Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (17): 2740-2746.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3196
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction of osteosarcoma miRNA-mRNA regulatory network based on bioinformatics
Yuan Changshen1, Rong Weiming2, Lu Zhixian2, Duan Kan1, Guo Jinrong1, Mei Qijie1
- 1The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2020-04-08Revised:2020-04-16Accepted:2020-05-30Online:2021-06-18Published:2021-01-08 -
Contact:Mei Qijie, Master, Associate chief physician, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yuan Changshen, Master, Associate chief physician, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Traditional Chinese Medicine and Ethnic Medicine Self-funded Research Project of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. GZZC15-12 (to MQJ); Natural Science Research Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2015MS007 (to GJR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yuan Changshen, Rong Weiming, Lu Zhixian, Duan Kan, Guo Jinrong, Mei Qijie. Construction of osteosarcoma miRNA-mRNA regulatory network based on bioinformatics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2740-2746.
share this article
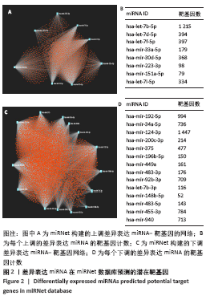
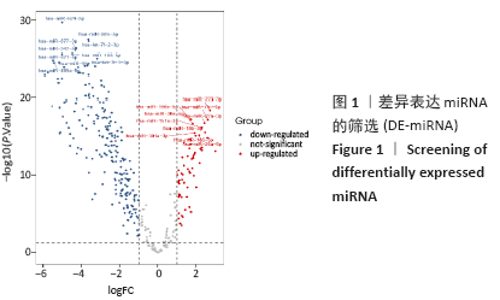
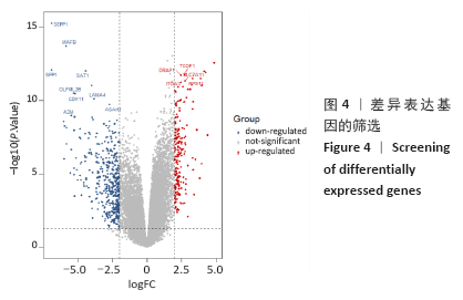
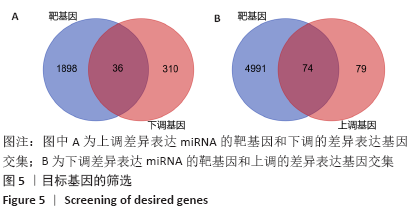
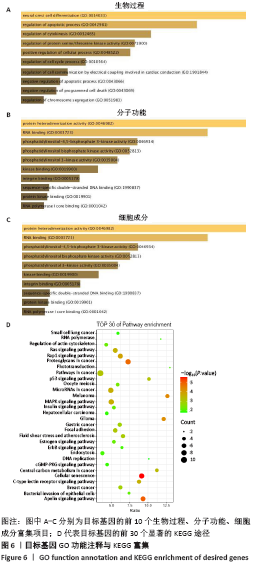
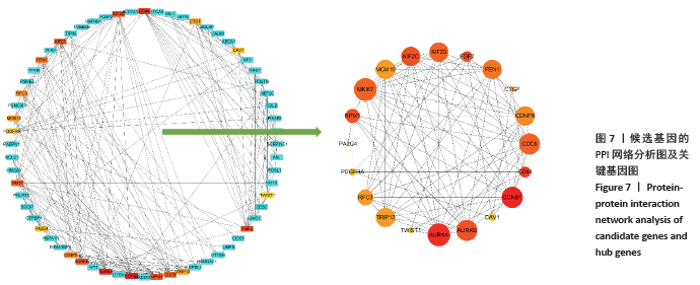
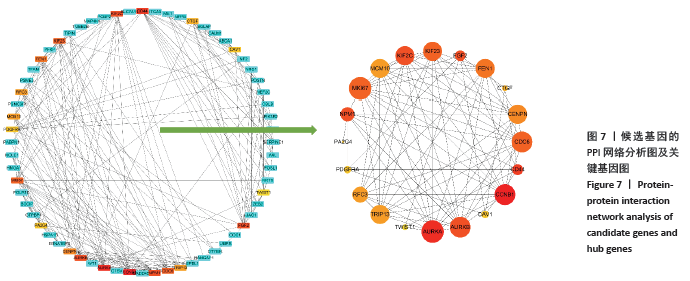
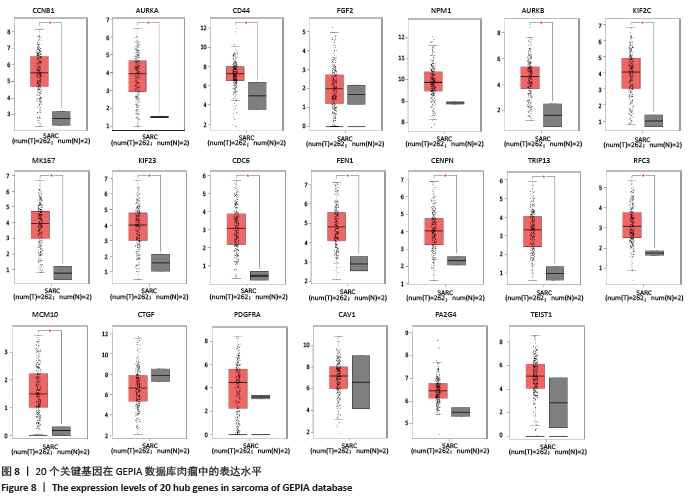
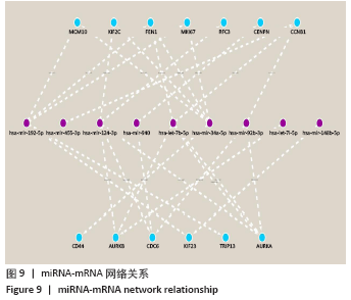
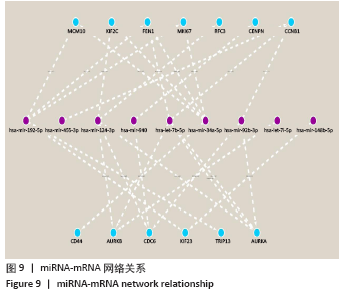
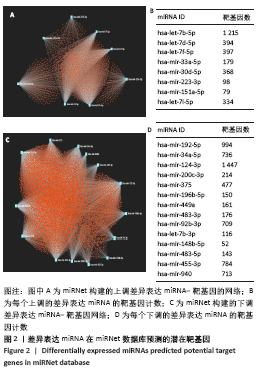
2.3 差异表达miRNA下游靶基因的预测 通过miRNet数据库分析265个差异表达miRNA,最终筛选出在骨中有靶基因的22个差异表达miRNA,包括8个上调的差异表达miRNA,分别为hsa-let-7b-5p、hsa-let-7d-5p、hsa-let-7f-5p、hsa-mir-33a-5p、 hsa-mir-30d-5p、hsa-mir-223-3p、hsa-let-7i-5p、hsa-mir- 151a-5p;14个下调差异表达miRNA,分别为hsa-mir-192-5p、 hsa-mir-34a-5p、hsa-mir-124-3p、hsa-mir-200c-3p、hsa-mir-375、 hsa-mir-196b-5p、hsa-mir-449a、hsa-mir-483-3p、hsa-mir-92b-3p、hsa-let-7b-3p、hsa-mir-148b-5p、hsa-mir-483-5p、hsa-mir-455-3p、hsa-mir-940。在数据库中分别有1 934和5 065个独立靶基因。为了更好展示差异表达miRNA与靶基因的关系,分别建立了上调差异表达miRNA-靶基因网络和下调差异表达miRNA-靶基因网络,见图2A、C;同时,也列出每个差异表达miRNA靶基因计数,见图2B、D。"
