401-404.
[44] 刘一飞,王宇辰,朱昱,等.尿源性干细胞的外泌体修复骨不连的作用研究[J].上海医学,2019,42(7):411-417.
[45] LIANG X, ZHANG L, WANG S, et al. Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-125a. J Cell Sci. 2016; 129(11):2182-2189.
[46] KUCHARZEWSKA P, CHRISTIANSON HC, WELCH JE, et al. Exosomes reflect the hypoxic status of glioma cells and mediate hypoxia-dependent activation of vascular cells during tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(18): 7312-7317.
[47] LI XC, CHEN CY, WEI LM, et al. Exosomes derived from endothelial progenitor cells attenuate vascular repair and accelerate reendothelialization by enhancing endothelial function. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(2):253-262.
[48] ABDELALI A, PIERRE-HENRI D, TAREK B, et al. Microparticles from patients with metabolic syndrome induce vascular hypo-reactivity via fas/fas-ligand pathway in mice. PLoS ONE. 2011; 6(11):e27809.
[49] SU T, XIAO Y, XIAO Y, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal mir-29b-3p regulates aging-associated insulin resistance. ACS Nano. 2019;13: 2450-2462. [50] FURUTA T, MIYAKI S, ISHITOBI H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote fracture healing in a mouse model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(12):1620-1630. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [3] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [4] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [5] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [6] | Wang Qiufei, Gu Ye, Peng Yuqin, Xue Feng, Ju Rong, Zhu Feng, Wang Yijun, Geng Dechun, Xu Yaozeng. Effect of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway on osteoblasts under the action of wear particles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3894-3901. |
| [7] | Gao Kun, Chen Dayu, Zhang Yong, Liu Weidong, Sun Shufen, Lai Wenqiang, Ma Dujun, Wu Yihong, Lin Zhanpeng, Jiang Yinglu, Yu Weiji. Achyranthes bidentata alcohol extract inhibits extracellular matrix degradation of the cartilage by regulating synovial fibroblast exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3636-3640. |
| [8] | Li Ping, Lin Yu, Chen Xiang, Liu Zhentao, Xiao Lili, Lin Xueyi, Hua Peng . Characteristics of bone remodeling in female ovariectomized rat models of osteoporosis undergoing Erzhi Pill extract intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 191-195. |
| [9] | Wang Kang, Zhi Xiaodong, Wang Wei. Effect of stem cell derived exosomes on repairing peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3083-3089. |
| [10] | Zhao Shuangdan, Zheng Jiahua, Qi Wenbo, Huang Xianghua. Role and mechanism of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in reproductive system diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3097-3102. |
| [11] | Zhu Shiqiang, Xu Jianfeng, Hei Xiaoyan, Chen Yundong, Tian Xinbao, Zhang Jinchen, Lin Ruizhu. Effect of internal heat-type acupuncture needle therapy on the expression of type I collagen, matrix metalloproteinase-3 and osteopontin in the subchondral bone of rabbit knee osteoarthritis model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2636-2642. |
| [12] | Yuan Changshen, Rong Weiming, Lu Zhixian, Duan Kan, Guo Jinrong, Mei Qijie. Construction of osteosarcoma miRNA-mRNA regulatory network based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2740-2746. |
| [13] | Liu Feng, Zhang Yu, Wang Yanli, Luo Wei, Han Chaoshan, Li Yangxin. Application of temperature-sensitive chitosan hydrogel encapsulated exosomes in ischemic diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2479-2487. |
| [14] | Cai Yuan, Deng Chengliang. Therapeutic application of adipose stem cell-free liquid extracts: skin aging, wound healing, scar recovery and nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2097-2102. |
| [15] | Liu Tao, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin . Relationship between extracellular vesicles and radiation-induced tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2121-2126. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||