Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (27): 4013-4019.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.27.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of mild hypothermia on nerve regeneration microenvironment of infarcted area in rat models of cerebral infarction
Zheng Rui-juan, Gao Yu-hong
- Tangshan Union Medical College Hospital, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
-
Revised:2016-05-10Online:2016-06-30Published:2016-06-30 -
About author:Zheng Rui-juan, Attending physician, Tangshan Union Medical College Hospital, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zheng Rui-juan, Gao Yu-hong. Effect of mild hypothermia on nerve regeneration microenvironment of infarcted area in rat models of cerebral infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(27): 4013-4019.
share this article
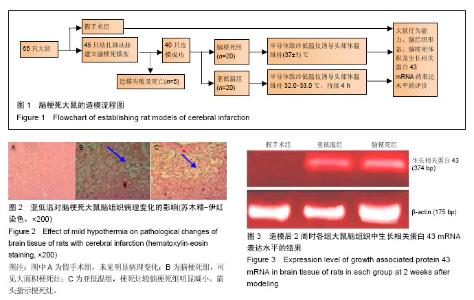
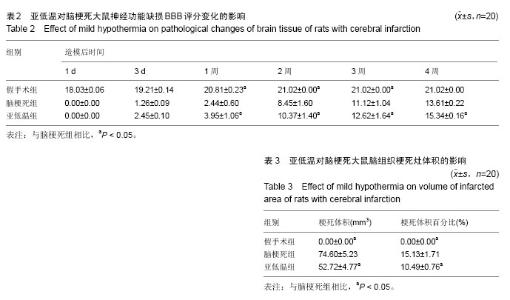
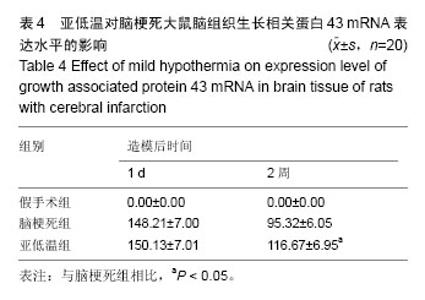
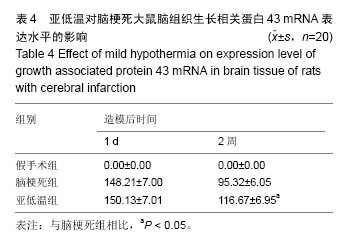
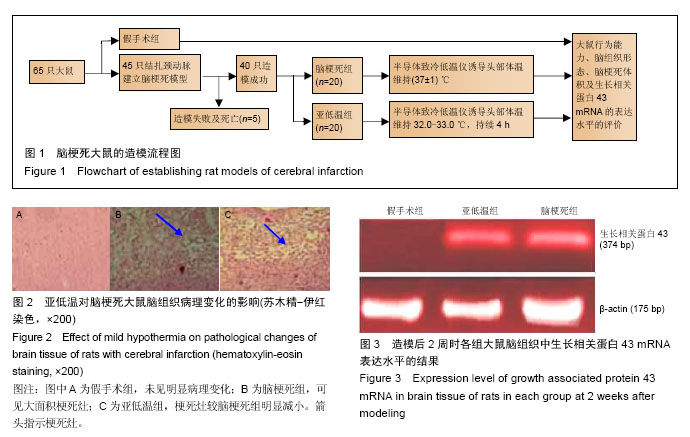
2.1 造模成功动物数量及过程 从65只大鼠中随机取20只作为假手术组,其余45只结扎颈动脉建立脑梗死模型,排除造模失败及死亡的5只,余下40只大鼠随机等分为脑梗死组及亚低温组。最终共60只大鼠进入结果分析。造模流程图见图1。 2.2 模型创新性 结扎颈内动脉制备的局灶性脑缺血大鼠模型可以选择性地阻断进入大脑中动脉的血流,阻断颈内动脉的下丘脑分支,仅少量出现下丘脑梗死,更 符合临床情况。 2.3 模型更接近临床实践 实验以结扎颈动脉方法建立脑梗死模型,经TTC染色确认脑梗死灶明显。 2.4 脑组织病理变化 苏木精-伊红染色显示,假手术组大鼠脑组织未见明显病理改变;脑梗死组大鼠脑组织可见大面积梗死灶,神经元出现典型的缺血性改变,在梗死区周围及梗死区可见散在胶质细胞增生,病变部位与周围组织界限较清楚,其中心区神经元数量明显减少;亚低温组大鼠脑组织较脑梗死组梗死灶明显减小,梗死灶内残存的神经元较多,可见轻度缺血性改变(图2)。 2.5 运动功能 造模前各组大鼠BBB评分差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。与假手术组相比,脑梗死组大鼠BBB评分降低(P < 0.05)。治疗2周后,亚低温组大鼠BBB评分较脑梗死组显著增加(P < 0.05;表2)。 2.6 脑梗死体积 TTC染色发现,假手术组大鼠脑组织未见梗死灶,脑梗死组大鼠梗死灶主要位于皮质和纹状体,而亚低温组大鼠梗死灶仅限于纹状体,且亚低温组大鼠梗死灶体积小于脑梗死组(P < 0.05;表3)。 2.7 脑组织中生长相关蛋白43 mRNA表达 反转录PCR检测结果显示,造模后1 d,亚低温组大鼠脑组织生长相关蛋白43 mRNA表达水平与脑梗死组接近(P > 0.05),2周时亚低温组大鼠脑组织生长相关蛋白43 mRNA表达较脑梗死组显著升高(P < 0.05;图3,表4)。"
| [1] 周国庆,金怡,张鹏.沉默RhoA基因对骨髓间充质干细胞静脉移植治疗脑梗死大鼠的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(45):8416-8420. [2] Pereira BM, Weinstein PR, Zea-Longa E, et al. Effect of blood flow rate and donor vessel diameter on the patency of carotid venous bypass grafts in dogs. Surg Neurol. 1989;31(3):195-199. [3] Leonardo CC, Hall AA, Collier LA, et al. Human umbilical cord blood cell therapy blocks the morphological change and recruitment of CD11b-expressing, isolectin-binding proinflammatory cells after middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88(6):1213-1222. [4] Phuc PV, Nhung TH, Loan DT, et al. Differentiating of banked human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-secreting cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011; 47(1):54-63. [5] 陈雪扉,莫万斌.