| [1] PERUT F, RONCUZZI L, BALDINI N. The Emerging Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in Osteosarcoma. Front Oncol. 2019;9:1342. [2] ABU-HALIMA M, BACKES C, LEIDINGER P, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles in human testicular tissues of infertile men with different histopathologic patterns. Fertil Steril. 2014;101(1):78-86.e2. [3] HUERTA-ZAVALA ML, LOPEZ-CASTILLEJOS ES, REQUENEZ-CONTRERAS JL, et al. A single miRNA and miRNA sponge expression system for efficient modulation of miR-223 availability in mammalian cells. J Gene Med. 2019; 21(8):e3100. [4] ANDERSEN GB, KNUDSEN A, HAGER H, et al. miRNA profiling identifies deregulated miRNAs associated with osteosarcoma development and time to metastasis in two large cohorts. Mol Oncol. 2018;12(1):114-131. [5] GONG N, GONG M. MiRNA-221 from tissue may predict the prognosis of patients with osteosarcoma. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(29):e11100. [6] 张琨. miR-125b, miR-126, miR-145在骨肉瘤病人血清中的表达[D].长沙:中南大学,2014. [7] 陈康.骨肉瘤病人血清中miRNA的表达谱研究[D]. 南京:南京大学, 2012. [8] 刘书中,劳立峰,王以朋.外周血miRNAs检测在骨肉瘤中的意义[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2016,29(5):552-556. [9] PLOTNIKOVA OM, SKOBLOV MY. Efficiency of the miRNA- mRNA Interaction Prediction Programs. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2018;52(3):543-554. [10] BHOWMICK SS, BHATTACHARJEE D, RATO L. Integrated analysis of the miRNA-mRNA next-generation sequencing data for finding their associations in different cancer types. Comput Biol Chem. 2020;84:107152. [11] SHEKHAR R, PRIYANKA P, KUMAR P, et al. The microRNAs miR-449a and miR-424 suppress osteosarcoma by targeting cyclin A2 expression. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(12):4381-4400. [12] LIU G, HUANG K, JIE Z, et al. CircFAT1 sponges miR-375 to promote the expression of Yes-associated protein 1 in osteosarcoma cells. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):170. [13] WANG Y, ZHANG S, XU Y, et al. Upregulation of miR-192 inhibits cell growth and invasion and induces cell apoptosis by targeting TCF7 in human osteosarcoma. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(11):15211-15220. [14] 隆姝孜,周寒静,刘静姝,等. mir-151a-5p对肺癌A549细胞生物学功能和化疗敏感性的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2019,41(8):770-777. [15] LONG HD, MA YS, YANG HQ, et al. Reduced hsa-miR-124-3p levels are associated with the poor survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 2018;45(6):2615-2623. [16] LI S, WU X, PEI Y, et al. PTHR1 May Be Involved in Progression of Osteosarcoma by Regulating miR-124-3p-AR-Tgfb1i1, miR-27a-3p-PPARG-Abca1, and miR-103/590-3p-AXIN2 Axes. DNA Cell Biol. 2019;38(11):1323-1337. [17] JI Q, XU X, SONG Q, et al. miR-223-3p Inhibits Human Osteosarcoma Metastasis and Progression by Directly Targeting CDH6. Mol Ther. 2018; 26(5):1299-1312. [18] MULLANY LE, HERRICK JS, WOLFF RK, et al. MicroRNA-transcription factor interactions and their combined effect on target gene expression in colon cancer cases. Version 2. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2018;57(4):192-202. [19] DHARAP A, POKRZYWA C, MURALI S, et al. Mutual induction of transcription factor PPARγ and microRNAs miR-145 and miR-329. J Neurochem. 2015; 135(1):139-146. [20] YANG W, LU Z, ZHI Z, et al. Increased miRNA-518b inhibits trophoblast migration and angiogenesis by targeting EGR1 in early embryonic arrest. Biol Reprod. 2019;101(4):664-674. [21] 秦丽,张惠华,郭淑军,等.外源性EGR1瞬时表达对骨肉瘤细胞细胞周期和凋亡的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2011,27(2):293-299. [22] NG MC, LAM VK, TAM CH, et al. Association of the POU class 2 homeobox 1 gene (POU2F1) with susceptibility to Type 2 diabetes in Chinese populations. Diabet Med. 2010;27(12):1443-1449. [23] STEPCHENKO AG, GEORGIEVA SG, PANKRATOVA EV. Multiple Interactions of the Oct-1 (POU2F1) Transcription Factor with PORE and MORE Sites. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2019;53(3):430-435. [24] VÁZQUEZ-ARREGUÍN K, TANTIN D. The Oct1 transcription factor and epithelial malignancies: Old protein learns new tricks. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1859(6):792-804. [25] XIE CH, CAO YM, HUANG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 contributes to tumorigenesis of human osteosarcoma by sponging miR-9-5p and regulating POU2F1 expression. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(11):15031-15041. [26] PENG F, ZHOU Y, WANG J, et al. The transcription factor Sp1 modulates RNA polymerase III gene transcription by controlling BRF1 and GTF3C2 expression in human cells. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(14):4617-4630. [27] MENG Y, HAO D, HUANG Y, et al. Positive feedback loop SP1/MIR17HG/miR-130a-3p promotes osteosarcoma proliferation and cisplatin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;521(3):739-745. [28] HOU Z, GUO K, SUN X, et al. TRIB2 functions as novel oncogene in colorectal cancer by blocking cellular senescence through AP4/p21 signaling. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):172. [29] HE L, XU J, CHEN L, et al. Apelin/APJ signaling in hypoxia-related diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;451(Pt B):191-198. [30] CHENG B, CHEN J, BAI B, et al. Neuroprotection of apelin and its signaling pathway. Peptides. 2012;37(1):171-173. [31] 郝延璋. Apelin对胃癌生物学功能的影响及其分子机制的研究[D].