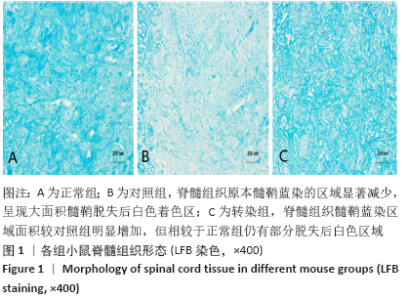
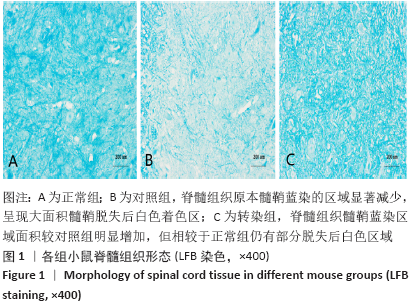
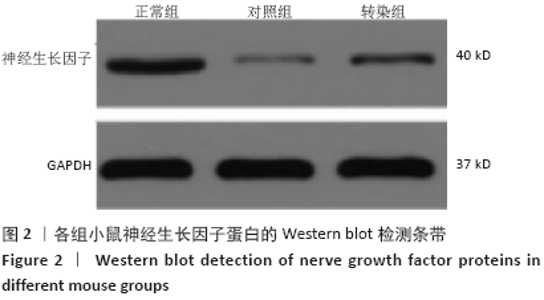
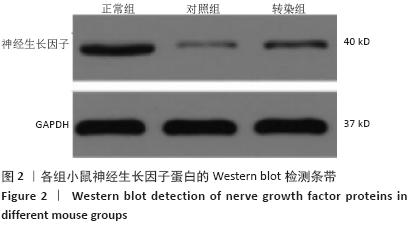
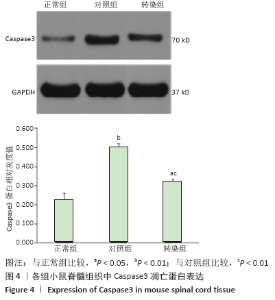
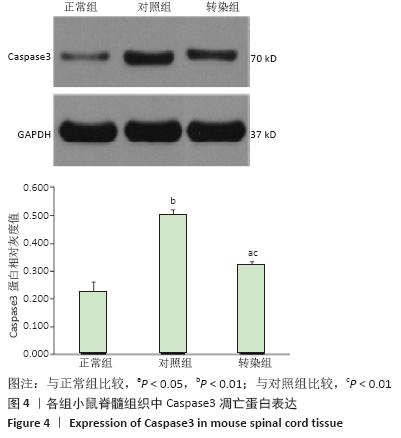
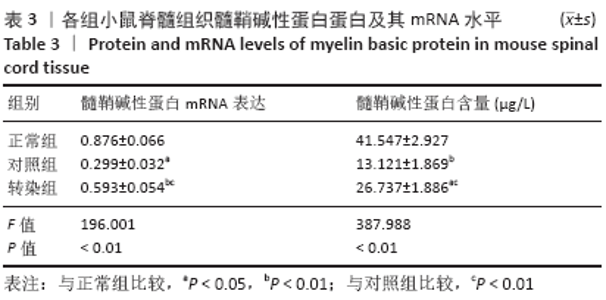
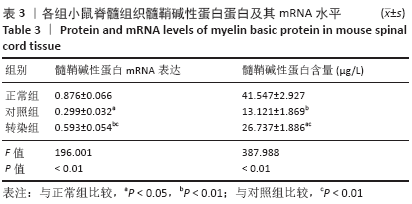
[1] SOSPEDRA M, MARTIN R. Immunology of Multiple Sclerosis. Semin Neurol. 2016;36(2):115-127.
[2] ZHOU X, LI X, FENG M, et al. Analysis of the direct injury effector of oligodendroglia cells or myelin sheath in an experimental allergic encephalomyelitis model induced by the MOG35-55 peptide. Mol Med Rep. 2015;27(8):124-131.
[3] LI Q, HOUDAYER T, LIU S, et al. Induced neural activity promotes an oligodendroglia regenerative response in the injured spinal cord and improves motor function after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2017; 34(24):3351-3361.
[4] DULAMEA AO. The contribution of oligodendrocytes and oligodendrocyte progenitor cells to central nervous system repair in multiple sclerosis: perspectives for remyelination therapeutic strategies. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(12):1939-1944.