注射用七叶皂苷钠联合脐带间充质干细胞移植改善脑梗死大鼠神经功能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,27(15):5080-5084. [6] Mutlu O, Ulak G, Celikyurt IK, et al. Effects of olanzapine, sertindole and clozapine on learning and memory in the Morris water maze test in naive and MK-801-treated mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2011;98(3):398-404. [7] 曹绪政,苏志强,徐建民,等.局部亚低温对大鼠脑梗死体积和神经功能及血清神经元特异性烯醇化酶的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2003,25(5)260-262. [8] 包龙.亚低温脑保护的基础研究进展[J].中国急救医学, 2013,33(8):762-766. [9] Kim JY, Kim N, Yenari MA, et al. Mild hypothermia suppresses calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) induction following forebrain ischemia while increasing GABA-B receptor 1 (GABA-B-R1) expression. Transl Stroke Res. 2011;2(2):195-201. [10] Tissier R, Cohen MV, Downey JM. Does mild hypothermia protect against reperfusion injury? The debate continues. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011;106(5): 691-695. [11] Yokobori S, Gajavelli S, Mondello S, et al. Neuroprotective effect of preoperatively induced mild hypothermia as determined by biomarkers and histopathological estimation in a rat subdural hematoma decompression model. J Neurosurg. 2013;118(2): 370-380. [12] 宋祖军,马俊清,余厚友,等.亚低温对急性脊髓损伤后炎症性细胞因子表达的影响[J].中国急救医学,2009,29(2): 137-139. [13] 陶晓峰,刘畅,华正宇.亚低温对大鼠局灶性脑缺血再灌注后HIF-1a及凋亡相关蛋白变化的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志, 2010,27(10):3858-3860. [14] 塔长峰,吴定奇,马腾飞,等.亚低温治疗特重型颅脑损伤疗效观察[J].海南医学院学报,2011,17(3):369-371. [15] Hua Y, Hisano K, Morimoto Y. Effect of mild and moderate hypothermia on hypoxic injury in nearly pure neuronal culture. J Anesth. 2010;24(5):726-732. [16] 冯金周,钱骏,刘发健,等.动态亚低温治疗重型颅脑损伤[J].中华神经医学杂志,2010,9(2):187-189. [17] Webster CM, Kelly S, Koike MA, et al. Inflammation and NFkappaB activation is decreased by hypothermia following global cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol Dis. 2009; 33(2):301-312. [18] 李晓宾,鹿寒冰,董瑞国,等.大鼠脑梗死后脑水肿MRI动态变化及亚低温的干预效应[J].中华神经医学杂志, 2012, 11(7): 676-680. [19] 管玉华,赵东刚.亚低温抗脑缺血后神经细胞凋亡的信号传导途径[J].广东医学,2010,31(3):1759-1761. [20] Horn M, Schlote W, Henrich HA. Global cerebral ischemia and subsequent selective hypothermia. A neuropathological and morphometrical study on ischemic neuronal damage in cat. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;81(4):443-449. [21] 任文博,刘振林,赵玉军.亚低温脑保护在重型创伤性颅脑损伤治疗中的应用[J].现代诊断与治疗,2012,23(12): 2102-2103. [22] 薄丰山,王迪芬,刘文悦,等.亚低温预处理对谷氨酸诱导原代大鼠皮质神经细胞损伤的保护作用[J].中华危重病急救医学, 2014,26(4): 264-268. [23] 杨家斐,余新光,周定标,等.亚低温预处理对大鼠局灶性脑缺血的保护作用[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2003,20(2):185. [24] 只达石,张赛,肖绪林,等.亚低温对急性重型颅脑损伤病人治疗机理及临床疗效研究[J].中华神经外科杂志, 2001, 17(5): 316-320. [25] 姜美子,吴光,朱惠京,等.亚低温和甘露醇对大鼠局灶性脑梗死体积影响的比较[J].临床神经病学杂志, 2002,15(6): 350-351. [26] 张允岭,刘雪梅,柳洪胜,等.心脑舒通胶囊对大鼠缺血再灌注脑损伤后细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国中药杂志, 2008, 33(10): 1188-1191. [27] 袁转弟,戴志辉,张扬文,等.