济南:山东大学,2017. [32] CHEN T, LIU N, XU GM, et al. Apelin13/APJ promotes proliferation of colon carcinoma by activating Notch3 signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8(60): 101697-101706. [33] THEOCHARIS AD, KARAMANOS NK. Proteoglycans remodeling in cancer: Underlying molecular mechanisms. Matrix Biol. 2019;75-76:220-259. [34] YE C, WANG J, WU P, et al. Prognostic role of cyclin B1 in solid tumors: a meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(2):2224-2232. [35] ZHANG J, ZHU X, LI H, et al. Piperine inhibits proliferation of human osteosarcoma cells via G2/M phase arrest and metastasis by suppressing MMP-2/-9 expression. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015;24(1):50-58. [36] VADER G, LENS SM. The Aurora kinase family in cell division and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1786(1):60-72. [37] D’ASSORO AB, HADDAD T, GALANIS E. Aurora-A Kinase as a Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Front Oncol. 2016;5:295. [38] JIANG Z, JIANG J, YANG H, et al. Silencing of Aurora kinase A by RNA interference inhibits tumor growth in human osteosarcoma cells by inducing apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest. Oncol Rep. 2014;31(3):1249-1254. [39] CICHY J, PURÉ E. The liberation of CD44. J Cell Biol. 2003;161(5):839-843. [40] PONTA H, SHERMAN L, HERRLICH PA. CD44: from adhesion molecules to signalling regulators. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4(1):33-45. [41] SKANDALIS SS, GIALELI C, THEOCHARIS AD, et al. Advances and advantages of nanomedicine in the pharmacological targeting of hyaluronan-CD44 interactions and signaling in cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 2014;123:277-317. [42] XIAO Z, WAN J, NUR AA, et al. Targeting CD44 by CRISPR-Cas9 in Multi-Drug Resistant Osteosarcoma Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(4):1879-1893. |
| [1] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [3] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [4] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [5] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [6] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [7] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [8] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [9] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [10] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [11] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [12] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [13] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [14] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [15] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||