[5] GHASEMI N. The Evaluation of Astaxanthin Effects on Differentiation of Human Adipose Derived Stem Cells into Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2018;10(2):69-74.
[6] CARDOUAT G, DOUARD M, ROBILLARD P, et al. Short-term mechanisms activated by the nerve growth factor NGF to induce pulmonary arterial hyperreactivity. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2019;11(2):045.
[7] CHI J, SONG WZ, FAN QS, et al. Transfection characters of NGF recombination adenoviral in spiral ganglion cells. Med J National. 2015; 11(1):1004-0188.
[8] DE PAULA FARIA D. Myelin positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in multiple sclerosis. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(10):1842-1843.
[9] SKARLIS C, ANAGNOSTOULI M. The role of melatonin in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurol Sci. 2020;41(4):769-781.
[10] TALEB HAA, ALGHAMDI BS. Neuroprotective Effects of Melatonin during Demyelination and Remyelination Stages in a Mouse Model of Multiple Sclerosis. J Mol Neurosci. 2019;70(3):386-402.
[11] STEINMAN L. Inverse Vaccination to Silence Immunity to Myelin in Multiple Sclerosis. Can J Neurol Sci. 2010; 37(2):49-58.
[12] DE PAULA FARIA D. Myelin positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in multiple sclerosis. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(10):1842-1843.
[13] LISAK RP, BENJAMINS JA, NEDELKOSKA L, et al. Secretory products of multiple sclerosis B cells are cytotoxic to oligodendroglia in vitro. J Neuroimmunol. 2012;246(1-2):85-95.
[14] NOTTINGHAM S, KNAPP P, SPRINGER J. FK506 Treatment Inhibits Caspase-3 Activation and Promotes Oligodendroglial Survival Following Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Exp Neurol. 2002;177(1):242-251.
[15] OLFA R, MOHAMED A. Chlorogenic Acid Prevents AMPA-Mediated Excitotoxicity in Optic Nerve Oligodendrocytes Through a PKC and Caspase-Dependent Pathways. Neurotox Res. 2018;13(4):104-129.
[16] DAS A, GUYTON M, BUTLER J, et al. Activation of Calpain and Caspase Pathways in Demyelination and Neurodegeneration in Animal Model of Multiple Sclerosis. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008;7(3):313-320.
[17] DENG C, LI J, LI L, et al. Effects of hypoxia ischemia on caspase-3 expression and neuronal apoptosis in the brain of neonatal mice. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(6):4517.
[18] LI R, LI YY, LI DH, et al. NGF Promotes Myelin Debris Clearance after Peripheral Nerve Injury by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Chin J Biochem Mol Biol. 2018;5(2):89-96.
[19] KANG WB, CHEN YJ, LU DY, et al. Folic acid contributes to peripheral nerve injury repair by promoting Schwann cell proliferation, migration, and secretion of nerve growth factor. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(1):132-139.
[20] MIR S, ALI F, CHAUHAN D, et al. Accumulation of reactivity to MBP sensitizes TRAIL mediated oligodendrocyte apoptosis in adult sub cortical white matter in a model for human multiple sclerosis. Metab Brain Dis. 2016;31(2):299-309.
[21] YE JL, CHEN XS, SU L, et al. Progesterone Alleviates Neural Behavioral Deficits and Demyelination with Reduced Degeneration of Oligodendroglial Cells in Cuprizone-Induced Mice. PLoS One. 2013; 8(1):54590-54621.
[22] STEPANOV AV, BELOGUROV AA, MAMEDOV AÉ, et al. Therapeutic effect of encapsulated into the nanocontainers MBP immunodominant peptides on EAE development in DA rats. Bioorg Khim. 2012;38(3): 306-314.
[23] AULOVA KS, TOPORKOVA LB, LOPATNIKOVA JA, et al. Changes in haematopoietic progenitor colony differentiation and proliferation and the production of different abzymes in EAE mice treated with DNA.J Cell Mol Med. 2017;42(2):109-123.
[24] LEI J. Evolutionary dynamics of cancer: From epigenetic regulation to cell population dynamics—mathematical model framework, applications, and open problems. Ence China Mathematics. 2020;63(3):411-424.
[25] SHCHEPAREVA ME, KOCHERGIN IA, TOLPEEVA OA, et al. Diagnostic value of antibodies to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2019;119(2):18-23. |