选择性头部亚低温治疗新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病的临床疗效[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2009, 30(38):143-146. [28] Miyake K, Yamamoto W, Tadokoro M, et al. Alterations in hippocampal GAP-43, BDNF, and L1 following sustained cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2002;935(1-2):24-31. [29] Benowitz LI, Routtenberg A. GAP-43: an intrinsic determinant of neuronal development and plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 1997;20(2):84-91. [30] 李金艳,张哲成.骨髓间充质干细胞联合丹红注射液干预脑梗死组织GAP-43、Bcl-2的表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(32): 5871-5876. [31] 李阔,高俊淑,李娜,等.不同环境对局灶性脑梗死大鼠梗死灶周围皮质GFAP、GAP-43表达的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2007,22(7):581-583. [32] 刘广义.大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后GAP-43及IGF-1在神经系统中的表达[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2008,7(3): 223-226. [33] Denny JB. Molecular mechanisms, biological actions, and neuropharmacology of the growth-associated protein GAP-43. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2006;4(4): 293-304. [34] Krueger DD, Nairn AC. Expression of PKC substrate proteins, GAP-43 and neurogranin, is downregulated by cAMP signaling and alterations in synaptic activity. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;26(11):3043-3053. [35] Casoli T, Di Stefano G, Gracciotti N, et al. Cellular distribution of GAP-43 mRNA in hippocampus and cerebellum of adult rat brain by in situ RT-PCR. J Histochem Cytochem. 2001;49(9):1195-1196. [36] 马冉冉,李光勤,王进平,等.不同穴位电针对局灶性脑梗死大鼠梗死灶周围皮质GAP-43表达的影响[J].重庆医科大学学报.2011,36(1):38-41. [37] 谢利,刘福友.参麦注射液对大鼠脑梗死后GAP-43和SYP蛋白表达的影响[J].陕西中医,2011,32(9):1255-1257. [38] Miyake K, Yamamoto W, Tadokoro M, et al. Alterations in hippocampal GAP-43, BDNF, and L1 following sustained cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2002;935(1-2):24-31. [39] Kallmünzer B, Beck A, Schwab S, et al. Local head and neck cooling leads to hypothermia in healthy volunteers. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011;32(3):207-210. [40] 周坤,黄智武.亚低温治疗大面积脑梗死28例的疗效观察[J].广西医学.2010,32(11):1377-1379. [41] Schwartz AE, Finck AD, Stone JG, et al. Delayed selective cerebral hypothermia decreases infarct volume after reperfused stroke in baboons. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2011;23(2):124-130. [42] 梁成,晏红,施鑫鹤,等.缺血再灌注期实施亚低温与再建血运治疗时间窗的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2011,33 (18): 1956-1959. [43] Lubsczyk B, Kollars M, Hron G, et al. Low dose acetylsalicylic acid and shedding of microparticles in vivo in humans. Eur J Clin Invest. 2010;40(6): 477-482. [44] Hemmen TM, Raman R, Guluma KZ, et al. Intravenous thrombolysis plus hypothermia for acute treatment of ischemic stroke (ICTuS-L): final results. Stroke. 