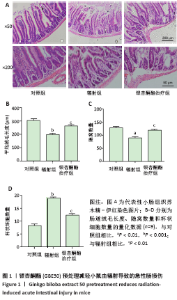
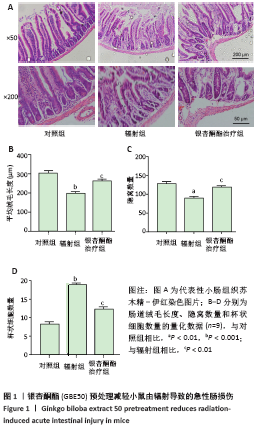
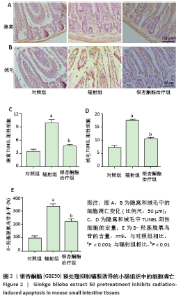
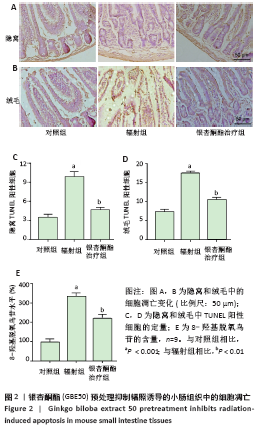
[1] ROCCO N, CATANUTO G, NAVA MB. Radiotherapy and breast reconstruction. Minerva Chir. 2018;73(3):322-328.
[2] Schaue D, McBride WH. Opportunities and challenges of radiotherapy for treating cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015;12(9):527-540.
[3] Lu L, Li W, Chen L, et al. Radiation-induced intestinal damage: latest molecular and clinical developments. Future Oncol. 2019;15(35): 4105-4118.
[4] Lu S, Guo X, Zhao P. Effect of Ginkgo biloba extract 50 on immunity and antioxidant enzyme activities in ischemia reperfusion rats. Molecules. 2011;16(11):9194-9206.
[5] 袁蓉, 张业昊, 程冰丽, 等. 银杏酮酯EGb50对缺氧/复氧损伤后SH-SY5Y细胞线粒体功能的影响[J]. 中国中药杂志 2018,43(22): 4486-4490.
[6] 任会菊, 郑东焕, 高园园, 等. 银杏酮酯滴丸联合阿加曲班注射液治疗急性脑梗死的临床研究[J]. 现代药物与临床,2020,35(4):701-705.
[7] 周子树, 申坤阳. 银杏酮酯片联合西洛他唑治疗非痴呆性血管性认知功能障碍的效果[J]. 河南医学研究,2020,29(9):1662-1663.
[8] Li Y, Ma S, Zhang Y, et al. (-)-Epicatechin mitigates radiation-induced intestinal injury and promotes intestinal regeneration via suppressing oxidative stress. Free Radic Res. 2019;53(8):851-864.
[9] Haton C, François A, Vandamme M, et al. Imbalance of the antioxidant network of mouse small intestinal mucosa after radiation exposure. Radiat Res. 2007;167(4):445-453.
[10] Li L, Zhao Y, Du F, et al. Intestinal absorption and presystemic elimination of various chemical constituents present in GBE50 extract, a standardized extract of Ginkgo biloba leaves. Curr Drug Metab. 2012; 13(5):494-509.
[11] 贺改英, 徐颖, 吴丽莉, 等. 银杏酮酯对衰老大鼠海马炎症相关细胞因子的调节作用[J]. 中国中药杂志,2012,37(14):2130-2134.
[12] Liu AH, Bao YM, Wang XY, et al. Cardio-protection by Ginkgo biloba extract 50 in rats with acute myocardial infarction is related to Na+-Ca²+ exchanger. Am J Chin Med. 2013;41(4):789-800.
[13] Wu J, Duan Y, Cui J, et al. Protective effects of zingerone derivate on ionizing radiation-induced intestinal injury. J Radiat Res. 2019;60(6): 740-746.
[14] Allen C, Her S, Jaffray DA. Radiotherapy for cancer: present and future. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;109:1-2.
[15] Klopp AH, Yeung AR, Deshmukh S, et al. Patient-reported toxicity during pelvic intensity-modulated radiation therapy: NRG Oncology-RTOG 1203.J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(24):2538-2544.
[16] Brand DH, Tree AC, Ostler P, et al.Intensity-modulated fractionated radiotherapy versus stereotactic body radiotherapy for prostate cancer (PACE-B): acute toxicity findings from an international, randomised, open-label, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(11):1531-1543.
[17] Bhanja P, Norris A, Gupta-Saraf P, et al. BCN057 induces intestinal stem cell repair and mitigates radiation-induced intestinal injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):26.
[18] Liu Z, Tian H, Jiang J, et al. β-Arrestin-2 modulates radiation-induced intestinal crypt progenitor/stem cell injury. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23(9):1529-1541.
[19] Kalita B, Ranjan R, Gupta ML. Combination treatment of podophyllotoxin and rutin promotes mouse Lgr5(+ ve) intestinal stem cells survival against lethal radiation injury through Wnt signaling. Apoptosis. 2019;24(3-4):326-340.
[20] Branca JJV, Gulisano M, Nicoletti C. Intestinal epithelial barrier functions in ageing. Ageing Res Rev. 2019;54:100938.
[21] Gao X, Hao S, Yan H, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to the intestine damage in endotoxemic rats. J Surg Res. 2015;195(1):211-218.
[22] Vancamelbeke M, Vanuytsel T, Farré R, et al. Genetic and transcriptomic bases of intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017;23(10): 1718-1729.
[23] Suzuki T. Regulation of intestinal epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(4):631-659.
[24] Zhao Z, Cheng W, Qu W, et al. Arabinoxylan rice bran (MGN-3/Biobran) alleviates radiation-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction of mice in a mitochondrion-dependent manner. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;124:109855.
[25] Datta K, Suman S, Fornace AJ Jr. Radiation persistently promoted oxidative stress, activated mTOR via PI3K/Akt, and downregulated autophagy pathway in mouse intestine. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014; 57:167-176.
[26] Sun L, Xu G, Dong Y, et al. Quercetin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal oxidative stress in broiler chickens through activation of Nrf2 pathway. Molecules. 2020;25(5):1053.
[27] Blasco H, Garcon G, Patin F, et al. Panel of oxidative stress and inflammatory biomarkers in ALS: A pilot study. Can J Neurol Sci. 2017;44(1):90-95.
[28] CaginYF, Parlakpinar H, POLAT A, et al. The protective effects of apocynin on ionizing radiation-induced intestinal damage in rats. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016;42(2):317-324.
[29] Jin LG, Chu JJ, Pang QF, et al. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester attenuates ionize radiation-induced intestinal injury through modulation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and p38MAPK in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015;40(1):156-163.
|