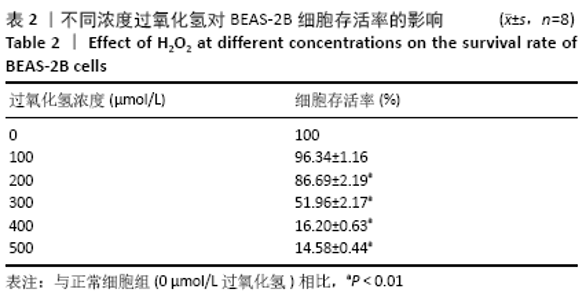
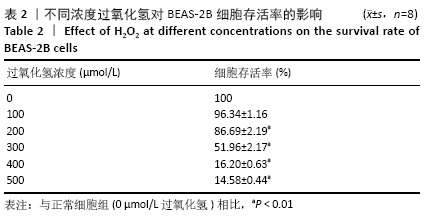
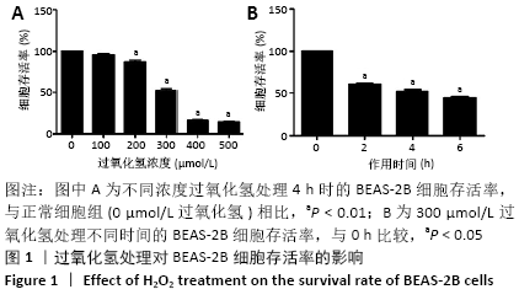
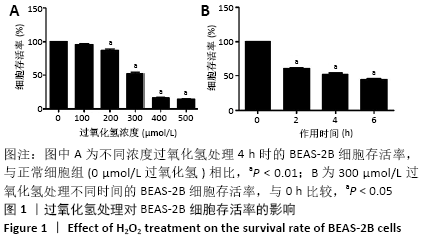
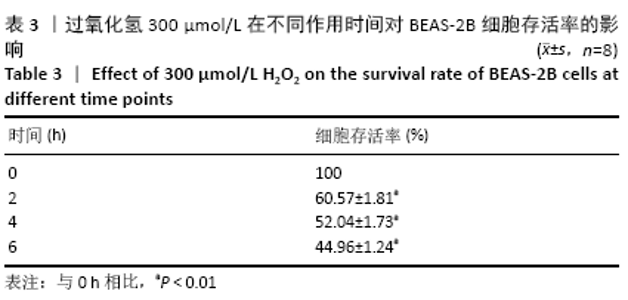
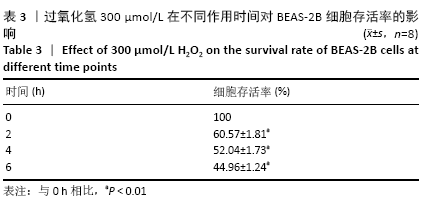
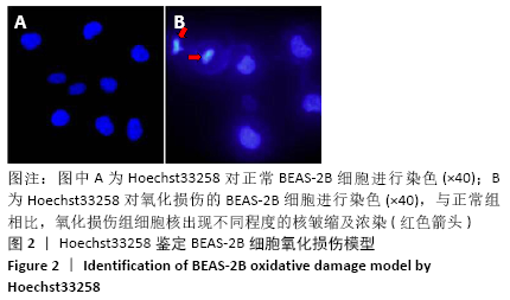
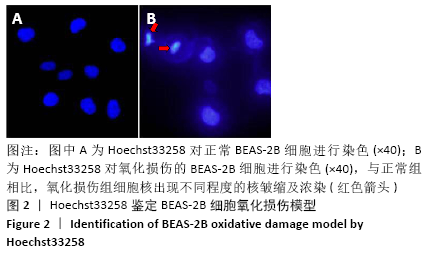
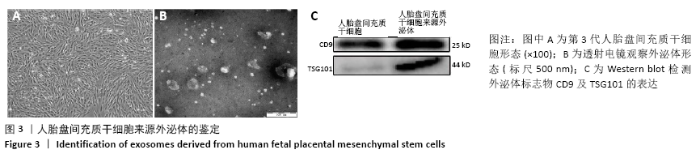
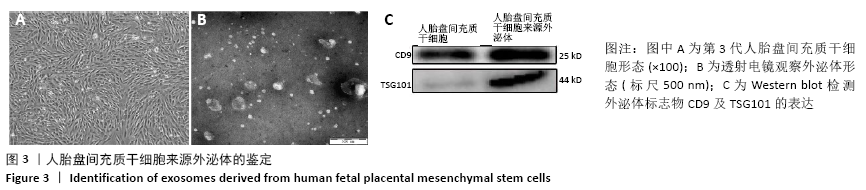
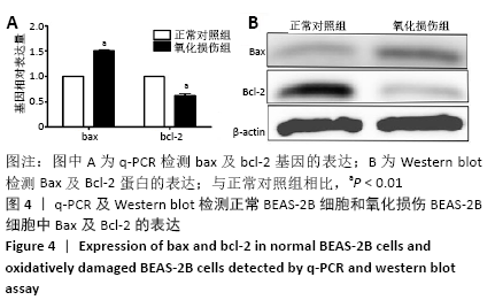
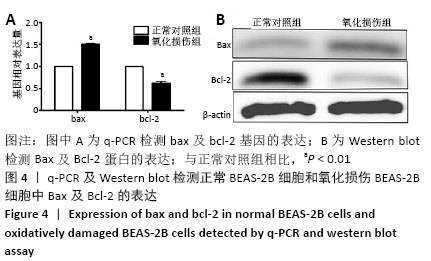
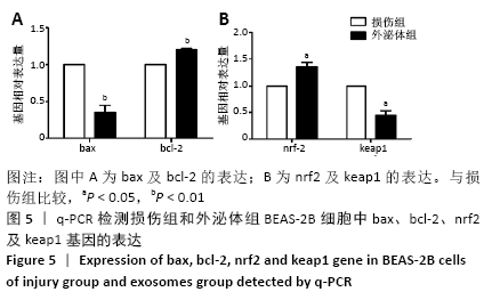
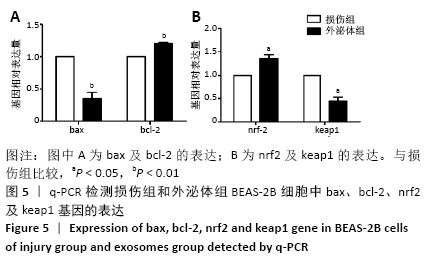
[1] PIZZINO G, IRRERA N, CUCINOTTA M, et al. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:8416763.