2010;41(10):2265-2270. [45] Lees KR, Bluhmki E, von Kummer R, et al. Time to treatment with intravenous alteplase and outcome in stroke: an updated pooled analysis of ECASS, ATLANTIS, NINDS, and EPITHET trials. Lancet. 2010; 375(9727):1695-1703. [46] Kollmar R, Schwab S. Hypothermia in focal ischemia: implications of experiments and experience. J Neurotrauma. 2009;26(3):377-386. [47] 伍丽红,王德生,周勇,等.帖敷式局部亚低温治疗急性脑卒中临床观察[J].中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志, 2010, 17(2):117-119. [48] Ceulemans AG, Zgavc T, Kooijman R, et al. The dual role of the neuroinflammatory response after ischemic stroke: modulatory effects of hypothermia. J Neuroinflammation. 2010;7:74. [49] Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A, Hofer M. Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: therapeutic approaches. J Transl Med. 2009;7:97. [50] Shah IM, Macrae IM, Di Napoli M. Neuroinflammation and neuroprotective strategies in acute ischaemic stroke -from bench to bedside. Curr Mol Med. 2009;9(3): 336-354. [51] Candelario-Jalil E. Injury and repair mechanisms in ischemic stroke: considerations for the development of novel neurotherapeutics. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009; 10(7): 644-654. [52] Kleinig TJ, Vink R. Suppression of inflammation in ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: therapeutic options. Curr Opin Neurol. 2009;22(3):294-301. [53] D'Ambrosio AL, Pinsky DJ, Connolly ES. The role of the complement cascade in ischemia/reperfusion injury: implications for neuroprotection. Mol Med. 2001; 7(6): 367-382. [54] Stoll G, Jander S, Schroeter M. Detrimental and beneficial effects of injury-induced inflammation and cytokine expression in the nervous system. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;513:87-113. [55] Sahuquillo J, Vilalta A. Cooling the injured brain: how does moderate hypothermia influence the pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury. Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(22): 2310-2322. [56] Meloni BP, Campbell K, Zhu H, et al. In search of clinical neuroprotection after brain ischemia: the case for mild hypothermia (35 degrees C) and magnesium. Stroke. 2009; 40(6):2236-2240. [57] 胡以慧,朱双成,岑跃南.脑局部亚低温治疗急性脑梗塞的临床研究[J].国际医药卫生导报,2013,19(16):2449-2451. [58] 黄盘冰,王建辉,瞿永梅,等.亚低温联合依达拉奉治疗对急性脑梗死患者近期预后的影响[J].中国医师进修杂志, 2012,35(27): 1673-1674. [59] 王学义,马承君,王莹莹,等.亚低温治疗方案的临床应用[J].中华急诊医学,2012,21(7):741-745. 刁新峰.亚低温治疗重型颅脑损伤的疗效观察[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2010, 13(20):39-40. [60] 刘宏海.杨春光.闫方.亚低温治疗重型颅脑损伤22例应用研究[J].中国当代医药,2010,17(33):170-175. [61] 张劲松,孙昊.对我国亚低温治疗现状的认识[J].实用医院临床杂志,2012,9(1):31-33. |