[2] 付雪,张玉洁,严秀蕊,等.人胎盘胎儿侧间充质干细胞无血清培养上清的抗氧化活性分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(5): 773-779.
[3] 付雪,刘国攀,张玉洁,等.人胎盘胎儿侧间充质干细胞无血清培养上清对肺脏上皮细胞氧化应激的保护作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(33): 5369-5374.
[4] 金鹿.维生素A 对奶牛乳腺硒蛋白合成及抗氧化功能影响机理的研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2014.
[5] COSTA S, REINA-COUTO M, ALBINO-TEIXEIRA A, et al. Statins and oxidative stress in chronic heart failure. Rev Port Cardiol. 2016;35(1): 41-57.
[6] MOTA SI, COSTA RO, FERREIRA IL, et al. Oxidative stress involving changes in Nrf2 and ER stress in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1852(7):1428-1441.
[7] KATTOOR AJ, POTHINENI NVK, PALAGIRI D, et al. Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2017;19(11):42.
[8] AOUACHERI O, SAKA S, KRIM M, et al. The investigation of the oxidative stress-related parameters in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Can J Diabetes. 2015;39(1):44-49.
[9] BISHT S, FAIQ M, TOLAHUNASE M, et al. Oxidative stress and male infertility. Nat Rev Urol. 2017;14(8):470-485.
[10] OKON IS, ZOU MH. Mitochondrial ROS and cancer drug resistance: Implications for therapy. Pharmacol Res. 2015;100:170-174.
[11] CHAI NL, ZHANG XB, CHEN SW, et al. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(26):6036-6048.
[12] MATTHAY MA. Extracellular Vesicle Transfer from Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Modulates Macrophage Function in Acute Lung Injury. Basic Science and Clinical Implications. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196(10):1234-1236.
[13] PHINNEY DG, PITTENGER MF. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4):851-858.
[14] MUNIR H, MCGETTRICK HM. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Disease: Risks and Rewards. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(18): 2091-2100.
[15] TURINETTO V, VITALE E, GIACHINO C. Senescence in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Functional Changes and Implications in Stem Cell-Based Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(7):1164.
[16] DOYLE LM, WANG MZ. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells. 2019;8(7):727.
[17] SCHNITZER JK, BERZEL S, FAJARDO-MOSER M, et al. Fragments of antigen-loaded dendritic cells (DC) and DC-derived exosomes induce protective immunity against Leishmania major. Vaccine. 2010;28(36):5785-5793.
[18] ADMYRE C, JOHANSSON SM, QAZI KR, et al. Exosomes with immune modulatory features are present in human breast milk. J Immunol. 2007;179(3):1969-1978.
[19] ZONNEVELD MI, BRISSON AR, VAN HERWIJNEN MJ, et al. Recovery of extracellular vesicles from human breast milk is influenced by sample collection and vesicle isolation procedures. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3.doi: 10.3402/jev.v3.24215. eCollection 2014.
[20] MOI P, CHAN K, ASUNIS I, et al. Isolation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like basic leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(21):9926-9930.
[21] LU MC, JI JA, JIANG ZY, et al. The Keap1-Nrf2-ARE Pathway As a Potential Preventive and Therapeutic Target: An Update. Med Res Rev. 2016;36(5):924-963.
[22] WANG C, LI C, PENG H, et al. Activation of the Nrf2-ARE pathway attenuates hyperglycemia-mediated injuries in mouse podocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34(3):891-902.
[23] SAHINER UM, BIRBEN E, ERZURUM S, et al. Oxidative stress in asthma: Part of the puzzle. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2018;29(8):789-800.
[24] YANG H, LV H, LI H, et al. Oridonin protects LPS-induced acute lung injury by modulating Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress and Nrf2-independent NLRP3 and NF-κB pathways. Cell Commun Signal. 2019;17(1):62.
[25] GONÇALVES PB, ROMEIRO NC. Multi-target natural products as alternatives against oxidative stress in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Eur J Med Chem. 2019;163:911-931.
[26] MIZUMURA K, MARUOKA S, SHIMIZU T, et al. Role of Nrf2 in the pathogenesis of respiratory diseases. Respir Investig. 2020;58(1):28-35.
[27] LIU Q, GAO Y, CI X. Role of Nrf2 and Its Activators in Respiratory Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:7090534.
[28] ZHANG L, LI Q, LIU W, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Acute Lung Injury and Inflammatory Responses Induced by Paraquat Poisoning. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:2623-2632.
[29] YAN X, FU X, JIA Y, et al. Nrf2/Keap1/ARE Signaling Mediated an Antioxidative Protection of Human Placental Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Fetal Origin in Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:2654910.
[30] JIANG W, TAN Y, CAI M, et al. Human Umbilical Cord MSC-Derived Exosomes Suppress the Development of CCl4-Induced Liver Injury through Antioxidant Effect. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:6079642.
|