| [1] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [2] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [3] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [4] | Xu Yinqin, Shi Hongmei, Wang Guangyi. Effects of Tongbi prescription hot compress combined with acupuncture on mRNA expressions of apoptosis-related genes,Caspase-3 and Bcl-2, in degenerative intervertebral discs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 713-718. |
| [5] | Zhang Wenwen, Jin Songfeng, Zhao Guoliang, Gong Lihong. Mechanism by which Wenban Decoction reduces homocysteine-induced apoptosis of myocardial microvascular endothelial cells in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 723-728. |
| [6] | Liu Qing, Wan Bijiang. Effect of acupotomy therapy on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 729-734. |
| [7] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [8] | Su Liping, Lu Ziyang, Liu Li, Zhang Wei, Su Tianyuan, Hu Xiayun, Pu Hongwei, Han Dengfeng. C-jun, Cytc and Caspase-9 in the apoptosis of cerebellar granule neurons induced by diacetylmorphine in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3943-3948. |
| [9] | Zuo Zhenkui, Han Jiarui, Ji Shuling, He Lulu. Pretreatment with ginkgo biloba extract 50 alleviates radiation-induced acute intestinal injury in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3666-3671. |
| [10] | Zhang Liang, Ma Xiaoyan, Wang Jiahong. Regulatory mechanism of Shenshuai Yin on cell apoptosis in the kidney of chronic renal failure rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3672-3677. |
| [11] | Xie Yang, Lü Zhiyu, Zhang Shujiang, Long Ting, Li Zuoxiao. Effects of recombinant adeno-associated virus mediated nerve growth factor gene transfection on oligodendrocyte apoptosis and myelination in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3678-3683. |
| [12] | Xu Bin, Yang Xiushu, Liu Xuan, Wang Zhenxing. Changes of intestinal epithelial cells and their apoptotic factors Caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 under urinary environment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3173-3177. |
| [13] | Song Shilei, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi. Potential molecular mechanism of Wuling powder in treating osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3185-3193. |
| [14] | Liu Kun, Xie Lin, Cao Jun, Ding Ning, Xu Lingbo, Ma Shengchao, Li Guizhong , Jiang Yideng, Lu Guanjun. Increased FoxO1 DNA methylation level in homocysteine-induced podocyte apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 269-273. |
| [15] | Yan Xiurui, Tao Jin, Liang Xueyun. Mechanism by which exosomes from human fetal placental mesenchymal stem cells protect lung epithelial cells against oxidative stress injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2994-2999. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||